

10 Accounting Problem Solving Skills and How To Improve Them
Discover 10 Accounting Problem Solving skills along with some of the best tips to help you improve these abilities.

Accounting is an important skill for anyone who wants to be financially successful. Without a basic understanding of accounting, it can be difficult to make sound financial decisions. However, even if you have a strong understanding of accounting principles, you may still encounter occasional accounting problems.
When these problems arise, it is important to have strong problem solving skills in order to find a resolution. In this guide, we will discuss some tips for solving accounting problems. We will also provide an overview of some common accounting problems so that you can be prepared in the event that one arises.
Financial Statements
Regulatory filings, revenue projections, account reconciliation, general ledger, business knowledge, problem solving.
Financial statements are important because they provide a snapshot of a company’s financial health. They can be used to make decisions about whether or not to invest in a company, and they can also be used to track a company’s performance over time. Financial statements include the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement.
Payroll is an important skill for accountants because it allows them to process and manage employee compensation and benefits. Payroll processing includes calculating gross wages, deductions, and net wages; preparing payroll tax returns; and managing benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off.
Accountants who can effectively manage payroll can help businesses save time and money. They can also help businesses comply with federal and state tax laws and regulations.
Regulatory filings are important because they are required by law. Companies must file certain documents with government agencies in order to operate. These filings include tax returns, annual reports, and shareholder communications. Failure to file these documents can result in penalties or even the closure of a company.
Regulatory filings are important because they provide transparency. By law, companies must file certain documents with government agencies. These filings are public, which means that anyone can access them. This transparency allows investors and other stakeholders to see how a company is operating.
Revenue projections are important for businesses because they help businesses plan for future income. Revenue projections can be used to determine how much money a business will need to operate and grow. Revenue projections can also be used to help businesses raise money from investors.
Revenue projections are important because they help businesses plan for future income. Revenue projections can be used to determine how much money a business will need to operate and grow. Revenue projections can also be used to help businesses raise money from investors.
Account reconciliation is the process of ensuring that all transactions in a company’s books are accurate. This process is important because it helps ensure that the company’s financial statements are accurate and can be relied upon by investors, creditors and other stakeholders.
Account reconciliation involves comparing the company’s books with the records kept by its banks, vendors and other parties with whom it does business. If there are any differences, they need to be investigated and resolved. This process can be time-consuming, but it is important to ensure that the company’s books are accurate.
Compliance is the process of ensuring that you are in compliance with the laws and regulations that apply to your business. It is important for businesses to be compliant because it helps to protect them from penalties and fines. Compliance also helps to build trust with customers and regulators.
To be compliant, businesses need to understand the laws and regulations that apply to them and then take the necessary steps to ensure that they are following the rules. For example, businesses that sell products to consumers need to be aware of the consumer protection laws that apply to them. Businesses that operate in certain industries, such as healthcare, need to be aware of the regulations that apply to them.
General ledger is an important accounting problem solving skill because it is used to track and report financial information for a business. The general ledger is a summary of all of the accounts that make up the financial statements, and it is used to keep track of the money coming in and going out of the business. The general ledger is also used to prepare financial statements, and it is important that the information in the general ledger is accurate and up to date.
Quickbooks is an important skill for anyone in the accounting field. Quickbooks is a software program that helps accountants and business owners keep track of their finances. Quickbooks can help you track invoices, manage payroll, and create financial reports. Quickbooks is a valuable skill because it can save you time and make your job easier.
Business knowledge is important for accounting problem solving because it helps accountants understand the context of the problem they are trying to solve. It also helps them identify the root cause of the problem and develop a solution that will be effective in the real world.
Accounting problem solving often involves looking at a company’s financial statements and trying to identify where the company is spending too much money or where it is making mistakes in its accounting practices. To do this, accountants need to understand the company’s business and the industry in which it operates. They also need to be familiar with the latest accounting standards and best practices.
Problem solving is an important skill for accountants because they often have to solve complex problems. Problem solving requires the ability to identify the problem, gather information, develop a plan and implement the plan. Accountants must be able to think critically and creatively to solve problems.
Problem solving often requires good communication skills. Accountants must be able to explain the problem, gather information and develop a plan with the client. They also need to be able to follow up to make sure the plan is working and to troubleshoot if there are any issues.
How to Improve Your Accounting Problem Solving Skills
1. Understand the basics of accounting If you want to improve your accounting problem solving skills, it is important to have a strong foundation in accounting principles. You should be able to read and understand financial statements, as well as have a working knowledge of payroll, regulatory filings, revenue projections and account reconciliation.
2. Be well-versed in accounting software In order to be an effective problem solver, you need to be well-versed in accounting software. This will allow you to quickly and efficiently find solutions to accounting problems.
3. Stay up-to-date on accounting news and changes It is also important to stay up-to-date on accounting news and changes. This will help you anticipate problems and find solutions more quickly.
4. Be proactive in solving problems When you encounter an accounting problem, it is important to be proactive in solving it. This means taking the time to understand the problem and researching potential solutions.
5. Communicate effectively with your team When you are working on a team, it is important to communicate effectively. This means being clear about what you need from your team members and keeping them updated on your progress.
6. Be organized and efficient When solving accounting problems, it is important to be organized and efficient. This means having a system in place for tracking your progress and keeping your work area tidy.
7. Practice problem solving One of the best ways to improve your accounting problem solving skills is to practice. This can be done by working on practice problems or by taking on small projects in your personal life.
8. Seek out feedback When you are working on solving accounting problems, it is important to seek out feedback. This can be done by asking for feedback from your team members or by seeking out feedback from a mentor.
10 Linguistic Skills and How To Improve Them
10 stakeholder management skills and how to improve them, you may also be interested in..., what does a maintenance director do, what does a market development manager do, what does a wells fargo phone banker do, what does a personal driver do.
INSIGHTS + Info

