- Our Writers
- How to Order
- Assignment Writing Service
- Report Writing Service
- Buy Coursework
- Dissertation Writing Service
- Research Paper Writing Service
- All Essay Services
Writing A Case Study
Types Of Case Study

Understand the Types of Case Study Here
People also read
A Complete Case Study Writing Guide With Examples
Simple Case Study Format for Students to Follow
Brilliant Case Study Examples and Templates For Your Help
Case studies are effective research methods that focus on one specific case over time. This gives a detailed view that's great for learning.
Writing a case study is a very useful form of study in the educational process. With real-life examples, students can learn more effectively.
A case study also has different types and forms. As a rule of thumb, all of them require a detailed and convincing answer based on a thorough analysis.
In this blog, we are going to discuss the different types of case study research methods in detail.
So, let’s dive right in!
- 1. Understanding Case Studies
- 2. What are the Types of Case Study?
- 3. Types of Subjects of Case Study
- 4. Benefits of Case Study for Students
Understanding Case Studies
Case studies are a type of research methodology. Case study research designs examine subjects, projects, or organizations to provide an analysis based on the evidence.
It allows you to get insight into what causes any subject’s decisions and actions. This makes case studies a great way for students to develop their research skills.
A case study focuses on a single project for an extended period, which allows students to explore the topic in depth.
What are the Types of Case Study?
Multiple case studies are used for different purposes. The main purpose of case studies is to analyze problems within the boundaries of a specific organization, environment, or situation.
Many aspects of a case study such as data collection and analysis, qualitative research questions, etc. are dependent on the researcher and what the study is looking to address.
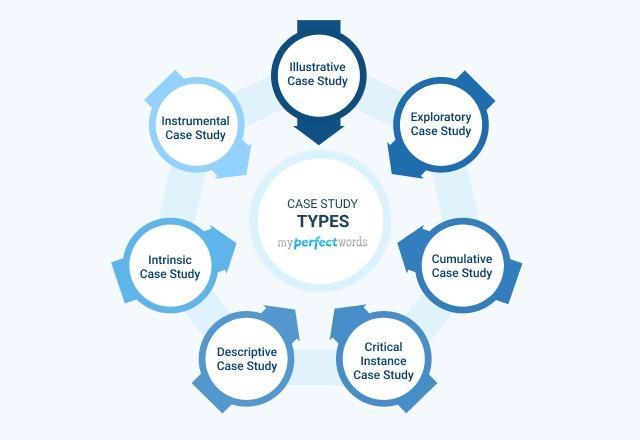
Case studies can be divided into the following categories:
Illustrative Case Study
Exploratory case study, cumulative case study, critical instance case study, descriptive case study, intrinsic case study, instrumental case study.
Let’s take a look at the detailed description of each type of case study with examples.
An illustrative case study is used to examine a familiar case to help others understand it. It is one of the main types of case studies in research methodology and is primarily descriptive.
In this type of case study, usually, one or two instances are used to explain what a situation is like.
Here is an example to help you understand it better:
Illustrative Case Study Example
An exploratory case study is usually done before a larger-scale research. These types of case studies are very popular in the social sciences like political science and primarily focus on real-life contexts and situations.
This method is useful in identifying research questions and methods for a large and complex study.
Let’s take a look at this example to help you have a better understanding:
Exploratory Case Study Example
A cumulative case study is one of the main types of case studies in qualitative research. It is used to collect information from different sources at different times.
This case study aims to summarize the past studies without spending additional cost and time on new investigations.
Let’s take a look at the example below:
Cumulative Case Study Example
Critical instances case studies are used to determine the cause and consequence of an event.
The main reason for this type of case study is to investigate one or more sources with unique interests and sometimes with no interest in general.
Take a look at this example below:
Critical Instance Case Study Example
When you have a hypothesis, you can design a descriptive study. It aims to find connections between the subject being studied and a theory.
After making these connections, the study can be concluded. The results of the descriptive case study will usually suggest how to develop a theory further.
This example can help you understand the concept better:
Descriptive Case Study Example
Intrinsic studies are more commonly used in psychology, healthcare, or social work. So, if you were looking for types of case studies in sociology, or types of case studies in social research, this is it.
The focus of intrinsic studies is on the individual. The aim of such studies is not only to understand the subject better but also their history and how they interact with their environment.
Here is an example to help you understand;
Intrinsic Case Study Example
This type of case study is mostly used in qualitative research. In an instrumental case study, the specific case is selected to provide information about the research question.
It offers a lens through which researchers can explore complex concepts, theories, or generalizations.
Take a look at the example below to have a better understanding of the concepts:
Instrumental Case Study Example
Review some case study examples to help you understand how a specific case study is conducted.
Types of Subjects of Case Study
In general, there are 5 types of subjects that case studies address. Every case study fits into the following subject categories.
- Person: This type of study focuses on one subject or individual and can use several research methods to determine the outcome.
- Group: This type of study takes into account a group of individuals. This could be a group of friends, coworkers, or family.
- Location: The main focus of this type of study is the place. It also takes into account how and why people use the place.
- Organization: This study focuses on an organization or company. This could also include the company employees or people who work in an event at the organization.
- Event: This type of study focuses on a specific event. It could be societal or cultural and examines how it affects the surroundings.
Benefits of Case Study for Students
Here's a closer look at the multitude of benefits students can have with case studies:
Real-world Application
Case studies serve as a crucial link between theory and practice. By immersing themselves in real-world scenarios, students can apply theoretical knowledge to practical situations.
Critical Thinking Skills
Analyzing case studies demands critical thinking and informed decision-making. Students cultivate the ability to evaluate information, identify key factors, and develop well-reasoned solutions – essential skills in both academic and professional contexts.
Enhanced Problem-solving Abilities
Case studies often present complex problems that require creative and strategic solutions. Engaging with these challenges refines students' problem-solving skills, encouraging them to think innovatively and develop effective approaches.
Holistic Understanding
Going beyond theoretical concepts, case studies provide a holistic view of a subject. Students gain insights into the multifaceted aspects of a situation, helping them connect the dots and understand the broader context.
Exposure to Diverse Perspectives
Case studies often encompass a variety of industries, cultures, and situations. This exposure broadens students' perspectives, fostering a more comprehensive understanding of the world and the challenges faced by different entities.
So there you have it!
We have explored different types of case studies and their examples. Case studies act as the tools to understand and deal with the many challenges and opportunities around us.
Case studies are being used more and more in colleges and universities to help students understand how a hypothetical event can influence a person, group, or organization in real life.
Not everyone can handle the case study writing assignment easily. It is even scary to think that your time and work could be wasted if you don't do the case study paper right.
Our essay writing service online is here to make your academic journey easier.
Let us worry about your essay and buy case study today to ease your stress and achieve academic success.

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Dr. Barbara is a highly experienced writer and author who holds a Ph.D. degree in public health from an Ivy League school. She has worked in the medical field for many years, conducting extensive research on various health topics. Her writing has been featured in several top-tier publications.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
- Privacy Policy

Home » Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Table of Contents

A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth examination and analysis of a particular phenomenon or case, such as an individual, organization, community, event, or situation.
It is a qualitative research approach that aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the case being studied. Case studies typically involve multiple sources of data, including interviews, observations, documents, and artifacts, which are analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, and grounded theory. The findings of a case study are often used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Types of Case Study
Types and Methods of Case Study are as follows:
Single-Case Study
A single-case study is an in-depth analysis of a single case. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand a specific phenomenon in detail.
For Example , A researcher might conduct a single-case study on a particular individual to understand their experiences with a particular health condition or a specific organization to explore their management practices. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a single-case study are often used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Multiple-Case Study
A multiple-case study involves the analysis of several cases that are similar in nature. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to identify similarities and differences between the cases.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a multiple-case study on several companies to explore the factors that contribute to their success or failure. The researcher collects data from each case, compares and contrasts the findings, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as comparative analysis or pattern-matching. The findings of a multiple-case study can be used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Exploratory Case Study
An exploratory case study is used to explore a new or understudied phenomenon. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to generate hypotheses or theories about the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an exploratory case study on a new technology to understand its potential impact on society. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as grounded theory or content analysis. The findings of an exploratory case study can be used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Descriptive Case Study
A descriptive case study is used to describe a particular phenomenon in detail. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to provide a comprehensive account of the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a descriptive case study on a particular community to understand its social and economic characteristics. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a descriptive case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Instrumental Case Study
An instrumental case study is used to understand a particular phenomenon that is instrumental in achieving a particular goal. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand the role of the phenomenon in achieving the goal.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an instrumental case study on a particular policy to understand its impact on achieving a particular goal, such as reducing poverty. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of an instrumental case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Case Study Data Collection Methods
Here are some common data collection methods for case studies:
Interviews involve asking questions to individuals who have knowledge or experience relevant to the case study. Interviews can be structured (where the same questions are asked to all participants) or unstructured (where the interviewer follows up on the responses with further questions). Interviews can be conducted in person, over the phone, or through video conferencing.
Observations
Observations involve watching and recording the behavior and activities of individuals or groups relevant to the case study. Observations can be participant (where the researcher actively participates in the activities) or non-participant (where the researcher observes from a distance). Observations can be recorded using notes, audio or video recordings, or photographs.
Documents can be used as a source of information for case studies. Documents can include reports, memos, emails, letters, and other written materials related to the case study. Documents can be collected from the case study participants or from public sources.
Surveys involve asking a set of questions to a sample of individuals relevant to the case study. Surveys can be administered in person, over the phone, through mail or email, or online. Surveys can be used to gather information on attitudes, opinions, or behaviors related to the case study.
Artifacts are physical objects relevant to the case study. Artifacts can include tools, equipment, products, or other objects that provide insights into the case study phenomenon.
How to conduct Case Study Research
Conducting a case study research involves several steps that need to be followed to ensure the quality and rigor of the study. Here are the steps to conduct case study research:
- Define the research questions: The first step in conducting a case study research is to define the research questions. The research questions should be specific, measurable, and relevant to the case study phenomenon under investigation.
- Select the case: The next step is to select the case or cases to be studied. The case should be relevant to the research questions and should provide rich and diverse data that can be used to answer the research questions.
- Collect data: Data can be collected using various methods, such as interviews, observations, documents, surveys, and artifacts. The data collection method should be selected based on the research questions and the nature of the case study phenomenon.
- Analyze the data: The data collected from the case study should be analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, or grounded theory. The analysis should be guided by the research questions and should aim to provide insights and conclusions relevant to the research questions.
- Draw conclusions: The conclusions drawn from the case study should be based on the data analysis and should be relevant to the research questions. The conclusions should be supported by evidence and should be clearly stated.
- Validate the findings: The findings of the case study should be validated by reviewing the data and the analysis with participants or other experts in the field. This helps to ensure the validity and reliability of the findings.
- Write the report: The final step is to write the report of the case study research. The report should provide a clear description of the case study phenomenon, the research questions, the data collection methods, the data analysis, the findings, and the conclusions. The report should be written in a clear and concise manner and should follow the guidelines for academic writing.
Examples of Case Study
Here are some examples of case study research:
- The Hawthorne Studies : Conducted between 1924 and 1932, the Hawthorne Studies were a series of case studies conducted by Elton Mayo and his colleagues to examine the impact of work environment on employee productivity. The studies were conducted at the Hawthorne Works plant of the Western Electric Company in Chicago and included interviews, observations, and experiments.
- The Stanford Prison Experiment: Conducted in 1971, the Stanford Prison Experiment was a case study conducted by Philip Zimbardo to examine the psychological effects of power and authority. The study involved simulating a prison environment and assigning participants to the role of guards or prisoners. The study was controversial due to the ethical issues it raised.
- The Challenger Disaster: The Challenger Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Space Shuttle Challenger explosion in 1986. The study included interviews, observations, and analysis of data to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
- The Enron Scandal: The Enron Scandal was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Enron Corporation’s bankruptcy in 2001. The study included interviews, analysis of financial data, and review of documents to identify the accounting practices, corporate culture, and ethical issues that led to the company’s downfall.
- The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster : The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the nuclear accident that occurred at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Japan in 2011. The study included interviews, analysis of data, and review of documents to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
Application of Case Study
Case studies have a wide range of applications across various fields and industries. Here are some examples:
Business and Management
Case studies are widely used in business and management to examine real-life situations and develop problem-solving skills. Case studies can help students and professionals to develop a deep understanding of business concepts, theories, and best practices.
Case studies are used in healthcare to examine patient care, treatment options, and outcomes. Case studies can help healthcare professionals to develop critical thinking skills, diagnose complex medical conditions, and develop effective treatment plans.
Case studies are used in education to examine teaching and learning practices. Case studies can help educators to develop effective teaching strategies, evaluate student progress, and identify areas for improvement.
Social Sciences
Case studies are widely used in social sciences to examine human behavior, social phenomena, and cultural practices. Case studies can help researchers to develop theories, test hypotheses, and gain insights into complex social issues.
Law and Ethics
Case studies are used in law and ethics to examine legal and ethical dilemmas. Case studies can help lawyers, policymakers, and ethical professionals to develop critical thinking skills, analyze complex cases, and make informed decisions.
Purpose of Case Study
The purpose of a case study is to provide a detailed analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. A case study is a qualitative research method that involves the in-depth exploration and analysis of a particular case, which can be an individual, group, organization, event, or community.
The primary purpose of a case study is to generate a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the case, including its history, context, and dynamics. Case studies can help researchers to identify and examine the underlying factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and detailed understanding of the case, which can inform future research, practice, or policy.
Case studies can also serve other purposes, including:
- Illustrating a theory or concept: Case studies can be used to illustrate and explain theoretical concepts and frameworks, providing concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Developing hypotheses: Case studies can help to generate hypotheses about the causal relationships between different factors and outcomes, which can be tested through further research.
- Providing insight into complex issues: Case studies can provide insights into complex and multifaceted issues, which may be difficult to understand through other research methods.
- Informing practice or policy: Case studies can be used to inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
Advantages of Case Study Research
There are several advantages of case study research, including:
- In-depth exploration: Case study research allows for a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. This can provide a comprehensive understanding of the case and its dynamics, which may not be possible through other research methods.
- Rich data: Case study research can generate rich and detailed data, including qualitative data such as interviews, observations, and documents. This can provide a nuanced understanding of the case and its complexity.
- Holistic perspective: Case study research allows for a holistic perspective of the case, taking into account the various factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and comprehensive understanding of the case.
- Theory development: Case study research can help to develop and refine theories and concepts by providing empirical evidence and concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Practical application: Case study research can inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
- Contextualization: Case study research takes into account the specific context in which the case is situated, which can help to understand how the case is influenced by the social, cultural, and historical factors of its environment.
Limitations of Case Study Research
There are several limitations of case study research, including:
- Limited generalizability : Case studies are typically focused on a single case or a small number of cases, which limits the generalizability of the findings. The unique characteristics of the case may not be applicable to other contexts or populations, which may limit the external validity of the research.
- Biased sampling: Case studies may rely on purposive or convenience sampling, which can introduce bias into the sample selection process. This may limit the representativeness of the sample and the generalizability of the findings.
- Subjectivity: Case studies rely on the interpretation of the researcher, which can introduce subjectivity into the analysis. The researcher’s own biases, assumptions, and perspectives may influence the findings, which may limit the objectivity of the research.
- Limited control: Case studies are typically conducted in naturalistic settings, which limits the control that the researcher has over the environment and the variables being studied. This may limit the ability to establish causal relationships between variables.
- Time-consuming: Case studies can be time-consuming to conduct, as they typically involve a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific case. This may limit the feasibility of conducting multiple case studies or conducting case studies in a timely manner.
- Resource-intensive: Case studies may require significant resources, including time, funding, and expertise. This may limit the ability of researchers to conduct case studies in resource-constrained settings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Experimental Design – Types, Methods, Guide

Exploratory Research – Types, Methods and...

Triangulation in Research – Types, Methods and...

Descriptive Research Design – Types, Methods and...

Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples

Transformative Design – Methods, Types, Guide

The Ultimate Guide to Qualitative Research - Part 1: The Basics

- Introduction and overview
- What is qualitative research?
- What is qualitative data?
- Examples of qualitative data
- Qualitative vs. quantitative research
- Mixed methods
- Qualitative research preparation
- Theoretical perspective
- Theoretical framework
- Literature reviews
Research question
- Conceptual framework
- Conceptual vs. theoretical framework
Data collection
- Qualitative research methods
- Focus groups
- Observational research
What is a case study?
Applications for case study research, what is a good case study, process of case study design, benefits and limitations of case studies.
- Ethnographical research
- Ethical considerations
- Confidentiality and privacy
- Power dynamics
- Reflexivity
Case studies
Case studies are essential to qualitative research , offering a lens through which researchers can investigate complex phenomena within their real-life contexts. This chapter explores the concept, purpose, applications, examples, and types of case studies and provides guidance on how to conduct case study research effectively.

Whereas quantitative methods look at phenomena at scale, case study research looks at a concept or phenomenon in considerable detail. While analyzing a single case can help understand one perspective regarding the object of research inquiry, analyzing multiple cases can help obtain a more holistic sense of the topic or issue. Let's provide a basic definition of a case study, then explore its characteristics and role in the qualitative research process.
Definition of a case study
A case study in qualitative research is a strategy of inquiry that involves an in-depth investigation of a phenomenon within its real-world context. It provides researchers with the opportunity to acquire an in-depth understanding of intricate details that might not be as apparent or accessible through other methods of research. The specific case or cases being studied can be a single person, group, or organization – demarcating what constitutes a relevant case worth studying depends on the researcher and their research question .
Among qualitative research methods , a case study relies on multiple sources of evidence, such as documents, artifacts, interviews , or observations , to present a complete and nuanced understanding of the phenomenon under investigation. The objective is to illuminate the readers' understanding of the phenomenon beyond its abstract statistical or theoretical explanations.
Characteristics of case studies
Case studies typically possess a number of distinct characteristics that set them apart from other research methods. These characteristics include a focus on holistic description and explanation, flexibility in the design and data collection methods, reliance on multiple sources of evidence, and emphasis on the context in which the phenomenon occurs.
Furthermore, case studies can often involve a longitudinal examination of the case, meaning they study the case over a period of time. These characteristics allow case studies to yield comprehensive, in-depth, and richly contextualized insights about the phenomenon of interest.
The role of case studies in research
Case studies hold a unique position in the broader landscape of research methods aimed at theory development. They are instrumental when the primary research interest is to gain an intensive, detailed understanding of a phenomenon in its real-life context.
In addition, case studies can serve different purposes within research - they can be used for exploratory, descriptive, or explanatory purposes, depending on the research question and objectives. This flexibility and depth make case studies a valuable tool in the toolkit of qualitative researchers.
Remember, a well-conducted case study can offer a rich, insightful contribution to both academic and practical knowledge through theory development or theory verification, thus enhancing our understanding of complex phenomena in their real-world contexts.
What is the purpose of a case study?
Case study research aims for a more comprehensive understanding of phenomena, requiring various research methods to gather information for qualitative analysis . Ultimately, a case study can allow the researcher to gain insight into a particular object of inquiry and develop a theoretical framework relevant to the research inquiry.
Why use case studies in qualitative research?
Using case studies as a research strategy depends mainly on the nature of the research question and the researcher's access to the data.
Conducting case study research provides a level of detail and contextual richness that other research methods might not offer. They are beneficial when there's a need to understand complex social phenomena within their natural contexts.
The explanatory, exploratory, and descriptive roles of case studies
Case studies can take on various roles depending on the research objectives. They can be exploratory when the research aims to discover new phenomena or define new research questions; they are descriptive when the objective is to depict a phenomenon within its context in a detailed manner; and they can be explanatory if the goal is to understand specific relationships within the studied context. Thus, the versatility of case studies allows researchers to approach their topic from different angles, offering multiple ways to uncover and interpret the data .
The impact of case studies on knowledge development
Case studies play a significant role in knowledge development across various disciplines. Analysis of cases provides an avenue for researchers to explore phenomena within their context based on the collected data.

This can result in the production of rich, practical insights that can be instrumental in both theory-building and practice. Case studies allow researchers to delve into the intricacies and complexities of real-life situations, uncovering insights that might otherwise remain hidden.
Types of case studies
In qualitative research , a case study is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Depending on the nature of the research question and the specific objectives of the study, researchers might choose to use different types of case studies. These types differ in their focus, methodology, and the level of detail they provide about the phenomenon under investigation.
Understanding these types is crucial for selecting the most appropriate approach for your research project and effectively achieving your research goals. Let's briefly look at the main types of case studies.
Exploratory case studies
Exploratory case studies are typically conducted to develop a theory or framework around an understudied phenomenon. They can also serve as a precursor to a larger-scale research project. Exploratory case studies are useful when a researcher wants to identify the key issues or questions which can spur more extensive study or be used to develop propositions for further research. These case studies are characterized by flexibility, allowing researchers to explore various aspects of a phenomenon as they emerge, which can also form the foundation for subsequent studies.
Descriptive case studies
Descriptive case studies aim to provide a complete and accurate representation of a phenomenon or event within its context. These case studies are often based on an established theoretical framework, which guides how data is collected and analyzed. The researcher is concerned with describing the phenomenon in detail, as it occurs naturally, without trying to influence or manipulate it.
Explanatory case studies
Explanatory case studies are focused on explanation - they seek to clarify how or why certain phenomena occur. Often used in complex, real-life situations, they can be particularly valuable in clarifying causal relationships among concepts and understanding the interplay between different factors within a specific context.

Intrinsic, instrumental, and collective case studies
These three categories of case studies focus on the nature and purpose of the study. An intrinsic case study is conducted when a researcher has an inherent interest in the case itself. Instrumental case studies are employed when the case is used to provide insight into a particular issue or phenomenon. A collective case study, on the other hand, involves studying multiple cases simultaneously to investigate some general phenomena.
Each type of case study serves a different purpose and has its own strengths and challenges. The selection of the type should be guided by the research question and objectives, as well as the context and constraints of the research.
The flexibility, depth, and contextual richness offered by case studies make this approach an excellent research method for various fields of study. They enable researchers to investigate real-world phenomena within their specific contexts, capturing nuances that other research methods might miss. Across numerous fields, case studies provide valuable insights into complex issues.
Critical information systems research
Case studies provide a detailed understanding of the role and impact of information systems in different contexts. They offer a platform to explore how information systems are designed, implemented, and used and how they interact with various social, economic, and political factors. Case studies in this field often focus on examining the intricate relationship between technology, organizational processes, and user behavior, helping to uncover insights that can inform better system design and implementation.
Health research
Health research is another field where case studies are highly valuable. They offer a way to explore patient experiences, healthcare delivery processes, and the impact of various interventions in a real-world context.

Case studies can provide a deep understanding of a patient's journey, giving insights into the intricacies of disease progression, treatment effects, and the psychosocial aspects of health and illness.
Asthma research studies
Specifically within medical research, studies on asthma often employ case studies to explore the individual and environmental factors that influence asthma development, management, and outcomes. A case study can provide rich, detailed data about individual patients' experiences, from the triggers and symptoms they experience to the effectiveness of various management strategies. This can be crucial for developing patient-centered asthma care approaches.
Other fields
Apart from the fields mentioned, case studies are also extensively used in business and management research, education research, and political sciences, among many others. They provide an opportunity to delve into the intricacies of real-world situations, allowing for a comprehensive understanding of various phenomena.
Case studies, with their depth and contextual focus, offer unique insights across these varied fields. They allow researchers to illuminate the complexities of real-life situations, contributing to both theory and practice.
Whatever field you're in, ATLAS.ti puts your data to work for you
Download a free trial of ATLAS.ti to turn your data into insights.
Understanding the key elements of case study design is crucial for conducting rigorous and impactful case study research. A well-structured design guides the researcher through the process, ensuring that the study is methodologically sound and its findings are reliable and valid. The main elements of case study design include the research question , propositions, units of analysis, and the logic linking the data to the propositions.
The research question is the foundation of any research study. A good research question guides the direction of the study and informs the selection of the case, the methods of collecting data, and the analysis techniques. A well-formulated research question in case study research is typically clear, focused, and complex enough to merit further detailed examination of the relevant case(s).
Propositions
Propositions, though not necessary in every case study, provide a direction by stating what we might expect to find in the data collected. They guide how data is collected and analyzed by helping researchers focus on specific aspects of the case. They are particularly important in explanatory case studies, which seek to understand the relationships among concepts within the studied phenomenon.
Units of analysis
The unit of analysis refers to the case, or the main entity or entities that are being analyzed in the study. In case study research, the unit of analysis can be an individual, a group, an organization, a decision, an event, or even a time period. It's crucial to clearly define the unit of analysis, as it shapes the qualitative data analysis process by allowing the researcher to analyze a particular case and synthesize analysis across multiple case studies to draw conclusions.
Argumentation
This refers to the inferential model that allows researchers to draw conclusions from the data. The researcher needs to ensure that there is a clear link between the data, the propositions (if any), and the conclusions drawn. This argumentation is what enables the researcher to make valid and credible inferences about the phenomenon under study.
Understanding and carefully considering these elements in the design phase of a case study can significantly enhance the quality of the research. It can help ensure that the study is methodologically sound and its findings contribute meaningful insights about the case.
Ready to jumpstart your research with ATLAS.ti?
Conceptualize your research project with our intuitive data analysis interface. Download a free trial today.
Conducting a case study involves several steps, from defining the research question and selecting the case to collecting and analyzing data . This section outlines these key stages, providing a practical guide on how to conduct case study research.
Defining the research question
The first step in case study research is defining a clear, focused research question. This question should guide the entire research process, from case selection to analysis. It's crucial to ensure that the research question is suitable for a case study approach. Typically, such questions are exploratory or descriptive in nature and focus on understanding a phenomenon within its real-life context.
Selecting and defining the case
The selection of the case should be based on the research question and the objectives of the study. It involves choosing a unique example or a set of examples that provide rich, in-depth data about the phenomenon under investigation. After selecting the case, it's crucial to define it clearly, setting the boundaries of the case, including the time period and the specific context.
Previous research can help guide the case study design. When considering a case study, an example of a case could be taken from previous case study research and used to define cases in a new research inquiry. Considering recently published examples can help understand how to select and define cases effectively.
Developing a detailed case study protocol
A case study protocol outlines the procedures and general rules to be followed during the case study. This includes the data collection methods to be used, the sources of data, and the procedures for analysis. Having a detailed case study protocol ensures consistency and reliability in the study.
The protocol should also consider how to work with the people involved in the research context to grant the research team access to collecting data. As mentioned in previous sections of this guide, establishing rapport is an essential component of qualitative research as it shapes the overall potential for collecting and analyzing data.
Collecting data
Gathering data in case study research often involves multiple sources of evidence, including documents, archival records, interviews, observations, and physical artifacts. This allows for a comprehensive understanding of the case. The process for gathering data should be systematic and carefully documented to ensure the reliability and validity of the study.
Analyzing and interpreting data
The next step is analyzing the data. This involves organizing the data , categorizing it into themes or patterns , and interpreting these patterns to answer the research question. The analysis might also involve comparing the findings with prior research or theoretical propositions.
Writing the case study report
The final step is writing the case study report . This should provide a detailed description of the case, the data, the analysis process, and the findings. The report should be clear, organized, and carefully written to ensure that the reader can understand the case and the conclusions drawn from it.
Each of these steps is crucial in ensuring that the case study research is rigorous, reliable, and provides valuable insights about the case.
The type, depth, and quality of data in your study can significantly influence the validity and utility of the study. In case study research, data is usually collected from multiple sources to provide a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the case. This section will outline the various methods of collecting data used in case study research and discuss considerations for ensuring the quality of the data.
Interviews are a common method of gathering data in case study research. They can provide rich, in-depth data about the perspectives, experiences, and interpretations of the individuals involved in the case. Interviews can be structured , semi-structured , or unstructured , depending on the research question and the degree of flexibility needed.
Observations
Observations involve the researcher observing the case in its natural setting, providing first-hand information about the case and its context. Observations can provide data that might not be revealed in interviews or documents, such as non-verbal cues or contextual information.
Documents and artifacts
Documents and archival records provide a valuable source of data in case study research. They can include reports, letters, memos, meeting minutes, email correspondence, and various public and private documents related to the case.

These records can provide historical context, corroborate evidence from other sources, and offer insights into the case that might not be apparent from interviews or observations.
Physical artifacts refer to any physical evidence related to the case, such as tools, products, or physical environments. These artifacts can provide tangible insights into the case, complementing the data gathered from other sources.
Ensuring the quality of data collection
Determining the quality of data in case study research requires careful planning and execution. It's crucial to ensure that the data is reliable, accurate, and relevant to the research question. This involves selecting appropriate methods of collecting data, properly training interviewers or observers, and systematically recording and storing the data. It also includes considering ethical issues related to collecting and handling data, such as obtaining informed consent and ensuring the privacy and confidentiality of the participants.
Data analysis
Analyzing case study research involves making sense of the rich, detailed data to answer the research question. This process can be challenging due to the volume and complexity of case study data. However, a systematic and rigorous approach to analysis can ensure that the findings are credible and meaningful. This section outlines the main steps and considerations in analyzing data in case study research.
Organizing the data
The first step in the analysis is organizing the data. This involves sorting the data into manageable sections, often according to the data source or the theme. This step can also involve transcribing interviews, digitizing physical artifacts, or organizing observational data.
Categorizing and coding the data
Once the data is organized, the next step is to categorize or code the data. This involves identifying common themes, patterns, or concepts in the data and assigning codes to relevant data segments. Coding can be done manually or with the help of software tools, and in either case, qualitative analysis software can greatly facilitate the entire coding process. Coding helps to reduce the data to a set of themes or categories that can be more easily analyzed.
Identifying patterns and themes
After coding the data, the researcher looks for patterns or themes in the coded data. This involves comparing and contrasting the codes and looking for relationships or patterns among them. The identified patterns and themes should help answer the research question.
Interpreting the data
Once patterns and themes have been identified, the next step is to interpret these findings. This involves explaining what the patterns or themes mean in the context of the research question and the case. This interpretation should be grounded in the data, but it can also involve drawing on theoretical concepts or prior research.
Verification of the data
The last step in the analysis is verification. This involves checking the accuracy and consistency of the analysis process and confirming that the findings are supported by the data. This can involve re-checking the original data, checking the consistency of codes, or seeking feedback from research participants or peers.
Like any research method , case study research has its strengths and limitations. Researchers must be aware of these, as they can influence the design, conduct, and interpretation of the study.
Understanding the strengths and limitations of case study research can also guide researchers in deciding whether this approach is suitable for their research question . This section outlines some of the key strengths and limitations of case study research.
Benefits include the following:
- Rich, detailed data: One of the main strengths of case study research is that it can generate rich, detailed data about the case. This can provide a deep understanding of the case and its context, which can be valuable in exploring complex phenomena.
- Flexibility: Case study research is flexible in terms of design , data collection , and analysis . A sufficient degree of flexibility allows the researcher to adapt the study according to the case and the emerging findings.
- Real-world context: Case study research involves studying the case in its real-world context, which can provide valuable insights into the interplay between the case and its context.
- Multiple sources of evidence: Case study research often involves collecting data from multiple sources , which can enhance the robustness and validity of the findings.
On the other hand, researchers should consider the following limitations:
- Generalizability: A common criticism of case study research is that its findings might not be generalizable to other cases due to the specificity and uniqueness of each case.
- Time and resource intensive: Case study research can be time and resource intensive due to the depth of the investigation and the amount of collected data.
- Complexity of analysis: The rich, detailed data generated in case study research can make analyzing the data challenging.
- Subjectivity: Given the nature of case study research, there may be a higher degree of subjectivity in interpreting the data , so researchers need to reflect on this and transparently convey to audiences how the research was conducted.
Being aware of these strengths and limitations can help researchers design and conduct case study research effectively and interpret and report the findings appropriately.

Ready to analyze your data with ATLAS.ti?
See how our intuitive software can draw key insights from your data with a free trial today.
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Beginner Guides 6 Types of Case Studies to Inspire Your Research and Analysis
6 Types of Case Studies to Inspire Your Research and Analysis
Written by: Ronita Mohan Sep 20, 2021

Case studies have become powerful business tools. But what is a case study? What are the benefits of creating one? Are there limitations to the format?
If you’ve asked yourself these questions, our helpful guide will clear things up. Learn how to use a case study for business. Find out how cases analysis works in psychology and research.
We’ve also got examples of case studies to inspire you.
Haven’t made a case study before? You can easily create a case study with Venngage’s customizable case study templates .
Click to jump ahead:
What is a case study?
6 types of case studies, what is a business case study, what is a case study in research, what is a case study in psychology, what is the case study method, benefits of case studies, limitations of case studies, faqs about case studies.
A case study is a research process aimed at learning about a subject, an event or an organization. Case studies are use in business, the social sciences and healthcare.
A case study may focus on one observation or many. It can also examine a series of events or a single case. An effective case study tells a story and provides a conclusion.

Healthcare industries write reports on patients and diagnoses. Marketing case study examples , like the one below, highlight the benefits of a business product.

Now that you know what a case study is, let’s look at the six different types of case studies next.
There are six common types of case reports. Depending on your industry, you might use one of these types.
Descriptive case studies
Explanatory case studies, exploratory case reports, intrinsic case studies, instrumental case studies, collective case reports.