- All Insights
- By Resource
- Ask the CFO
- eBooks/Guides
- Interactive Tools
- Case Studies
- Infographics
- White Papers
- By Role / Industry
- CFO / Corporate Finance
- Investor / PE Firm
- CPA / Accounting Firm
- Corporate Operations
- By Solution
- General Finance & Accounting
- Accounts Payable
- Accounts Receivable
- Back Office
- Why Outsourced Accounting?
- Data & Automation
- Managing Human Capital
- Accounting Staffing
- Cost Containment
- Streamlining Private Equity
- Personiv's Virtual Accounting Solution
- CFO Weekly Podcast
Problem Solving in Accounting
- Share this Article
Problem-solving in accounting is a critical skill that can always be improved upon. Master problem-solver and CFO at Musselman & Hall Contractors LLC, Adam Porter, shares his insight and experience with us in the latest episode of CFO Weekly.
What Makes a Great Problem-solver?
If you know, you know, right? Adam instinctively knew he was a problem-solver when he was younger. Something as simple as going from point A to point B became an opportunity to experiment with which route got him to his destination quicker. And his quest for discovery hasn't stopped.
“If we don’t understand the ‘why’ behind the actions we take, how do we know if we’re really doing the right thing,” Porter said.
To solve is to correct or optimize, and none of us can do that if we don’t first recognize an opportunity to get involved. Problem-solving goes hand in hand with the willingness to roll up your sleeves and get stuck in, take an active role in, and see through the potential outcome. Adam empowers each of his team members to become (and grow as) problem-solvers, by recognizing them and their contributions to identifying and solving issues.
Involving people in the problem-solving process and connecting the dots for them, showing them how they make the business a better organism, is how you create more great problem-solvers and amplify your ability to tackle problems as they appear.
Accounting Problem-solving in Action
Problem-solving is a term that gets thrown around in interviews and on resumes quite a bit. When the time comes, real problem-solvers like Adam approach things in a specific way.
System Upgrades
If you’ve navigated a system change and survived to tell the tale, some would say you have superpowers. Upgrading something like an ERP system is a mammoth task, even for a seasoned team of executives. During a project like this, you’re reviewing and possibly amending every single organizational process.
You’re also required to identify how everything you do during this project starts to affect other areas of the business: finance, accounting, HR, IT and so on.
Adam’s own experience with one such project led him through a GL restructure. At the end of a six-month series of efforts, with the support of a Controller whom he had brought it to, Adam succeeded and was able to present information back to the business, which could be used to inform business decisions.
The domino effect: once more information became available, and it was clear how it related to each portion of the business, the people in charge of those respective portions became more engaged and more curious and more willing to work with that information.
Problem-solving is just one of those skills where nobody needs to formally identify the need for it. It’s the problem-solvers who are constantly on the lookout for opportunities to apply themselves.
The result is that everybody benefits.
The Problem-solving Process in Accounting
Adam’s very first step in his problem-solving process is to absorb as much information from as many sources as he can. Whether it’s listening to the news every day or speaking with different people inside the business, there’s this ongoing effort to find out more, learn about topical challenges that others might be facing, and use that to drive questions internally about further opportunities to solve problems.
It doesn’t necessarily need to reach the state of being a ‘problem’ to receive attention for optimization. You just need to listen and pay attention to where things might be slower, costing more than usual or requiring manual input from too many people.
Once you have this information, you can gather the right people into the room to start looking at that information, gathering more of it from different sources.
One of the key components of fully resolving any issue is to understand the full scope and depth of its current and future impact: What happens if you leave it alone, or if it gets worse, or if it’s completely resolved? Who gets more time in a day when you resolve something? Whose budget gets some breathing room? Can you reduce the amount of manual input that everybody’s required to give?
Finding the Right People to Solve the Problem in Your Accounting Department
So, once you know what the problem is, you need to get the right people in to solve it.
How do you know who that is? The team behind your solution is critical. As a CFO, you have the responsibility of setting your team up for success when they’re working on solving problems. All execs have this responsibility.
In any organization, cross-functional training is the quickest way to widen perspectives when approaching any problems. If your execs are regularly making time to get down to the operational level, and understand how and why things work a certain way, it becomes so much easier to strategically recommend a resolution when one is needed.
Problem-solving isn’t a one-way road.
Solve the Problem, Not the Symptom
How do you know when you’re solving the right thing? So many times, we see something blatantly creating a bottleneck in an operation and we’ll head right toward that point to clear the blockage. Is that really solving the problem, though?
Most times, it isn’t. Once you clear the blockage, if you don’t look a little deeper or follow it upstream, it’s probably going to reappear not long after you put in all that effort.
Adam explains that sometimes, you already know what the real root cause is, of one or more bottlenecks in the business. Sometimes it’s trial and error. Always, though, it requires you to dig deeper, uncover more detail, more links and connections to other parts of the business operation or the stakeholder network.
Adam goes on to say that getting to the root of the issue can also be achieved by just getting the right people in the room with you. Musselman & Hall Contractors does a great job of this, getting executives together at least once weekly, to just help others on the team evaluate elements, ask more questions, different questions, and gain a different perspective on things that can be missed during the daily routine.
Dealing with Resistance
Resistance is natural. Inertia affects every company in the world to some degree. When problem-solving, it’s likely that this will occur too.
You need to follow the process and listen as much as you convey messages. Cultivate the mindset within your business that someone else learning about your job is a positive thing. Take the time to explain that it’s because a fresh pair of eyes and a fresh mind might ask a different question that can enable you to work faster, reduce manual input, take on more responsibility, and actually achieve a promotion.
The right mindset about problem-solving enables it to benefit everyone on the team. No matter who is working on which problem or when, another major benefit to your business is to thoroughly document your procedures and changes thereto. It enriches the context of every issue that gets identified and resolved now and in the future, creating even greater efficiency for you as time passes.
Overcoming resistance is made possible by including and involving the right people, and enabling regular two-way communication with them through the problem-solving process.
For more interviews from the CFO Weekly podcast, check us out on Apple or Spotify or your favorite podcast player.
Previous Article

Not all accounting tasks are created equal. Before you automate, explore some of the top accounting automat...
Next Article

Uncover the hidden profit drain! Learn the top mistakes plaguing your accounting process and discover prove...
Most Recent Articles

High staff turnover draining your accounting team's budget? Learn how the hidden cost of turnover in accounting impacts your bottom line and discover strategies to reduce recruitment costs today!

Leaders, storytelling isn't a luxury, it's essential! The Chief Storyteller role is booming. Learn why & unlock your leadership potential with the power of narrative.

Real estate agents, the recent NAR settlement brings new challenges. Learn how outsourcing can streamline operations, ensure compliance, and free up your time to focus on clients.

Unlock the power of AI for all! Explore the benefits, learn how to overcome accessibility challenges, and build inclusive AI for everyone. Tune in now.

Overwhelmed by accounting tasks? Outsourcing accounting services can be your secret weapon! Discover 3 unexpected benefits to streamline your finances and free up your time today.

Let's talk about gender imbalance in finance! Join the conversation and learn how we can create a more equitable financial industry.

The key to growth you might be missing! Learn about the power of cross-department collaboration and how to foster a winning team. Click to learn more!

Cut costs, and boost efficiency! Learn the top 5 ways companies leverage outsourcing to significantly reduce accounting expenses and achieve success. Discover how much you can save today!

Unlock the secrets of financial team efficiency! Dive deep into strategies for making finance accessible and achieving streamlined operations within your business.

Learn how machine learning in accounts payable can enhance efficiency and reduce costs. Learn how businesses can do more with less by leveraging innovative technology for smarter financial management.

Understanding the evolving role of the pharma CFO. Discover how the CFO is becoming a crucial partner in driving strategic decision-making for growth and expansion within the pharmaceutical industry.

Become an accounts receivable outsourcing expert! Our in-depth guide walks you through every step of the process, from understanding and developing a strategic AR plan to successful implementation.

Modern CFOs are more than number crunchers! Learn how a CFO navigates the shift from bookkeeping to becoming a strategic partner, aligning financial leadership with organizational goals and more.

The CFO role in early-stage startups: Balancing growth, structure, and financial health. Discover essential skills, get expert insights, and learn strategies for thriving in the early stages.

Explore insights from an expert on cash flow forecasting for CFOs. Discover key strategies to improve cash management, optimize financial planning, and support business growth. Read now!

Explore the key differences between accounts payable outsourcing and AI automation in this in-depth comparison. Discover which approach is best for your business today!

Explore the power of systemized decision-making and how it's transforming business decisions. Discover the benefits and see why many companies are adopting this innovative method to drive success.

Unlock the secrets to scaling your startup! Hear from a leading financial strategist as he shares proven strategies for explosive growth. Propel your startup to success.