We go into more detail about each type of study in the guide below.
Related: 15+ Professional Case Study Examples [Design Tips + Templates]
When you have an existing hypothesis, you can design a descriptive study. This type of report starts with a description. The aim is to find connections between the subject being studied and a theory.
Once these connections are found, the study can conclude. The results of this type of study will usually suggest how to develop a theory further.
A study like the one below has concrete results. A descriptive report would use the quantitative data as a suggestion for researching the subject deeply.

When an incident occurs in a field, an explanation is required. An explanatory report investigates the cause of the event. It will include explanations for that cause.
The study will also share details about the impact of the event. In most cases, this report will use evidence to predict future occurrences. The results of explanatory reports are definitive.
Note that there is no room for interpretation here. The results are absolute.
The study below is a good example. It explains how one brand used the services of another. It concludes by showing definitive proof that the collaboration was successful.

Another example of this study would be in the automotive industry. If a vehicle fails a test, an explanatory study will examine why. The results could show that the failure was because of a particular part.
Related: How to Write a Case Study [+ Design Tips]
An explanatory report is a self-contained document. An exploratory one is only the beginning of an investigation.
Exploratory cases act as the starting point of studies. This is usually conducted as a precursor to large-scale investigations. The research is used to suggest why further investigations are needed.
An exploratory study can also be used to suggest methods for further examination.
For example, the below analysis could have found inconclusive results. In that situation, it would be the basis for an in-depth study.

Intrinsic studies are more common in the field of psychology. These reports can also be conducted in healthcare or social work.
These types of studies focus on a unique subject, such as a patient. They can sometimes study groups close to the researcher.
The aim of such studies is to understand the subject better. This requires learning their history. The researcher will also examine how they interact with their environment.
For instance, if the case study below was about a unique brand, it could be an intrinsic study.

Once the study is complete, the researcher will have developed a better understanding of a phenomenon. This phenomenon will likely not have been studied or theorized about before.
Examples of intrinsic case analysis can be found across psychology. For example, Jean Piaget’s theories on cognitive development. He established the theory from intrinsic studies into his own children.
Related: What Disney Villains Can Tell Us About Color Psychology [Infographic]
This is another type of study seen in medical and psychology fields. Instrumental reports are created to examine more than just the primary subject.
When research is conducted for an instrumental study, it is to provide the basis for a larger phenomenon. The subject matter is usually the best example of the phenomenon. This is why it is being studied.
Take the example of the fictional brand below.

Assume it’s examining lead generation strategies. It may want to show that visual marketing is the definitive lead generation tool. The brand can conduct an instrumental case study to examine this phenomenon.
Collective studies are based on instrumental case reports. These types of studies examine multiple reports.
There are a number of reasons why collective reports are created:
- To provide evidence for starting a new study
- To find pattens between multiple instrumental reports
- To find differences in similar types of cases
- Gain a deeper understanding of a complex phenomenon
- Understand a phenomenon from diverse contexts
A researcher could use multiple reports, like the one below, to build a collective case report.

Related: 10+ Case Study Infographic Templates That Convert
A business or marketing case study aims at showcasing a successful partnership. This can be between a brand and a client. Or the case study can examine a brand’s project.
There is a perception that case studies are used to advertise a brand. But effective reports, like the one below, can show clients how a brand can support them.

Hubspot created a case study on a customer that successfully scaled its business. The report outlines the various Hubspot tools used to achieve these results.

Hubspot also added a video with testimonials from the client company’s employees.
So, what is the purpose of a case study for businesses? There is a lot of competition in the corporate world. Companies are run by people. They can be on the fence about which brand to work with.
Business reports stand out aesthetically, as well. They use brand colors and brand fonts . Usually, a combination of the client’s and the brand’s.
With the Venngage My Brand Kit feature, businesses can automatically apply their brand to designs.
A business case study, like the one below, acts as social proof. This helps customers decide between your brand and your competitors.

Don’t know how to design a report? You can learn how to write a case study with Venngage’s guide. We also share design tips and examples that will help you convert.
Related: 55+ Annual Report Design Templates, Inspirational Examples & Tips [Updated]
Research is a necessary part of every case study. But specific research fields are required to create studies. These fields include user research, healthcare, education, or social work.
For example, this UX Design report examined the public perception of a client. The brand researched and implemented new visuals to improve it. The study breaks down this research through lessons learned.

Clinical reports are a necessity in the medical field. These documents are used to share knowledge with other professionals. They also help examine new or unusual diseases or symptoms.
The pandemic has led to a significant increase in research. For example, Spectrum Health studied the value of health systems in the pandemic. They created the study by examining community outreach.

The pandemic has significantly impacted the field of education. This has led to numerous examinations on remote studying. There have also been studies on how students react to decreased peer communication.
Social work case reports often have a community focus. They can also examine public health responses. In certain regions, social workers study disaster responses.
You now know what case studies in various fields are. In the next step of our guide, we explain the case study method.
In the field of psychology, case studies focus on a particular subject. Psychology case histories also examine human behaviors.
Case reports search for commonalities between humans. They are also used to prescribe further research. Or these studies can elaborate on a solution for a behavioral ailment.
The American Psychology Association has a number of case studies on real-life clients. Note how the reports are more text-heavy than a business case study.

Famous psychologists such as Sigmund Freud and Anna O popularised the use of case studies in the field. They did so by regularly interviewing subjects. Their detailed observations build the field of psychology.
It is important to note that psychological studies must be conducted by professionals. Psychologists, psychiatrists and therapists should be the researchers in these cases.
Related: What Netflix’s Top 50 Shows Can Teach Us About Font Psychology [Infographic]
The case study method, or case method, is a learning technique where you’re presented with a real-world business challenge and asked how you’d solve it.
After working through it independently and with peers, you learn how the actual scenario unfolded. This approach helps develop problem-solving skills and practical knowledge.
This method often uses various data sources like interviews, observations, and documents to provide comprehensive insights. The below example would have been created after numerous interviews.
Case studies are largely qualitative. They analyze and describe phenomena. While some data is included, a case analysis is not quantitative.
There are a few steps in the case method. You have to start by identifying the subject of your study. Then determine what kind of research is required.
In natural sciences, case studies can take years to complete. Business reports, like this one, don’t take that long. A few weeks of interviews should be enough.

The case method will vary depending on the industry. Reports will also look different once produced.
As you will have seen, business reports are more colorful. The design is also more accessible . Healthcare and psychology reports are more text-heavy.
Designing case reports takes time and energy. So, is it worth taking the time to write them? Here are the benefits of creating case studies.
- Collects large amounts of information
- Helps formulate hypotheses
- Builds the case for further research
- Discovers new insights into a subject
- Builds brand trust and loyalty
- Engages customers through stories
For example, the business study below creates a story around a brand partnership. It makes for engaging reading. The study also shows evidence backing up the information.

We’ve shared the benefits of why studies are needed. We will also look at the limitations of creating them.
Related: How to Present a Case Study like a Pro (With Examples)
There are a few disadvantages to conducting a case analysis. The limitations will vary according to the industry.
- Responses from interviews are subjective
- Subjects may tailor responses to the researcher
- Studies can’t always be replicated
- In certain industries, analyses can take time and be expensive
- Risk of generalizing the results among a larger population
These are some of the common weaknesses of creating case reports. If you’re on the fence, look at the competition in your industry.
Other brands or professionals are building reports, like this example. In that case, you may want to do the same.

What makes a case study a case study?
A case study has a very particular research methodology. They are an in-depth study of a person or a group of individuals. They can also study a community or an organization. Case reports examine real-world phenomena within a set context.
How long should a case study be?
The length of studies depends on the industry. It also depends on the story you’re telling. Most case studies should be at least 500-1500 words long. But you can increase the length if you have more details to share.
What should you ask in a case study?
The one thing you shouldn’t ask is ‘yes’ or ‘no’ questions. Case studies are qualitative. These questions won’t give you the information you need.
Ask your client about the problems they faced. Ask them about solutions they found. Or what they think is the ideal solution. Leave room to ask them follow-up questions. This will help build out the study.
How to present a case study?
When you’re ready to present a case study, begin by providing a summary of the problem or challenge you were addressing. Follow this with an outline of the solution you implemented, and support this with the results you achieved, backed by relevant data. Incorporate visual aids like slides, graphs, and images to make your case study presentation more engaging and impactful.
Now you know what a case study means, you can begin creating one. These reports are a great tool for analyzing brands. They are also useful in a variety of other fields.
Use a visual communication platform like Venngage to design case studies. With Venngage’s templates, you can design easily. Create branded, engaging reports, all without design experience.
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
What is case study research?
Last updated
8 February 2023
Reviewed by
Cathy Heath
Short on time? Get an AI generated summary of this article instead
Suppose a company receives a spike in the number of customer complaints, or medical experts discover an outbreak of illness affecting children but are not quite sure of the reason. In both cases, carrying out a case study could be the best way to get answers.
Organization
Case studies can be carried out across different disciplines, including education, medicine, sociology, and business.
Most case studies employ qualitative methods, but quantitative methods can also be used. Researchers can then describe, compare, evaluate, and identify patterns or cause-and-effect relationships between the various variables under study. They can then use this knowledge to decide what action to take.
Another thing to note is that case studies are generally singular in their focus. This means they narrow focus to a particular area, making them highly subjective. You cannot always generalize the results of a case study and apply them to a larger population. However, they are valuable tools to illustrate a principle or develop a thesis.
Analyze case study research
Dovetail streamlines case study research to help you uncover and share actionable insights
- What are the different types of case study designs?
Researchers can choose from a variety of case study designs. The design they choose is dependent on what questions they need to answer, the context of the research environment, how much data they already have, and what resources are available.
Here are the common types of case study design:
Explanatory
An explanatory case study is an initial explanation of the how or why that is behind something. This design is commonly used when studying a real-life phenomenon or event. Once the organization understands the reasons behind a phenomenon, it can then make changes to enhance or eliminate the variables causing it.
Here is an example: How is co-teaching implemented in elementary schools? The title for a case study of this subject could be “Case Study of the Implementation of Co-Teaching in Elementary Schools.”
Descriptive
An illustrative or descriptive case study helps researchers shed light on an unfamiliar object or subject after a period of time. The case study provides an in-depth review of the issue at hand and adds real-world examples in the area the researcher wants the audience to understand.
The researcher makes no inferences or causal statements about the object or subject under review. This type of design is often used to understand cultural shifts.
Here is an example: How did people cope with the 2004 Indian Ocean Tsunami? This case study could be titled "A Case Study of the 2004 Indian Ocean Tsunami and its Effect on the Indonesian Population."
Exploratory
Exploratory research is also called a pilot case study. It is usually the first step within a larger research project, often relying on questionnaires and surveys . Researchers use exploratory research to help narrow down their focus, define parameters, draft a specific research question , and/or identify variables in a larger study. This research design usually covers a wider area than others, and focuses on the ‘what’ and ‘who’ of a topic.
Here is an example: How do nutrition and socialization in early childhood affect learning in children? The title of the exploratory study may be “Case Study of the Effects of Nutrition and Socialization on Learning in Early Childhood.”
An intrinsic case study is specifically designed to look at a unique and special phenomenon. At the start of the study, the researcher defines the phenomenon and the uniqueness that differentiates it from others.
In this case, researchers do not attempt to generalize, compare, or challenge the existing assumptions. Instead, they explore the unique variables to enhance understanding. Here is an example: “Case Study of Volcanic Lightning.”
This design can also be identified as a cumulative case study. It uses information from past studies or observations of groups of people in certain settings as the foundation of the new study. Given that it takes multiple areas into account, it allows for greater generalization than a single case study.
The researchers also get an in-depth look at a particular subject from different viewpoints. Here is an example: “Case Study of how PTSD affected Vietnam and Gulf War Veterans Differently Due to Advances in Military Technology.”
Critical instance
A critical case study incorporates both explanatory and intrinsic study designs. It does not have predetermined purposes beyond an investigation of the said subject. It can be used for a deeper explanation of the cause-and-effect relationship. It can also be used to question a common assumption or myth.
The findings can then be used further to generalize whether they would also apply in a different environment. Here is an example: “What Effect Does Prolonged Use of Social Media Have on the Mind of American Youth?”
Instrumental
Instrumental research attempts to achieve goals beyond understanding the object at hand. Researchers explore a larger subject through different, separate studies and use the findings to understand its relationship to another subject. This type of design also provides insight into an issue or helps refine a theory.
For example, you may want to determine if violent behavior in children predisposes them to crime later in life. The focus is on the relationship between children and violent behavior, and why certain children do become violent. Here is an example: “Violence Breeds Violence: Childhood Exposure and Participation in Adult Crime.”
Evaluation case study design is employed to research the effects of a program, policy, or intervention, and assess its effectiveness and impact on future decision-making.
For example, you might want to see whether children learn times tables quicker through an educational game on their iPad versus a more teacher-led intervention. Here is an example: “An Investigation of the Impact of an iPad Multiplication Game for Primary School Children.”
- When do you use case studies?
Case studies are ideal when you want to gain a contextual, concrete, or in-depth understanding of a particular subject. It helps you understand the characteristics, implications, and meanings of the subject.
They are also an excellent choice for those writing a thesis or dissertation, as they help keep the project focused on a particular area when resources or time may be too limited to cover a wider one. You may have to conduct several case studies to explore different aspects of the subject in question and understand the problem.
- What are the steps to follow when conducting a case study?
1. Select a case
Once you identify the problem at hand and come up with questions, identify the case you will focus on. The study can provide insights into the subject at hand, challenge existing assumptions, propose a course of action, and/or open up new areas for further research.
2. Create a theoretical framework
While you will be focusing on a specific detail, the case study design you choose should be linked to existing knowledge on the topic. This prevents it from becoming an isolated description and allows for enhancing the existing information.
It may expand the current theory by bringing up new ideas or concepts, challenge established assumptions, or exemplify a theory by exploring how it answers the problem at hand. A theoretical framework starts with a literature review of the sources relevant to the topic in focus. This helps in identifying key concepts to guide analysis and interpretation.
3. Collect the data
Case studies are frequently supplemented with qualitative data such as observations, interviews, and a review of both primary and secondary sources such as official records, news articles, and photographs. There may also be quantitative data —this data assists in understanding the case thoroughly.
4. Analyze your case
The results of the research depend on the research design. Most case studies are structured with chapters or topic headings for easy explanation and presentation. Others may be written as narratives to allow researchers to explore various angles of the topic and analyze its meanings and implications.
In all areas, always give a detailed contextual understanding of the case and connect it to the existing theory and literature before discussing how it fits into your problem area.
- What are some case study examples?
What are the best approaches for introducing our product into the Kenyan market?
How does the change in marketing strategy aid in increasing the sales volumes of product Y?
How can teachers enhance student participation in classrooms?
How does poverty affect literacy levels in children?
Case study topics
Case study of product marketing strategies in the Kenyan market
Case study of the effects of a marketing strategy change on product Y sales volumes
Case study of X school teachers that encourage active student participation in the classroom
Case study of the effects of poverty on literacy levels in children
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 18 April 2023
Last updated: 27 February 2023
Last updated: 6 February 2023
Last updated: 6 October 2023
Last updated: 5 February 2023
Last updated: 16 April 2023
Last updated: 7 March 2023
Last updated: 9 March 2023
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next.

Users report unexpectedly high data usage, especially during streaming sessions.

Users find it hard to navigate from the home page to relevant playlists in the app.

It would be great to have a sleep timer feature, especially for bedtime listening.

I need better filters to find the songs or artists I’m looking for.
Log in or sign up
Get started for free
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods
Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods
Published on 5 May 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 30 January 2023.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organisation, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research.
A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods , but quantitative methods are sometimes also used. Case studies are good for describing , comparing, evaluating, and understanding different aspects of a research problem .
Table of contents
When to do a case study, step 1: select a case, step 2: build a theoretical framework, step 3: collect your data, step 4: describe and analyse the case.
A case study is an appropriate research design when you want to gain concrete, contextual, in-depth knowledge about a specific real-world subject. It allows you to explore the key characteristics, meanings, and implications of the case.
Case studies are often a good choice in a thesis or dissertation . They keep your project focused and manageable when you don’t have the time or resources to do large-scale research.
You might use just one complex case study where you explore a single subject in depth, or conduct multiple case studies to compare and illuminate different aspects of your research problem.
| Research question | Case study |
|---|---|
| What are the ecological effects of wolf reintroduction? | Case study of wolf reintroduction in Yellowstone National Park in the US |
| How do populist politicians use narratives about history to gain support? | Case studies of Hungarian prime minister Viktor Orbán and US president Donald Trump |
| How can teachers implement active learning strategies in mixed-level classrooms? | Case study of a local school that promotes active learning |
| What are the main advantages and disadvantages of wind farms for rural communities? | Case studies of three rural wind farm development projects in different parts of the country |
| How are viral marketing strategies changing the relationship between companies and consumers? | Case study of the iPhone X marketing campaign |
| How do experiences of work in the gig economy differ by gender, race, and age? | Case studies of Deliveroo and Uber drivers in London |
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Once you have developed your problem statement and research questions , you should be ready to choose the specific case that you want to focus on. A good case study should have the potential to:
- Provide new or unexpected insights into the subject
- Challenge or complicate existing assumptions and theories
- Propose practical courses of action to resolve a problem
- Open up new directions for future research
Unlike quantitative or experimental research, a strong case study does not require a random or representative sample. In fact, case studies often deliberately focus on unusual, neglected, or outlying cases which may shed new light on the research problem.
If you find yourself aiming to simultaneously investigate and solve an issue, consider conducting action research . As its name suggests, action research conducts research and takes action at the same time, and is highly iterative and flexible.
However, you can also choose a more common or representative case to exemplify a particular category, experience, or phenomenon.
While case studies focus more on concrete details than general theories, they should usually have some connection with theory in the field. This way the case study is not just an isolated description, but is integrated into existing knowledge about the topic. It might aim to:
- Exemplify a theory by showing how it explains the case under investigation
- Expand on a theory by uncovering new concepts and ideas that need to be incorporated
- Challenge a theory by exploring an outlier case that doesn’t fit with established assumptions
To ensure that your analysis of the case has a solid academic grounding, you should conduct a literature review of sources related to the topic and develop a theoretical framework . This means identifying key concepts and theories to guide your analysis and interpretation.
There are many different research methods you can use to collect data on your subject. Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews, observations, and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data .
The aim is to gain as thorough an understanding as possible of the case and its context.
In writing up the case study, you need to bring together all the relevant aspects to give as complete a picture as possible of the subject.
How you report your findings depends on the type of research you are doing. Some case studies are structured like a standard scientific paper or thesis, with separate sections or chapters for the methods , results , and discussion .
Others are written in a more narrative style, aiming to explore the case from various angles and analyse its meanings and implications (for example, by using textual analysis or discourse analysis ).
In all cases, though, make sure to give contextual details about the case, connect it back to the literature and theory, and discuss how it fits into wider patterns or debates.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, January 30). Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved 24 June 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/case-studies/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, correlational research | guide, design & examples, a quick guide to experimental design | 5 steps & examples, descriptive research design | definition, methods & examples.

Research Writing and Analysis
- NVivo Group and Study Sessions
- SPSS This link opens in a new window
- Statistical Analysis Group sessions
- Using Qualtrics
- Dissertation and Data Analysis Group Sessions
- Defense Schedule - Commons Calendar This link opens in a new window
- Research Process Flow Chart
- Research Alignment Chapter 1 This link opens in a new window
- Step 1: Seek Out Evidence
- Step 2: Explain
- Step 3: The Big Picture
- Step 4: Own It
- Step 5: Illustrate
- Annotated Bibliography
- Literature Review This link opens in a new window
- Systematic Reviews & Meta-Analyses
- How to Synthesize and Analyze
- Synthesis and Analysis Practice
- Synthesis and Analysis Group Sessions
- Problem Statement
- Purpose Statement
- Conceptual Framework
- Theoretical Framework
- Locating Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks This link opens in a new window
- Quantitative Research Questions
- Qualitative Research Questions
- Trustworthiness of Qualitative Data
- Analysis and Coding Example- Qualitative Data
- Thematic Data Analysis in Qualitative Design
- Dissertation to Journal Article This link opens in a new window
- International Journal of Online Graduate Education (IJOGE) This link opens in a new window
- Journal of Research in Innovative Teaching & Learning (JRIT&L) This link opens in a new window
Writing a Case Study

What is a case study?

A Case study is:
- An in-depth research design that primarily uses a qualitative methodology but sometimes includes quantitative methodology.
- Used to examine an identifiable problem confirmed through research.
- Used to investigate an individual, group of people, organization, or event.
- Used to mostly answer "how" and "why" questions.
What are the different types of case studies?

| Descriptive | This type of case study allows the researcher to: | How has the implementation and use of the instructional coaching intervention for elementary teachers impacted students’ attitudes toward reading? |
| Explanatory | This type of case study allows the researcher to: | Why do differences exist when implementing the same online reading curriculum in three elementary classrooms? |
| Exploratory | This type of case study allows the researcher to:
| What are potential barriers to student’s reading success when middle school teachers implement the Ready Reader curriculum online? |
| Multiple Case Studies or Collective Case Study | This type of case study allows the researcher to: | How are individual school districts addressing student engagement in an online classroom? |
| Intrinsic | This type of case study allows the researcher to: | How does a student’s familial background influence a teacher’s ability to provide meaningful instruction? |
| Instrumental | This type of case study allows the researcher to: | How a rural school district’s integration of a reward system maximized student engagement? |
Note: These are the primary case studies. As you continue to research and learn
about case studies you will begin to find a robust list of different types.
Who are your case study participants?

|
|
This type of study is implemented to understand an individual by developing a detailed explanation of the individual’s lived experiences or perceptions.
|
|
| This type of study is implemented to explore a particular group of people’s perceptions. |
|
| This type of study is implemented to explore the perspectives of people who work for or had interaction with a specific organization or company. |
|
| This type of study is implemented to explore participant’s perceptions of an event. |
What is triangulation ?
Validity and credibility are an essential part of the case study. Therefore, the researcher should include triangulation to ensure trustworthiness while accurately reflecting what the researcher seeks to investigate.

How to write a Case Study?
When developing a case study, there are different ways you could present the information, but remember to include the five parts for your case study.

|
|
|
|
|
|

Was this resource helpful?
- << Previous: Thematic Data Analysis in Qualitative Design
- Next: Journal Article Reporting Standards (JARS) >>
- Last Updated: May 29, 2024 8:05 AM
- URL: https://resources.nu.edu/researchtools

- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
What Is a Case Study?
Weighing the pros and cons of this method of research
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Cara Lustik is a fact-checker and copywriter.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Cara-Lustik-1000-77abe13cf6c14a34a58c2a0ffb7297da.jpg)
Verywell / Colleen Tighe
- Pros and Cons
What Types of Case Studies Are Out There?
Where do you find data for a case study, how do i write a psychology case study.
A case study is an in-depth study of one person, group, or event. In a case study, nearly every aspect of the subject's life and history is analyzed to seek patterns and causes of behavior. Case studies can be used in many different fields, including psychology, medicine, education, anthropology, political science, and social work.
The point of a case study is to learn as much as possible about an individual or group so that the information can be generalized to many others. Unfortunately, case studies tend to be highly subjective, and it is sometimes difficult to generalize results to a larger population.
While case studies focus on a single individual or group, they follow a format similar to other types of psychology writing. If you are writing a case study, we got you—here are some rules of APA format to reference.
At a Glance
A case study, or an in-depth study of a person, group, or event, can be a useful research tool when used wisely. In many cases, case studies are best used in situations where it would be difficult or impossible for you to conduct an experiment. They are helpful for looking at unique situations and allow researchers to gather a lot of˜ information about a specific individual or group of people. However, it's important to be cautious of any bias we draw from them as they are highly subjective.
What Are the Benefits and Limitations of Case Studies?
A case study can have its strengths and weaknesses. Researchers must consider these pros and cons before deciding if this type of study is appropriate for their needs.
One of the greatest advantages of a case study is that it allows researchers to investigate things that are often difficult or impossible to replicate in a lab. Some other benefits of a case study:
- Allows researchers to capture information on the 'how,' 'what,' and 'why,' of something that's implemented
- Gives researchers the chance to collect information on why one strategy might be chosen over another
- Permits researchers to develop hypotheses that can be explored in experimental research
On the other hand, a case study can have some drawbacks:
- It cannot necessarily be generalized to the larger population
- Cannot demonstrate cause and effect
- It may not be scientifically rigorous
- It can lead to bias
Researchers may choose to perform a case study if they want to explore a unique or recently discovered phenomenon. Through their insights, researchers develop additional ideas and study questions that might be explored in future studies.
It's important to remember that the insights from case studies cannot be used to determine cause-and-effect relationships between variables. However, case studies may be used to develop hypotheses that can then be addressed in experimental research.
Case Study Examples
There have been a number of notable case studies in the history of psychology. Much of Freud's work and theories were developed through individual case studies. Some great examples of case studies in psychology include:
- Anna O : Anna O. was a pseudonym of a woman named Bertha Pappenheim, a patient of a physician named Josef Breuer. While she was never a patient of Freud's, Freud and Breuer discussed her case extensively. The woman was experiencing symptoms of a condition that was then known as hysteria and found that talking about her problems helped relieve her symptoms. Her case played an important part in the development of talk therapy as an approach to mental health treatment.
- Phineas Gage : Phineas Gage was a railroad employee who experienced a terrible accident in which an explosion sent a metal rod through his skull, damaging important portions of his brain. Gage recovered from his accident but was left with serious changes in both personality and behavior.
- Genie : Genie was a young girl subjected to horrific abuse and isolation. The case study of Genie allowed researchers to study whether language learning was possible, even after missing critical periods for language development. Her case also served as an example of how scientific research may interfere with treatment and lead to further abuse of vulnerable individuals.
Such cases demonstrate how case research can be used to study things that researchers could not replicate in experimental settings. In Genie's case, her horrific abuse denied her the opportunity to learn a language at critical points in her development.
This is clearly not something researchers could ethically replicate, but conducting a case study on Genie allowed researchers to study phenomena that are otherwise impossible to reproduce.
There are a few different types of case studies that psychologists and other researchers might use:
- Collective case studies : These involve studying a group of individuals. Researchers might study a group of people in a certain setting or look at an entire community. For example, psychologists might explore how access to resources in a community has affected the collective mental well-being of those who live there.
- Descriptive case studies : These involve starting with a descriptive theory. The subjects are then observed, and the information gathered is compared to the pre-existing theory.
- Explanatory case studies : These are often used to do causal investigations. In other words, researchers are interested in looking at factors that may have caused certain things to occur.
- Exploratory case studies : These are sometimes used as a prelude to further, more in-depth research. This allows researchers to gather more information before developing their research questions and hypotheses .
- Instrumental case studies : These occur when the individual or group allows researchers to understand more than what is initially obvious to observers.
- Intrinsic case studies : This type of case study is when the researcher has a personal interest in the case. Jean Piaget's observations of his own children are good examples of how an intrinsic case study can contribute to the development of a psychological theory.
The three main case study types often used are intrinsic, instrumental, and collective. Intrinsic case studies are useful for learning about unique cases. Instrumental case studies help look at an individual to learn more about a broader issue. A collective case study can be useful for looking at several cases simultaneously.
The type of case study that psychology researchers use depends on the unique characteristics of the situation and the case itself.
There are a number of different sources and methods that researchers can use to gather information about an individual or group. Six major sources that have been identified by researchers are:
- Archival records : Census records, survey records, and name lists are examples of archival records.
- Direct observation : This strategy involves observing the subject, often in a natural setting . While an individual observer is sometimes used, it is more common to utilize a group of observers.
- Documents : Letters, newspaper articles, administrative records, etc., are the types of documents often used as sources.
- Interviews : Interviews are one of the most important methods for gathering information in case studies. An interview can involve structured survey questions or more open-ended questions.
- Participant observation : When the researcher serves as a participant in events and observes the actions and outcomes, it is called participant observation.
- Physical artifacts : Tools, objects, instruments, and other artifacts are often observed during a direct observation of the subject.
If you have been directed to write a case study for a psychology course, be sure to check with your instructor for any specific guidelines you need to follow. If you are writing your case study for a professional publication, check with the publisher for their specific guidelines for submitting a case study.
Here is a general outline of what should be included in a case study.
Section 1: A Case History
This section will have the following structure and content:
Background information : The first section of your paper will present your client's background. Include factors such as age, gender, work, health status, family mental health history, family and social relationships, drug and alcohol history, life difficulties, goals, and coping skills and weaknesses.
Description of the presenting problem : In the next section of your case study, you will describe the problem or symptoms that the client presented with.
Describe any physical, emotional, or sensory symptoms reported by the client. Thoughts, feelings, and perceptions related to the symptoms should also be noted. Any screening or diagnostic assessments that are used should also be described in detail and all scores reported.
Your diagnosis : Provide your diagnosis and give the appropriate Diagnostic and Statistical Manual code. Explain how you reached your diagnosis, how the client's symptoms fit the diagnostic criteria for the disorder(s), or any possible difficulties in reaching a diagnosis.
Section 2: Treatment Plan
This portion of the paper will address the chosen treatment for the condition. This might also include the theoretical basis for the chosen treatment or any other evidence that might exist to support why this approach was chosen.
- Cognitive behavioral approach : Explain how a cognitive behavioral therapist would approach treatment. Offer background information on cognitive behavioral therapy and describe the treatment sessions, client response, and outcome of this type of treatment. Make note of any difficulties or successes encountered by your client during treatment.
- Humanistic approach : Describe a humanistic approach that could be used to treat your client, such as client-centered therapy . Provide information on the type of treatment you chose, the client's reaction to the treatment, and the end result of this approach. Explain why the treatment was successful or unsuccessful.
- Psychoanalytic approach : Describe how a psychoanalytic therapist would view the client's problem. Provide some background on the psychoanalytic approach and cite relevant references. Explain how psychoanalytic therapy would be used to treat the client, how the client would respond to therapy, and the effectiveness of this treatment approach.
- Pharmacological approach : If treatment primarily involves the use of medications, explain which medications were used and why. Provide background on the effectiveness of these medications and how monotherapy may compare with an approach that combines medications with therapy or other treatments.
This section of a case study should also include information about the treatment goals, process, and outcomes.
When you are writing a case study, you should also include a section where you discuss the case study itself, including the strengths and limitiations of the study. You should note how the findings of your case study might support previous research.
In your discussion section, you should also describe some of the implications of your case study. What ideas or findings might require further exploration? How might researchers go about exploring some of these questions in additional studies?
Need More Tips?
Here are a few additional pointers to keep in mind when formatting your case study:
- Never refer to the subject of your case study as "the client." Instead, use their name or a pseudonym.
- Read examples of case studies to gain an idea about the style and format.
- Remember to use APA format when citing references .
Crowe S, Cresswell K, Robertson A, Huby G, Avery A, Sheikh A. The case study approach . BMC Med Res Methodol . 2011;11:100.
Crowe S, Cresswell K, Robertson A, Huby G, Avery A, Sheikh A. The case study approach . BMC Med Res Methodol . 2011 Jun 27;11:100. doi:10.1186/1471-2288-11-100
Gagnon, Yves-Chantal. The Case Study as Research Method: A Practical Handbook . Canada, Chicago Review Press Incorporated DBA Independent Pub Group, 2010.
Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research and Applications: Design and Methods . United States, SAGE Publications, 2017.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
Case Studies
This guide examines case studies, a form of qualitative descriptive research that is used to look at individuals, a small group of participants, or a group as a whole. Researchers collect data about participants using participant and direct observations, interviews, protocols, tests, examinations of records, and collections of writing samples. Starting with a definition of the case study, the guide moves to a brief history of this research method. Using several well documented case studies, the guide then looks at applications and methods including data collection and analysis. A discussion of ways to handle validity, reliability, and generalizability follows, with special attention to case studies as they are applied to composition studies. Finally, this guide examines the strengths and weaknesses of case studies.
Definition and Overview
Case study refers to the collection and presentation of detailed information about a particular participant or small group, frequently including the accounts of subjects themselves. A form of qualitative descriptive research, the case study looks intensely at an individual or small participant pool, drawing conclusions only about that participant or group and only in that specific context. Researchers do not focus on the discovery of a universal, generalizable truth, nor do they typically look for cause-effect relationships; instead, emphasis is placed on exploration and description.
Case studies typically examine the interplay of all variables in order to provide as complete an understanding of an event or situation as possible. This type of comprehensive understanding is arrived at through a process known as thick description, which involves an in-depth description of the entity being evaluated, the circumstances under which it is used, the characteristics of the people involved in it, and the nature of the community in which it is located. Thick description also involves interpreting the meaning of demographic and descriptive data such as cultural norms and mores, community values, ingrained attitudes, and motives.
Unlike quantitative methods of research, like the survey, which focus on the questions of who, what, where, how much, and how many, and archival analysis, which often situates the participant in some form of historical context, case studies are the preferred strategy when how or why questions are asked. Likewise, they are the preferred method when the researcher has little control over the events, and when there is a contemporary focus within a real life context. In addition, unlike more specifically directed experiments, case studies require a problem that seeks a holistic understanding of the event or situation in question using inductive logic--reasoning from specific to more general terms.
In scholarly circles, case studies are frequently discussed within the context of qualitative research and naturalistic inquiry. Case studies are often referred to interchangeably with ethnography, field study, and participant observation. The underlying philosophical assumptions in the case are similar to these types of qualitative research because each takes place in a natural setting (such as a classroom, neighborhood, or private home), and strives for a more holistic interpretation of the event or situation under study.
Unlike more statistically-based studies which search for quantifiable data, the goal of a case study is to offer new variables and questions for further research. F.H. Giddings, a sociologist in the early part of the century, compares statistical methods to the case study on the basis that the former are concerned with the distribution of a particular trait, or a small number of traits, in a population, whereas the case study is concerned with the whole variety of traits to be found in a particular instance" (Hammersley 95).
Case studies are not a new form of research; naturalistic inquiry was the primary research tool until the development of the scientific method. The fields of sociology and anthropology are credited with the primary shaping of the concept as we know it today. However, case study research has drawn from a number of other areas as well: the clinical methods of doctors; the casework technique being developed by social workers; the methods of historians and anthropologists, plus the qualitative descriptions provided by quantitative researchers like LePlay; and, in the case of Robert Park, the techniques of newspaper reporters and novelists.
Park was an ex-newspaper reporter and editor who became very influential in developing sociological case studies at the University of Chicago in the 1920s. As a newspaper professional he coined the term "scientific" or "depth" reporting: the description of local events in a way that pointed to major social trends. Park viewed the sociologist as "merely a more accurate, responsible, and scientific reporter." Park stressed the variety and value of human experience. He believed that sociology sought to arrive at natural, but fluid, laws and generalizations in regard to human nature and society. These laws weren't static laws of the kind sought by many positivists and natural law theorists, but rather, they were laws of becoming--with a constant possibility of change. Park encouraged students to get out of the library, to quit looking at papers and books, and to view the constant experiment of human experience. He writes, "Go and sit in the lounges of the luxury hotels and on the doorsteps of the flophouses; sit on the Gold Coast settees and on the slum shakedowns; sit in the Orchestra Hall and in the Star and Garter Burlesque. In short, gentlemen [sic], go get the seats of your pants dirty in real research."
But over the years, case studies have drawn their share of criticism. In fact, the method had its detractors from the start. In the 1920s, the debate between pro-qualitative and pro-quantitative became quite heated. Case studies, when compared to statistics, were considered by many to be unscientific. From the 1930's on, the rise of positivism had a growing influence on quantitative methods in sociology. People wanted static, generalizable laws in science. The sociological positivists were looking for stable laws of social phenomena. They criticized case study research because it failed to provide evidence of inter subjective agreement. Also, they condemned it because of the few number of cases studied and that the under-standardized character of their descriptions made generalization impossible. By the 1950s, quantitative methods, in the form of survey research, had become the dominant sociological approach and case study had become a minority practice.
Educational Applications
The 1950's marked the dawning of a new era in case study research, namely that of the utilization of the case study as a teaching method. "Instituted at Harvard Business School in the 1950s as a primary method of teaching, cases have since been used in classrooms and lecture halls alike, either as part of a course of study or as the main focus of the course to which other teaching material is added" (Armisted 1984). The basic purpose of instituting the case method as a teaching strategy was "to transfer much of the responsibility for learning from the teacher on to the student, whose role, as a result, shifts away from passive absorption toward active construction" (Boehrer 1990). Through careful examination and discussion of various cases, "students learn to identify actual problems, to recognize key players and their agendas, and to become aware of those aspects of the situation that contribute to the problem" (Merseth 1991). In addition, students are encouraged to "generate their own analysis of the problems under consideration, to develop their own solutions, and to practically apply their own knowledge of theory to these problems" (Boyce 1993). Along the way, students also develop "the power to analyze and to master a tangled circumstance by identifying and delineating important factors; the ability to utilize ideas, to test them against facts, and to throw them into fresh combinations" (Merseth 1991).
In addition to the practical application and testing of scholarly knowledge, case discussions can also help students prepare for real-world problems, situations and crises by providing an approximation of various professional environments (i.e. classroom, board room, courtroom, or hospital). Thus, through the examination of specific cases, students are given the opportunity to work out their own professional issues through the trials, tribulations, experiences, and research findings of others. An obvious advantage to this mode of instruction is that it allows students the exposure to settings and contexts that they might not otherwise experience. For example, a student interested in studying the effects of poverty on minority secondary student's grade point averages and S.A.T. scores could access and analyze information from schools as geographically diverse as Los Angeles, New York City, Miami, and New Mexico without ever having to leave the classroom.
The case study method also incorporates the idea that students can learn from one another "by engaging with each other and with each other's ideas, by asserting something and then having it questioned, challenged and thrown back at them so that they can reflect on what they hear, and then refine what they say" (Boehrer 1990). In summary, students can direct their own learning by formulating questions and taking responsibility for the study.
Types and Design Concerns
Researchers use multiple methods and approaches to conduct case studies.
Types of Case Studies
Under the more generalized category of case study exist several subdivisions, each of which is custom selected for use depending upon the goals and/or objectives of the investigator. These types of case study include the following:
Illustrative Case Studies These are primarily descriptive studies. They typically utilize one or two instances of an event to show what a situation is like. Illustrative case studies serve primarily to make the unfamiliar familiar and to give readers a common language about the topic in question.
Exploratory (or pilot) Case Studies These are condensed case studies performed before implementing a large scale investigation. Their basic function is to help identify questions and select types of measurement prior to the main investigation. The primary pitfall of this type of study is that initial findings may seem convincing enough to be released prematurely as conclusions.
Cumulative Case Studies These serve to aggregate information from several sites collected at different times. The idea behind these studies is the collection of past studies will allow for greater generalization without additional cost or time being expended on new, possibly repetitive studies.
Critical Instance Case Studies These examine one or more sites for either the purpose of examining a situation of unique interest with little to no interest in generalizability, or to call into question or challenge a highly generalized or universal assertion. This method is useful for answering cause and effect questions.
Identifying a Theoretical Perspective
Much of the case study's design is inherently determined for researchers, depending on the field from which they are working. In composition studies, researchers are typically working from a qualitative, descriptive standpoint. In contrast, physicists will approach their research from a more quantitative perspective. Still, in designing the study, researchers need to make explicit the questions to be explored and the theoretical perspective from which they will approach the case. The three most commonly adopted theories are listed below:
Individual Theories These focus primarily on the individual development, cognitive behavior, personality, learning and disability, and interpersonal interactions of a particular subject.
Organizational Theories These focus on bureaucracies, institutions, organizational structure and functions, or excellence in organizational performance.
Social Theories These focus on urban development, group behavior, cultural institutions, or marketplace functions.
Two examples of case studies are used consistently throughout this chapter. The first, a study produced by Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman (1988), looks at a first year graduate student's initiation into an academic writing program. The study uses participant-observer and linguistic data collecting techniques to assess the student's knowledge of appropriate discourse conventions. Using the pseudonym Nate to refer to the subject, the study sought to illuminate the particular experience rather than to generalize about the experience of fledgling academic writers collectively.
For example, in Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman's (1988) study we are told that the researchers are interested in disciplinary communities. In the first paragraph, they ask what constitutes membership in a disciplinary community and how achieving membership might affect a writer's understanding and production of texts. In the third paragraph they state that researchers must negotiate their claims "within the context of his sub specialty's accepted knowledge and methodology." In the next paragraph they ask, "How is literacy acquired? What is the process through which novices gain community membership? And what factors either aid or hinder students learning the requisite linguistic behaviors?" This introductory section ends with a paragraph in which the study's authors claim that during the course of the study, the subject, Nate, successfully makes the transition from "skilled novice" to become an initiated member of the academic discourse community and that his texts exhibit linguistic changes which indicate this transition. In the next section the authors make explicit the sociolinguistic theoretical and methodological assumptions on which the study is based (1988). Thus the reader has a good understanding of the authors' theoretical background and purpose in conducting the study even before it is explicitly stated on the fourth page of the study. "Our purpose was to examine the effects of the educational context on one graduate student's production of texts as he wrote in different courses and for different faculty members over the academic year 1984-85." The goal of the study then, was to explore the idea that writers must be initiated into a writing community, and that this initiation will change the way one writes.
The second example is Janet Emig's (1971) study of the composing process of a group of twelfth graders. In this study, Emig seeks to answer the question of what happens to the self as a result educational stimuli in terms of academic writing. The case study used methods such as protocol analysis, tape-recorded interviews, and discourse analysis.
In the case of Janet Emig's (1971) study of the composing process of eight twelfth graders, four specific hypotheses were made:
- Twelfth grade writers engage in two modes of composing: reflexive and extensive.
- These differences can be ascertained and characterized through having the writers compose aloud their composition process.
- A set of implied stylistic principles governs the writing process.
- For twelfth grade writers, extensive writing occurs chiefly as a school-sponsored activity, or reflexive, as a self-sponsored activity.
In this study, the chief distinction is between the two dominant modes of composing among older, secondary school students. The distinctions are:
- The reflexive mode, which focuses on the writer's thoughts and feelings.
- The extensive mode, which focuses on conveying a message.
Emig also outlines the specific questions which guided the research in the opening pages of her Review of Literature , preceding the report.
Designing a Case Study
After considering the different sub categories of case study and identifying a theoretical perspective, researchers can begin to design their study. Research design is the string of logic that ultimately links the data to be collected and the conclusions to be drawn to the initial questions of the study. Typically, research designs deal with at least four problems:
- What questions to study
- What data are relevant
- What data to collect
- How to analyze that data
In other words, a research design is basically a blueprint for getting from the beginning to the end of a study. The beginning is an initial set of questions to be answered, and the end is some set of conclusions about those questions.
Because case studies are conducted on topics as diverse as Anglo-Saxon Literature (Thrane 1986) and AIDS prevention (Van Vugt 1994), it is virtually impossible to outline any strict or universal method or design for conducting the case study. However, Robert K. Yin (1993) does offer five basic components of a research design:
- A study's questions.
- A study's propositions (if any).
- A study's units of analysis.
- The logic that links the data to the propositions.
- The criteria for interpreting the findings.
In addition to these five basic components, Yin also stresses the importance of clearly articulating one's theoretical perspective, determining the goals of the study, selecting one's subject(s), selecting the appropriate method(s) of collecting data, and providing some considerations to the composition of the final report.
Conducting Case Studies
To obtain as complete a picture of the participant as possible, case study researchers can employ a variety of approaches and methods. These approaches, methods, and related issues are discussed in depth in this section.
Method: Single or Multi-modal?
To obtain as complete a picture of the participant as possible, case study researchers can employ a variety of methods. Some common methods include interviews , protocol analyses, field studies, and participant-observations. Emig (1971) chose to use several methods of data collection. Her sources included conversations with the students, protocol analysis, discrete observations of actual composition, writing samples from each student, and school records (Lauer and Asher 1988).
Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman (1988) collected data by observing classrooms, conducting faculty and student interviews, collecting self reports from the subject, and by looking at the subject's written work.
A study that was criticized for using a single method model was done by Flower and Hayes (1984). In this study that explores the ways in which writers use different forms of knowing to create space, the authors used only protocol analysis to gather data. The study came under heavy fire because of their decision to use only one method.
Participant Selection
Case studies can use one participant, or a small group of participants. However, it is important that the participant pool remain relatively small. The participants can represent a diverse cross section of society, but this isn't necessary.
For example, the Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman (1988) study looked at just one participant, Nate. By contrast, in Janet Emig's (1971) study of the composition process of twelfth graders, eight participants were selected representing a diverse cross section of the community, with volunteers from an all-white upper-middle-class suburban school, an all-black inner-city school, a racially mixed lower-middle-class school, an economically and racially mixed school, and a university school.
Often, a brief "case history" is done on the participants of the study in order to provide researchers with a clearer understanding of their participants, as well as some insight as to how their own personal histories might affect the outcome of the study. For instance, in Emig's study, the investigator had access to the school records of five of the participants, and to standardized test scores for the remaining three. Also made available to the researcher was the information that three of the eight students were selected as NCTE Achievement Award winners. These personal histories can be useful in later stages of the study when data are being analyzed and conclusions drawn.
Data Collection
There are six types of data collected in case studies:
- Archival records.
- Interviews.
- Direct observation.
- Participant observation.
In the field of composition research, these six sources might be:
- A writer's drafts.
- School records of student writers.
- Transcripts of interviews with a writer.
- Transcripts of conversations between writers (and protocols).
- Videotapes and notes from direct field observations.
- Hard copies of a writer's work on computer.
Depending on whether researchers have chosen to use a single or multi-modal approach for the case study, they may choose to collect data from one or any combination of these sources.
Protocols, that is, transcriptions of participants talking aloud about what they are doing as they do it, have been particularly common in composition case studies. For example, in Emig's (1971) study, the students were asked, in four different sessions, to give oral autobiographies of their writing experiences and to compose aloud three themes in the presence of a tape recorder and the investigator.
In some studies, only one method of data collection is conducted. For example, the Flower and Hayes (1981) report on the cognitive process theory of writing depends on protocol analysis alone. However, using multiple sources of evidence to increase the reliability and validity of the data can be advantageous.
Case studies are likely to be much more convincing and accurate if they are based on several different sources of information, following a corroborating mode. This conclusion is echoed among many composition researchers. For example, in her study of predrafting processes of high and low-apprehensive writers, Cynthia Selfe (1985) argues that because "methods of indirect observation provide only an incomplete reflection of the complex set of processes involved in composing, a combination of several such methods should be used to gather data in any one study." Thus, in this study, Selfe collected her data from protocols, observations of students role playing their writing processes, audio taped interviews with the students, and videotaped observations of the students in the process of composing.
It can be said then, that cross checking data from multiple sources can help provide a multidimensional profile of composing activities in a particular setting. Sharan Merriam (1985) suggests "checking, verifying, testing, probing, and confirming collected data as you go, arguing that this process will follow in a funnel-like design resulting in less data gathering in later phases of the study along with a congruent increase in analysis checking, verifying, and confirming."
It is important to note that in case studies, as in any qualitative descriptive research, while researchers begin their studies with one or several questions driving the inquiry (which influence the key factors the researcher will be looking for during data collection), a researcher may find new key factors emerging during data collection. These might be unexpected patterns or linguistic features which become evident only during the course of the research. While not bearing directly on the researcher's guiding questions, these variables may become the basis for new questions asked at the end of the report, thus linking to the possibility of further research.
Data Analysis
As the information is collected, researchers strive to make sense of their data. Generally, researchers interpret their data in one of two ways: holistically or through coding. Holistic analysis does not attempt to break the evidence into parts, but rather to draw conclusions based on the text as a whole. Flower and Hayes (1981), for example, make inferences from entire sections of their students' protocols, rather than searching through the transcripts to look for isolatable characteristics.
However, composition researchers commonly interpret their data by coding, that is by systematically searching data to identify and/or categorize specific observable actions or characteristics. These observable actions then become the key variables in the study. Sharan Merriam (1988) suggests seven analytic frameworks for the organization and presentation of data:
- The role of participants.
- The network analysis of formal and informal exchanges among groups.
- Historical.
- Thematical.
- Ritual and symbolism.
- Critical incidents that challenge or reinforce fundamental beliefs, practices, and values.
There are two purposes of these frameworks: to look for patterns among the data and to look for patterns that give meaning to the case study.
As stated above, while most researchers begin their case studies expecting to look for particular observable characteristics, it is not unusual for key variables to emerge during data collection. Typical variables coded in case studies of writers include pauses writers make in the production of a text, the use of specific linguistic units (such as nouns or verbs), and writing processes (planning, drafting, revising, and editing). In the Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman (1988) study, for example, researchers coded the participant's texts for use of connectives, discourse demonstratives, average sentence length, off-register words, use of the first person pronoun, and the ratio of definite articles to indefinite articles.
Since coding is inherently subjective, more than one coder is usually employed. In the Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman (1988) study, for example, three rhetoricians were employed to code the participant's texts for off-register phrases. The researchers established the agreement among the coders before concluding that the participant used fewer off-register words as the graduate program progressed.
Composing the Case Study Report
In the many forms it can take, "a case study is generically a story; it presents the concrete narrative detail of actual, or at least realistic events, it has a plot, exposition, characters, and sometimes even dialogue" (Boehrer 1990). Generally, case study reports are extensively descriptive, with "the most problematic issue often referred to as being the determination of the right combination of description and analysis" (1990). Typically, authors address each step of the research process, and attempt to give the reader as much context as possible for the decisions made in the research design and for the conclusions drawn.
This contextualization usually includes a detailed explanation of the researchers' theoretical positions, of how those theories drove the inquiry or led to the guiding research questions, of the participants' backgrounds, of the processes of data collection, of the training and limitations of the coders, along with a strong attempt to make connections between the data and the conclusions evident.
Although the Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman (1988) study does not, case study reports often include the reactions of the participants to the study or to the researchers' conclusions. Because case studies tend to be exploratory, most end with implications for further study. Here researchers may identify significant variables that emerged during the research and suggest studies related to these, or the authors may suggest further general questions that their case study generated.
For example, Emig's (1971) study concludes with a section dedicated solely to the topic of implications for further research, in which she suggests several means by which this particular study could have been improved, as well as questions and ideas raised by this study which other researchers might like to address, such as: is there a correlation between a certain personality and a certain composing process profile (e.g. is there a positive correlation between ego strength and persistence in revising)?
Also included in Emig's study is a section dedicated to implications for teaching, which outlines the pedagogical ramifications of the study's findings for teachers currently involved in high school writing programs.
Sharan Merriam (1985) also offers several suggestions for alternative presentations of data:
- Prepare specialized condensations for appropriate groups.
- Replace narrative sections with a series of answers to open-ended questions.
- Present "skimmer's" summaries at beginning of each section.
- Incorporate headlines that encapsulate information from text.
- Prepare analytic summaries with supporting data appendixes.
- Present data in colorful and/or unique graphic representations.
Issues of Validity and Reliability
Once key variables have been identified, they can be analyzed. Reliability becomes a key concern at this stage, and many case study researchers go to great lengths to ensure that their interpretations of the data will be both reliable and valid. Because issues of validity and reliability are an important part of any study in the social sciences, it is important to identify some ways of dealing with results.
Multi-modal case study researchers often balance the results of their coding with data from interviews or writer's reflections upon their own work. Consequently, the researchers' conclusions become highly contextualized. For example, in a case study which looked at the time spent in different stages of the writing process, Berkenkotter concluded that her participant, Donald Murray, spent more time planning his essays than in other writing stages. The report of this case study is followed by Murray's reply, wherein he agrees with some of Berkenkotter's conclusions and disagrees with others.
As is the case with other research methodologies, issues of external validity, construct validity, and reliability need to be carefully considered.
Commentary on Case Studies
Researchers often debate the relative merits of particular methods, among them case study. In this section, we comment on two key issues. To read the commentaries, choose any of the items below:
Strengths and Weaknesses of Case Studies
Most case study advocates point out that case studies produce much more detailed information than what is available through a statistical analysis. Advocates will also hold that while statistical methods might be able to deal with situations where behavior is homogeneous and routine, case studies are needed to deal with creativity, innovation, and context. Detractors argue that case studies are difficult to generalize because of inherent subjectivity and because they are based on qualitative subjective data, generalizable only to a particular context.
Flexibility
The case study approach is a comparatively flexible method of scientific research. Because its project designs seem to emphasize exploration rather than prescription or prediction, researchers are comparatively freer to discover and address issues as they arise in their experiments. In addition, the looser format of case studies allows researchers to begin with broad questions and narrow their focus as their experiment progresses rather than attempt to predict every possible outcome before the experiment is conducted.
Emphasis on Context
By seeking to understand as much as possible about a single subject or small group of subjects, case studies specialize in "deep data," or "thick description"--information based on particular contexts that can give research results a more human face. This emphasis can help bridge the gap between abstract research and concrete practice by allowing researchers to compare their firsthand observations with the quantitative results obtained through other methods of research.
Inherent Subjectivity
"The case study has long been stereotyped as the weak sibling among social science methods," and is often criticized as being too subjective and even pseudo-scientific. Likewise, "investigators who do case studies are often regarded as having deviated from their academic disciplines, and their investigations as having insufficient precision (that is, quantification), objectivity and rigor" (Yin 1989). Opponents cite opportunities for subjectivity in the implementation, presentation, and evaluation of case study research. The approach relies on personal interpretation of data and inferences. Results may not be generalizable, are difficult to test for validity, and rarely offer a problem-solving prescription. Simply put, relying on one or a few subjects as a basis for cognitive extrapolations runs the risk of inferring too much from what might be circumstance.
High Investment
Case studies can involve learning more about the subjects being tested than most researchers would care to know--their educational background, emotional background, perceptions of themselves and their surroundings, their likes, dislikes, and so on. Because of its emphasis on "deep data," the case study is out of reach for many large-scale research projects which look at a subject pool in the tens of thousands. A budget request of $10,000 to examine 200 subjects sounds more efficient than a similar request to examine four subjects.
Ethical Considerations
Researchers conducting case studies should consider certain ethical issues. For example, many educational case studies are often financed by people who have, either directly or indirectly, power over both those being studied and those conducting the investigation (1985). This conflict of interests can hinder the credibility of the study.
The personal integrity, sensitivity, and possible prejudices and/or biases of the investigators need to be taken into consideration as well. Personal biases can creep into how the research is conducted, alternative research methods used, and the preparation of surveys and questionnaires.
A common complaint in case study research is that investigators change direction during the course of the study unaware that their original research design was inadequate for the revised investigation. Thus, the researchers leave unknown gaps and biases in the study. To avoid this, researchers should report preliminary findings so that the likelihood of bias will be reduced.
Concerns about Reliability, Validity, and Generalizability
Merriam (1985) offers several suggestions for how case study researchers might actively combat the popular attacks on the validity, reliability, and generalizability of case studies:
- Prolong the Processes of Data Gathering on Site: This will help to insure the accuracy of the findings by providing the researcher with more concrete information upon which to formulate interpretations.
- Employ the Process of "Triangulation": Use a variety of data sources as opposed to relying solely upon one avenue of observation. One example of such a data check would be what McClintock, Brannon, and Maynard (1985) refer to as a "case cluster method," that is, when a single unit within a larger case is randomly sampled, and that data treated quantitatively." For instance, in Emig's (1971) study, the case cluster method was employed, singling out the productivity of a single student named Lynn. This cluster profile included an advanced case history of the subject, specific examination and analysis of individual compositions and protocols, and extensive interview sessions. The seven remaining students were then compared with the case of Lynn, to ascertain if there are any shared, or unique dimensions to the composing process engaged in by these eight students.
- Conduct Member Checks: Initiate and maintain an active corroboration on the interpretation of data between the researcher and those who provided the data. In other words, talk to your subjects.
- Collect Referential Materials: Complement the file of materials from the actual site with additional document support. For example, Emig (1971) supports her initial propositions with historical accounts by writers such as T.S. Eliot, James Joyce, and D.H. Lawrence. Emig also cites examples of theoretical research done with regards to the creative process, as well as examples of empirical research dealing with the writing of adolescents. Specific attention is then given to the four stages description of the composing process delineated by Helmoltz, Wallas, and Cowley, as it serves as the focal point in this study.
- Engage in Peer Consultation: Prior to composing the final draft of the report, researchers should consult with colleagues in order to establish validity through pooled judgment.
Although little can be done to combat challenges concerning the generalizability of case studies, "most writers suggest that qualitative research should be judged as credible and confirmable as opposed to valid and reliable" (Merriam 1985). Likewise, it has been argued that "rather than transplanting statistical, quantitative notions of generalizability and thus finding qualitative research inadequate, it makes more sense to develop an understanding of generalization that is congruent with the basic characteristics of qualitative inquiry" (1985). After all, criticizing the case study method for being ungeneralizable is comparable to criticizing a washing machine for not being able to tell the correct time. In other words, it is unjust to criticize a method for not being able to do something which it was never originally designed to do in the first place.
Annotated Bibliography
Armisted, C. (1984). How Useful are Case Studies. Training and Development Journal, 38 (2), 75-77.
This article looks at eight types of case studies, offers pros and cons of using case studies in the classroom, and gives suggestions for successfully writing and using case studies.
Bardovi-Harlig, K. (1997). Beyond Methods: Components of Second Language Teacher Education . New York: McGraw-Hill.
A compilation of various research essays which address issues of language teacher education. Essays included are: "Non-native reading research and theory" by Lee, "The case for Psycholinguistics" by VanPatten, and "Assessment and Second Language Teaching" by Gradman and Reed.
Bartlett, L. (1989). A Question of Good Judgment; Interpretation Theory and Qualitative Enquiry Address. 70th Annual Meeting of the American Educational Research Association. San Francisco.
Bartlett selected "quasi-historical" methodology, which focuses on the "truth" found in case records, as one that will provide "good judgments" in educational inquiry. He argues that although the method is not comprehensive, it can try to connect theory with practice.
Baydere, S. et. al. (1993). Multimedia conferencing as a tool for collaborative writing: a case study in Computer Supported Collaborative Writing. New York: Springer-Verlag.
The case study by Baydere et. al. is just one of the many essays in this book found in the series "Computer Supported Cooperative Work." Denley, Witefield and May explore similar issues in their essay, "A case study in task analysis for the design of a collaborative document production system."
Berkenkotter, C., Huckin, T., N., & Ackerman J. (1988). Conventions, Conversations, and the Writer: Case Study of a Student in a Rhetoric Ph.D. Program. Research in the Teaching of English, 22, 9-44.
The authors focused on how the writing of their subject, Nate or Ackerman, changed as he became more acquainted or familiar with his field's discourse community.
Berninger, V., W., and Gans, B., M. (1986). Language Profiles in Nonspeaking Individuals of Normal Intelligence with Severe Cerebral Palsy. Augmentative and Alternative Communication, 2, 45-50.
Argues that generalizations about language abilities in patients with severe cerebral palsy (CP) should be avoided. Standardized tests of different levels of processing oral language, of processing written language, and of producing written language were administered to 3 male participants (aged 9, 16, and 40 yrs).
Bockman, J., R., and Couture, B. (1984). The Case Method in Technical Communication: Theory and Models. Texas: Association of Teachers of Technical Writing.
Examines the study and teaching of technical writing, communication of technical information, and the case method in terms of those applications.
Boehrer, J. (1990). Teaching With Cases: Learning to Question. New Directions for Teaching and Learning, 42 41-57.
This article discusses the origins of the case method, looks at the question of what is a case, gives ideas about learning in case teaching, the purposes it can serve in the classroom, the ground rules for the case discussion, including the role of the question, and new directions for case teaching.
Bowman, W. R. (1993). Evaluating JTPA Programs for Economically Disadvantaged Adults: A Case Study of Utah and General Findings . Washington: National Commission for Employment Policy.
"To encourage state-level evaluations of JTPA, the Commission and the State of Utah co-sponsored this report on the effectiveness of JTPA Title II programs for adults in Utah. The technique used is non-experimental and the comparison group was selected from registrants with Utah's Employment Security. In a step-by-step approach, the report documents how non-experimental techniques can be applied and several specific technical issues can be addressed."
Boyce, A. (1993) The Case Study Approach for Pedagogists. Annual Meeting of the American Alliance for Health, Physical Education, Recreation and Dance. (Address). Washington DC.
This paper addresses how case studies 1) bridge the gap between teaching theory and application, 2) enable students to analyze problems and develop solutions for situations that will be encountered in the real world of teaching, and 3) helps students to evaluate the feasibility of alternatives and to understand the ramifications of a particular course of action.
Carson, J. (1993) The Case Study: Ideal Home of WAC Quantitative and Qualitative Data. Annual Meeting of the Conference on College Composition and Communication. (Address). San Diego.
"Increasingly, one of the most pressing questions for WAC advocates is how to keep [WAC] programs going in the face of numerous difficulties. Case histories offer the best chance for fashioning rhetorical arguments to keep WAC programs going because they offer the opportunity to provide a coherent narrative that contextualizes all documents and data, including what is generally considered scientific data. A case study of the WAC program, . . . at Robert Morris College in Pittsburgh demonstrates the advantages of this research method. Such studies are ideal homes for both naturalistic and positivistic data as well as both quantitative and qualitative information."
---. (1991). A Cognitive Process Theory of Writing. College Composition and Communication. 32. 365-87.
No abstract available.
Cromer, R. (1994) A Case Study of Dissociations Between Language and Cognition. Constraints on Language Acquisition: Studies of Atypical Children . Hillsdale: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 141-153.
Crossley, M. (1983) Case Study in Comparative and International Education: An Approach to Bridging the Theory-Practice Gap. Proceedings of the 11th Annual Conference of the Australian Comparative and International Education Society. Hamilton, NZ.
Case study research, as presented here, helps bridge the theory-practice gap in comparative and international research studies of education because it focuses on the practical, day-to-day context rather than on the national arena. The paper asserts that the case study method can be valuable at all levels of research, formation, and verification of theories in education.
Daillak, R., H., and Alkin, M., C. (1982). Qualitative Studies in Context: Reflections on the CSE Studies of Evaluation Use . California: EDRS
The report shows how the Center of the Study of Evaluation (CSE) applied qualitative techniques to a study of evaluation information use in local, Los Angeles schools. It critiques the effectiveness and the limitations of using case study, evaluation, field study, and user interview survey methodologies.
Davey, L. (1991). The Application of Case Study Evaluations. ERIC/TM Digest.
This article examines six types of case studies, the type of evaluation questions that can be answered, the functions served, some design features, and some pitfalls of the method.
Deutch, C. E. (1996). A course in research ethics for graduate students. College Teaching, 44, 2, 56-60.
This article describes a one-credit discussion course in research ethics for graduate students in biology. Case studies are focused on within the four parts of the course: 1) major issues, 2 )practical issues in scholarly work, 3) ownership of research results, and 4) training and personal decisions.
DeVoss, G. (1981). Ethics in Fieldwork Research. RIE 27p. (ERIC)
This article examines four of the ethical problems that can happen when conducting case study research: acquiring permission to do research, knowing when to stop digging, the pitfalls of doing collaborative research, and preserving the integrity of the participants.
Driscoll, A. (1985). Case Study of a Research Intervention: the University of Utah’s Collaborative Approach . San Francisco: Far West Library for Educational Research Development.
Paper presented at the annual meeting of the American Association of Colleges of Teacher Education, Denver, CO, March 1985. Offers information of in-service training, specifically case studies application.
Ellram, L. M. (1996). The Use of the Case Study Method in Logistics Research. Journal of Business Logistics, 17, 2, 93.
This article discusses the increased use of case study in business research, and the lack of understanding of when and how to use case study methodology in business.
Emig, J. (1971) The Composing Processes of Twelfth Graders . Urbana: NTCE.
This case study uses observation, tape recordings, writing samples, and school records to show that writing in reflexive and extensive situations caused different lengths of discourse and different clusterings of the components of the writing process.
Feagin, J. R. (1991). A Case For the Case Study . Chapel Hill: The University of North Carolina Press.
This book discusses the nature, characteristics, and basic methodological issues of the case study as a research method.
Feldman, H., Holland, A., & Keefe, K. (1989) Language Abilities after Left Hemisphere Brain Injury: A Case Study of Twins. Topics in Early Childhood Special Education, 9, 32-47.
"Describes the language abilities of 2 twin pairs in which 1 twin (the experimental) suffered brain injury to the left cerebral hemisphere around the time of birth and1 twin (the control) did not. One pair of twins was initially assessed at age 23 mo. and the other at about 30 mo.; they were subsequently evaluated in their homes 3 times at about 6-mo intervals."
Fidel, R. (1984). The Case Study Method: A Case Study. Library and Information Science Research, 6.
The article describes the use of case study methodology to systematically develop a model of online searching behavior in which study design is flexible, subject manner determines data gathering and analyses, and procedures adapt to the study's progressive change.
Flower, L., & Hayes, J. R. (1984). Images, Plans and Prose: The Representation of Meaning in Writing. Written Communication, 1, 120-160.
Explores the ways in which writers actually use different forms of knowing to create prose.
Frey, L. R. (1992). Interpreting Communication Research: A Case Study Approach Englewood Cliffs, N.J.: Prentice Hall.
The book discusses research methodologies in the Communication field. It focuses on how case studies bridge the gap between communication research, theory, and practice.
Gilbert, V. K. (1981). The Case Study as a Research Methodology: Difficulties and Advantages of Integrating the Positivistic, Phenomenological and Grounded Theory Approaches . The Annual Meeting of the Canadian Association for the Study of Educational Administration. (Address) Halifax, NS, Can.
This study on an innovative secondary school in England shows how a "low-profile" participant-observer case study was crucial to the initial observation, the testing of hypotheses, the interpretive approach, and the grounded theory.
Gilgun, J. F. (1994). A Case for Case Studies in Social Work Research. Social Work, 39, 4, 371-381.
This article defines case study research, presents guidelines for evaluation of case studies, and shows the relevance of case studies to social work research. It also looks at issues such as evaluation and interpretations of case studies.
Glennan, S. L., Sharp-Bittner, M. A. & Tullos, D. C. (1991). Augmentative and Alternative Communication Training with a Nonspeaking Adult: Lessons from MH. Augmentative and Alternative Communication, 7, 240-7.
"A response-guided case study documented changes in a nonspeaking 36-yr-old man's ability to communicate using 3 trained augmentative communication modes. . . . Data were collected in videotaped interaction sessions between the nonspeaking adult and a series of adult speaking."
Graves, D. (1981). An Examination of the Writing Processes of Seven Year Old Children. Research in the Teaching of English, 15, 113-134.
Hamel, J. (1993). Case Study Methods . Newbury Park: Sage. .
"In a most economical fashion, Hamel provides a practical guide for producing theoretically sharp and empirically sound sociological case studies. A central idea put forth by Hamel is that case studies must "locate the global in the local" thus making the careful selection of the research site the most critical decision in the analytic process."
Karthigesu, R. (1986, July). Television as a Tool for Nation-Building in the Third World: A Post-Colonial Pattern, Using Malaysia as a Case-Study. International Television Studies Conference. (Address). London, 10-12.
"The extent to which Television Malaysia, as a national mass media organization, has been able to play a role in nation building in the post-colonial period is . . . studied in two parts: how the choice of a model of nation building determines the character of the organization; and how the character of the organization influences the output of the organization."
Kenny, R. (1984). Making the Case for the Case Study. Journal of Curriculum Studies, 16, (1), 37-51.
The article looks at how and why the case study is justified as a viable and valuable approach to educational research and program evaluation.
Knirk, F. (1991). Case Materials: Research and Practice. Performance Improvement Quarterly, 4 (1 ), 73-81.
The article addresses the effectiveness of case studies, subject areas where case studies are commonly used, recent examples of their use, and case study design considerations.
Klos, D. (1976). Students as Case Writers. Teaching of Psychology, 3.2, 63-66.
This article reviews a course in which students gather data for an original case study of another person. The task requires the students to design the study, collect the data, write the narrative, and interpret the findings.
Leftwich, A. (1981). The Politics of Case Study: Problems of Innovation in University Education. Higher Education Review, 13.2, 38-64.
The article discusses the use of case studies as a teaching method. Emphasis is on the instructional materials, interdisciplinarity, and the complex relationships within the university that help or hinder the method.
Mabrito, M. (1991, Oct.). Electronic Mail as a Vehicle for Peer Response: Conversations of High and Low Apprehensive Writers. Written Communication, 509-32.
McCarthy, S., J. (1955). The Influence of Classroom Discourse on Student Texts: The Case of Ella . East Lansing: Institute for Research on Teaching.
A look at how students of color become marginalized within traditional classroom discourse. The essay follows the struggles of one black student: Ella.
Matsuhashi, A., ed. (1987). Writing in Real Time: Modeling Production Processes Norwood, NJ: Ablex Publishing Corporation.
Investigates how writers plan to produce discourse for different purposes to report, to generalize, and to persuade, as well as how writers plan for sentence level units of language. To learn about planning, an observational measure of pause time was used" (ERIC).
Merriam, S. B. (1985). The Case Study in Educational Research: A Review of Selected Literature. Journal of Educational Thought, 19.3, 204-17.
The article examines the characteristics of, philosophical assumptions underlying the case study, the mechanics of conducting a case study, and the concerns about the reliability, validity, and generalizability of the method.
---. (1988). Case Study Research in Education: A Qualitative Approach San Francisco: Jossey Bass.
Merry, S. E., & Milner, N. eds. (1993). The Possibility of Popular Justice: A Case Study of Community Mediation in the United States . Ann Arbor: U of Michigan.
". . . this volume presents a case study of one experiment in popular justice, the San Francisco Community Boards. This program has made an explicit claim to create an alternative justice, or new justice, in the midst of a society ordered by state law. The contributors to this volume explore the history and experience of the program and compare it to other versions of popular justice in the United States, Europe, and the Third World."
Merseth, K. K. (1991). The Case for Cases in Teacher Education. RIE. 42p. (ERIC).
This monograph argues that the case method of instruction offers unique potential for revitalizing the field of teacher education.
Michaels, S. (1987). Text and Context: A New Approach to the Study of Classroom Writing. Discourse Processes, 10, 321-346.
"This paper argues for and illustrates an approach to the study of writing that integrates ethnographic analysis of classroom interaction with linguistic analysis of written texts and teacher/student conversational exchanges. The approach is illustrated through a case study of writing in a single sixth grade classroom during a single writing assignment."
Milburn, G. (1995). Deciphering a Code or Unraveling a Riddle: A Case Study in the Application of a Humanistic Metaphor to the Reporting of Social Studies Teaching. Theory and Research in Education, 13.
This citation serves as an example of how case studies document learning procedures in a senior-level economics course.
Milley, J. E. (1979). An Investigation of Case Study as an Approach to Program Evaluation. 19th Annual Forum of the Association for Institutional Research. (Address). San Diego.
The case study method merged a narrative report focusing on the evaluator as participant-observer with document review, interview, content analysis, attitude questionnaire survey, and sociogram analysis. Milley argues that case study program evaluation has great potential for widespread use.
Minnis, J. R. (1985, Sept.). Ethnography, Case Study, Grounded Theory, and Distance Education Research. Distance Education, 6.2.
This article describes and defines the strengths and weaknesses of ethnography, case study, and grounded theory.
Nunan, D. (1992). Collaborative language learning and teaching . New York: Cambridge University Press.
Included in this series of essays is Peter Sturman’s "Team Teaching: a case study from Japan" and David Nunan’s own "Toward a collaborative approach to curriculum development: a case study."
Nystrand, M., ed. (1982). What Writers Know: The Language, Process, and Structure of Written Discourse . New York: Academic Press.
Owenby, P. H. (1992). Making Case Studies Come Alive. Training, 29, (1), 43-46. (ERIC)
This article provides tips for writing more effective case studies.
---. (1981). Pausing and Planning: The Tempo of Writer Discourse Production. Research in the Teaching of English, 15 (2),113-34.
Perl, S. (1979). The Composing Processes of Unskilled College Writers. Research in the Teaching of English, 13, 317-336.
"Summarizes a study of five unskilled college writers, focusing especially on one of the five, and discusses the findings in light of current pedagogical practice and research design."
Pilcher J. and A. Coffey. eds. (1996). Gender and Qualitative Research . Brookfield: Aldershot, Hants, England.
This book provides a series of essays which look at gender identity research, qualitative research and applications of case study to questions of gendered pedagogy.
Pirie, B. S. (1993). The Case of Morty: A Four Year Study. Gifted Education International, 9 (2), 105-109.
This case study describes a boy from kindergarten through third grade with above average intelligence but difficulty in learning to read, write, and spell.
Popkewitz, T. (1993). Changing Patterns of Power: Social Regulation and Teacher Education Reform. Albany: SUNY Press.
Popkewitz edits this series of essays that address case studies on educational change and the training of teachers. The essays vary in terms of discipline and scope. Also, several authors include case studies of educational practices in countries other than the United States.
---. (1984). The Predrafting Processes of Four High- and Four Low Apprehensive Writers. Research in the Teaching of English, 18, (1), 45-64.
Rasmussen, P. (1985, March) A Case Study on the Evaluation of Research at the Technical University of Denmark. International Journal of Institutional Management in Higher Education, 9 (1).
This is an example of a case study methodology used to evaluate the chemistry and chemical engineering departments at the University of Denmark.
Roth, K. J. (1986). Curriculum Materials, Teacher Talk, and Student Learning: Case Studies in Fifth-Grade Science Teaching . East Lansing: Institute for Research on Teaching.
Roth offers case studies on elementary teachers, elementary school teaching, science studies and teaching, and verbal learning.
Selfe, C. L. (1985). An Apprehensive Writer Composes. When a Writer Can't Write: Studies in Writer's Block and Other Composing-Process Problems . (pp. 83-95). Ed. Mike Rose. NMY: Guilford.
Smith-Lewis, M., R. and Ford, A. (1987). A User's Perspective on Augmentative Communication. Augmentative and Alternative Communication, 3, 12-7.
"During a series of in-depth interviews, a 25-yr-old woman with cerebral palsy who utilized augmentative communication reflected on the effectiveness of the devices designed for her during her school career."
St. Pierre, R., G. (1980, April). Follow Through: A Case Study in Metaevaluation Research . 64th Annual Meeting of the American Educational Research Association. (Address).
The three approaches to metaevaluation are evaluation of primary evaluations, integrative meta-analysis with combined primary evaluation results, and re-analysis of the raw data from a primary evaluation.
Stahler, T., M. (1996, Feb.) Early Field Experiences: A Model That Worked. ERIC.
"This case study of a field and theory class examines a model designed to provide meaningful field experiences for preservice teachers while remaining consistent with the instructor's beliefs about the role of teacher education in preparing teachers for the classroom."
Stake, R. E. (1995). The Art of Case Study Research. Thousand Oaks: Sage Publications.
This book examines case study research in education and case study methodology.
Stiegelbauer, S. (1984) Community, Context, and Co-curriculum: Situational Factors Influencing School Improvements in a Study of High Schools. Presented at the annual meeting of the American Educational Research Association, New Orleans, LA.
Discussion of several case studies: one looking at high school environments, another examining educational innovations.
Stolovitch, H. (1990). Case Study Method. Performance And Instruction, 29, (9), 35-37.
This article describes the case study method as a form of simulation and presents guidelines for their use in professional training situations.
Thaller, E. (1994). Bibliography for the Case Method: Using Case Studies in Teacher Education. RIE. 37 p.
This bibliography presents approximately 450 citations on the use of case studies in teacher education from 1921-1993.
Thrane, T. (1986). On Delimiting the Senses of Near-Synonyms in Historical Semantics: A Case Study of Adjectives of 'Moral Sufficiency' in the Old English Andreas. Linguistics Across Historical and Geographical Boundaries: In Honor of Jacek Fisiak on the Occasion of his Fiftieth Birthday . Berlin: Mouton de Gruyter.
United Nations. (1975). Food and Agriculture Organization. Report on the FAO/UNFPA Seminar on Methodology, Research and Country: Case Studies on Population, Employment and Productivity . Rome: United Nations.
This example case study shows how the methodology can be used in a demographic and psychographic evaluation. At the same time, it discusses the formation and instigation of the case study methodology itself.
Van Vugt, J. P., ed. (1994). Aids Prevention and Services: Community Based Research . Westport: Bergin and Garvey.
"This volume has been five years in the making. In the process, some of the policy applications called for have met with limited success, such as free needle exchange programs in a limited number of American cities, providing condoms to prison inmates, and advertisements that depict same-sex couples. Rather than dating our chapters that deal with such subjects, such policy applications are verifications of the type of research demonstrated here. Furthermore, they indicate the critical need to continue community based research in the various communities threatened by acquired immuno-deficiency syndrome (AIDS) . . . "
Welch, W., ed. (1981, May). Case Study Methodology in Educational Evaluation. Proceedings of the Minnesota Evaluation Conference. Minnesota. (Address).
The four papers in these proceedings provide a comprehensive picture of the rationale, methodology, strengths, and limitations of case studies.
Williams, G. (1987). The Case Method: An Approach to Teaching and Learning in Educational Administration. RIE, 31p.
This paper examines the viability of the case method as a teaching and learning strategy in instructional systems geared toward the training of personnel of the administration of various aspects of educational systems.
Yin, R. K. (1993). Advancing Rigorous Methodologies: A Review of 'Towards Rigor in Reviews of Multivocal Literatures.' Review of Educational Research, 61, (3).
"R. T. Ogawa and B. Malen's article does not meet its own recommended standards for rigorous testing and presentation of its own conclusions. Use of the exploratory case study to analyze multivocal literatures is not supported, and the claim of grounded theory to analyze multivocal literatures may be stronger."
---. (1989). Case Study Research: Design and Methods. London: Sage Publications Inc.
This book discusses in great detail, the entire design process of the case study, including entire chapters on collecting evidence, analyzing evidence, composing the case study report, and designing single and multiple case studies.
Related Links
Consider the following list of related Web sites for more information on the topic of case study research. Note: although many of the links cover the general category of qualitative research, all have sections that address issues of case studies.
- Sage Publications on Qualitative Methodology: Search here for a comprehensive list of new books being published about "Qualitative Methodology" http://www.sagepub.co.uk/
- The International Journal of Qualitative Studies in Education: An on-line journal "to enhance the theory and practice of qualitative research in education." On-line submissions are welcome. http://www.tandf.co.uk/journals/tf/09518398.html
- Qualitative Research Resources on the Internet: From syllabi to home pages to bibliographies. All links relate somehow to qualitative research. http://www.nova.edu/ssss/QR/qualres.html
Citation Information
Bronwyn Becker, Patrick Dawson, Karen Devine, Carla Hannum, Steve Hill, Jon Leydens, Debbie Matuskevich, Carol Traver, and Mike Palmquist. (1994-2024). Case Studies. The WAC Clearinghouse. Colorado State University. Available at https://wac.colostate.edu/repository/writing/guides/.
Copyright Information
Copyright © 1994-2024 Colorado State University and/or this site's authors, developers, and contributors . Some material displayed on this site is used with permission.
Case Study Research Method in Psychology
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
Case studies are in-depth investigations of a person, group, event, or community. Typically, data is gathered from various sources using several methods (e.g., observations & interviews).
The case study research method originated in clinical medicine (the case history, i.e., the patient’s personal history). In psychology, case studies are often confined to the study of a particular individual.
The information is mainly biographical and relates to events in the individual’s past (i.e., retrospective), as well as to significant events that are currently occurring in his or her everyday life.
The case study is not a research method, but researchers select methods of data collection and analysis that will generate material suitable for case studies.
Freud (1909a, 1909b) conducted very detailed investigations into the private lives of his patients in an attempt to both understand and help them overcome their illnesses.
This makes it clear that the case study is a method that should only be used by a psychologist, therapist, or psychiatrist, i.e., someone with a professional qualification.
There is an ethical issue of competence. Only someone qualified to diagnose and treat a person can conduct a formal case study relating to atypical (i.e., abnormal) behavior or atypical development.
Famous Case Studies
- Anna O – One of the most famous case studies, documenting psychoanalyst Josef Breuer’s treatment of “Anna O” (real name Bertha Pappenheim) for hysteria in the late 1800s using early psychoanalytic theory.
- Little Hans – A child psychoanalysis case study published by Sigmund Freud in 1909 analyzing his five-year-old patient Herbert Graf’s house phobia as related to the Oedipus complex.
- Bruce/Brenda – Gender identity case of the boy (Bruce) whose botched circumcision led psychologist John Money to advise gender reassignment and raise him as a girl (Brenda) in the 1960s.
- Genie Wiley – Linguistics/psychological development case of the victim of extreme isolation abuse who was studied in 1970s California for effects of early language deprivation on acquiring speech later in life.
- Phineas Gage – One of the most famous neuropsychology case studies analyzes personality changes in railroad worker Phineas Gage after an 1848 brain injury involving a tamping iron piercing his skull.
Clinical Case Studies
- Studying the effectiveness of psychotherapy approaches with an individual patient
- Assessing and treating mental illnesses like depression, anxiety disorders, PTSD
- Neuropsychological cases investigating brain injuries or disorders
Child Psychology Case Studies
- Studying psychological development from birth through adolescence
- Cases of learning disabilities, autism spectrum disorders, ADHD
- Effects of trauma, abuse, deprivation on development
Types of Case Studies
- Explanatory case studies : Used to explore causation in order to find underlying principles. Helpful for doing qualitative analysis to explain presumed causal links.
- Exploratory case studies : Used to explore situations where an intervention being evaluated has no clear set of outcomes. It helps define questions and hypotheses for future research.
- Descriptive case studies : Describe an intervention or phenomenon and the real-life context in which it occurred. It is helpful for illustrating certain topics within an evaluation.
- Multiple-case studies : Used to explore differences between cases and replicate findings across cases. Helpful for comparing and contrasting specific cases.
- Intrinsic : Used to gain a better understanding of a particular case. Helpful for capturing the complexity of a single case.
- Collective : Used to explore a general phenomenon using multiple case studies. Helpful for jointly studying a group of cases in order to inquire into the phenomenon.
Where Do You Find Data for a Case Study?
There are several places to find data for a case study. The key is to gather data from multiple sources to get a complete picture of the case and corroborate facts or findings through triangulation of evidence. Most of this information is likely qualitative (i.e., verbal description rather than measurement), but the psychologist might also collect numerical data.
1. Primary sources
- Interviews – Interviewing key people related to the case to get their perspectives and insights. The interview is an extremely effective procedure for obtaining information about an individual, and it may be used to collect comments from the person’s friends, parents, employer, workmates, and others who have a good knowledge of the person, as well as to obtain facts from the person him or herself.
- Observations – Observing behaviors, interactions, processes, etc., related to the case as they unfold in real-time.
- Documents & Records – Reviewing private documents, diaries, public records, correspondence, meeting minutes, etc., relevant to the case.
2. Secondary sources
- News/Media – News coverage of events related to the case study.
- Academic articles – Journal articles, dissertations etc. that discuss the case.
- Government reports – Official data and records related to the case context.
- Books/films – Books, documentaries or films discussing the case.
3. Archival records
Searching historical archives, museum collections and databases to find relevant documents, visual/audio records related to the case history and context.
Public archives like newspapers, organizational records, photographic collections could all include potentially relevant pieces of information to shed light on attitudes, cultural perspectives, common practices and historical contexts related to psychology.
4. Organizational records
Organizational records offer the advantage of often having large datasets collected over time that can reveal or confirm psychological insights.
Of course, privacy and ethical concerns regarding confidential data must be navigated carefully.
However, with proper protocols, organizational records can provide invaluable context and empirical depth to qualitative case studies exploring the intersection of psychology and organizations.
- Organizational/industrial psychology research : Organizational records like employee surveys, turnover/retention data, policies, incident reports etc. may provide insight into topics like job satisfaction, workplace culture and dynamics, leadership issues, employee behaviors etc.
- Clinical psychology : Therapists/hospitals may grant access to anonymized medical records to study aspects like assessments, diagnoses, treatment plans etc. This could shed light on clinical practices.
- School psychology : Studies could utilize anonymized student records like test scores, grades, disciplinary issues, and counseling referrals to study child development, learning barriers, effectiveness of support programs, and more.
How do I Write a Case Study in Psychology?
Follow specified case study guidelines provided by a journal or your psychology tutor. General components of clinical case studies include: background, symptoms, assessments, diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes. Interpreting the information means the researcher decides what to include or leave out. A good case study should always clarify which information is the factual description and which is an inference or the researcher’s opinion.
1. Introduction
- Provide background on the case context and why it is of interest, presenting background information like demographics, relevant history, and presenting problem.
- Compare briefly to similar published cases if applicable. Clearly state the focus/importance of the case.
2. Case Presentation
- Describe the presenting problem in detail, including symptoms, duration,and impact on daily life.
- Include client demographics like age and gender, information about social relationships, and mental health history.
- Describe all physical, emotional, and/or sensory symptoms reported by the client.
- Use patient quotes to describe the initial complaint verbatim. Follow with full-sentence summaries of relevant history details gathered, including key components that led to a working diagnosis.
- Summarize clinical exam results, namely orthopedic/neurological tests, imaging, lab tests, etc. Note actual results rather than subjective conclusions. Provide images if clearly reproducible/anonymized.
- Clearly state the working diagnosis or clinical impression before transitioning to management.
3. Management and Outcome
- Indicate the total duration of care and number of treatments given over what timeframe. Use specific names/descriptions for any therapies/interventions applied.
- Present the results of the intervention,including any quantitative or qualitative data collected.
- For outcomes, utilize visual analog scales for pain, medication usage logs, etc., if possible. Include patient self-reports of improvement/worsening of symptoms. Note the reason for discharge/end of care.
4. Discussion
- Analyze the case, exploring contributing factors, limitations of the study, and connections to existing research.
- Analyze the effectiveness of the intervention,considering factors like participant adherence, limitations of the study, and potential alternative explanations for the results.
- Identify any questions raised in the case analysis and relate insights to established theories and current research if applicable. Avoid definitive claims about physiological explanations.
- Offer clinical implications, and suggest future research directions.
5. Additional Items
- Thank specific assistants for writing support only. No patient acknowledgments.
- References should directly support any key claims or quotes included.
- Use tables/figures/images only if substantially informative. Include permissions and legends/explanatory notes.
- Provides detailed (rich qualitative) information.
- Provides insight for further research.
- Permitting investigation of otherwise impractical (or unethical) situations.
Case studies allow a researcher to investigate a topic in far more detail than might be possible if they were trying to deal with a large number of research participants (nomothetic approach) with the aim of ‘averaging’.
Because of their in-depth, multi-sided approach, case studies often shed light on aspects of human thinking and behavior that would be unethical or impractical to study in other ways.
Research that only looks into the measurable aspects of human behavior is not likely to give us insights into the subjective dimension of experience, which is important to psychoanalytic and humanistic psychologists.
Case studies are often used in exploratory research. They can help us generate new ideas (that might be tested by other methods). They are an important way of illustrating theories and can help show how different aspects of a person’s life are related to each other.
The method is, therefore, important for psychologists who adopt a holistic point of view (i.e., humanistic psychologists ).
Limitations
- Lacking scientific rigor and providing little basis for generalization of results to the wider population.
- Researchers’ own subjective feelings may influence the case study (researcher bias).
- Difficult to replicate.
- Time-consuming and expensive.
- The volume of data, together with the time restrictions in place, impacted the depth of analysis that was possible within the available resources.
Because a case study deals with only one person/event/group, we can never be sure if the case study investigated is representative of the wider body of “similar” instances. This means the conclusions drawn from a particular case may not be transferable to other settings.
Because case studies are based on the analysis of qualitative (i.e., descriptive) data , a lot depends on the psychologist’s interpretation of the information she has acquired.
This means that there is a lot of scope for Anna O , and it could be that the subjective opinions of the psychologist intrude in the assessment of what the data means.
For example, Freud has been criticized for producing case studies in which the information was sometimes distorted to fit particular behavioral theories (e.g., Little Hans ).
This is also true of Money’s interpretation of the Bruce/Brenda case study (Diamond, 1997) when he ignored evidence that went against his theory.
Breuer, J., & Freud, S. (1895). Studies on hysteria . Standard Edition 2: London.
Curtiss, S. (1981). Genie: The case of a modern wild child .
Diamond, M., & Sigmundson, K. (1997). Sex Reassignment at Birth: Long-term Review and Clinical Implications. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine , 151(3), 298-304
Freud, S. (1909a). Analysis of a phobia of a five year old boy. In The Pelican Freud Library (1977), Vol 8, Case Histories 1, pages 169-306
Freud, S. (1909b). Bemerkungen über einen Fall von Zwangsneurose (Der “Rattenmann”). Jb. psychoanal. psychopathol. Forsch ., I, p. 357-421; GW, VII, p. 379-463; Notes upon a case of obsessional neurosis, SE , 10: 151-318.
Harlow J. M. (1848). Passage of an iron rod through the head. Boston Medical and Surgical Journal, 39 , 389–393.
Harlow, J. M. (1868). Recovery from the Passage of an Iron Bar through the Head . Publications of the Massachusetts Medical Society. 2 (3), 327-347.
Money, J., & Ehrhardt, A. A. (1972). Man & Woman, Boy & Girl : The Differentiation and Dimorphism of Gender Identity from Conception to Maturity. Baltimore, Maryland: Johns Hopkins University Press.
Money, J., & Tucker, P. (1975). Sexual signatures: On being a man or a woman.
Further Information
- Case Study Approach
- Case Study Method
- Enhancing the Quality of Case Studies in Health Services Research
- “We do things together” A case study of “couplehood” in dementia
- Using mixed methods for evaluating an integrative approach to cancer care: a case study
Related Articles