Explore the exciting world of technological innovation in finance! We chat with a leading expert about the impact of technological innovation in finance. Discover how these advancements affect you.

Unleash the power of your finance department! Learn how effective communication can transform operations, unlock insights, and drive financial success. Get expert tips now!
This site uses cookies, including third-party cookies, to improve your experience and deliver personalized content.
By continuing to use this website, you agree to our use of all cookies. For more information visit IMA's Cookie Policy .

Change username?
Create a new account, forgot password, sign in to myima.
Multiple Categories
Accountants as Problem Solvers
August 01, 2020
By: Linda McCann , DBA, CMA, CPA ; David Horn , CPA ; Jennifer Dosch , CMA

Managers often complain that accounting graduates aren’t prepared for today’s business environment. The complexity of our global economy and the increasing influence of, and reliance on, technology leads to practitioners and instructors questioning if undergraduate accounting programs focus on the right curriculum to prepare students for careers.
One soft skill that can help prepare accounting students for their careers is problem solving. Management accountants need to be able to work cross-functionally to solve problems and provide meaningful analyses. Many colleges, universities, and accrediting bodies in academia incorporate strategic goals requiring curriculum that facilitates problem-solving skills.
As instructors, we teach technical accounting skills by demonstrating and providing practice with accounting concepts and structured problems, which we assess via homework and exams. Teaching soft skills, such as unstructured problem solving, poses greater challenges that are more difficult to incorporate into the curriculum. How can students learn and approach unstructured problem solving?
A SLOW-THINKING APPROACH
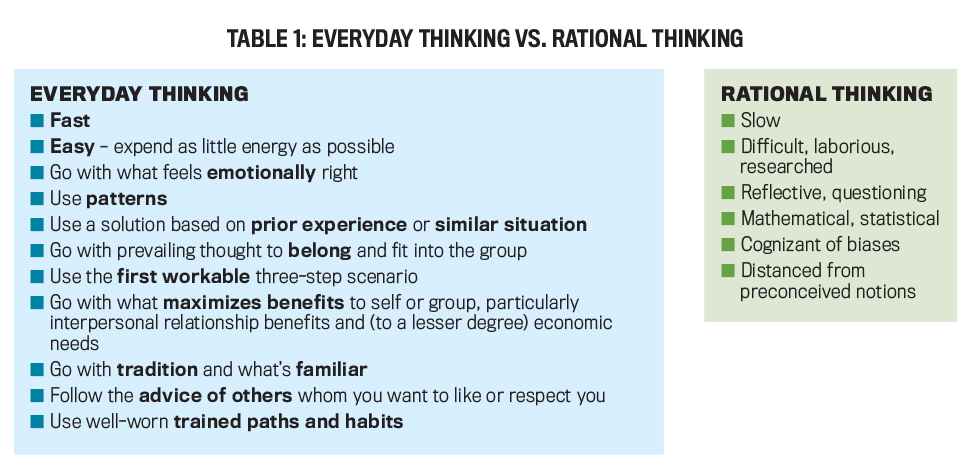
Recent scientific discoveries into the brain reveal that humans employ fast and slow thinking to solve problems. The brain especially prefers making decisions and solving problems quickly based on recognized patterns, visual and verbal cues, prior knowledge, routines, familiar preferences, prejudices, and emotions.
In contrast, decision making and problem solving often require slow thinking to digest new information, hypothesize alternatives, employ quantitative mathematical and statistical analysis, overtly recognize and break free from cognitive biases, challenge preconceived notions, synthesize ideas, and create new knowledge. To support this kind of slow, rational thinking, accountants can learn a methodical process for problem solving (see Table 1).
Many common business models—such as Six Sigma, A3 Lean, and Appreciative Inquiry—and the Association of American Colleges and Universities value problem solving, and critical-thinking grading rubrics describe specific steps for rational (i.e., slow thinking) problem solving. Business students, however, learn and apply these models in various courses, typically with no thread that ties them specifically to the accounting profession. Students learn bits and pieces of rational thinking throughout their undergraduate coursework, but instructors often don’t teach a common framework to apply these skills in a relevant and value-added way (see “Survey of Practitioners”).