Research Methodology
Mixed Methods Research

Conversation Analysis

Discourse Analysis

Phenomenology In Qualitative Research

Ethnography In Qualitative Research

Narrative Analysis In Qualitative Research
- Ask a Librarian
- Case Study Research
- What is a Case Study?
- Finding a Case Study
Related Guides
- Abstracts - A Guide to Writing by David Woolard Last Updated May 1, 2024 652 views this year
- Annotated Bibliography by Clara Volker Last Updated Jan 16, 2024 2415 views this year
- Literature Reviews by Clara Volker Last Updated Oct 25, 2023 5703 views this year
- Qualitative & Quantitative Research by Suzanne Eichler Last Updated Nov 16, 2023 304 views this year
- The Research Paper Process by Clara Volker Last Updated Nov 16, 2023 2590 views this year
- SAGE Research Methods by Kristen Davis Last Updated Oct 25, 2023 558 views this year
What is a case study?
A case study is a type of research method. In case studies, the unit of analysis is a case . The case typically provides a detailed account of a situation that usually focuses on a conflict or complexity that one might encounter in the workplace.
- Case studies help explain the process by which a unit (a person, department, business, organization, industry, country, etc.) deals with the issue or problem confronting it, and offers possible solutions that can be applied to other units facing similar situations.
- The information presented in case studies is usually qualitative in nature - gathered through methods such as interview, observation, and document collection.
- There are different types of case study, including intrinsic, instrumental, naturalistic, and pragmatic.
This research guide will assist you in finding individual case studies, as well as providing information on designing case studies. If you need assistance locating information, please Ask a Librarian .
- Next: Case Study Research >>
- Last Updated: Nov 2, 2023 2:39 PM
- URL: https://guides.erau.edu/case-studies
Hunt Library
Mori Hosseini Student Union 1 Aerospace Boulevard Daytona Beach, FL 32114
Phone: 386-226-6595 Toll-Free: 800-678-9428
Maps and Parking
- Report a Problem
- Suggest a Purchase
Library Information
- Departments and Staff
- Library Collections
- Library Facilities
- Library Newsletter
- Hunt Library Employment

University Initiatives
- Scholarly Commons
- Data Commons
- University Archives
- Open and Affordable Textbooks
Warning: The NCBI web site requires JavaScript to function. more...
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Browse Titles
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
InformedHealth.org [Internet]. Cologne, Germany: Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG); 2006-.

InformedHealth.org [Internet].
In brief: what types of studies are there.
Last Update: September 8, 2016 ; Next update: 2024.
There are various types of scientific studies such as experiments and comparative analyses, observational studies, surveys, or interviews. The choice of study type will mainly depend on the research question being asked.
When making decisions, patients and doctors need reliable answers to a number of questions. Depending on the medical condition and patient's personal situation, the following questions may be asked:
- What is the cause of the condition?
- What is the natural course of the disease if left untreated?
- What will change because of the treatment?
- How many other people have the same condition?
- How do other people cope with it?
Each of these questions can best be answered by a different type of study.
In order to get reliable results, a study has to be carefully planned right from the start. One thing that is especially important to consider is which type of study is best suited to the research question. A study protocol should be written and complete documentation of the study's process should also be done. This is vital in order for other scientists to be able to reproduce and check the results afterwards.
The main types of studies are randomized controlled trials (RCTs), cohort studies, case-control studies and qualitative studies.
- Randomized controlled trials
If you want to know how effective a treatment or diagnostic test is, randomized trials provide the most reliable answers. Because the effect of the treatment is often compared with "no treatment" (or a different treatment), they can also show what happens if you opt to not have the treatment or diagnostic test.
When planning this type of study, a research question is stipulated first. This involves deciding what exactly should be tested and in what group of people. In order to be able to reliably assess how effective the treatment is, the following things also need to be determined before the study is started:
- How long the study should last
- How many participants are needed
- How the effect of the treatment should be measured
For instance, a medication used to treat menopause symptoms needs to be tested on a different group of people than a flu medicine. And a study on treatment for a stuffy nose may be much shorter than a study on a drug taken to prevent strokes .
“Randomized” means divided into groups by chance. In RCTs participants are randomly assigned to one of two or more groups. Then one group receives the new drug A, for example, while the other group receives the conventional drug B or a placebo (dummy drug). Things like the appearance and taste of the drug and the placebo should be as similar as possible. Ideally, the assignment to the various groups is done "double blinded," meaning that neither the participants nor their doctors know who is in which group.
The assignment to groups has to be random in order to make sure that only the effects of the medications are compared, and no other factors influence the results. If doctors decided themselves which patients should receive which treatment, they might – for instance – give the more promising drug to patients who have better chances of recovery. This would distort the results. Random allocation ensures that differences between the results of the two groups at the end of the study are actually due to the treatment and not something else.
Randomized controlled trials provide the best results when trying to find out if there is a cause-and-effect relationship. RCTs can answer questions such as these:
- Is the new drug A better than the standard treatment for medical condition X?
- Does regular physical activity speed up recovery after a slipped disk when compared to passive waiting?
- Cohort studies
A cohort is a group of people who are observed frequently over a period of many years – for instance, to determine how often a certain disease occurs. In a cohort study, two (or more) groups that are exposed to different things are compared with each other: For example, one group might smoke while the other doesn't. Or one group may be exposed to a hazardous substance at work, while the comparison group isn't. The researchers then observe how the health of the people in both groups develops over the course of several years, whether they become ill, and how many of them pass away. Cohort studies often include people who are healthy at the start of the study. Cohort studies can have a prospective (forward-looking) design or a retrospective (backward-looking) design. In a prospective study, the result that the researchers are interested in (such as a specific illness) has not yet occurred by the time the study starts. But the outcomes that they want to measure and other possible influential factors can be precisely defined beforehand. In a retrospective study, the result (the illness) has already occurred before the study starts, and the researchers look at the patient's history to find risk factors.
Cohort studies are especially useful if you want to find out how common a medical condition is and which factors increase the risk of developing it. They can answer questions such as:
- How does high blood pressure affect heart health?
- Does smoking increase your risk of lung cancer?
For example, one famous long-term cohort study observed a group of 40,000 British doctors, many of whom smoked. It tracked how many doctors died over the years, and what they died of. The study showed that smoking caused a lot of deaths, and that people who smoked more were more likely to get ill and die.
- Case-control studies
Case-control studies compare people who have a certain medical condition with people who do not have the medical condition, but who are otherwise as similar as possible, for example in terms of their sex and age. Then the two groups are interviewed, or their medical files are analyzed, to find anything that might be risk factors for the disease. So case-control studies are generally retrospective.
Case-control studies are one way to gain knowledge about rare diseases. They are also not as expensive or time-consuming as RCTs or cohort studies. But it is often difficult to tell which people are the most similar to each other and should therefore be compared with each other. Because the researchers usually ask about past events, they are dependent on the participants’ memories. But the people they interview might no longer remember whether they were, for instance, exposed to certain risk factors in the past.
Still, case-control studies can help to investigate the causes of a specific disease, and answer questions like these:
- Do HPV infections increase the risk of cervical cancer ?
- Is the risk of sudden infant death syndrome (“cot death”) increased by parents smoking at home?
Cohort studies and case-control studies are types of "observational studies."
- Cross-sectional studies
Many people will be familiar with this kind of study. The classic type of cross-sectional study is the survey: A representative group of people – usually a random sample – are interviewed or examined in order to find out their opinions or facts. Because this data is collected only once, cross-sectional studies are relatively quick and inexpensive. They can provide information on things like the prevalence of a particular disease (how common it is). But they can't tell us anything about the cause of a disease or what the best treatment might be.
Cross-sectional studies can answer questions such as these:
- How tall are German men and women at age 20?
- How many people have cancer screening?
- Qualitative studies
This type of study helps us understand, for instance, what it is like for people to live with a certain disease. Unlike other kinds of research, qualitative research does not rely on numbers and data. Instead, it is based on information collected by talking to people who have a particular medical condition and people close to them. Written documents and observations are used too. The information that is obtained is then analyzed and interpreted using a number of methods.
Qualitative studies can answer questions such as these:
- How do women experience a Cesarean section?
- What aspects of treatment are especially important to men who have prostate cancer ?
- How reliable are the different types of studies?
Each type of study has its advantages and disadvantages. It is always important to find out the following: Did the researchers select a study type that will actually allow them to find the answers they are looking for? You can’t use a survey to find out what is causing a particular disease, for instance.
It is really only possible to draw reliable conclusions about cause and effect by using randomized controlled trials. Other types of studies usually only allow us to establish correlations (relationships where it isn’t clear whether one thing is causing the other). For instance, data from a cohort study may show that people who eat more red meat develop bowel cancer more often than people who don't. This might suggest that eating red meat can increase your risk of getting bowel cancer. But people who eat a lot of red meat might also smoke more, drink more alcohol, or tend to be overweight. The influence of these and other possible risk factors can only be determined by comparing two equal-sized groups made up of randomly assigned participants.
That is why randomized controlled trials are usually the only suitable way to find out how effective a treatment is. Systematic reviews, which summarize multiple RCTs , are even better. In order to be good-quality, though, all studies and systematic reviews need to be designed properly and eliminate as many potential sources of error as possible.
- German Network for Evidence-based Medicine. Glossar: Qualitative Forschung. Berlin: DNEbM; 2011.
- Greenhalgh T. Einführung in die Evidence-based Medicine: kritische Beurteilung klinischer Studien als Basis einer rationalen Medizin. Bern: Huber; 2003.
- Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG, Germany). General methods . Version 5.0. Cologne: IQWiG; 2017.
- Klug SJ, Bender R, Blettner M, Lange S. Wichtige epidemiologische Studientypen. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 2007; 132:e45-e47. [ PubMed : 17530597 ]
- Schäfer T. Kritische Bewertung von Studien zur Ätiologie. In: Kunz R, Ollenschläger G, Raspe H, Jonitz G, Donner-Banzhoff N (eds.). Lehrbuch evidenzbasierte Medizin in Klinik und Praxis. Cologne: Deutscher Ärzte-Verlag; 2007.
IQWiG health information is written with the aim of helping people understand the advantages and disadvantages of the main treatment options and health care services.
Because IQWiG is a German institute, some of the information provided here is specific to the German health care system. The suitability of any of the described options in an individual case can be determined by talking to a doctor. informedhealth.org can provide support for talks with doctors and other medical professionals, but cannot replace them. We do not offer individual consultations.
Our information is based on the results of good-quality studies. It is written by a team of health care professionals, scientists and editors, and reviewed by external experts. You can find a detailed description of how our health information is produced and updated in our methods.
- Cite this Page InformedHealth.org [Internet]. Cologne, Germany: Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG); 2006-. In brief: What types of studies are there? [Updated 2016 Sep 8].
In this Page
Informed health links, related information.
- PubMed Links to PubMed
Recent Activity
- In brief: What types of studies are there? - InformedHealth.org In brief: What types of studies are there? - InformedHealth.org
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
Turn recording back on
Connect with NLM
National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894
Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
Help Accessibility Careers

Case Studies
Case studies are a popular research method in business area. Case studies aim to analyze specific issues within the boundaries of a specific environment, situation or organization.
According to its design, case studies in business research can be divided into three categories: explanatory, descriptive and exploratory.
Explanatory case studies aim to answer ‘how’ or ’why’ questions with little control on behalf of researcher over occurrence of events. This type of case studies focus on phenomena within the contexts of real-life situations. Example: “An investigation into the reasons of the global financial and economic crisis of 2008 – 2010.”
Descriptive case studies aim to analyze the sequence of interpersonal events after a certain amount of time has passed. Studies in business research belonging to this category usually describe culture or sub-culture, and they attempt to discover the key phenomena. Example: “Impact of increasing levels of multiculturalism on marketing practices: A case study of McDonald’s Indonesia.”
Exploratory case studies aim to find answers to the questions of ‘what’ or ‘who’. Exploratory case study data collection method is often accompanied by additional data collection method(s) such as interviews, questionnaires, experiments etc. Example: “A study into differences of leadership practices between private and public sector organizations in Atlanta, USA.”
Advantages of case study method include data collection and analysis within the context of phenomenon, integration of qualitative and quantitative data in data analysis, and the ability to capture complexities of real-life situations so that the phenomenon can be studied in greater levels of depth. Case studies do have certain disadvantages that may include lack of rigor, challenges associated with data analysis and very little basis for generalizations of findings and conclusions.

John Dudovskiy
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- Types of Research Designs Compared | Guide & Examples
Types of Research Designs Compared | Guide & Examples
Published on June 20, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on June 22, 2023.
When you start planning a research project, developing research questions and creating a research design , you will have to make various decisions about the type of research you want to do.
There are many ways to categorize different types of research. The words you use to describe your research depend on your discipline and field. In general, though, the form your research design takes will be shaped by:
- The type of knowledge you aim to produce
- The type of data you will collect and analyze
- The sampling methods , timescale and location of the research
This article takes a look at some common distinctions made between different types of research and outlines the key differences between them.
Table of contents
Types of research aims, types of research data, types of sampling, timescale, and location, other interesting articles.
The first thing to consider is what kind of knowledge your research aims to contribute.
| Type of research | What’s the difference? | What to consider |
|---|---|---|
| Basic vs. applied | Basic research aims to , while applied research aims to . | Do you want to expand scientific understanding or solve a practical problem? |
| vs. | Exploratory research aims to , while explanatory research aims to . | How much is already known about your research problem? Are you conducting initial research on a newly-identified issue, or seeking precise conclusions about an established issue? |
| aims to , while aims to . | Is there already some theory on your research problem that you can use to develop , or do you want to propose new theories based on your findings? |
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

The next thing to consider is what type of data you will collect. Each kind of data is associated with a range of specific research methods and procedures.
| Type of research | What’s the difference? | What to consider |
|---|---|---|
| Primary research vs secondary research | Primary data is (e.g., through or ), while secondary data (e.g., in government or scientific publications). | How much data is already available on your topic? Do you want to collect original data or analyze existing data (e.g., through a )? |
| , while . | Is your research more concerned with measuring something or interpreting something? You can also create a research design that has elements of both. | |
| vs | Descriptive research gathers data , while experimental research . | Do you want to identify characteristics, patterns and or test causal relationships between ? |
Finally, you have to consider three closely related questions: how will you select the subjects or participants of the research? When and how often will you collect data from your subjects? And where will the research take place?
Keep in mind that the methods that you choose bring with them different risk factors and types of research bias . Biases aren’t completely avoidable, but can heavily impact the validity and reliability of your findings if left unchecked.
| Type of research | What’s the difference? | What to consider |
|---|---|---|
| allows you to , while allows you to draw conclusions . | Do you want to produce knowledge that applies to many contexts or detailed knowledge about a specific context (e.g. in a )? | |
| vs | Cross-sectional studies , while longitudinal studies . | Is your research question focused on understanding the current situation or tracking changes over time? |
| Field research vs laboratory research | Field research takes place in , while laboratory research takes place in . | Do you want to find out how something occurs in the real world or draw firm conclusions about cause and effect? Laboratory experiments have higher but lower . |
| Fixed design vs flexible design | In a fixed research design the subjects, timescale and location are begins, while in a flexible design these aspects may . | Do you want to test hypotheses and establish generalizable facts, or explore concepts and develop understanding? For measuring, testing and making generalizations, a fixed research design has higher . |
Choosing between all these different research types is part of the process of creating your research design , which determines exactly how your research will be conducted. But the type of research is only the first step: next, you have to make more concrete decisions about your research methods and the details of the study.
Read more about creating a research design
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Ecological validity
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, June 22). Types of Research Designs Compared | Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved June 24, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/types-of-research/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a research design | types, guide & examples, qualitative vs. quantitative research | differences, examples & methods, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
- Small Business

Exploring 10 Types of Case Studies with Ringflow: Unlocking Power

Table of Contents
Types of case studies, introduction.
Case studies are a common research methodology in various disciplines, including business, psychology, sociology, and political science. The purpose of a case study is to provide an in-depth analysis of a particular phenomenon or situation. This can include anything from examining the factors that led to a business’s success or failure to explore the causes behind an unexpected social trend.
Definition of a Case Study
A case study is an in-depth analysis of a phenomenon or situation based on detailed research and investigation. A case study aims to provide an understanding of the complex factors that contribute to the occurrence or outcome of the phenomenon being studied. Case studies typically involve collecting and analyzing multiple data sources, including interviews with key stakeholders, surveys, and archival records. One important feature of case studies is their focus on context. Unlike quantitative research methods such as surveys or experiments that often seek to isolate specific variables or relationships, case studies analyze phenomena within their broader social, economic, political, and cultural contexts. This allows researchers to capture the complexity and nuances often missed by more simplistic approaches.
Importance of Case Studies in Research and Analysis
Case studies have several advantages over other research methods. For one thing, they allow researchers to examine phenomena in real-world settings rather than artificial laboratory environments. Additionally, they can be used to explore complex processes and relationships that are difficult to capture using traditional quantitative methods. Another advantage of case studies is their ability to generate rich qualitative data that can be analyzed using content analysis or grounded theory techniques. This allows researchers to develop more nuanced understandings of the phenomena being studied. Case studies are useful for generating hypotheses for future research. By carefully examining one particular instance or situation, researchers can identify potential causal mechanisms operating more broadly across different contexts.
A type of Case study is a type of research method that involves an in-depth and detailed analysis of a particular phenomenon or situation. Generally, case studies gain insights into complex issues or problems that cannot be adequately explained through quantitative data alone. They are particularly useful for exploring cause-and-effect relationships, understanding the root causes of problems, and identifying potential solutions to those problems. There are various case studies, each with a unique focus and purpose.
Historical Case Studies
Historical case studies involve the analysis of past events to gain insights into the present. These types of case studies are particularly useful for developing an understanding of how certain historical events have shaped current social, economic, and political conditions. Historical case studies typically involve a detailed description and analysis of past events, such as wars, revolutions, or major disasters like the sinking of the Titanic or The Watergate Scandal.
Exploratory Case Studies
Exploratory case studies involve preliminary investigation to gather information and identify key issues related to a particular problem or phenomenon. These types of case studies seek to provide an initial understanding of the problem by identifying key variables that may be contributing to it. Examples include market research to identify customer preferences or feasibility studies on new product development.
Descriptive Case Studies
Descriptive case studies involve detailed descriptions and analyses of a particular phenomenon or situation. The goal is often to understand how certain factors contribute to a particular outcome or result. Examples include analyzing a company’s marketing strategy or examining how a community responded to a natural disaster.
Explanatory Case Studies
Explanatory case studies focus on explaining why certain events occur or phenomena exist. These case studies aim to identify causal relationships between factors and outcomes . Examples include analyzing the causes behind an economic recession or examining factors contributing to high crime rates in a particular city.
Instrumental Case Studies
Instrumental case studies are focused on identifying solutions to specific problems or issues. These case studies aim to identify strategies for addressing problems or improving outcomes. Examples include developing effective strategies for reducing carbon emissions or improving employee retention rates in a company.
Collective Case Studies
Collective case studies involve analysis focused on multiple cases that have similarities. The goal is often to identify applicable patterns or trends across multiple situations. Examples include studying the effectiveness of different healthcare policies across various countries.

Social Media
Most popular.
![types of research case studies Canada Phone Number Example [With Country Code]](https://www.ringflow.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/Add-a-heading-75-1.webp)
Canada Phone Number Example [With Country Code]

Understanding German Phone Number Formats: Calling from Abroad, Costs, and More

Comparing The Best SIP Trunk Providers of 2024
Free us phone number: enhance your connectivity – get yours now, related posts.
Canada Phone Number Example [With Country Code] How to call
Introduction Understanding German phone numbers, associated costs, and international
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on the best SIP trunk
Furkan Mistry

1 917-254-4289
Marasi Drive Al Abraj Street 29th Floor Prime Tower , Office 15, Shuraa Business Centre Business Bay 2901
The power of digital transformation
- Ai-Contact Center
- Self-Service
- Remote Center
- Inbound Center
- Mobile Center
- Omnichannel Center
- Video Center
- Outbound Center
- Real-Estate
- Legal Service
- Team Management
- Country Codes
- Testimonials
- Privacy Policy
- Virtual Phone Number
- Automatic Call Ditribution
- Voip Number
- Call Forwarding
- power dialer
- Contact center analysis
- voip services
- Small Business Phone Number
© Copyright 2024 – Ringflow. All Rights Reserved
8 800 2534 236
27 Division St, New York, NY 10002, United States
We focus on the needs of small to middle market businesses to improve and grow their return.
- Ai-Meetings
- Local presence
- Omnichannal
- Call Recording
- Conference call app
- Screen sharing
- Ringflow's Ai
- Call analytics
- Speech analytics
- Essay Editor
Types of Case Studies: a Comprehensive Guide

The art of writing involves multiple types of materials, which makes both writing and reading a pleasure that is informative and conducive to conveying knowledge and experience. However, when it comes to academic writing, there is a need to distinguish between the many types of materials based on their appropriateness to a certain kind of information.
Each type of material with its own structure and manner of writing is best suited for certain types of topics. The latter can range from anything like scientific articles or presentations of projects to various informative materials that tell the reader about new releases of products or services. In the given material, we shall identify the examples of a case study that can be used to great extent in a variety of topics. We shall also include examples of case study research to better illustrate how such a material can benefit the writer to effectively convey information, and the reader to better understand the key takeaways and evaluate value.
What is a case study?
The most common question that arises among new entrants into the art of writing when confronted with the need to write a case study is “ what are case studies ”? There is a wide variety of case studies meaning definitions available in the Internet, but all of them converge on a single one that essentially defines case studies as an in-depth analysis of a certain case, occurrence, story, or subject, with a detailed explanation of the impact thereof in the context of the real world.
Just as in hard science there are case study methods , so too in writing, there are numerous ways in which a case study can be written, elaborated, and explored to better divulge its value and meaning to the reader. The general concept of a case study is to better explain how that particular case arose, evolved, developed, and concluded, with well-defined and analyzed expressions of the consequences for the parties involved and even a statistical analysis.
The most common areas in which case studies are employed as a means of convening informational value are storytelling in business and scientific settings. As both areas are dominated by various cases of precedents and success or failure, the need to examine each in detail and allow readers to draw conclusions makes case studies an ideal go-to type of material for such purposes.
Types of subjects in a case study
The subjects that case studies can encompass are as numerous as there are topics to explore. Most commonly, case studies are used in science, legislative matters, technology-related areas, business, and other domains.
Most common subjects explored in case studies include success stories, certain technological, medical, or scientific breakthroughs, historical studies, and even academic writing.
What are the case study benefits?
The case study can provide a number of considerable advantages to writers as a type of material, which can help clearly define a relationship between the subject involved in the case and its context. The flexibility with which the data included in the material can be presented helps achieve both clarity and the necessary effect on the reader. Most importantly, case studies provide a clear outline of events in extensive detail and help establish a cause-effect relationship.
Essential types of case studies
There are many types of case studies available to writers that they choose from in their strive to elaborate a certain instance and tailor the material for better digestibility by readers. The following is a short overview of the main types of case studies and their purposes:
Illustrative
As the name implies, an illustrative case study serves the purpose of illustrating a certain case. This type of material is used to describe a certain event in greater detail and delves into the circumstances of the underlying situation, with an emphasis on the causes and effects thereof.
Illustrative case studies are ideal for describing medical cases and patient illness histories, especially in the case of rare diseases. By exploring the course of the case and the circumstances that took place during it, the reader will have a clear picture of the situation and will be able to relate it to their own real-world standing to either replicate the case or avoid any pitfalls that might have been described in the material.
Such materials are also used to great effect in the business world, whereby companies describe their success stories and thus highlight their competencies to attract new clients and inspire awe in customers.
Exploratory
An exploratory case study is a very specific type of material that has the aim of encompassing a set of data as an initial research attempt for the purpose of identifying possible patterns. Such patterns, if any exist, can help create a model based on the data and then extrapolate it for further analysis, application, or research.
Exploratory case studies are primarily used in the scientific community by researchers who conduct experiments, or data analysts tasked with sifting through large arrays of data. The point of an exploratory case study is basically to make sense of a large buildup of information.
Cumulative case studies, as the name might suggest, accumulate information from various sources and compile it in a single material for the purpose of analysis, comparison, or evaluation. The data can be collected from different time periods, sources, or even places and combined for analysis in the search for patterns or other purposes.
As a rule, every cumulative case study must start with a founding question that will act as a hypothesis for further exploration of the compiled data.
Critical instance
As in critical thinking, which seeks to find relations between cause and effect, a critical instance case study is used to answer questions pertaining to the causes and consequences of a certain case. Such materials are ideal for making certain points about established concepts, placing emphasis on certain topics of interest within a larger framework of questions as outliers, and diving into the reasons for certain events.
Critical instance case studies are used extensively in criminalistics, legal proceedings, and experimental science, where a fresh look on certain questions is sometimes in order to identify a potential cause, or cause-effect relationship.
Intrinsic case studies perfectly leverage the term to explain the value of a certain question, rather than its relevance. Such materials are ideal for delving into the finer details of a case, explaining its uniqueness, qualities, characteristics, and other aspects.
Such materials are perfectly suited for focusing on certain topics, or highlighting previously unnoticed qualities about them.
Descriptive
As the term implies, descriptive case studies simply describe a certain case without any additional emphasis on questions, qualities, or effects. Such materials offer an objective look on a case and provide a hard, fact-based overview of the event.
A descriptive case study is commonly used in government-related materials, scientific research, medical records, and other areas, where there is no need to appeal to a reader, or to “sell” them a certain concept, company, or product.
Related articles
Expository essay examples: developing skills in informative writing.
Is your assignment to prepare a fine and well-structured expository essay but you don't know what point to start with? This material lends a helping hand to you. Here we discuss how to begin an expository essay, what parts should be in the text, and what linguistic means a person should use when creating a project mentioned above. We also introduce you a few tips on how to sharpen your skills in informative writing. So be ready to read and learn, the adventure to the land of expository papers ge ...
How to Make an Essay Longer: 7 Useful Tips
Are you having trouble getting your essay to the right length? Do you look at your essay and think, "It's too short!" but don't know what to do? Don't worry, we've got some great ideas on how to make an essay longer without making it worse. Why is it Important to Make an Essay Longer? When you're writing an essay, it's important to make sure it's long enough. If your essay isn't as long as required, you might get a lower grade, even if the content of your essay is exceptional. By making your ...
What is an Appendix in a Research Paper? | Aithor
What is an appendix in a research paper? An appendix is a supplementary section at the end of a research paper after the list of references. It contains more information that helps explain the main ideas in the paper. It's not needed in the main part because it would make the paper too long or go “off-topic." The appendix gives readers more details to help them understand the research better without making the main argument hard to follow. The length of an appendix can differ depending on what ...
Essay Format Tips from an English Teacher
Writing a solid and well-crafted essay is crucial for students and researchers, as it involves presenting arguments clearly and succinctly. Whether you are writing a paper for an assignment, a scientific journal, or a personal statement, understanding the correct essay format is pivotal. This meticulously collated guide covers key features of essay formatting and provides tips to refine your writing. What is an Essay Format? An essay format is a blueprint for shaping your written assignment, ...
Diagnostic Essay Writing Guide and Outline Sample
Imagine stepping into a classroom on the first day and being asked to write an essay. This exercise, commonly referred to as a diagnostic essay, is a common tool used by instructors to gauge their students' writing proficiency. Interestingly, in a study exploring the effectiveness of evaluation papers, over 70% of participants reported that these tasks significantly improved their understanding of their writing strengths and challenges. This finding underscores the assessment assignment's role i ...
The Basics of Crafting an Outstanding Persuasive Essay Outline
When writing a persuasive essay, having a well-structured outline is critical to effectively presenting your argument and convincing your audience. An outline serves as a roadmap for your essay, organizing your thoughts and supporting evidence in a logical sequence that flows cohesively. In this guide, we will explore the essential components of a persuasive essay outline and provide tips on how to craft a compelling structure for your writing. Whether you are a beginner or a seasoned writer, ma ...
How to Conclude an Essay: A Guide for Academic Writing
Every essay requires a proper conclusion. It is particularly important in academic writing where texts can be several dozen pages long. A conclusion helps the audience remember the contents of your essay and retain important information. In this article, you will learn how to write a conclusion for an essay. Why the conclusion matters When writing essays, we always strive to conduct a comprehensive analysis of the topic. We do our research, present different perspectives, and provide examples ...
How to Write Essay Thesis Statement: A Comprehensive Analysis
In academic writing, creating an impactful text that can deftly relay your opinion and persuade your audience is one of the key skills. That’s why it is essential to learn how to write a strong thesis statement. In this article, you will find all you need to know for creating a persuasive thesis statement. What is an essay thesis? In academic essays, a thesis is a part of the introduction that expresses the main idea and purpose of the essay. It aims to give the audience a brief overview of t ...