To help address this issue, we developed a problem-solving rubric for accounting students (see Table 2). The three of us are faculty members from Metropolitan State University in Minneapolis/St. Paul, Minn., and represent three different parts of the curriculum (auditing, business taxation, and management accounting), so it was important that it could be used across the entire accounting program.
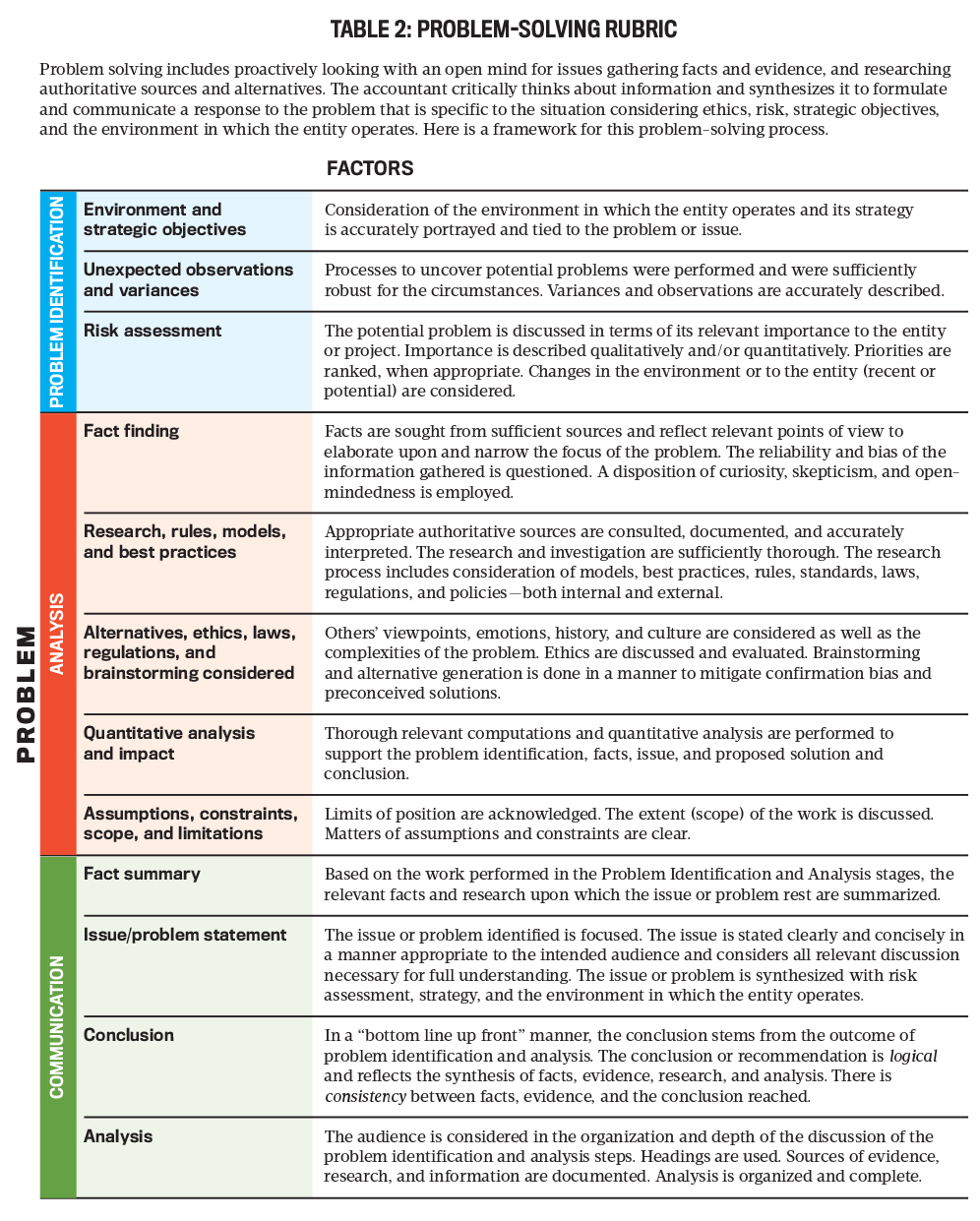
The rubric assesses learning in an organized way, providing a common framework (criteria) for students to consistently approach problem solving. The criteria include problem identification, analysis, and communication of results. It guides students through a series of problem-solving steps using terms and vocabulary specific to the accounting profession. The rubric also reminds us, as instructors, to create a learning environment where problem solving can occur (see “Setting the Tone”).