AI Generator

Research is a systematic investigation to establish facts and reach new conclusions. It involves collecting and analyzing data, often using a research questionnaire , and presenting findings to expand knowledge in a specific field. Key aspects include adhering to research ethics and exploring crisis communication research topics to manage and communicate effectively during crises.
What is Research?
Research is a systematic investigation and study of materials, sources, and data to establish facts and reach new conclusions. It involves gathering information, analyzing it critically, and presenting findings in a structured manner to increase knowledge in a specific field or address a particular problem. This process is fundamental in various disciplines, including science, humanities, and social sciences, and it helps to develop theories, inform policy, and contribute to the advancement of society.
Examples of Research
- Medical Research
- Educational Research
- Environmental Research
- Psychological Research
- Market Research
- Historical Research
- Sociological Research
- Technological Research
- Crisis Communication Research
- Agricultural Research
- Economic Research
- Political Research
- Linguistic Research
- Public Health Researc h
- Cultural Research
- Genetic Research
- Behavioral Research
- Engineering Research
- Legal Research
- Anthropological Research
Examples of Research in a Sentence
- The research conducted by the university scientists led to a breakthrough in renewable energy technology.
- She spent several months doing research for her thesis on ancient Greek literature.
- Our team is currently engaged in market research to understand consumer preferences better.
- The research findings were published in a prestigious medical journal.
- He was awarded a grant to continue his research on climate change and its impact on coastal ecosystems.
- Before launching the new product, the company conducted extensive research to ensure its success.
- Her research into the effects of sleep deprivation on cognitive function provided valuable insights.
- The research project aims to develop more effective treatments for Alzheimer’s disease.
- During the conference, many scholars presented their research on the latest advancements in artificial intelligence.
- The research paper highlighted the importance of early childhood education in academic achievement.
Research Examples for Students
- Science Fair Projects: Students conduct experiments to test hypotheses, such as examining the effects of different fertilizers on plant growth.
- History Papers: Students research a historical event, like the Civil Rights Movement, analyzing primary and secondary sources to understand its impact.
- Environmental Studies: Students investigate local water sources to assess pollution levels and propose solutions for improvement.
- Literature Analysis: Students research the themes and symbols in a novel, such as analyzing the use of symbolism in “To Kill a Mockingbird” by Harper Lee.
- Social Studies Projects: Students explore different cultures by researching their customs, traditions, and societal structures.
- Health Studies: Students study the effects of nutrition on adolescent health, conducting surveys and reviewing scientific literature.
- Technology Projects: Students research the development of artificial intelligence and its potential impacts on various industries.
- Business Studies: Students analyze market trends and consumer behavior to develop a marketing plan for a hypothetical product.
- Psychology Experiments: Students conduct research on human behavior, such as studying the effects of sleep on memory retention.
- Creative Arts: Students research different art movements, like Impressionism, and create a presentation showcasing key artists and their works.
Quantitative Research Examples
- Survey on Consumer Preferences: A company surveys 1,000 customers to quantify their preferences for different product features, such as color, size, and price.
- Medical Trials: A pharmaceutical company conducts a clinical trial involving 500 participants to measure the effectiveness of a new drug.
- Educational Achievement Study: Researchers collect standardized test scores from 10,000 students across various schools to analyze the impact of different teaching methods on student performance.
- Market Analysis: An economist analyzes sales data from 50 retail stores to identify trends and predict future sales patterns.
- Census Data Analysis: Government agencies use census data to quantify population growth, demographic changes, and housing needs over a decade.
- Customer Satisfaction Survey: A restaurant chain distributes a survey to 2,000 customers to measure satisfaction levels and identify areas for improvement.
- Behavioral Economics Study: Researchers conduct an experiment with 300 participants to quantify the effects of different incentives on saving behaviors.
- Workplace Productivity Study: A company tracks the productivity levels of 1,200 employees over six months to assess the impact of flexible working hours.
- Public Health Research: Health researchers analyze data from 20,000 participants to determine the correlation between exercise frequency and incidence of chronic diseases.
- Political Polling: Pollsters survey 5,000 voters to predict election outcomes and understand voter preferences and behavior.
Qualitative Research Examples
- Interview Studies: Researchers conduct in-depth interviews with participants to explore their experiences and perspectives on a specific topic, such as the impact of remote learning on student engagement.
- Focus Groups: A group of participants discusses a particular issue, like consumer attitudes towards sustainable fashion, allowing researchers to gather diverse opinions and insights.
- Ethnography: Researchers immerse themselves in a community or organization to observe and document cultural practices, social interactions, and daily routines, such as studying the work culture in a tech startup.
- Case Studies: An in-depth analysis of an individual, group, or event, like examining the recovery process of a patient with a rare medical condition, to understand the complexities involved.
- Narrative Research: Collecting and analyzing stories from individuals to understand how they make sense of their experiences, such as exploring the life stories of immigrants adapting to a new country.
- Phenomenological Research: Investigating the lived experiences of individuals regarding a particular phenomenon, such as the experiences of first-time mothers during childbirth.
- Grounded Theory: Developing a theory based on data collected from participants, like studying the coping mechanisms of people living with chronic pain to formulate a new psychological model.
- Content Analysis: Analyzing texts, media, or documents to identify patterns and themes, such as examining newspaper articles to understand media representation of climate change.
- Action Research: Collaborating with participants to address a problem and implement solutions, such as working with teachers to develop and test new classroom management strategies.
- Discourse Analysis: Studying communication patterns, language use, and social interactions within a specific context, like analyzing political speeches to understand how leaders frame policy issues.
Types of Research with Examples
Research is a systematic investigation aimed at discovering new information, understanding existing phenomena, and solving problems. There are several types of research, each with its own methodologies and purposes. Below are the main types of research with examples.
1. Basic Research
Basic research, also known as pure or fundamental research, is conducted to increase knowledge and understanding of fundamental principles. It is not aimed at solving immediate practical problems but rather at gaining a deeper insight into the subject. Example: A study investigating the molecular structure of proteins to understand how they function in the human body.
2. Applied Research
Applied research is designed to solve practical problems and improve the human condition. It uses the knowledge gained from basic research to develop new products, processes, or techniques. Example: Developing a new medication to treat Alzheimer’s disease based on findings from basic research on brain cell functions.
3. Quantitative Research
Quantitative research involves the systematic empirical investigation of observable phenomena via statistical, mathematical, or computational techniques. It seeks to quantify data and typically uses surveys, questionnaires, or experiments. Example: Conducting a survey to measure customer satisfaction levels among users of a new smartphone.
4. Qualitative Research
Qualitative research aims to understand human behavior and the reasons that govern such behavior. It involves collecting non-numerical data, such as interviews, observations, and open-ended surveys. Example: Interviewing patients to understand their experiences and feelings about a new healthcare program.
5. Descriptive Research
Descriptive research seeks to describe characteristics of a population or phenomenon being studied. It does not answer questions about how/when/why the characteristics occurred, but rather “what” is happening. Example: A study detailing the demographics of students in a particular school district.
6. Experimental Research
Experimental research is used to establish cause-and-effect relationships among variables. It involves manipulating one variable to determine if changes in one variable cause changes in another variable. Example: Testing the effectiveness of a new drug by administering it to one group of patients and a placebo to another group.
7. Correlational Research
Correlational research investigates the relationship between two or more variables without manipulating them. It identifies patterns, trends, and associations between variables. Example: Studying the correlation between hours of study and academic performance among high school students.
8. Exploratory Research
Exploratory research is conducted to explore a problem or a new area where little information exists. It is often the initial research conducted before more conclusive research. Example: Exploring the potential uses of a newly discovered plant with medicinal properties.
9. Longitudinal Research
Longitudinal research involves repeated observations of the same variables over a period of time. It is useful for studying changes and developments over time. Example: Following a group of children from kindergarten through high school to study the impact of early education on later academic success.
10. Cross-sectional Research
Cross-sectional research analyzes data from a population, or a representative subset, at a specific point in time. It provides a snapshot of the variables of interest. Example: A survey assessing the health status of a community at a single point in time.
11. Case Study Research
Case study research involves an in-depth, detailed examination of a single subject, group, or event. It provides a comprehensive understanding of the case being studied. Example: Analyzing the business strategies of a successful startup to understand the factors contributing to its success.
12. Action Research
Action research is conducted to solve an immediate problem or improve p Example: Implementing and assessing a new teaching method in a classroom to improve student engagement and learning outcomes.
Types of Research Methods and Example
- Method: Distributing questionnaires or online surveys to collect data from a large group of people.
- Example: Conducting a national survey to assess public opinion on climate change policies.
- Method: Manipulating one or more variables to determine their effect on another variable in a controlled environment.
- Example: Testing the impact of a new educational program on student performance by comparing test scores of participants and non-participants.
- Method: Observing subjects in their natural environment without interference.
- Example: Studying children’s behavior in playgrounds to understand social interactions and play patterns.
- Method: Conducting an in-depth analysis of a single subject or a small group of subjects.
- Example: Analyzing the business strategies of a successful startup to identify key factors contributing to its growth.
- Method: Systematically examining texts, media, and documents to identify patterns and themes.
- Example: Analyzing social media posts to understand public sentiment during a major political event.
What are the Characteristics of Research?
- Research follows a structured and organized approach, involving specific steps and methodologies to ensure consistency and reliability.
- Research includes control mechanisms to minimize bias and external variables that may influence the results, especially in experimental studies.
- Research relies on observable and measurable evidence. Data is collected through direct or indirect observation and experimentation.
- Research is based on logical reasoning and sound theoretical frameworks. Conclusions are drawn from data analysis and established principles.
- Research can be repeated by other researchers to verify results. Replication helps to confirm the validity and reliability of findings.
- Research aims to be unbiased and impartial. The researcher’s personal beliefs and opinions should not influence the study’s outcomes.
- Research involves critical analysis and interpretation of data. Researchers seek to understand patterns, relationships, and causality within the data.
- Research can involve numerical data (quantitative) or non-numerical data (qualitative), depending on the nature of the study and the research questions.
- Research adheres to ethical standards, ensuring the rights and well-being of participants are protected. Informed consent, confidentiality, and integrity are essential.
- Research seeks to explore new ideas, develop new theories, and discover new knowledge. It often addresses gaps in existing literature.
Importance of Research
Research is crucial in various fields, offering numerous benefits and advancing knowledge in significant ways. Here are some key reasons why research is important:
1. Advancement of Knowledge
Research pushes the boundaries of what is known and explores new areas of inquiry. It helps to uncover new facts, theories, and insights that contribute to the collective understanding of a subject.
2. Informed Decision-Making
Research provides reliable data and evidence that guide decisions in fields such as healthcare, business, education, and public policy. For example, medical research can lead to the development of new treatments and drugs.
3. Problem-Solving
Research identifies and analyzes problems, proposing effective solutions. For instance, environmental research can help address climate change by finding sustainable practices and technologies.
4. Innovation and Development
Research fosters innovation by developing new products, technologies, and processes. Technological advancements, such as smartphones and renewable energy sources, are direct results of extensive research.
5. Economic Growth
Research drives economic development by creating new industries and improving existing ones. It leads to job creation, enhances productivity, and contributes to a nation’s economic stability.
6. Educational Enrichment
Research enhances educational content and teaching methods. It provides a deeper understanding of subjects, helping educators develop better curricula and instructional strategies.
FAQ’s
What is a hypothesis in research.
A hypothesis is a testable prediction about the relationship between two or more variables. It guides the research process.
How do you choose a research topic?
Select a topic that interests you, fills a gap in existing literature, and is feasible in terms of resources and time.
What is a literature review?
A literature review is a comprehensive summary of previous research on a topic. It identifies trends, gaps, and key findings.
What is the difference between primary and secondary data?
Primary data is collected firsthand by the researcher. Secondary data is gathered from existing sources like books, articles, and reports.
What are research ethics?
Research ethics involve principles like honesty, integrity, and respect for participants. Ethical guidelines ensure research is conducted responsibly.
What is a research design?
A research design is a plan that outlines how to collect and analyze data. It includes methods, sampling, and procedures.
What is sampling in research?
Sampling is selecting a subset of individuals from a population to represent the entire group. It can be random or non-random.
What is data analysis?
Data analysis involves processing and interpreting data to draw meaningful conclusions. Techniques vary based on the research type.
How do you write a research paper?
A research paper includes an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion. Follow a clear and logical structure.
What is peer review?
Peer review is a process where experts evaluate a researcher’s work for quality, accuracy, and validity before publication.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
- Open access
- Published: 28 June 2024
Perceived efficacy of case analysis as an assessment method for clinical competencies in nursing education: a mixed methods study
- Basma Mohammed Al Yazeedi ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2327-6918 1 ,
- Lina Mohamed Wali Shakman 1 ,
- Sheeba Elizabeth John Sunderraj ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-9171-7239 1 ,
- Harshita Prabhakaran ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5470-7066 1 ,
- Judie Arulappan 1 ,
- Erna Judith Roach ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5817-8886 1 ,
- Aysha Al Hashmi 1 , 2 &
- Zeinab Al Azri ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3376-9380 1
BMC Nursing volume 23 , Article number: 441 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
Case analysis is a dynamic and interactive teaching and learning strategy that improves critical thinking and problem-solving skills. However, there is limited evidence about its efficacy as an assessment strategy in nursing education.
This study aimed to explore nursing students’ perceived efficacy of case analysis as an assessment method for clinical competencies in nursing education.
This study used a mixed methods design. Students filled out a 13-item study-advised questionnaire, and qualitative data from the four focus groups was collected. The setting of the study was the College of Nursing at Sultan Qaboos University, Oman. Descriptive and independent t-test analysis was used for the quantitative data, and the framework analysis method was used for the qualitative data.
The descriptive analysis of 67 participants showed that the mean value of the perceived efficacy of case analysis as an assessment method was 3.20 (SD = 0.53), demonstrating an 80% agreement rate. Further analysis indicated that 78.5% of the students concurred with the acceptability of case analysis as an assessment method (mean = 3.14, SD = 0.58), and 80.3% assented its association with clinical competencies as reflected by knowledge and cognitive skills (m = 3.21, SD = 0.60). No significant difference in the perceived efficacy between students with lower and higher GPAs (t [61] = 0.05, p > 0.05) was identified Three qualitative findings were discerned: case analysis is a preferred assessment method for students when compared to MCQs, case analysis assesses students’ knowledge, and case analysis assesses students’ cognitive skills.
Conclusions
This study adds a potential for the case analysis to be acceptable and relevant to the clinical competencies when used as an assessment method. Future research is needed to validate the effectiveness of case analysis exams in other nursing clinical courses and examine their effects on academic and clinical performance.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
Nurses play a critical role in preserving human health by upholding core competencies [ 1 ]. Clinical competence in nursing involves a constant process of acquiring knowledge, values, attitudes, and abilities to deliver safe and high-quality care [ 2 , 3 ]. Nurses possessing such competencies can analyze and judge complicated problems, including those involving crucial patient care, ethical decision-making, and nurse-patient disputes, meeting the constantly altering health needs [ 4 , 5 ]. To optimize the readiness of the new graduates for the challenging clinical work environment needs, nurse leaders call for integrating clinical competencies into the nursing curriculum [ 6 , 7 ] In 2021, the American Association of Colleges of Nursing (AACN) released updated core competencies for professional nursing education [ 8 ]. These competencies were classified into ten fundamental essentials, including knowledge of nursing practice and person-centered care (e.g. integrate assessment skills in practice, diagnose actual or potential health problems and needs, develop a plan of care), representing clinical core competencies.
Nursing programs emphasize clinical competencies through innovative and effective teaching strategies, including case-based teaching (CBT) [ 9 ]. CBT is a dynamic teaching method that enhances the focus on learning goals and increases the chances of the instructor and students actively participating in teaching and learning [ 10 , 11 ]. Additionally, it improves the students’ critical thinking and problem-solving skills and enriches their capacity for independent study, cooperation capacity, and communication skills [ 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 ]. It also broadens students’ perspectives and helps develop greater creativity in fusing theory and practice [ 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 , 20 ]. As the learning environment significantly impacts the students’ satisfaction, case analysis fosters a supportive learning atmosphere and encourages active participation in learning, ultimately improving their satisfaction [ 21 , 22 ].
In addition to proper teaching strategies for clinical competencies, programs are anticipated to evaluate the students’ attainment of such competencies through effective evaluation strategies [ 23 ]. However, deploying objective assessment methods for the competencies remains challenging for most educators [ 24 ]. The standard assessment methods used in clinical nursing courses, for instance, include clinical evaluations (direct observation), skills checklists, Objective Structured Clinical Examination (OSCE), and multiple-choice questions (MCQs) written exams [ 25 ]. MCQs tend to test the recall of factual information rather than the application of knowledge and cognitive skills, potentially leading to assessment inaccuracies [ 26 ].
Given the aforementioned outcomes of CBT, the deployment of case analysis as a clinical written exam is more closely aligned with the course’s expected competencies. A mixed methods study was conducted among forty nursing students at the University of Southern Taiwan study concluded that the unfolding case studies create a safe setting where nursing students can learn and apply their knowledge to safe patient care [ 6 ]. In a case analysis, the patient’s sickness emerges in stages including the signs and symptoms of the disease, urgent care to stabilize the patient, and bedside care to enhance recovery. Thus, unfolding the case with several scenarios helps educators track students’ attained competencies [ 27 ]. However, case analysis as an assessment method is sparsely researched [ 28 ]. A literature review over the past five years yielded no studies investigating case analysis as an assessment method, necessitating new evidence. There remains uncertainty regarding its efficacy as an assessment method, particularly from the students’ perspectives [ 29 ]. In this study, we explored the undergraduate nursing students’ perceived efficacy of case analysis as an assessment method for clinical competencies. Results from this study will elucidate the position of case analysis as an assessment method in nursing education. The potential benefits are improved standardization of clinical assessment and the ability to efficiently evaluate a broad range of competencies.
Research design
Mixed-method research with a convergent parallel design was adopted in the study. This approach intends to converge two data types (quantitative and qualitative) at the interpretation stage to ensure an inclusive research problem analysis [ 30 ]. The quantitative aspect of the study was implemented through a cross-sectional survey. The survey captured the perceived efficacy of using case analysis as an assessment method in clinical nursing education. The qualitative part of the study was carried out through a descriptive qualitative method using focus groups to provide an in-depth understanding of the perceived strengths experienced by the students.
Study setting
Data were collected in the College of Nursing at Sultan Qaboos University (SQU), Oman, during the Spring and Fall semesters of 2023. At the end of each clinical course, the students have a clinical written exam and a clinical practical exam, which constitute their final exam. Most clinical courses use multiple-choice questions (MCQs) in their written exam. However, the child health clinical course team initiated the case analysis as an assessment method in the clinical written exam, replacing the MCQs format.
Participants
For this study, the investigators invited undergraduate students enrolled in the child health nursing clinical course in the Spring and Fall semesters of 2023. Currently, the only course that uses case analysis is child health. Other courses use MCQs. A total enumeration sampling technique was adopted. All the students enrolled in child health nursing clinical courses in the Spring and Fall 2023 semesters were invited to participate in the study. In the Spring, 36 students registered for the course, while 55 students were enrolled in the Fall. We included students who completed the case analysis as a final clinical written exam on the scheduled exam time. Students who did not show up for the exam during the scheduled time and students not enrolled in the course during the Spring and Fall of 2023 were excluded. Although different cases were used each semester, both had the same structure and level of complexity. Further, both cases were peer-reviewed.
Case analysis format
The format presents open-ended questions related to a clinical case scenario. It comprises three main sections: Knowledge, Emergency Room, and Ward. The questions in the sections varied in difficulty based on Bloom’s cognitive taxonomy levels, as presented in Table 1 . An answer key was generated to ensure consistency among course team members when correcting the exam. Three experts in child health nursing peer-reviewed both the case analysis exam paper and the answer key paper. The students were allocated two hours to complete the exam.
Study instruments
Quantitative stage.
The researchers developed a study questionnaire to meet the study objectives. It included two parts. The first was about the demographic data, including age, gender, type of residence, year in the program, and cumulative grade point average (GPA). The second part comprised a 13-item questionnaire assessing the perceived efficacy of case analysis as an assessment method. The perceived efficacy was represented by the acceptability of case analysis as an assessment method (Items 1–5 and 13) and the association with clinical competencies (Items 6 to 12). Acceptability involved format organization and clarity, time adequacy, alignment with course objectives, appropriateness to students’ level, and recommendation for implementation in other clinical nursing courses. Clinical competencies-related items were relevant to knowledge (motivation to prepare well for the exam, active learning, interest in topics, collaboration while studying) and cognitive skills (critical thinking, decision-making, and problem-solving skills) (The questionnaire is attached as a supplementary document).
The questionnaire is answered on a 4-point Likert scale: 1 = strongly disagree, 2 = disagree, 3 = agree, 4 = strongly agree. Higher scores indicated better perceived efficacy and vice versa. The tool underwent content validity testing with five experts in nursing clinical education, resulting in an item-content validity index ranging from 0.7 to 1. The Cronbach alpha was 0.83 for acceptability and 0.90 for clinical competencies.
Qualitative stage
For the focus group interviews, the investigators created a semi-structured interview guide to obtain an in-depth understanding of the students’ perceived strengths of case analysis as an assessment method. See Table 2 .
Data collection
Data was collected from the students after they gave their written informed consent. Students were invited to fill out the study questionnaire after they completed the case analysis as a clinical written exam.
All students in the child health course were invited to participate in focus group discussions. Students who approached the PI to participate in the focus group discussion were offered to participate in four different time slots. So, the students chose their time preferences. Four focus groups were conducted in private rooms at the College of Nursing. Two trained and bilingual interviewers attended the focus groups, one as a moderator while the other took notes on the group dynamics and non-verbal communication. The discussion duration ranged between 30 and 60 min. After each discussion, the moderator transcribed the audio recording. The transcriptions were rechecked against the audio recording for accuracy. Later, the transcriptions were translated into English by bilingual researchers fluent in Arabic and English for the analysis.
Rigor and trustworthiness
The rigor and trustworthiness of the qualitative method were enhanced using multiple techniques. Firstly, quantitative data, literature reviews, and focus groups were triangulated. Participants validated the summary after each discussion using member checking to ensure the moderator’s understanding was accurate. Third, the principal investigator (PI) reflected on her assumptions, experiences, expectations, and feelings weekly. In addition, the PI maintained a detailed audit trail of study details and progress. The nursing faculty conducted the study with experience in qualitative research and nursing education. This report was prepared following the Standard for Reporting Qualitative Research (SRQR) protocol [ 31 ].
Data analysis
Quantitative data were entered in SPSS version 24 and analyzed using simple descriptive analysis using means, standard deviations, and percentages. After computing the means of each questionnaire item, an average of the means was calculated to identify the perceived efficacy rate. A similar technique was used to calculate the rate of acceptability and clinical competencies. The percentage was calculated based on the mean: gained score/total score* 100. In addition, the investigators carried out an independent t-test to determine the relationship between the perceived efficacy and students’ GPA.
The qualitative data were analyzed using the framework analysis method. In our analysis, we followed the seven interconnected stages of framework analysis: (1) transcription, (2) familiarization with the interview, (3) coding, (4) developing a working analytical framework, (5) applying the analytical framework, (6) charting data into framework matrix and (7) interpreting the data [ 32 ]. Two members of the team separately analyzed the transcriptions. Then, they discussed the coding, and discrepancies were solved with discussion.
Mixed method integration
In our study, the quantitative and qualitative data were analyzed separately, and integration occurred at the interpretation level by merging the data [ 33 ]. As a measure of integration between qualitative and quantitative data, findings were assessed through confirmation, expansion, and discordance. If both data sets confirmed each other’s findings, it was considered confirmation, and if they expanded each other’s insight, it was considered expansion. Discordance was determined if the findings were contradictory.
Ethical considerations
Ethical approval was obtained from the Research and Ethics Committee of the College of Nursing, SQU (CON/NF/2023/18). Informed consent was collected, and no identifiable information was reported. For the focus group interviews, students were reassured that their grades were finalized, and their participation would not affect their grades. Also, the interviewers were instructed to maintain a non-judgmental and non-biased position during the interview. Data were saved in a locked cabinet inside a locked office room. The electronic data were saved in a password-protected computer.
The results section will present findings from the study’s quantitative and qualitative components. The integration of the two data types is described after each qualitative finding.
Quantitative findings
We analyzed the data of 67 participants, representing a 73.6% response rate. The mean age was 21.0 years old (SD 0.73) and 36.4% were male students. See Table 3 for more details.
The descriptive analysis showed that the mean value of the perceived efficacy of case analysis as an assessment method was 3.20 (SD = 0.53), demonstrating an 80% agreement rate. Further analysis indicated that 78.5% of the students concurred the acceptability of case analysis as an assessment method (mean = 3.14, SD = 0.58) and 80.3% (m = 3.21, SD = 0.60) assented the clinical competencies associated with it.
For the items representing acceptability, 81.8% of the students agreed that the case analysis was written clearly, and 80.3% reported that it was well organized. As per the questions, 81% described they were appropriate to their level, and 79.8% agreed upon their alignment with the course objectives. Moreover, the time allocated was adequate for 74.5% of the students, and 73.5% recommend using case analysis as an evaluation strategy for other clinical written examinations.
Regarding the clinical competencies, 77.3% of students agreed that the case analysis motivated them to prepare well for the exam, 81.3% reported that it encouraged them to be active in learning, and 81.0% indicated that it stimulated their interest in the topics discussed in the course. Additionally, 76.5% of the students agreed that the case analysis encouraged them to collaborate with other students when studying for the exam. Among the students, 82.5% reported that the case analysis as an assessment method enhanced their critical thinking skills, 81.0% agreed that it helped them practice decision-making skills, and 81.8% indicated that it improved their problem-solving abilities. See Table 4 .
The independent t-test analysis revealed no significant difference in the perceived efficacy between students with lower and higher GPAs (t [61] = 0.05, p > 0.05). Further analysis showed that the means of acceptability and clinical competencies were not significantly different between the lower GPA group and higher GPA group, t [62] = 0.72, p > 0.05 and t [63] = -0.83, p > 0.05, respectively (Table 5 ).
Qualitative findings
A total of 22 had participated in four focus groups, each group had 5–6 students. The qualitative framework analysis revealed three main findings; case analysis is a preferred assessment method to students when compared to MCQs, case analysis assesses students’ knowledge, and case analysis assesses students’ cognitive skills.
Qualitative Finding 1: case analysis is a preferred assessment method to students when compared to MCQs
Most of the students’ statements about the case analysis as an assessment method were positive. One student stated, “Previously, we have MCQs in clinical exams, but they look as if they are theory exams. This exam makes me deal with cases like a patient, which is good for clinical courses.” . At the same time, many students conveyed optimism about obtaining better grades with this exam format. A student stated, “Our grades, with case analysis format, will be better, … may be because we can write more in open-ended questions, so we can get some marks, in contrast to MCQs where we may get it right or wrong” . On the other hand, a few students suggested adding multiple-choice questions, deleting the emergency department section, and lessening the number of care plans in the ward section to secure better grades.
Although the case analysis was generally acceptable to students, they have repeatedly expressed a need to allocate more time for this type of exam. A student stated, “The limited time with the type of questions was a problem, …” . When further discussion was prompted to understand this challenge, we figured that students are not used to handwriting, which has caused them to be exhausted during the exam. An example is “writing is time-consuming and energy consuming in contrast to MCQs …” . These statements elucidate that the students don’t necessarily mind writing but recommend more practice as one student stated, “More experience of this type of examination is required, more examples during clinical practice are needed.” Some even recommended adopting this format with other clinical course exams by saying “It’s better to start this method from the first year for the new cohort and to apply it in all other courses.”
Mixed Methods Inference 1: Confirmation and Expansion
The abovementioned qualitative impression supports the high acceptability rate in quantitative analysis. In fact, there is a general agreement that the case analysis format surpasses the MCQs when it comes to the proper evaluation strategies for clinical courses. Expressions in the qualitative data revealed more details, such as the limited opportunities to practice handwriting, which negatively impacted the perceived adequacy of exam time.
Qualitative Finding 2: case analysis assesses students’ knowledge
Students conferred that they were reading more about the disease pathophysiology, lab values, and nursing care plans, which they did not usually do with traditional means of examination. Examples of statements include “… before we were not paying attention to the normal lab results but …in this exam, we went back and studied them which was good for our knowledge” and “we cared about the care plan. In previous exams, we were not bothered by these care plans”. Regarding the burden that could be perceived with this type of preparation, the students expressed that this has helped them prepare for the theory course exam; as one student said, “We also focus on theory lectures to prepare for this exam …. this was very helpful to prepare us for the theory final exam as well.” However, others have highlighted the risks of limiting the exam’s content to one case analysis. The argument was that some students may have not studied the case completely or been adequately exposed to the case in the clinical setting. To solve this risk, the students themselves advocated for frequent case group discussions in the clinical setting as stated by one student: “There could be some differences in the cases that we see during our clinical posting, for that I recommend that instructors allocate some time to gather all the students and discuss different cases.” Also, the participants advocated for more paper-based case analysis exercises as it is helpful to prepare them for the exams and enhance their knowledge and skills.
Mixed Methods Inferences 2: Confirmation and Expansion
The qualitative finding supports the quantitative data relevant to items 6, 7, and 8. Students’ expressions revealed more insights, including the acquisition of deeper knowledge, practicing concept mapping, and readiness for other course-related exams. At the same time, students recommended that faculty ensure all students’ exposure to common cases in the clinical setting for fair exam preparation.
Qualitative Finding 3. case analysis assesses students’ cognitive skills
Several statements conveyed how the case analysis format helped the students use their critical thinking and analysis skills. One student stated, “It, the case analysis format, enhanced our critical thinking skills as there is a case with given data and we analyze the case….” . Therefore, the case analysis format as an exam is potentially a valid means to assess the student’s critical thinking skills. Students also conveyed that the case analysis format helped them link theory to practice and provided them with the platform to think like real nurses and be professional. Examples of statements are: “…we connect our knowledge gained from theory with the clinical experience to get the answers…” and “The questions were about managing a case, which is what actual nurses are doing daily.” Another interesting cognitive benefit to case analysis described by the students was holistic thinking. For example, one student said, “Case analysis format helped us to see the case as a whole and not only from one perspective.”
Mixed Methods Inferences 3: Confirmation
The quantitative data indicated mutual agreement among the students that the case analysis enhanced their critical thinking, decision-making, and problem-solving skills. The students’ statements from the interviews, including critical thinking, linking theory to practice, and holistic thinking, further supported these presumptions.
This research presents the findings from a mixed methods study that explored undergraduate nursing students’ perceived efficacy of using case analysis as an assessment method. The perceived efficacy was reflected through acceptability and association with two core competencies: knowledge and cognitive skills. The study findings showed a high rate of perceived efficacy of case analysis as an assessment method among nursing students. Additionally, three findings were extracted from the qualitative data that further confirmed the perceived efficacy: (1) case analysis is a preferred assessment method to students compared to MCQs, (2) case analysis assesses students’ knowledge, and (3) case analysis assesses students’ cognitive skills. Moreover, the qualitative findings revealed details that expanded the understanding of the perceived efficacy among nursing students.
Previous literature reported students’ preference for case analysis as a teaching method. A randomized controlled study investigated student’s satisfaction levels with case-based teaching, in addition to comparing certain outcomes between a traditional teaching group and a case-based teaching group. They reported that most students favored the use of case-based teaching, whom at the same time had significantly better OSCE scores compared to the other group [ 34 ]. As noted, this favorable teaching method ultimately resulted in better learning outcomes and academic performance. Although it may be challenging since no answer options are provided, students appreciate the use of case analysis format in their exams because it aligns better with the course objectives and expected clinical competencies. The reason behind students’ preference for case analysis is that it allows them to interact with the teaching content and visualize the problem, leading to a better understanding. When case analysis is used as an assessment method, students can connect the case scenario presented in the exam to their clinical training, making it more relevant.
In this study, students recognized the incorporation of nursing knowledge in the case analysis exam. They also acknowledged improved knowledge and learning abilities similar to those observed in case-based teaching. Boney et al. (2015) reported that students perceived increased learning gains and a better ability to identify links between different concepts and other aspects of life through case-based teaching [ 35 ]. Additionally, case analysis as an exam promotes students’ in-depth acquirement of knowledge through the type of preparation it entails. Literature suggested that case-based teaching promotes self-directed learning with high autonomous learning ability [ 34 , 36 ]. Thus, better achievement in the case analysis exam could be linked with a higher level of knowledge, making it a suitable assessment method for knowledge integration in nursing care.
The findings of this study suggest that case analysis can be a useful tool for evaluating students’ cognitive skills, such as critical thinking, decision-making, and problem-solving. A randomized controlled study implied better problem-solving abilities among the students in the case-based learning group compared to those in the traditional teaching methods group [ 12 ]. Moreover, students in our study conveyed that case analysis as an exam was an opportunity for them to think like real nurses. Similar to our findings, a qualitative study on undergraduate nutrition students found that case-based learning helped students develop professional competencies for their future practice, in addition to higher-level cognitive skills [ 37 ]. Therefore, testing students through case analysis allows educators to assess the student’s readiness for entry-level professional competencies, including the thinking process. Also, to evaluate students’ high-level cognitive skills according to Bloom’s taxonomy (analysis, synthesis, and evaluation), which educators often find challenging.
Case analysis as an assessment method for clinical courses is partially integrated in case presentation or OSCE evaluation methods. However, the written format is considered to be more beneficial for both assessment and learning processes. A qualitative study was conducted to examine the impact of paper-based case learning versus video-based case learning on clinical decision-making skills among midwifery students. The study revealed that students paid more attention and were able to focus better on the details when the case was presented in a paper format [ 38 ]. Concurrently, the students in our study recommended more paper-based exercises, which they believed would improve their academic performance.
This study has possible limitations. The sample size was small due to the limited experience of case analysis as a clinical written exam in the program. Future studies with larger sample sizes and diverse nursing courses are needed for better generalizability.
Implications
Little evidence relates to the efficacy of case analysis as an evaluation method, suggesting the novelty of this study. Despite the scarcity of case-based assessment studies, a reader can speculate from this study’s findings that there is a potential efficacy of case analysis as an assessment method in nursing education. Future research is warranted to validate the effectiveness of case-analysis assessment methods and investigate the effects of case-analysis exams on academic and clinical performance.
Overall, our findings are in accordance with the evidence suggesting students’ perceived efficacy of case analysis as a teaching method. This study adds a potential for the case analysis to be acceptable and relevant to the clinical competencies when used as an assessment method. Future research is needed to validate the effectiveness of case analysis exams in other nursing clinical courses and examine their effects on academic and clinical performance.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available fromthe Principal Investigator (BAY) upon reasonable request.
Iriarte-Roteta A, Lopez‐Dicastillo O, Mujika A, Ruiz‐Zaldibar C, Hernantes N, Bermejo‐Martins E, Pumar‐Méndez MJ. Nurses’ role in health promotion and prevention: a critical interpretive synthesis. J Clin Nurs. 2020;29(21–22):3937–49. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocn.15441
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Fukada M. Nursing competency: definition, structure and development. Yonago Acta Med. 2018;61(1):001–7. https://doi.org/10.33160/yam.2018.03.001
Article Google Scholar
Nabizadeh-Gharghozar Z, Alavi NM, Ajorpaz NM. Clinical competence in nursing: a hybrid concept analysis. Nurse Educ Today. 2021;97:104728. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2020.104728
Allande-Cussó R, Fernández-García E, Porcel-Gálvez AM. Defining and characterising the nurse–patient relationship: a concept analysis. Nurs Ethics. 2021;29(2):462–84. https://doi.org/10.1177/09697330211046651
Butts JB, Rich KL. Nursing ethics: across the curriculum and into practice. Jones & Bartlett Learning; 2019.
Chen W, Shah UV, Brechtelsbauer C. A framework for hands-on learning in chemical engineering education—training students with the end goal in mind. Educ Chem Eng. 2019;28:25–9.
Willman A, Bjuresäter K, Nilsson J. Newly graduated registered nurses’ self-assessed clinical competence and their need for further training. Nurs Open. 2020;7(3):720–30. https://doi.org/10.1002/nop2.443
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
American Association of Colleges of Nursing. (2021). The essentials: Core competencies for professional nursing education. In. Retrieved from n.d.). American Association of Colleges of Nursing. https://www.aacnnursing.org/Portals/0/PDFs/Publications/Essentials-2021.pdf
Kaur G, Rehncy J, Kahal KS, Singh J, Sharma V, Matreja PS, Grewal H. Case-based learning as an effective tool in teaching pharmacology to undergraduate medical students in a large group setting. J Med Educ Curric Dev. 2020;7:2382120520920640.
Patiraki E, Katsaragakis S, Dreliozi A, Prezerakos P. Nursing care plans based on NANDA, nursing interventions classification, and nursing outcomes classification: the investigation of the effectiveness of an educational intervention in Greece. Int J Nurs Knowl. 2017;28:88–93.
Cui C, Li Y, Geng D, Zhang H, Jin C. The effectiveness of evidence-based nursing on development of nursing students ‘critical thinking: a meta-analysis. Nurse Educ Today. 2018;65:46–53.
Bi M, Zhao Z, Yang J, Wang Y. Comparison of case-based learning and traditional method in teaching postgraduate students of medical oncology. Med Teach. 2019;41(10):1124–8.
Seshan V, Matua GA, Raghavan D, Arulappan J, Al Hashmi I, Roach EJ, Prince EJ. Case study analysis as an effective teaching strategy: perceptions of undergraduate nursing students from a Middle Eastern Country. SAGE Open Nurs. 2021;7:23779608211059265.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Slieman TA, Camarata T. Case-based group learning using concept maps to achieve multiple educational objectives and behavioral outcomes. J Med Educ Curric Dev. 2019;6:2382120519872510.
Yu Z, Hu R, Ling S, Zhuang J, Chen Y, Chen M, Lin Y. Effects of blended versus offline case-centered learning on the academic performance and critical thinking ability of undergraduate nursing students: a cluster randomized controlled trial. Nurse Educ Pract. 2021;53:103080.
Chan AW, Chair SY, Sit JW, Wong EM, Lee DT, Fung OW. Case-based web learning versus face-to-face learning: a mixed-method study on university nursing students. J Nurs Res. 2016;24(1):31–40.
Hong S, Yu P. Comparison of the effectiveness of two styles of case-based learning implemented in lectures for developing nursing students’ critical thinking ability: a randomized controlled trial. Int J Nurs Stud. 2017;68:16–24.
Shohani M, Bastami M, Gheshlaghi LA, Nasrollahi A. Nursing student’s satisfaction with two methods of CBL and lecture-based learning. BMC Med Educ. 2023;23(1):1–5.
Tan KW. Using Teaching Cases for Achieving Bloom’s High-Order Cognitive Levels: An Application in Technically-Oriented Information Systems Course (2017). 2017 Proceedings. 1. http://aisel.aisnet.org/siged2017/1
Farashahi M, Tajeddin M. Effectiveness of teaching methods in business education: a comparison study on the learning outcomes of lectures, case studies and simulations. Int J Manage Educ. 2018;16(1):131–42.
Google Scholar
Farha RJA, Zein MH, Al Kawas S. Introducing integrated case-based learning to clinical nutrition training and evaluating students’ learning performance. J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2021;16(4):558–64.
Picciano AG. Theories and frameworks for Online Education: seeking an Integrated Model. Online Learn. 2017;213:166–90.
Bezanilla MJ, Fernández-Nogueira D, Poblete M, Galindo-Domínguez H. Methodologies for teaching-learning critical thinking in higher education: the teacher’s view. Think Skills Creativity. 2019;33:100584.
Immonen K, Oikarainen A, Tomietto M, Kääriäinen M, Tuomikoski A-M, Kaučič BM, Perez-Canaveras RM. Assessment of nursing students’ competence in clinical practice: a systematic review of reviews. Int J Nurs Stud. 2019;100:103414.
Oermann MH, Gaberson KB, De Gagne JC, NPD-BC C. Evaluation and testing in nursing education. Springer Publishing Company; 2024.
McCarty T. (2020). How to Build Assessments for Clinical Learners. Roberts Academic Medicine Handbook: A Guide to Achievement and Fulfillment for Academic Faculty, 83–90.
Gholami M, Changaee F, Karami K, Shahsavaripour Z, Veiskaramian A, Birjandi M. Effects of multiepisode case-based learning (CBL) on problem-solving ability and learning motivation of nursing students in an emergency care course. J Prof Nurs. 2021;37(3):612–9.
King N. (2016, April). Case-based exams for learning and assessment: Experiences in an information systems course [ Confeence presentation]. In 2016 IEEE Global Engineering Education Conference (EDUCON) , Abu Dhabi, UAE.
Pereira D, Flores MA, Niklasson L. Assessment revisited: a review of research in Assessment and evaluation in Higher Education. Assess Evaluation High Educ. 2016;41(7):1008–32.
Creswell JW, Poth CN. Qualitative inquiry and research design: choosing among five approaches. SAGE; 2016.
O’Brien BC, Harris IB, Beckman TJ, Reed DA, Cook DA. Standards for reporting qualitative research. Acad Med. 2014;89(9):1245–51.
Gale NK, Heath G, Cameron E, Rashid S, Redwood S. Using the framework method for the analysis of qualitative data in multi-disciplinary health research. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2013;13(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-13-117
Fetters MD, Curry LA, Creswell JW. Achieving integration in mixed methods designs—principles and practices. Health Serv Res. 2013;48(6pt2):2134–56. https://doi.org/10.1111/1475-6773.12117
Liu L, Li M, Zheng Q, Jiang H. The effects of case-based teaching in nursing skill education: cases do matter. INQUIRY. J Health Care Organ Provis Financing. 2020;57:004695802096442.
Bonney KM. Case study teaching methods improve student performance and perceptions of learning gains. J Microbiol Biology Educ. 2015;16(1):21–8.
Rezaee R, Mosalanejad L. The effects of case-based team learning on students’ learning, self-regulation, and self-direction. Global J Health Sci. 2015;7(4):295.
Harman T, Bertrand B, Greer A, Pettus A, Jennings J, Wall-Bassett E, Babatunde OT. Case-based learning facilitates critical thinking in undergraduate nutrition education: students describe the big picture. J Acad Nutr Dietetics. 2015;115(3):378–88.
Nunohara K, Imafuku R, Saiki T, Bridges SM, Kawakami C, Tsunekawa K, Niwa M, Fujisaki K, Suzuki Y. (2020). How does video case-based learning influence clinical decision-making by midwifery students? An exploratory study. BMC Med Educ, 20 (1).
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the nursing students at SQU who voluntarily participated in this study.
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Sultan Qaboos University, Al Khodh 66, Muscat, 123, Oman
Basma Mohammed Al Yazeedi, Lina Mohamed Wali Shakman, Sheeba Elizabeth John Sunderraj, Harshita Prabhakaran, Judie Arulappan, Erna Judith Roach, Aysha Al Hashmi & Zeinab Al Azri
Oman College of Health Science, Norht Sharqia Branch, Ibra 66, Ibra, 124, Oman
Aysha Al Hashmi
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Dr. Basma Mohammed Al Yazeedi contributed to conceptualization, methods, data collection, data analysis, writing the draft, and reviewing the final draft. Ms. Lina Mohamed Wali Shakman contributed to conceptualization, data collection, data analysis, writing the draft, and reviewing the final draft. Ms. Sheeba Elizabeth John Sunderraj contributed to conceptualization, methods, data collection, writing the draft, and reviewing the final draft.Ms. Harshita Prabhakaran contributed to conceptualization, data collection, writing the draft, and reviewing the final draft.Dr. Judie Arulappan contributed to conceptualization and reviewing the final draft.Dr. Erna Roach contributed to conceptualization writing the draft and reviewing the final draft.Ms. Aysha Al Hashmi contributed to the conceptualization and reviewing the final draft. Dr. Zeinab Al Azri contributed to data collection, data analysis, writing the draft, and reviewing the final draft.All auhors reviewed and approved the final version of the manuscirpt.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Zeinab Al Azri .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Ethical approval was obtained from the Research and Ethics Committee of the College of Nursing, Sultan Qaboos University SQU (CON/NF/2023/18). All data was held and stored following the SQU data policy retention. Informed consent to participate was obtained from all of the participants in the study.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1:
The questionnaire used in this study is attached as a supplementary document.
Supplementary Material 2
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Yazeedi, B.M.A., Shakman, L.M.W., Sunderraj, S.E.J. et al. Perceived efficacy of case analysis as an assessment method for clinical competencies in nursing education: a mixed methods study. BMC Nurs 23 , 441 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-024-02102-9
Download citation
Received : 07 April 2024
Accepted : 17 June 2024
Published : 28 June 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-024-02102-9
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Case-analysis
- Clinical competency
- Nursing education
BMC Nursing
ISSN: 1472-6955
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Information
- Author Services
Initiatives
You are accessing a machine-readable page. In order to be human-readable, please install an RSS reader.
All articles published by MDPI are made immediately available worldwide under an open access license. No special permission is required to reuse all or part of the article published by MDPI, including figures and tables. For articles published under an open access Creative Common CC BY license, any part of the article may be reused without permission provided that the original article is clearly cited. For more information, please refer to https://www.mdpi.com/openaccess .
Feature papers represent the most advanced research with significant potential for high impact in the field. A Feature Paper should be a substantial original Article that involves several techniques or approaches, provides an outlook for future research directions and describes possible research applications.
Feature papers are submitted upon individual invitation or recommendation by the scientific editors and must receive positive feedback from the reviewers.
Editor’s Choice articles are based on recommendations by the scientific editors of MDPI journals from around the world. Editors select a small number of articles recently published in the journal that they believe will be particularly interesting to readers, or important in the respective research area. The aim is to provide a snapshot of some of the most exciting work published in the various research areas of the journal.
Original Submission Date Received: .
- Active Journals
- Find a Journal
- Proceedings Series
- For Authors
- For Reviewers
- For Editors
- For Librarians
- For Publishers
- For Societies
- For Conference Organizers
- Open Access Policy
- Institutional Open Access Program
- Special Issues Guidelines
- Editorial Process
- Research and Publication Ethics
- Article Processing Charges
- Testimonials
- Preprints.org
- SciProfiles
- Encyclopedia

Article Menu

- Subscribe SciFeed
- Recommended Articles
- Google Scholar
- on Google Scholar
- Table of Contents
Find support for a specific problem in the support section of our website.
Please let us know what you think of our products and services.
Visit our dedicated information section to learn more about MDPI.
JSmol Viewer
Enhancing urban–rural integration in china: a comparative case study of introducing small rural industries in huangyan-taizhou.