STEP 1: PROBLEM IDENTIFICATION
The iterative and looping nature of problem solving confounds inexperienced accountants. Where does one begin? Students tell us using a rubric provides a starting point.
To implement the rubric, we assign students projects with unclear goals, incomplete information, and more than one possible solution. Assignment topics vary. It could have students develop a cost-benefit analysis between adding employees or adopting Lean manufacturing techniques, analyze tax outcomes of business decisions, create a risk assessment and audit response for a fictitious client, or some other accounting-related issue.
Students begin by developing one or several hypotheses as to the nature of the problem. To generate ideas, we assist students in their brainstorming discussions. The rubric leads students to consider the environment, strategy, unexpected observations, overall importance, and risk assessment. At this stage, the identified problem may change, but the original hypothesized problem gives direction for next steps. Upon completing the assignment, we assess students on how they identified the problem.
Metropolitan State University’s business taxation course used the rubric in a case study that involves assessing the implication of the Wayfair v. South Dakota U.S. Supreme Court decision on a company’s sales tax collection. Prior to Wayfair , companies operated under a physical presence nexus established in Quill v. North Dakota . The Quill decision required companies to have a physical presence in a taxing jurisdiction in order to require collection and remittance of sales taxes on transactions.
In Wayfair , the U.S. Supreme Court overturned Quill in favor of an economic nexus standard, where companies only needed to have a certain level of economic activity. For example, in South Dakota, the threshold economic activity is 200 transactions or $100,000 in sales. The change from Quill to Wayfair was a major development in how companies operate and collect sales tax. It required companies to assess all jurisdictions in which they operate and evaluate how the change in the nexus standards impact its operations.
To apply this rubric to the change, students learn about a fictitious company that sells inventory to multiple states and collects and remits sales tax under the Quill physical presence nexus standard. We give students a subledger with all sales data for the given year. The rubric leads students to ask about implications of the Wayfair decision on the company, how the ruling impacts the company’s strategic objectives, and risks to the company because of the change in the law. Using the rubric, students are guided to discover the issue at hand, which is whether the company will have a significant number of new sales tax jurisdictions requiring collections and remittance from its customers.
Students tell us that without the rubric, they often feel like they have no road map at the beginning of a project or case study; identifying the problem seems too big and undefined to tackle. Many students initially resist engaging with unstructured problem-solving assignments because they differ from past assignments. Similar to what one might find in cross-functional teams opposed to change, students show their displeasure with crossed arms and distant body language.
Many college courses still rely on testing facts and use formulas and calculations, an approach that doesn’t put the student in the decision-making role but is familiar to them. With a rubric, students see smaller doable steps, where the assignment is heading, and how they can move forward and loop backward, when necessary. The rubric breaks down the initial intimidation students feel with unstructured problems.
STEP 2: ANALYSIS
Next, the rubric guides students through analyzing the problem using accounting-specific skills they’ve acquired in each course. For example, students consider tax laws, financial reporting and audit principles, or cost accounting techniques.
Continuing the sales and use tax example, at this stage, students apply the rubric to perform a complete analysis, enabling them to form a conclusion to communicate. What are the relevant facts to determine Wayfair ’s impact? What facts are irrelevant? What primary and secondary tax authority is needed to conduct research? Are there alternatives and exceptions to applying Wayfair ? Have all states adopted an economic nexus standard? Have all states adopted South Dakota’s transactional thresholds? What’s the quantitative impact to the company? Are there financial accounting implications to the Wayfair decision? What’s the scope of the necessary research, and are there limitations, constraints, and so on? Through the rubric, students formulate and answer questions and perform analysis to solve the problem at hand.
We assess students on their ability to gather and identify relevant facts, research any applicable rules and laws, assess alternatives, and perform any needed qualitative and quantitative analyses. At this stage, students apply theories and best practices learned in specific course fields, such as management accounting, taxation, and auditing.
To encourage elaboration, the rubric uses words such as curious, skeptical, model, assumption, authoritative, best practices, relevant, and sufficient sources. Like many accountants, students want to get their work done quickly, but problem solving takes time and slow thinking. Thanks to the rubric, more students turned in papers with greater depth, less “cut and paste,” and more relevant supporting details.
As in the real world, students often discover their original hypothesis or identified problem is incorrect, incomplete, or irrelevant. They confront the iterative nature of problem solving as they work through the analysis stage and build evidence to support their hypothesis. When evidence doesn’t support an identified problem, students go back and redefine their problem, gather new evidence, explore new alternative solutions, and build a case for their conclusion.
STEP 3: COMMUNICATION
Finally, students present their results in a memorandum to a hypothetical manager or audit partner. The memorandum mirrors common styles, such as IFRAC (issues, facts, rules, analysis, and conclusion) and BLUF (bottom line up front). Students state the problem and include the conclusion (i.e., solution) up front along with a summary of relevant facts and assumptions. Supporting documentation presents additional in-depth analysis.
This format familiarizes students with a presentation style that allows management to quickly understand conclusions while also providing more depth to support the up-front conclusion. We expect students to write and present findings in a clear and concise manner as if in a professional accounting setting. The rubric grading criteria helps students solve problems using rational thinking and delivering a memorandum that directly supports management decision making.
In the Wayfair case study, students draft a memorandum to management addressing the implications of the sales tax nexus precedence change. The facts section should discuss the company’s current sales and use tax policies. Students identify the issue as the change from physical presence nexus to economic nexus. The up-front conclusion should identify new jurisdictions from which the company needs to register and collect sales tax and quantify the volume of sales tax it expects to collect. Finally, the analysis provides an in-depth discussion of the change from Quill to Wayfair . Students should discuss how they determined new jurisdictions, limitations, and further required resources for the company.
PREPARING STUDENTS FOR THEIR CAREERS
We use the rubric format for projects or cases at different stages throughout the accounting curriculum. The problem-solving rubric measures student learning and reinforces rational thinking with each assignment. The projects that use the rubric vary in length, depth, and complexity as students move from management accounting to tax and then finally to audit. We find the rubric flexible enough to adapt to an instructor’s needs, yet it provides consistent core steps—identify the problem, analyze, and communicate—to solve problems.
The rubric helps students organize their communication through the memorandum. Setting up a memorandum so the problem and solution appear “up front” highlights mismatches between the problem, evidence, and conclusion. Further, it encourages students to decide—rather than ramble and include information that isn’t relevant. We find students often get to the communication stage and realize that their analysis doesn’t support their conclusion or identified problem. Fortunately, the rubric allows them to loop back and redefine and reanalyze.
By using the same grading criteria in multiple courses, we provide students with a familiar approach to problem solving that turns fast thinking to slow, rational thinking. The process and steps become routine and less daunting for the student. While each step still requires arduous thinking, the approach itself is a recognized pattern for students.
From our point of view as accounting instructors, the rubric helps provide consistent and fair grading. We provide separate points for milestones in problem identification, analysis, and communication, which further encourages students to go through each step of the process. Metropolitan State University plans to expand the use of this rubric in the accounting curriculum. This common framework provides students with a process to identify problems, research and investigate facts, conduct analyses, and communicate results across all accounting disciplines.
This process reinforces the problem-solving skills that students will need in their professional careers. These capabilities will help them perform their roles in today’s strategic, fast-paced business environment. Solving problems is critical for today’s management accountant. Through implementing the rubric, instructors can help students systematically apply a problem-solving process that they can take with them as they move from student to management accountant.
About the Authors