1. Introduction
2. literature review: urban–rural linkage and urban–rural integration, 3. methods and case selection, 3.1. mixed method research, 3.2. urban–rural interface as the focusing region for uri, 3.3. selected case region: taizhou in the yangtze river delta, 3.4. obtaining qualitative and quantitative data, 4. the changing role of rural industries in the trajectory of urbanisation in china, 4.1. an overview of relevant policies affecting rural industries, 4.2. inadequate rural land transfer limited rural industries, 4.3. rapid urban sprawl further ‘squeezed’ rural space for development, 4.4. transitory periods for rural industry development between the 1980s and 1990s, 4.5. small industries as the main approach of rural revitalisation guided by uri, 5. case study: village transformation under uri, 5.1. xiapuzheng village: driven by plastic manufacture and endogenous industry, 5.2. luoyu village: driven by industries related to global production chain, 5.3. waciyao village: driven by improvement in the physical environment and future rural tourism, 5.4. discussions, 6. conclusions, author contributions, data availability statement, acknowledgments, conflicts of interest, ethics statement.
- Remy, S.; Kago, J.; Zhang, X.Q.; Augustinus, C.; Tuts, R. Role of Urban–Rural Linkages in Promoting Sustainable Urbanization. Environ. Urban. ASIA 2014 , 5 , 219–234. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- United Nations. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development ; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [ Google Scholar ]
- UN Habitat. Implementing the New Urban Agenda by Strengthening Urban-Rural Linkages—Leave no One and no Space Behind ; UN Habitat: Nairobi, Kenya, 2017. [ Google Scholar ]
- UN Habitat. Urban-Rural Linkages: Guiding Principles Framework for Action to Advance Integrated Territorial Development ; UN Habitat: Nairobi, Kenya, 2019; Available online: https://www.unccd.int/resources/manuals-and-guides/urban-rural-linkages-guiding-principles (accessed on 25 March 2024).
- Brenner, N. Introduction: Urban theory without an outside. In Implosions/Explosions: Towards a Study of Planetary Urbanization ; Academia: Prague, Czechoslovakia, 2014; Volume 17. [ Google Scholar ]
- The State Council of the PRC. The National Land Use Planning Framework ; Xinhua News Agency: Beijing, China, 2008.
- Liu, Y. Scientifically promoting the strategy of reclamation and readjustment of rural land in China. China Land Sci. 2011 , 25 , 3–8. [ Google Scholar ]
- Liu, Y.; Fang, F.; Li, Y. Key issues of land use in China and implications for policy making. Land Use Policy 2014 , 40 , 6–12. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Huang, H.; Yang, G.Q.; Misselwitz, P.; Langguth, H. Post-rural urbanisation andrural revitalisation: Can China learn from new planning approaches in contemporary Germany. City Plan. Rev. 2017 , 41 , 111–119. (In Chinese) [ Google Scholar ]
- Huang, H. Learning from exploratory rural practices of the Yangtze River Delta in China: New initiatives, networks and empowerment shifts, and sustainability. J. Rural. Stud. 2020 , 77 , 63–74. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- CPC Central Committee and The State Council of the PRC. Opinions on Establishing and Improving the System, Mechanism and Policy System of Urban-Rural Integrated Development ; Xinhua News Agency: Beijing, China, 2019. (In Chinese)
- Lefebvre, H. The Urban Revolution ; University of Minnesota Press: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2003. [ Google Scholar ]
- Brenner, N.; Madden, D.J.; Wachsmuth, D. Assemblage urbanism and the challenges of critical urban theory. City 2011 , 15 , 225–240. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Angelo, H. From the City Lens toward Urbanisation as a Way of Seeing: Country/City Binaries on an Urbanising Planet. Urban Stud. 2017 , 54 , 158–178. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Heley, J.; Jones, L. Relational rurals: Some thoughts on relating things and theory in rural studies. J. Rural. Stud. 2012 , 28 , 208–217. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Brenner, N.; Katsikis, N. Operational Landscapes: Hinterlands of the Capitalocene. Archit. Des. 2020 , 90 , 22–31. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- López-Goyburu, P.; García-Montero, L.G. The Urban-Rural Interface as an Area with Characteristics of Its Own in Urban Planning: A Review. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018 , 43 , 157–165. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- de Bruin, S.; Dengerink, J.; van Vliet, J. Urbanisation as driver of food system transformation and opportunities for rural livelihoods. Food Sec. 2021 , 13 , 781–798. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Eakin, H.; DeFries, R.; Kerr, S.; Lambin, E.F.; Liu, J.; Marcotullio, P.J.; Messerli, P.; Reenberg, A.; Rueda, X.; Swaffield, S.R.; et al. Significance of telecoupling for exploration of land-use change. In Rethinking Global Land Use in an Urban Era ; Seto, K.C., Reenberg, A., Eds.; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 141–161. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gutu Sakketa, T. Urbanisation and rural development in sub-Saharan Africa: A review of pathways and impacts. Res. Glob. 2023 , 6 , 100133. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development) & European Commission. Cities in the World: A New Perspective on Urbanization ; OECD: Paris, France, 2020. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Muffp—Milan Urban Food Policy Pact. Milan Urban Food Policy Pact and Framework for Action[EB/OL]. 2015. Available online: https://www.foodpolicymilano.org/en/the-text-of-the-milan-urban-food-policy-pact/ (accessed on 25 March 2024).
- Wolff, F.; Mederake, L.; Bleher, D.; Sosath, O.; Westphal, I. Rahmenbedingungen und Instrumente für Die Gestaltung Nachhaltiger Stadt-Land-Verknüpfungen[M/OL]. Im Auftrag des Umweltbundesamtes. 2019. Available online: https://www.umweltbundesamt.de/sites/default/files/medien/1410/publikationen/2019-08-15_texte_86-2019_run-bericht_ap3-1_3-2.pdf (accessed on 25 March 2024).
- United Nations. New Urban Agenda ; Habitat III Secretariat: Quito, Ecuador, 2017; ISBN 978-92-1-132731-1. [ Google Scholar ]
- Potts, D. Conflict and collisions in Sub-Saharan African urban definitions: Interpreting recent urbanization data from Kenya. World Dev. 2017 , 97 , 67–78. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Wineman, A.; Alia, D.Y.; Anderson, C.L. Definitions of “rural” and “urban” and understandings of economic transformation: Evidence from Tanzania. J. Rural. Stud. 2020 , 79 , 254–268. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Azmi, H.N.H.; Wijaya, B.; Wijaya, M.I.H.; Novandaya, Z.; Kurniawati, H. Mapping urban-rural linkage in promoting sustainable regional development to support rural creative economy entrepreneurs. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021 , 887 , 012023. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Chen, C.; Yang, G.; Xu, H.; Wang, Y. Understanding Rural Development Driven by Small Local Industries and Its Planning Strategies: The Case of Zhejiang Province. Planners 2021 , 37 , 21–27. [ Google Scholar ]
- Yang, G. Rural Evolution: Reviewing the Rebirth of Traditional Rural Settlements from the Perspective of “Productivity-Spatial Form” Theory. J. Tongji Univ. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2022 , 33 , 66–73. [ Google Scholar ]
- Castillo, C.P.; van Heerden, S.; Barranco, R.; Jacobs-Crisioni, C.; Kompil, M.; Kučas, A.; Aurambout, J.P.; Silva, F.B.E.; Lavalle, C. Urban–rural continuum: An overview of their interactions and territorial disparities. Reg. Sci. Policy Pract. 2023 , 15 , 729–768. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Wang, M. Spatial Characteristics and Planning Strategies of Rural Industries Guided by Industrial Revitalization: A Case Study of the Urban Pastoral Complex in the Dongxihu District of Wuhan. City Plan. Rev. 2023 , 47 , 105–114. [ Google Scholar ]
- Wang, L.; Yang, G. The Mechanism of Socio-Spatial Evolution in Rural Areas Driven by the Development of the Planting Industry—A Case Study of Yuezhuang Village in Shandong Province, China. Land 2024 , 13 , 768. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- UN-Habitat. Compendium of case studies. In For the Implementation of the “Urban-Rural Linkages”: Guiding Principles (URL-GP) and Framework for Action , 1st ed.; UN-Habitat: Nairobi, Kenya, 2020. [ Google Scholar ]
- UN-Habitat. Compendium of Inspiring Practices on Urban-Rural Linkages: Implementation of Guiding Principles and Framework for Action to Advance Integrated Territorial Development , 2nd ed.; (UN-Habitat: Nairobi, Kenya, 2021. [ Google Scholar ]
- UN-Habitat. Compendium of Inspiring Practices on Urban-Rural Linkages: Implementation of Guiding Principles and Framework for Action to Advance Integrated Territorial Development , 3rd ed.; UN-Habitat: Nairobi, Kenya, 2023. [ Google Scholar ]
- Liu, Y.; Zang, Y.; Yang, Y. China’s rural revitalization and development: Theory, technology and management. J. Geogr. Sci. 2020 , 30 , 1923–1942. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Li, Y. Urban–rural interaction patterns and dynamic land use: Implications for urban–rural integration in China. Reg. Environ. Change 2012 , 12 , 803–812. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Yang, Y.; Bao, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y. Measurement of urban-rural integration level and its spatial differentiation in China in the new century. Habitat Int. 2021 , 117 , 102420. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Yan, J.; Chen, H.; Xia, F. Toward improved land elements for urban–rural integration: A cell concept of an urban–rural mixed community. Habitat Int. 2018 , 77 , 110–120. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Gong, H.; Tong, D.; Zhang, C.; Pan, X. Optimization of Comprehensive Land Consolidation Model under the Context of Urban-Rural Integration. Planners 2023 , 39 , 44–52. [ Google Scholar ]
- Luo, X.; Jin, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Ying, S.; Zhou, Y. Mechanism and model of comprehensive land consolidation promoting urban-rural integration in peri-urban from the perspective of symbiosis theory. J. Nat. Resour. 2024 , 39 , 1053–1067. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Guo, M.; Lu, X.; Ma, Q.; Qiu, L. Review and Prospect of Settlement System in County Territory Under the Background of Urban Rural Integration. Dev. Small Cities Towns 2023 , 41 , 5–11. [ Google Scholar ]
- Wang, J.; Sun, S.; Xu, M.; Li, S.; Wu, X. Analysis on Refined Construction of Public Facilities in Agglomeration and Upgrading Villages Based on Resident Demand: A Case Study of Dongying District, Dongying City. Urban Dev. Stud. 2022 , 29 , 112–118. [ Google Scholar ]
- Wang, L.; Huang, H.; Yang, G. Research on Rural Revitalization Driven by Agricultural Headquarters from a Network Perspective: A Case Study in Huangyan District, Zhejiang Province. Dev. Small Cities Towns 2024 , 42 , 55–61. [ Google Scholar ]
- He, X.; Yan, Y. Differentiation Characteristics, Influencing Factors and Zoning Optimization of County Digital Village. Geogr. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2024 , 40 , 88–95. [ Google Scholar ]
- Li, X.; Ma, X.D.; Khuong, M.H.; Zhu, J.Y. Dynamic mechanism of rural development oriented urban-rural integration. J. Nat. Resour. 2020 , 35 , 1926–1939. [ Google Scholar ]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, F.; Li, Q. The path of rural revitalisation in rapidly urbanising area: The case of Southern Jiangsu Provice. Urban Forum 2018 , 2 , 98–105. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Luo, Z. E-garden city: Reconstruction of urbanization theory in the mobile internet era. City Plan. Rev. 2020 , 44 , 9–16. [ Google Scholar ]
- Wu, Z. Research on the Realistic Path of How to Promote the coordinated Development of Rural Revitalization Strategy and New Urbanization in Typical Resource-based Cities. Mod. Agric. Res. 2024 , 30 , 41–43. [ Google Scholar ]
- Shortall, S.; Brown, D.L. Guest editorial for special issue on rural inequalities: Thinking about rural inequalities as a cross-national research project. J. Rural. Stud. 2019 , 68 , 213–218. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Phillipson, J.; Tiwasing, P.; Gorton, M.; Maioli, S.; Newbery, R.; Turner, R. Shining a spotlight on small rural businesses: How does their performance compare with urban? J. Rural. Stud. 2019 , 68 , 230–239. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Spinney, J.E. Mobile positioning and LBS applications. Geography 2003 , 88 , 256–265. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sadoun, B.; Al-Bayari, O. LBS and GIS technology combination and applications. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE/ACS International Conference on Computer Systems and Applications, Amman, Jordan, 13–16 May 2007; pp. 578–583. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lynam, A.; Li, F.; Xiao, G.; Fei, L.; Huang, H.; Utzig, L. Capturing socio-spatial inequality in planetary urbanisation: A multi-dimensional methodological framework. Cities 2023 , 132 , 104076. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Ros-Tonen, M.; Pouw, N.; Bavinck, M. Governing beyond cities: The urban-rural interface. In Geographies of Urban Governance: Advanced Theories, Methods and Practices ; Springer International Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 85–105. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hiner, C.C. Beyond the edge and in between:(Re) conceptualizing the rural–urban interface as meaning–model–metaphor. Prof. Geogr. 2016 , 68 , 520–532. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Ortiz-Báez, P.; Cabrera-Barona, P.; Bogaert, J. Characterizing landscape patterns in urban-rural interfaces. J. Urban Manag. 2021 , 10 , 46–56. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Wu, Z.; Li, D. Principles of Urban and Rural Planning ; China Architecture Publishing & Media Co., Ltd.: Beijing, China, 2010. [ Google Scholar ]
- The Standing Committee of National People’s Congress. Land Administration Law of the People’s Republic of China. 2019. Available online: http://www.npc.gov.cn/npc/c2/c30834/201909/t20190905_300663.html (accessed on 25 March 2024).
- Zhejiang Provincial Development and Reform Commission. The 14th Five-Year Plan for the Development of New Urbanization in Zhejiang Province. 2021. Available online: https://www.zj.gov.cn/art/2021/5/31/art_1229505857_2302659.html (accessed on 30 May 2024).
- National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC). Notice on Carrying Out the Work of the National Pilot Zone for Integrated Urban and Rural Development ; NDRC: Beijing, China, 2019. (In Chinese)
- Han, J. Prioritizing Agricultural, Rural Development and Implementing the Rural Revitalization Strategy. China Agric. Econ. Rev. 2020 , 12 , 14–19. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Ke, M.; Huang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Luo, C. Research on Building Urban-rural Integration Node in the Merged Township Government Resident Market Town Under the Background of Common Prosperity: A Case of Zhejiang Province. Dev. Small Cities Towns 2024 , 42 , 83–91. [ Google Scholar ]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, M. Evaluation and Determinants of Satisfaction with Rural Livability in China’s Less-Developed Eastern Areas: A Case Study of Xianju County in Zhejiang Province. Ecol. Indic. 2019 , 104 , 711–722. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Taizhou Survey Team of the National Bureau of Statistics. A Study on the High-Quality Development of Private Economy in Taizhou: Based on a Comparative Analysis of Taizhou, Jiaxing and Jinhua. Available online: https://www.zjtz.gov.cn/art/2022/11/29/art_1229207956_3835358.html (accessed on 30 May 2024).
- National Bureau of Statistics. China Statistical Yearbook ; China Statistic Press: Beijing, China, 2021. [ Google Scholar ]
- Office of the Leading Group of the State Council for the Seventh National Population Census. Major Figures on 2020 Population Census of China ; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2021. (In Chinese) [ Google Scholar ]
- Harvey, D. The Condition of Postmodernity: An Enquiry into the Origins of Cultural Change ; Wiley-Blackwell: Oxford, UK; Cambridge, MA, USA, 1991. [ Google Scholar ]
- Zhang, W.; Chong, Z.; Li, X.; Nie, G. Spatial Patterns and Determinant Factors of Population Flow Networks in China: Analysis on Tencent Location Big Data. Cities 2020 , 99 , 102640. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Luo, J.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Shen, J.; Shen, L.; Xing, X. Urban Land Expansion and the Floating Population in China: For Production or for Living? Cities 2018 , 74 , 219–228. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Zhang, Z.; Lu, Y. China’s Urban-Rural Relationship: Evolution and Prospects. China Agric. Econ. Rev. 2018 , 10 , 260–276. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Zhu, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, K.; Yuan, S.; Yang, L.; Skitmore, M. Urban–Rural Construction Land Transition and Its Coupling Relationship with Population Flow in China’s Urban Agglomeration Region. Cities 2020 , 101 , 102701. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Li, Y. Urban-Rural Interaction in China: Historic Scenario and Assessment. China Agric. Econ. Rev. 2011 , 3 , 335–349. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Liu, S. The reform of rural land system: From the household contract responsibility system to the separation of three rights. Econ. Res. J. 2022 , 57 , 18–26. [ Google Scholar ]
- Zhang, Y.-Q. Dilemma of China’s Urbanization and Land Expropriation—Based on the Farmland Property Rights of Thinking. J. Northwest AF Univ. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2014 , 14 , 16–31. (In Chinese) [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Xing, Z.; Chen, Y.; Deng, C. The Evolution and Enlightenment of Urban-Rural Relations of the PRC from 1949 to 2019. Reform 2019 , 6 , 20–31. [ Google Scholar ]
- The State Council of the PRC. Notice on Further Deepening the Reform of Urban Housing System and Accelerating Housing Construction ; People’s Daily: Beijing, China, 1998. (In Chinese) [ Google Scholar ]
- Fei, X. Urban-Rural Development in China-My Lifetime Reasearch Project. Chin. J. Sociol. 1993 , 01 , 3–13. [ Google Scholar ]
- Xu, S. A review of the impact of urban-rural relations on rural areas and farmers. Rural. Econ. Sci.-Technol. 2014 , 25 , 122–125. [ Google Scholar ]
- General Office of the State Council of the People’s Republic of China. Notice on Cleaning Up and Rectifying Various Development Zones and Strengthening the Management of Construction Land. 2003. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/zwgk/2005-08/14/content_22445.htm (accessed on 25 March 2024). (In Chinese)
- CPC Central Committee. Suggestions for the 11th Five-Year Plan ; CPC Central Committee: Beijing, China, 2005. (In Chinese) [ Google Scholar ]
- Yang, R.; Yang, Q. Restructuring the State: Policy Transition of Construction Land Supply in Urban and Rural China. Land 2021 , 10 , 1–17. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Hu, J. Report to the Eighteenth National Congress of the Communist Party of China: Family March on the Path of Socialism with Chinese Characteristics and Strive to Complete the Building of a Moderately Prosperous Society in All Respects. 2012. Available online: https://www.gov.cn/ldhd/2012-11/17/content_2268826.htm (accessed on 25 March 2024). (In Chinese)
- CPC Central Committee and The State Council of the PRC. Strategy for Rural Revitalization (2018–2022) ; Xinhua News Agency: Beijing, China, 2018. (In Chinese)
- Cheng, H.; Yang, Z.; Liu, S.J. Rural Stay: A New Type of Rural Tourism in China. J. Travel Tour. Mark. 2020 , 37 , 711–726. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Lin, J.; Li, H.; Lin, M.; Li, C. Rural e-commerce in China: Spatial dynamics of Taobao Villages development in Zhejiang Province. Growth Change Grow 2021 , 53 , 12560. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Crang, M.; Zhang, J. Transient Dwelling: Trains as Places of Identification for the Floating Population of China. Soc. Cult. Geogr. 2012 , 13 , 895–914. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Liu, Y. Research on the urban-rural integration and rural revitalization in the new era in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2018 , 73 , 637–650. [ Google Scholar ]
- Yang, G. Multiple Approaches of Rural Revitalization from the Viewpoint of Urban-rural Co-construction. Planners 2019 , 35 , 5–10. [ Google Scholar ]
- Fang, C. Theoretical analysis on the mechanism and evolution law of urban-rural integration development. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2022 , 77 , 759–776. [ Google Scholar ]
- Mubangizi, B. What is ‘Rural’ in South Africa, and Why Does it Matter? Afr. J. Gov. Dev. 2023 , 12 , 1–6. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
Click here to enlarge figure
| The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
Share and Cite
Huang, H.; Song, D.; Wang, L.; Yang, G.; Wang, Y.; Fei, L.; Lynam, A. Enhancing Urban–Rural Integration in China: A Comparative Case Study of Introducing Small Rural Industries in Huangyan-Taizhou. Land 2024 , 13 , 946. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13070946
Huang H, Song D, Wang L, Yang G, Wang Y, Fei L, Lynam A. Enhancing Urban–Rural Integration in China: A Comparative Case Study of Introducing Small Rural Industries in Huangyan-Taizhou. Land . 2024; 13(7):946. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13070946
Huang, Huang, Daijun Song, Liyao Wang, Guiqing Yang, Yizheng Wang, Liyuan Fei, and Ava Lynam. 2024. "Enhancing Urban–Rural Integration in China: A Comparative Case Study of Introducing Small Rural Industries in Huangyan-Taizhou" Land 13, no. 7: 946. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13070946
Article Metrics
Further information, mdpi initiatives, follow mdpi.

Subscribe to receive issue release notifications and newsletters from MDPI journals
Performance and environmental sustainability studies on a dual-fuel IC engine working with producer gas of variable calorific values from rural biomass
- Recent Advances in Decarbonization Technologies for Sustainable Developments
- Published: 27 June 2024
Cite this article

- Arun Prasad Gunasekaran 1 ,
- Murugan Paradesi Chockalingam ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3166-7185 2 ,
- Joseph Sekhar Santhappan 3 ,
- Ahmed Said Ahmed Al-Shahri 3 &
- Saji Raveendran Padmavathy 1 , 4
Decentralized power generation using renewable gaseous biofuels faces challenges due to their inconsistent quality and availability. Mixing producer gas (PG) with diesel as a secondary fuel is a promising option, but the non-stable calorific value (CV) of PG from different biomasses poses a serious problem for the efficient operation of a dual-fuel engine. This study aims to examine how the CV of PG from various biomasses affects a 3.75-kW dual-fuel IC engine’s performance. The experimental facility, which has a dual-fuel engine and a 115-kW thermal gasifier, tested the blends of diesel and PG from different biomasses. We chose biomass based on its availability and PG’s CV of 3.4, 4.4, 5.2, and 6.3 MJ/Nm 3 . For this range of CV, the efficiency, energy consumption, and fuel replacement of a dual-fuel engine vary between 20.9 and 26.6%, 17.3 and 13.5 MJ/kWh, and 10.8 and 76.9%, respectively. Furthermore, the blend with the maximum CV of PG had a 69.64% lower specific diesel consumption and an 86% higher diesel replacement rate than the blend with the lowest CV of PG. In terms of emission characteristics, the comparison showed a 2.02–7.06% reduction in NO x and a 4.05–55.6% increase in hydrocarbons (HCs) for the tested conditions. The overall observations demonstrated that a significant enhancement in a dual-fuel engine’s performance is possible with a higher CV of PG. However, the emissions trade-offs demand additional optimization studies, as well as case-based research, in order to integrate renewable energy and emission management in smaller-scale applications across more geographies.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions

Data Availability
The datasets are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
Brake power (kW)
Brake specific fuel consumption
Before top dead center
Brake thermal efficiency (%)
Crank angle
Compression ignition
Coconut shell
Calorific value (MJ/Nm 3 )
Diesel mode
Diesel replacement rate (%)
Exhaust gas temperature (°C)
Hydrocarbon
Internal combustion
Oxides of nitrogen
Diesel and producer gas mixtures dual-fuel mode
- Producer gas
Rubber wood
Specific energy consumption (MJ/kWh)
Akkoli KM, Banapurmath NR, Shivashimpi MM et al (2021) Effect of injection parameters and producer gas derived from redgram stalk on the performance and emission characteristics of a diesel engine. Alex Eng J 60:3133–3142. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14185879
Article CAS Google Scholar
Alhassany HD, Abbas SM, Vera D, Jurado F (2023) Generating electricity from palm waste by gasification technique coupled with externally fired gas turbine: a case study. Energy Sources Part A Recover Util Environ Eff 45:1150–1167. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2023.2176569
Augustine MA, Sekhar SJ (2019) Improvement in the calorific value of producer gas from rice husk with addition of spent tea waste as secondary fuel. Energy Fuels 33. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.9b03052
Awais M, Omar MM, Munir A et al (2022) Co-gasification of different biomass feedstock in a pilot-scale (24 kWe) downdraft gasifier: an experimental approach. Energy 238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2021.121821
Baruah D, Kalita P, Moholkar VS (2021) A comprehensive study on utilization of producer gas as IC engine fuel. In Alternative Fuels and Advanced Combustion Techniques as Sustainable Solutions for Internal Combustion Engines. Springer Singapore, Singapore, pp 117–147
Chapter Google Scholar
Budiyono B, Matin HHA, Yasmin IY, Priogo IS (2023) Effect of pretreatment and C/N ratio in anaerobic digestion on biogas production from coffee grounds and rice husk mixtures. Int J Renew Energy Dev 12:209. https://doi.org/10.14710/ijred.2023.49298
Chen W-H, Lin B-J, Lin Y-Y et al (2021) Progress in biomass torrefaction: principles, applications and challenges. Prog Energy Combust Sci 82:100887. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pecs.2020.100887
Article Google Scholar
Chockalingam MP, Gunasekaran AP, Santhappan JS (2023) Multi-response optimization on the gasification of cocoa pod (Theobroma cacao) husk and its performance in a multi-fuel engine. Biomass Convers Biorefinery 13:10311–10326. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-022-02553-7
District statistical handbook for the Year (2022-2023) Department of Economics and Statistics, Kanyakumari District. Available in https://cdn.s3waas.gov.in/s38fe0093bb30d6f8c31474bd0764e6ac0/uploads/2024/01/2024012095.pdf
Dong Z, Bai X, Xu D, Li W (2023) Machine learning prediction of pyrolytic products of lignocellulosic biomass based on physicochemical characteristics and pyrolysis conditions. Bioresour Technol 367:128182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2022.128182
Edwin M, Sekhar SJ (2014) Hybrid thermal energy based cooling system for a remote seashore villages. Adv Mater Res 984:719–724. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.984-985.719
Ganesh R, Jaisankar S, Sheeba KN (2018) Effect of equivalence ratio on gasification of granular biomaterials in self circulating fluidised bed gasifier. Int J Environ Sustain Dev 17:193–201. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJESD.2018.094025
Ghodke PK, Sharma AK, Jayaseelan A, Gopinath KP (2023) Hydrogen-rich syngas production from the lignocellulosic biomass by catalytic gasification: a state of art review on advance technologies, economic challenges, and future prospectus. Fuel 342:127800. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2023.127800
Gopal K, Sathiyagnanam AP, Kumar BR et al (2020) Prediction and optimization of engine characteristics of a DI diesel engine fueled with cyclohexanol/diesel blends. Energy Sources Part A Recover Util Environ Eff 42:2006–2017. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2019.1607923
Hadkar T, Amarnath HK (2015) Performance and emission characteristics of producer gas derived from coconut shell (biomass) and honne biodiesel with different configuration of carburetor for dual fuel four stoke direct injection diesel engine. Int Res J Eng Technol 2:1804–1811
Google Scholar
Justus AR, Justus ER (2023) Overview of the rubber plantations in Kanyakumari District with special reference to rubberwood industry. J Trop Agric 61:78–90
Kashyap D, Das S, Kalita P (2021) Exploring the efficiency and pollutant emission of a dual fuel CI engine using biodiesel and producer gas: an optimization approach using response surface methodology. Sci Total Environ 773:145633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145633
Kohli S, Ravi MR (2003) Biomass gasification for rural electrification: prospects and challenges. SESI J 13:83–101
Korczewski Z (2022) Energy and emission quality ranking of newly produced low-sulphur marine fuels. Polish Marit Res 29:77–87. https://doi.org/10.2478/pomr-2022-0045
Kumar D, Narayan L (2021) International Journal of Research Publication and Reviews. Int J Res Publ Rev 2:386–392. https://doi.org/10.55248/gengpi.2023.4149
Lal S, Mohapatra SK (2017) The effect of compression ratio on the performance and emission characteristics of a dual fuel diesel engine using biomass derived producer gas. Appl Therm Eng 119:63–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.03.038
Martínez JD, Mahkamov K, Andrade RV, Lora EES (2012) Syngas production in downdraft biomass gasifiers and its application using internal combustion engines. Renew Energy 38:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2011.07.035
McKendry P (2002) Energy production from biomass (part 3): gasification technologies. Bioresour Technol 83:55–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(01)00120-1
Meydani A, Meidani A, Shahablavasani S (2023) Clean energy’s role in power plant development. In: 2023 8th International Conference on Technology and Energy Management (ICTEM). IEEE, pp 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICTEM56862.2023.10084297
Murugan PC, Joseph Sekhar S (2017a) Species – transport CFD model for the gasification of rice husk (Oryza Sativa) using downdraft gasifier. Comput Electron Agric 139:33–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2017.05.004
Murugan PC, Joseph Sekhar S (2017b) Numerical simulation of imbert biomass gasifier to select the feedstock available in remote areas. Environ Prog Sustain Energy 36:708–716. https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.12485
Murugan PC, Sekhar SJ (2017) Numerical studies to predict the impact of air nozzle position and inclination on the performance of downdraft gratifier. J Appl Fluid Mech 10:947–955. https://doi.org/10.18869/acadpub.jafm.73.240.26446
Nanjappan B, Kavandappa GM, Natarajan N (2015) Experimental investigation of evaporation rate and emission studies of diesel engine fuelled with blends of used vegetable oil biodiesel and producer gas. Therm Sci 19:1967–1975. https://doi.org/10.2298/TSCI150604106B
Nayak C, Sahoo SS, Rout LN (2021) Emission analysis of a dual fuel diesel engine fuelled with different gaseous fuels generated from waste biomass. Int J Ambient Energy 42:570–575. https://doi.org/10.1080/01430750.2018.1562971
Nema VK, Singh A, Chaurasiya PK et al (2023) Combustion, performance, and emission behavior of a CI engine fueled with different biodiesels: a modelling, forecasting and experimental study. Fuel 339:126976. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2022.126976
Papagiannakis RG, Hountalas DT (2003) Experimental investigation concerning the effect of natural gas percentage on performance and emissions of a DI dual fuel diesel engine. Appl Therm Eng 23:353–365. https://doi.org/10.4271/2007-01-1450
Pathak BS, Bining AS, Jain AK (1985) Final report of the project, energy in agriculture and first report of the school of energy studies for agriculture. Punjab Agricultural University, Ludhiana
Paykani A, Chehrmonavari H, Tsolakis A et al (2022) Synthesis gas as a fuel for internal combustion engines in transportation. Prog Energy Combust Sci 90:100995. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pecs.2022.100995
Prasad GA, Murugan PC, Wincy WB, Sekhar SJ (2021) Response surface methodology to predict the performance and emission characteristics of gas-diesel engine working on producer gases of non-uniform calorific values. Energy 234:121225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2021.121225
Purohit P (2009) Economic potential of biomass gasification projects under clean development mechanism in India. J Clean Prod 17:181–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2008.04.004
Rajak U, Singh TS, Verma TN et al (2022) Experimental and parametric studies on the effect of waste cooking oil methyl ester with diesel fuel in compression ignition engine. Sustain Energy Technol Assessments 53:102705. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seta.2022.102705
Ramadhas AS, Jayaraj S, Muraleedharan C (2006) Power generation using coir-pith and wood derived producer gas in diesel engines. Fuel Process Technol 87:849–853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2005.06.003
Ramadhas AS, Jayaraj S, Muraleedharan C (2008) Dual fuel mode operation in diesel engines using renewable fuels: rubber seed oil and coir-pith producer gas. Renew Energy 33:2077–2083. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2007.11.013
Rith M, Biona MM, Bienvenido J (2021) Development of mathematical models for engine performance and emissions of the producer gas-diesel dual fuel mode using response surface methodology. Eng Appl Sci Res 48. https://doi.org/10.14456/easr.2021.3
Roy PC, Datta A, Chakraborty N (2013) An assessment of different biomass feedstocks in a downdraft gasifier for engine application. Fuel 106:864–868. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2012.12.053
Salih AM, Raheem MM (2014) Effect of the magnetic field on the fuel consumption of a spark ignition engine. Eng Technol J 32. https://doi.org/10.30684/etj.32.11a.13
Sateesh KA, Yaliwal VS, Banapurmath NR et al (2023) Effect of MWCNTs nano-additive on a dual-fuel engine characteristics utilizing dairy scum oil methyl ester and producer gas. Case Stud Therm Eng 42:102661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csite.2022.102661
Sharma M, Kaushal R (2020) Performance and emission analysis of a dual fuel variable compression ratio (VCR) CI engine utilizing producer gas derived from walnut shells. Energy 192:116725
Sharma M, Kaushal R (2021) Performance and exhaust emission analysis of a variable compression ratio (VCR) dual fuel CI engine fuelled with producer gas generated from pistachio shells. Fuel 283:118924. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2020.118924
Shrivastava V, Jha AK, Wamankar AK, Murugan S (2013) Performance and emission studies of a CI engine coupled with gasifier running in dual fuel mode. Procedia Eng 51:600–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2013.01.085
Singh H, Mohapatra SK (2018) Production of producer gas from sugarcane bagasse and carpentry waste and its sustainable use in a dual fuel CI engine: a performance, emission, and noise investigation. J Energy Inst 91:43–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joei.2016.11.002
Singh VCJ, Sekhar SJ (2016) Performance studies on a downdraft biomass gasifier with blends of coconut shell and rubber seed shell as feedstock. Appl Therm Eng 97:22–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2015.09.099
Singh RN, Singh SP, Pathak BS (2005) Emission characteristics of a naturally aspirated multi-cylinder diesel engine with multi fuel. Int Energy J 5:69–80
Singh J, Singh S, Mohapatra SK (2020) Production of syngas from agricultural residue as a renewable fuel and its sustainable use in dual-fuel compression ignition engine to investigate performance, emission, and noise characteristics. Energy Sources Part A Recover Util Environ Eff 42:41–55. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2019.1587053
Suresh G, Kamath HC, Banapurmath NR (2014) Effects of injection timing, injector opening pressure and nozzle geometry on the performance of cottonseed oil methyl ester-fuelled diesel engine. Int J Sustain Eng 7:82–92. https://doi.org/10.1080/19397038.2013.811703
Uma R, Kandpal TC, Kishore VVN (2004) Emission characteristics of an electricity generation system in diesel alone and dual fuel modes. Biomass Bioenerg 27:195–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2004.01.003
Venkatesh G, Reddy PR, Kotari S (2017) Generation of producer gas using coconut shells and sugar cane bagasse in updraft gasifier. Mater Today Proc 4:9203–9209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2017.07.278
Viswanathan K, Paulraj A (2023) A comprehensive study on the performance and emission characteristics of a diesel engine with the blends of diesel, jojoba oil biodiesel, and butylated hydroxyl anisole as an alternative fuel. Energy Sources Part A Recover Util Environ Eff 45:3216–3230. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2020.1849451
Wang L, Weller CL, Jones DD, Hanna MA (2008) Contemporary issues in thermal gasification of biomass and its application to electricity and fuel production. Biomass Bioenerg 32:573–581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2007.12.007
Woltz VL, Stagg CL, Byrd KB et al (2023) Above-and belowground biomass carbon stock and net primary productivity maps for tidal herbaceous marshes of the United States. Remote Sens 15:1697. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15061697
Yaliwal VS, Banapurmath NR, Tewari PG (2014) Performance, combustion and emission characteristics of a single-cylinder, four-stroke, direct injection diesel engine operated on a dual-fuel mode using Honge oil methyl ester and producer gas derived from biomass feedstock of different origin. Int J Sustain Eng 7:253–268. https://doi.org/10.1080/19397038.2013.834395
Zhang Y, Salem M, Elmasry Y et al (2022) Triple-objective optimization and electrochemical/technical/environmental study of biomass gasification process for a novel high-temperature fuel cell/electrolyzer/desalination scheme. Renew Energy 201:379–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2022.10.059
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Kongu Engineering College, Erode, India
Arun Prasad Gunasekaran & Saji Raveendran Padmavathy
Department of Automobile Engineering, Kongu Engineering College, Erode, India
Murugan Paradesi Chockalingam
Department of Engineering, College of Engineering and Technology, University of Technology and Applied Sciences, Musandam, Oman
Joseph Sekhar Santhappan & Ahmed Said Ahmed Al-Shahri
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Builders Engineering College, Kangayam, Tirupur, Tamil Nadu, India
Saji Raveendran Padmavathy
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
G. Arun Prasad: investigation, formal analysis, and roles/writing—original draft. P. C. Murugan: conceptualization, investigation, methodology, and data curation. Joseph Sekhar Santhappan: supervision, validation, and writing—review and editing. Ahmed Said Ahmed Al-Shahri: formal analysis and review and editing. P. Saji Raveendran: formal analysis and data curation.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Murugan Paradesi Chockalingam .
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval.
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Consent for publication, competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Gunasekaran, A.P., Chockalingam, M.P., Santhappan, J.S. et al. Performance and environmental sustainability studies on a dual-fuel IC engine working with producer gas of variable calorific values from rural biomass. Environ Sci Pollut Res (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-34029-8
Download citation
Received : 08 September 2023
Accepted : 14 June 2024
Published : 27 June 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-34029-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Calorific value
- Diesel replacement
- Engine emissions
- Specific fuel consumption
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Case Report
- Open access
- Published: 22 June 2024
Right-sided ureteral hemangiosarcoma in a paraplegic dog
- Suellen Rodrigues Maia 1 ,
- Mayara Manochio 2 ,
- Lara Vilela Soares 3 ,
- Yury Carantino Costa Andrade 3 ,
- Alef Winter Oliveira Alvarenga 3 , 4 &
- Leandro Zuccolotto Crivellenti 3
BMC Veterinary Research volume 20 , Article number: 271 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
190 Accesses
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
This study aims to describe a rare case of primary ureteral hemangiosarcoma, in which surgical intervention preserved the kidney and ureter after tumor removal.
Case presentation
A 13-year-old, neutered male dog, weighing 14 kg, mixed-breed, presented with apathy, anorexia, acute-onset vomiting, and abdominal discomfort during the physical examination. Ultrasonography and pyelography revealed a right-sided dilation of the renal pelvis and ureter due to complete obstruction in the middle third of the ureter. A mass obstructing the lumen of the right ureter was completely resected, and ureteral suturing was performed, preserving the integrity of the involved structures. Histopathology confirmed primary ureteral hemangiosarcoma. Due to the local and non-invasive nature of the mass, chemotherapy was not initiated. The patient’s survival was approximately two years, and normal renal function was preserved throughout this period.
Conclusions
Considering this type of tumor in the differential diagnosis of upper urinary tract obstructive disorders. Furthermore, the preservation of the ureter and kidney is a suitable therapeutic option after surgical resection of non-invasive tumors.
Peer Review reports
Hemangiosarcoma is a rapidly growing and aggressive malignant neoplasm, demonstrating significant metastatic potential due to its vascular association [ 1 ]. In dogs, the primary site of development is typically the spleen, followed by other locations such as subcutaneous tissue, dermis, liver, and right atrium [ 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 ]. Less common sites include the retroperitoneum, reproductive system, lung, and urinary system [ 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 ].
Primary neoplasms in the ureteral region are rare in dogs, and most often benign, including fibropapillomas, fibroepithelial polyps, and transitional cell papillomas [ 10 , 11 , 12 ]. Limited reports in dogs describe the occurrence of malignant neoplasms in this region, such as leiomyosarcomas [ 13 , 14 ] and transitional cell carcinomas [ 15 ]. Even more rarely, only two cases of ureteral hemangiosarcoma have been reported to date [ 16 , 17 ]. Given the rarity of this presentation, this report aims to provide detailed insights into the occurrence of ureteral hemangiosarcoma in an elderly dog, encompassing clinical and pathological manifestations, surgical treatment, diagnosis, and survival. This contributes evidence to the literature, emphasizing the importance of considering this type of tumor in the differential diagnosis of upper urinary tract disorders. To the best of our knowledge, this is the third reported case of primary ureteral hemangiosarcoma and the first to preserve the ureter and kidney without subsequent recurrence.
Case report
A male mixed-breed dog, 13 years old, weighing 14 kg, neutered, with a history of paraplegia due to an old traumatic injury (occurring when the animal was a puppy), presented with acute onset apathy, hematuria, anorexia, and vomiting. Due to the animal’s neurological condition, the dog’s urination history involved the need for manual bladder compressions throughout the day to achieve minimally acceptable bladder emptying, performed by its owner since the onset of its paraplegic condition. The patient also had a history of recurrent urinary tract infections due to chronic neurological bladder dysfunction. Pronounced abdominal discomfort was noted upon physical examination. Laboratory findings revealed mild azotemia in the serum biochemistry (urea 84 mg/dL and creatinine 2.0 mg/dL), with no other abnormalities in either biochemical analyses or the complete blood count.
Ultrasonographic examination disclosed hydronephrosis in the right kidney and hydroureter extending to the middle third, originating from a likely point of obstruction; however, the reason possibly associated with the obstruction was not determined by this evaluation. A pyelogram was performed to delineate the involved structures and precisely identify the obstructive site for surgical planning. The contrast examination consisted of the percutaneous administration of iodinated contrast, at a dose of 600 mg/kg, directly into the right renal pelvis with the assistance of ultrasound (the volume of contrast applied was equivalent to the volume removed by pyelocentesis). This confirmed a complete obstruction in the middle third of the right ureter, with no contrast progression beyond the identified point (Fig. 1 ).

Ultrasound-guided percutaneous anterograde pyelography, in lateral ( A ) and ventrodorsal ( B ) projections. Radiographs were obtained immediately after injection of iodinated contrast, noting dilation of the right renal pelvis and ureter, obstruction of the contrast column in the middle third of the right ureter, as well as deviation of the bony axis of the lumbar spine, luxation of L3-L4, L5-L6, bone remodeling of L6 and articular processes of L3 and L4, due to a history of old trauma. Radiographic images were obtained after the administration of iodinated contrast at a dose of 600 mg/kg
After laparotomy, the right ureter was identified, isolating the previously revealed obstruction point from the imaging examination (Fig. 2 A). A longitudinal incision was made at the affected site, revealing tissue content causing obliteration of the ureteral lumen (Fig. 2 B). The mass was fully exposed, demonstrating weak adhesion to the ventral wall of the ureter only in a small portion (approximately 0.5 mm) (Fig. 2 C), and subsequently easily resected and removed from the ureteral lumen, along with the small portion of the involved ureter (Fig. 2 D). The absence of neoformations in other regions of the urinary tract, as well as in abdominal organs, suggested a possible primary ureteral neoplasm. The ureteral incision was sutured using simple interrupted sutures with absorbable suture (poliglecaprone 25, 6 − 0), preserving the patient’s upper urinary tract, followed by routine closure of the abdominal cavity. The surgery was completed in 1 h and 40 min.
There were no complications during the surgical/anesthetic procedure, and the animal was discharged with follow-up care.

Surgical Procedure. A ) Identification of the affected ureter and isolation of the obstruction site (region between the surgeon’s fingers). B ) Longitudinal incision of the ureter and appearance of the tissue obliterating the lumen. C ) Dissection and exposure of the mass within the ureter lumen. D ) Final appearance of the mass after complete removal. Only one mass was found and removed (fragmentation of the mass occurred after its manipulation)
The histopathological examination of the mass confirmed the neoplastic nature of the removed tissue (Fig. 3 ), revealing a neoplastic proliferation composed of endothelial cells, mimicking disorganized vascular formations. Elongated cells with pleomorphic nuclei and prominent nucleoli, mild mitotic activity, and extensive areas of necrosis and hemorrhage were observed upon evaluation. On the surface of the mass, well-differentiated urothelial epithelium composed of 3 to 6 layers of cells was present. Based on these characteristics, the final diagnosis was consistent with ureteral hemangiosarcoma.

Histopathological Findings. A ) Fragment lined by well-differentiated urothelial epithelium (EP). Submucosa (SM) with diffuse malignant mesenchymal neoplasia. Hematoxylin and Eosin (HE) staining. Magnification 200x. B ) Neoplastic cells with solid and diffuse organization. HE staining. Magnification 400x. C ) Mitotic figure, cell in metaphase (arrow). HE staining. Magnification 1,000x. D ) Malignant mesenchymal proliferation with the formation of irregular vascular spaces filled with erythrocytes. Neoplastic cells exhibit pleomorphic nuclei with vesicular appearance and prominent nucleoli. Mitotic figure, cells in prophase (arrow). HE staining. Magnification 1,000x
Following the diagnosis, thoracic radiographs were obtained, along with postoperative ultrasound monitoring, which did not reveal any changes consistent with metastases. Four months post-surgical procedure, the animal exhibited overall well-being, alertness, normal eating habits, and its usual behavior. There was complete reversal of hydronephrosis and hydroureter on ultrasound, and serum biochemistry assessment revealed a return of urea and creatinine levels to within the reference range (44 mg/dL and 0.6 mg/dL, respectively). The animal demonstrated a survival period of two years, maintaining a good quality of life and overall well-being. However, due to an acute and severe presentation of respiratory alterations apparently unrelated to metastases (thoracic radiographs did not show any changes that justified the clinical presentation), the patient deteriorated despite supportive treatment. Consequently, euthanasia was chosen by the owner.
Discussion and conclusions
Hemangiosarcoma is a malignant mesenchymal neoplasm that can be classified into visceral and non-visceral types based on its location [ 18 ]. Primary occurrence of this type of tumor in the canine ureter is rare [ 16 , 17 ], as are other types of tumors in this region [ 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 ]. In dogs, only two reports describe primary ureteral hemangiosarcoma [ 16 , 17 ]. In one of the cases, metastases developed shortly after tumor resection [ 16 ], differing from the presentation reported here. However, it is important to highlight that due to the acute worsening and respiratory evolution presented by the dog in this report, the possibility of pulmonary thromboembolism, together with metastases that may not have been radiographically identifiable, cannot be ruled out. In any case, despite being a highly metastatic tumor, the timing of metastatic presentations can be variable, as indicated by this and other cases described.
In contrast to previously reported cases [ 16 , 17 ], the affected dog in this report was male but was of a similar age range. Considering the overall occurrence of visceral hemangiosarcoma in dogs, those over 10 years old are generally more affected [ 21 ], aligning with the occurrence of primary ureteral hemangiosarcoma in this case.
The clinical signs presented in this report, including abdominal pain upon palpation, apathy, hematuria, anorexia, and vomiting, although nonspecific, resemble cases of malignant ureteral tumors previously reported, such as leiomyosarcoma [ 14 ], sarcoma [ 22 ], and urothelial carcinoma [ 23 ]. Renal dysfunction secondary to the condition or increased pressure in the renal capsule due to hydronephrosis may explain the observed clinical signs, as well as the presence of the tumor itself, considering that signs usually associated with visceral hemangiosarcoma are also vague and nonspecific [ 1 ]. It’s is noteworthy that specific signs of urinary tract involvement, such as hematuria, might not necessarily be present, as observed in the case described by Polit et al. [ 17 ].
The prolonged duration of paraplegia and recurrent urinary tract infections observed in the canine patient described here prompts discussion regarding the possibility of a relationship between these comorbidities and neoplastic condition. Although such presentations are not commonly described in veterinary literature, human studies have investigated the link between urinary tract neoplasms, particularly involving the bladder, in patients with spinal cord injuries [ 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 ]. The main risk factors in these cases include chronic urinary drainage using catheters, recurrent urinary infections, and a history of urolithiasis [ 28 , 29 ]. While definitive cause-and-effect relationships cannot be presumed, it is important to consider that paraplegic patients who are chronically managed to maintain urinary flow require increased attention to the occurrence of tumors involving the urinary tract.
In this report, ultrasonographic and contrast radiographic images revealed hydronephrosis and hydroureter affecting the right kidney and ureter, respectively, confirming complete ureteral obstruction in the middle third. This finding differs in location from previous case reports of the same tumor, which indicated tumors in the distal ureter [ 17 ] and proximal ureter [ 16 ]. According to literature on dogs, the location of the tumor along the ureteral length can be related to the malignancy of the neoplasm, with distal tumors generally being malignant, while proximal tumors tend to be benign [ 17 , 22 , 30 ]. However, although information regarding the location of the ureteral tumor and its malignancy is described, due to the lack of existing evidence, it is not possible to attribute characteristics of malignancy based on tumor location at this time. Just as described here and corroborating with Troiano and Zarelli [ 16 ], the occurrence of primary ureteral hemangiosarcoma can affect any portion of the ureteral extension.
According to literature on dogs, the location of the tumor along the ureteral length can be related to the malignancy of the neoplasm, with distal tumors generally being malignant, while proximal tumors tend to be benign [ 17 , 22 , 30 ].
However, as described here and corroborating with Troiano and Zarelli [ 16 ], the occurrence of primary ureteral hemangiosarcoma does not adhere strictly to this premise, revealing that any portion of the ureteral extension can be subject to this type of tumor.
Furthermore, this report differs from two others involving the same type of tumor [ 16 , 17 ] due to its non-invasive local nature, being easily resectable from the ureter and not presenting significant adhesions. This allowed for the preservation of the affected kidney and ureter. The two dogs affected by ureteral hemangiosarcoma previously described had radical surgical approaches as the treatment of choice. In one case, left nephrectomy and ureterectomy were performed, while in the other, left ureteronephrectomy, partial cystectomy were performed [ 16 , 17 ]. While many factors are involved in the surgical planning for each specific case, the majority of reports involving ureteral neoplasms in dogs resulted in ureterectomy and nephrectomy [ 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 , 22 , 23 ], making this the first account in which these noble structures were preserved.
It is essential to emphasize that preserving nephrons should always be the central goal of any surgical therapeutic approach to the urinary tract. This is because, despite imaging changes, it is not possible to estimate the residual functionality of the affected organ. The patient in this report was azotemic before the surgical procedure, indicating that the compensatory capacity of the contralateral kidney was also impaired. The return of urea and creatinine values for this patient to species reference ranges after the procedure reflects the impact on the functional reserve of the previously affected kidney. Similarly, in humans, although upper urinary tract tumors are also rare [ 31 , 32 , 33 ], it was reported that malignant ureteral tumors can be cured by local resection [ 34 , 35 , 36 ].
Adding to previously published data [ 16 , 17 ], where a survival of 40 days and a follow-up of 120 days were reported, the two-year survival along with the quality of life of the dog in this report demonstrates the variety of possible outcomes for this type of presentation. Due to the rarity of primary ureteral hemangiosarcoma in dogs, prognostic information is scarce and precludes any determinations regarding our results or predictions of outcomes.
Based on the data described here, it emphasizes the importance of including primary ureteral hemangiosarcoma in the differential diagnoses of obstructive conditions in the ureter of dogs, whether are associated with clinical signs of the urinary tract or metastases or not.
A possible association in dogs with spinal cord injuries is unclear. Preservation of affected urinary tract structures should be prioritized, especially when possible contralateral renal dysfunction is ongoing. Prognoses cannot yet be definitively determined due to the rarity of this tumor type.
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
Abbreviations
Hematoxylin and Eosin
Mullin C, Clifford CA. Histiocytic Sarcoma and Hemangiosarcoma Update. Veterinary Clin North America: Small Anim Pract. 2019;49(5):855–79.
Article Google Scholar
Griffin MA, Culp WTN, Rebhun RB. Canine and feline haemangiosarcoma. Vet Rec. 2021;189(9):585.
Ward H, Fox LE, Calderwood-Mays MB, Hammer AS, Couto CG. Cutaneous hemangiosarcoma in 25 dogs: a retrospective study. J Vet Intern Med. 1994;8(5):345–8.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Ware WA, Hopper DL. Cardiac tumors in dogs: 1982–1995. J Vet Intern Med. 1999;13(2):95–103.
Mullin C, Clifford CA. Miscellaneous tumours: Hemangiosarcoma. In: Withrow SJ, Vail DM, Pag RL, editors. Withrow and MacEwen’s Small Animal Clinical Oncology. 5th ed. St. Louis, MO, USA: Elsevier Saunders; 2020. pp. 773–8.
Google Scholar
Liptak JM, Dernell WS, Ehrhart EJ, Rizzo SA, Rooney MB, Withrow SJ. Retroperitoneal sarcomas in dogs: 14 cases (1992– 2002). J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2004;224(9):1471–7.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Liptak J, Dernell W, Withrow S. Haemangiosarcoma of the urinary bladder in a dog. Aust Vet J. 2004;82(4):215–7.
Townsend S, Regier PJ, More SN. Successful treatment of urinary bladder hemangiosarcoma by partial cystectomy in a dog. J Am Anim Hosp Assoc. 2020;56(4):231–5.
Meuten DJ, Meuten TLK. Tumors of the urinary system. In: Meuten DJ, editor. Tumors in domestic animals. Hoboken, New Jersey: Wiley-Blackwell; 2016. pp. 632–88.
Chapter Google Scholar
Hattel AL, Diters RW, Snavely DA. Ureteral fibropapilloma in a dog. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1986;188(8):873.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Matsumura K, Hosokawa A, Itoh D, Chino J, Sugita Y. Unilateral ureteral obstruction caused by Transitional Cell Papilloma in a dog. J Japan Veterinary Med Association. 2020;73(8):457–61.
Etzioni AL, Raskin RE, Van Alstine WG, Yu J. The cytologic and histologic diagnosis of ureteral fibroepithelial polyp in a dog. Vet Clin Pathol. 2020;49:646–51.
Berzon JL. Primary leiomyosarcoma of the ureter in a dog. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1979;175:374–6.
Yap F, Huizing X, Rasotto R, Bowlt-Blacklock K. Primary ureteral leiomyosarcoma in a dog. Aust Vet J. 2017;95:68–71.
Hanika C, Rebar AH. Ureteral Transitional Cell Carcinoma in the dog. Vet Pathol. 1980;17(5):643–6.
Troiano D, Zarelli M. Multimodality imaging of primary ureteral hemangiosarcoma with thoracic metastasis in an adult dog. Vet Radiol Ultrasound. 2019;60(4):38–41.
Polit JA, Moore EV, Epperson E. Primary Ureteral Hemangiosarcoma in a dog. BMC Vet Res. 2020;16:386.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
De Nardi AB, de Gomes OMS, Fonseca-Alves C, de Paiva CE, Linhares FN, Carra LCM, Cancers, et al. (Basel). 2023;15(7):2025.
Rigas JD, Smith TJ, Elena Gorman M, Valentine BA, Simpson JM, Seguin B. Primary ureteral giant cell sarcoma in a Pomeranian. Vet Clin Pathol. 2021;41:141–6.
Guilherme S, Polton G, Bray J, Blunden A, Corzo N. Ureteral spindle cell sarcoma in a dog. J Small Anim Pract. 2007;48:702–4.
Schultheiss PC. A retrospective study of visceral and nonvisceral hemangiosarcoma and hemangiomas in domestic animals. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2004;16(6):522–6.
Deschamps JY, Roux FA, Fantinato M, Albaric O. Ureteral sarcoma in a dog. J Small Anim Pract. 2007;48(12):699–701.
Kim MY, Aerin J, Traslavina RP, Yoon HY. Orthotopic ureterocele with concurrent ureteral urothelial carcinoma in a dog. Vet Med Sci. 2022;8(5):1881–6.
Pannek J. Transitional cell carcinoma in patients with spinal cord injury: a high risk malignancy? Urology. 2002;59(2):240–4.
Gui-Zhong L, Li-Bo M. Bladder cancer in individuals with spinal cord injuries: a meta-analysis. Spinal Cord. 2017;55(4):341–5.
Böthig R, Kurze I, Fiebag K, Kaufmann A, Schöps W, Kadhum T, et al. Clinical characteristics of bladder cancer in patients with spinal cord injury: the experience from a single centre. Int Urol Nephrol. 2017;49:983–94.
Böthig R, Tiburtius C, Schöps W, Zellner M, Balzer O, Kowald B, et al. Urinary bladder cancer as a late sequela of traumatic spinal cord injury. Mil Med Res. 2021;8(1):29.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Stonehill WH, Dmochowski RR, Patterson AL, Cox CE. Risk factors for bladder tumors in spinal cord injury patients. J Urol. 1996;155(4):1248–50.
West DA, Cummings JM, Longo WE, Virgo KS, Johnson FE, Parra RO. Role of chronic catheterization in the development of bladder cancer in patients with spinal cord injury. Urology. 1999;53(2):292–7.
Reichle JK, Peterson RA, Mahaffey MB, Schelling CG, Barthez PY. Ureteral fibroepithelial polyps in four dogs. Vet Radiol Ultrasound. 2003;44(4):433–7.
Morinaga S, Aoki S, Tobiume M, Nishikawa G, Muramatsu H, Tsuzuki T, et al. Primary leiomyoma of the ureter: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2021;15(1):423.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Wen S-C, Shen J-T, Jang M-Y, Tsai K-B, Chang S-F, Tsai L-J, et al. Lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma of ureter—A rare case report and review of the literature. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2023;28:509–13.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Aboutaleb HA, Khurana P, El-Shahat YM. Primary leiomyosarcoma of the middle ureter: a rare case report with literature review. Clin Case Rep. 2022;10(2):e05409.
Bin X, Roy OP, Ghiraldi E, Manglik N, Liang T, Vira M, et al. Impact of tumour location and surgical approach on recurrence-free and cancer-specific survival analysis in patients with ureteric tumours. BJU Int. 2012;110:514–9.
Yuan P, Li X, Yuan Y, Xu P, Wang H. Successful kidney-sparing systemic therapy for a high-risk Ureteral Carcinoma Case. Urol Int. 2023;107(9):895–8.
Jia Z, Gong YQ, Zhang CJ, Bao ZQ, Li XS, Hao H, et al. Segmental ureterectomy can be performed safely in patients with urothelial carcinoma of distal ureter. Can Urol Assoc J. 2019;13(7):202–9.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Vanessa Martins Fayad Milken for providing the radiographic description for one of the images in this study. Her expertise and attention to detail enhanced the quality of our research.
No external funding was secured for this case report.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Veterinary Medicine and Animal Science (FMVZ), Universidade Estadual Paulista (UNESP), Botucatu, São Paulo, Brazil
Suellen Rodrigues Maia
Self-employed veterinarian, Franca, São Paulo, Brazil
Mayara Manochio
Graduate Program in Veterinary Science (PPGCV), College of Veterinary Medicine (FAMEV), Universidade Federal de Uberlândia (UFU), Uberlândia, Minas Gerais, Brazil
Lara Vilela Soares, Yury Carantino Costa Andrade, Alef Winter Oliveira Alvarenga & Leandro Zuccolotto Crivellenti
Unidade Integrada de Veterinária (UNIVET), Ribeirão Preto, São Paulo, Brazil
Alef Winter Oliveira Alvarenga
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
SM conceived, designed, acquired data, and was involved in the writing, review, and editing of the work. MM performed the conceptualization and the acquisition of the work. LS performed the design, writing and the review of the work. YA performed the writing and the review of the work. AA performed the writing and the review of the work. LC performed the conceptualization, design, acquisition, writing, review and editing of the work. Furthermore, the approval of the submission.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Suellen Rodrigues Maia .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Maia, S.R., Manochio, M., Soares, L.V. et al. Right-sided ureteral hemangiosarcoma in a paraplegic dog. BMC Vet Res 20 , 271 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12917-024-04114-8
Download citation
Received : 06 December 2023
Accepted : 05 June 2024
Published : 22 June 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12917-024-04114-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Ureteral obstruction
- Pyelography
- Hydronephrosis
- Ureteral neoplasia
BMC Veterinary Research
ISSN: 1746-6148
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Case studies are effective research methods that focus on one specific case over time. This gives a detailed view that's great for learning. Writing a case study is a very useful form of study in the educational process. With real-life examples, students can learn more effectively.
The purpose of case study research is twofold: (1) to provide descriptive information and (2) to suggest theoretical relevance. Rich description enables an in-depth or sharpened understanding of the case. It is unique given one characteristic: case studies draw from more than one data source. Case studies are inherently multimodal or mixed ...
A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth examination and analysis of a particular phenomenon or case, such as an individual, organization, community, event, or situation. It is a qualitative research approach that aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the case being studied.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are sometimes also used.
What is a case study? Whereas quantitative methods look at phenomena at scale, case study research looks at a concept or phenomenon in considerable detail. While analyzing a single case can help understand one perspective regarding the object of research inquiry, analyzing multiple cases can help obtain a more holistic sense of the topic or issue.
A case study is a research process aimed at learning about a subject, an event or an organization. Case studies are use in business, the social sciences and healthcare. A case study may focus on one observation or many. It can also examine a series of events or a single case. An effective case study tells a story and provides a conclusion.
A case study is one of the most commonly used methodologies of social research. This article attempts to look into the various dimensions of a case study research strategy, the different epistemological strands which determine the particular case study type and approach adopted in the field, discusses the factors which can enhance the effectiveness of a case study research, and the debate ...
1. Select a case. Once you identify the problem at hand and come up with questions, identify the case you will focus on. The study can provide insights into the subject at hand, challenge existing assumptions, propose a course of action, and/or open up new areas for further research. 2.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organisation, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are sometimes also used.
Researchers, economists, and others frequently use case studies to answer questions across a wide spectrum of disciplines, from analyzing decades of climate data for conservation efforts to developing new theoretical frameworks in psychology. Learn about the different types of case studies, their benefits, and examples of successful case studies.
A Case study is: An in-depth research design that primarily uses a qualitative methodology but sometimes includes quantitative methodology. Used to examine an identifiable problem confirmed through research. Used to investigate an individual, group of people, organization, or event. Used to mostly answer "how" and "why" questions.
Although case studies have been discussed extensively in the literature, little has been written about the specific steps one may use to conduct case study research effectively (Gagnon, 2010; Hancock & Algozzine, 2016).Baskarada (2014) also emphasized the need to have a succinct guideline that can be practically followed as it is actually tough to execute a case study well in practice.
A case study is an in-depth study of one person, group, or event. In a case study, nearly every aspect of the subject's life and history is analyzed to seek patterns and causes of behavior. Case studies can be used in many different fields, including psychology, medicine, education, anthropology, political science, and social work.
This article examines six types of case studies, the type of evaluation questions that can be answered, the functions served, some design features, and some pitfalls of the method. Deutch, C. E. (1996). A course in research ethics for graduate students. College Teaching, 44, 2, 56-60.
Case studies are in-depth investigations of a person, group, event, or community. Typically, data is gathered from various sources using several methods (e.g., observations & interviews). The case study research method originated in clinical medicine (the case history, i.e., the patient's personal history). In psychology, case studies are ...
A case study is a type of research method. In case studies, the unit of analysis is a case. The case typically provides a detailed account of a situation that usually focuses on a conflict or complexity that one might encounter in the workplace. Case studies help explain the process by which a unit (a person, department, ...
A case study is a research approach that is used to generate an in-depth, multi-faceted understanding of a complex issue in its real-life context. It is an established research design that is used extensively in a wide variety of disciplines, particularly in the social sciences. A case study can be defined in a variety of ways (Table.
A study protocol should be written and complete documentation of the study's process should also be done. This is vital in order for other scientists to be able to reproduce and check the results afterwards. The main types of studies are randomized controlled trials (RCTs), cohort studies, case-control studies and qualitative studies.
Case Studies. Case studies are a popular research method in business area. Case studies aim to analyze specific issues within the boundaries of a specific environment, situation or organization. According to its design, case studies in business research can be divided into three categories: explanatory, descriptive and exploratory.
According to the book Understanding Case Study Research, case studies are "small scale research with meaning" that generally involve the following: The study of a particular case, or a number of cases. That the case will be complex and bounded. That it will be studied in its context. That the analysis undertaken will seek to be holistic.
Types of Research Designs Compared | Guide & Examples. Published on June 20, 2019 by Shona McCombes.Revised on June 22, 2023. When you start planning a research project, developing research questions and creating a research design, you will have to make various decisions about the type of research you want to do.. There are many ways to categorize different types of research.
A type of Case study is a type of research method that involves an in-depth and detailed analysis of a particular phenomenon or situation. Generally, case studies gain insights into complex issues or problems that cannot be adequately explained through quantitative data alone. They are particularly useful for exploring cause-and-effect ...
An exploratory case study is a very specific type of material that has the aim of encompassing a set of data as an initial research attempt for the purpose of identifying possible patterns. Such patterns, if any exist, can help create a model based on the data and then extrapolate it for further analysis, application, or research.
Here are six common types of research studies, along with examples that help explain the advantages and disadvantages of each: 1. Meta-analysis. A meta-analysis study helps researchers compile the quantitative data available from previous studies. It's an observational study in which the researchers don't manipulate variables.
11. Case Study Research. Case study research involves an in-depth, detailed examination of a single subject, group, or event. It provides a comprehensive understanding of the case being studied. Example: Analyzing the business strategies of a successful startup to understand the factors contributing to its success. 12. Action Research
In this paper, we put these considerations into practice by providing a transparent account of our qualitative study design. The methodological reflections which we present are centred around the areas where we feel there is the most uncertainty for big qualitative research: study design, sampling (of case sites and stakeholders) and analysis.
Research design. Mixed-method research with a convergent parallel design was adopted in the study. This approach intends to converge two data types (quantitative and qualitative) at the interpretation stage to ensure an inclusive research problem analysis [].The quantitative aspect of the study was implemented through a cross-sectional survey.
Research studies on this topic have indicated three patterns of urban-rural interaction: ... In line with the research methods, both qualitative and quantitative data were obtained. ... The three villages selected as case studies in this paper—Xiapuzheng, Luoyu, and Waciyao—are situated in close proximity to each other at the urban ...
However, the emissions trade-offs demand additional optimization studies, as well as case-based research, in order to integrate renewable energy and emission management in smaller-scale applications across more geographies. ... Therefore, this study aims to test the PG of four types of biomasses, commonly available in a small agriculturally ...
Background This study aims to describe a rare case of primary ureteral hemangiosarcoma, in which surgical intervention preserved the kidney and ureter after tumor removal. Case presentation A 13-year-old, neutered male dog, weighing 14 kg, mixed-breed, presented with apathy, anorexia, acute-onset vomiting, and abdominal discomfort during the physical examination. Ultrasonography and ...