August 2020
- Strategy, Planning & Performance
- Decision Analysis
- Negotiation
- Metropolitan State University
Publication Highlights
Call for Ethics Papers: Sept. 1 Deadline
Explore more.
Copyright Footer Message
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet

- Business Partner
- Strategic Partner
- Problem Solving
- Communication
- Strategic Thinking
- Influencing
Problem Solving Skills For Accountants
Problem solving skills for accountants are so valuable because businesses are full of problems that need solving – and almost all business problems have some kind of financial impact.
Therefore accountants with problem solving skills are highly valuable.
As a technically proficient accountant you understand many technical solutions to finance problems and issues.
You know what complies with the rules, what is possible and what is not.
However there comes a time when you are faced with problems that are difficult, eiether because they aren’t well-formed, are ambiguous or complex.
Complex problems
These are problems where there is no right answer and the issues span multiple disciplines and departments.
Developing problem-solving skills will set you apart from your colleagues, as you will be able to help solve these complex problems.
For instance, you will be a vital resource for developing the finance function.
You’ll also become a valued partner to other non-financial managers.
You will be able to propose solutions that work for you and them.
You can also ensure that they work within the financial constraints that you understand well.
Understanding business problems
The first step is to understand the problem thoroughly. To examine it from every relevant angle and understand it in context.
This means understanding the business, what is important and what would be right for the business – not just finance.
Lateral thinking for problem solving
Solving a business problem often requires lateral thinking – coming at things from a new perspective.
With your financial and analytical mind you can bring a valuable perspective that your colleagues may lack.
If you are able to develop lateral thinking skills you can make a significant contribution to the debate. Particularly when you use these alongside and combined with your technical and analytical approach.
Creative ideas
Accountants aren’t always noted for their creative thinking. Therefore being able to suspend judgement and think creatively and imaginatively can give you an edge over others. Because this enables you to bring something unique and different to the discussion.
Learning to think creatively can be liberating and fun. But it can also produce some new insights and innovations.
These can make everyone’s lives more productive and set you apart from your colleagues.
Proposing solutions
Having great ideas is one thing, but arguing the case for them and presenting your proposed solutions to your colleagues and decision-makers is another.
Being able to see – and sell – the benefits of a solution requires an insight into the business, your colleagues and the office politics that inevitably exist.
Why are problem solving skills for accountants so important?
Most business problems have a financial dimension and as accountant you have unrivalled expertise.
An accountant who can proactively solve business problems will be a highly valuable asset for any business..
Being a creative problem-solver may not be your natural strength, but these skills can be learnt and developed.
You have a huge opportunity to become a highly valued member of the team if you can develop your problem solving skills.
How are you developing your problem solving skills?
Do you have sufficient understanding of the business to propose solutions that will be accepted, how adept are you at persuading others of the merits of your solution, which of the other key soft skills for accountants do you need to develop, discover the seven essential soft skills for accountants download the report now.
There are some key soft skills to focus on as your finance career progresses.
Find out which they are by downloading the free report.

Never see this message again.
Mastering Problem Definition: A Beginner’s Guide
Introduction: Problem definition is a crucial step in problem-solving processes across various domains, including accounting and finance. It involves clearly identifying and understanding the nature and scope of the problem at hand. In this guide, we will delve into the concept of problem definition, its importance, and how learners in accounting and finance can effectively apply it in their field.
Key Points:
- Definition of Problem Definition: Problem definition refers to the process of clearly articulating and understanding the problem or challenge that needs to be addressed. It involves defining the scope, boundaries, and objectives of the problem-solving endeavor.
- Clarity: Clearly defining the problem helps in avoiding ambiguity and ensures that all stakeholders have a shared understanding of the issue.
- Focus: A well-defined problem allows individuals to concentrate their efforts and resources on finding relevant solutions, leading to more effective problem-solving outcomes.
- Efficiency: By precisely defining the problem, unnecessary time and resources spent on addressing irrelevant issues can be minimized, leading to increased efficiency.
- Alignment with Goals: Problem definition ensures that the identified problem aligns with the overall goals and objectives of the organization or project.
- Identifying the Problem: The first step involves recognizing the existence of a problem or challenge that needs to be addressed. This may arise from various sources such as financial discrepancies, operational inefficiencies, or strategic concerns.
- Clarifying the Objectives: Once the problem is identified, it is essential to clarify the specific objectives that need to be achieved through problem-solving efforts. These objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
- Understanding the Context: Understanding the context surrounding the problem, including its causes, stakeholders involved, and potential implications, is vital for effective problem definition.
- Setting Boundaries: Defining the scope and boundaries of the problem helps in focusing efforts on relevant aspects and avoiding unnecessary complexities.
- Identifying the problem: Declining profitability despite consistent sales.
- Clarifying the objectives: Increase profitability by reducing operational costs or increasing revenue streams.
- Understanding the context: Analyzing factors such as increasing raw material costs, inefficient production processes, or changing market dynamics.
- Setting boundaries: Focusing on internal operational factors directly impacting profitability rather than external market fluctuations.
- Kepner, C. H., & Tregoe, B. B. (1981). The New Rational Manager. Princeton Research Press. This book provides insights into structured problem-solving methodologies, including problem definition techniques, with practical examples.
Conclusion: Problem definition is a foundational step in problem-solving processes, enabling individuals to clearly understand and address the challenges they face. By defining the problem accurately, learners in accounting and finance can streamline their problem-solving efforts, leading to more efficient and effective outcomes. Understanding the importance of problem definition and mastering its techniques is essential for success in accounting and finance.
Related Posts
Written-down value (wdv) explained for beginners.
If you’re new to finance and accounting, terms like “Written-Down Value” or WDV might sound…
Activity Sampling (Work Sampling): Unveiling Insights into Work Efficiency
Activity Sampling, also known as Work Sampling, is a method used in various industries to…
- Portal Access
- ADP Employee Access
- ADP Employer Access
- QuickBooks Login
- New Business Client Questionnaire
- New Individual Client Questionnaire
- New York Tax Services
- Where’s My Refund?
- Individuals Refund
- Business Refund

- Accounting Firm Support
- Business Growth & Advisory Strategies
- Cloud Accounting Conversion & Maintenance
- Tax Minimization Strategies & Preparation
- Healthcare Accounting
- Outsourced Virtual CFO New York
- Casualty Loss – Reporting & Prevention
- Cloud Accounting
- Quickbooks Online
- QuickBooks Resources
- Newsletters
- Business Resources
- Business Worksheets & Compliance
- Preparing for Your Tax Appointment
- What is a 1099-Misc Form?
- What Should I Do About My Payroll Tax Withholding?
- Weekly News
- Retention Guides
- Video Library
- Our Company
- Our Philosophy
- How we work
- What our clients say
- Strategic Partners
- Tech-Forward Accounting Solution
- Trusted Accounting Partner in New York
Six ways to solve 80% of your accounting problems
Accounting problems can have serious consequences for your business and are definitely worth avoiding. Here we outline six ways to solve the majority of your accounting issues.
1. Know the difference between profit and cash flow
If you’re a new business owner, it can be easy to spend money on growing your business rather than earning that money back again in profits. You may have a profitable business, but it can still become bankrupt by having all its money tied-up in assets, leaving you unable to pay its expenses.
The problem with growing too quickly is that you can end up in a lot of debt and with very little cash flow, even though your business may be making solid profits. You can only stay afloat using loans, credit cards and lines of credit for so long.
In order to avoid this situation, it’s important to understand the difference between profit and cash flow. Your profit is what you’ll be taxed on at the end of the financial year, whereas your cash flow is what’s actually in your bank (each month) as money comes in and goes out of your business.
It can be easy (particularly for a new business owner) to make a profit but have issues with cash flow. Keep track of what you’re spending and selling. You might have bought too much stock, drawn out too much money, or paid cash for assets that depreciate. Take a thorough look at your books before taking on expansion plans that could put your business at excessive risk.
2. Understand the impact of purchasing assets
If you decide to buy assets like machinery or office equipment with cash, it will reduce your cash reserves. And by doing so, you might be placing your business at risk.
You also won’t be able to claim the whole cost of the asset as an expense. Leasing could be a better option as it spreads the cost over time, meaning your cash lasts longer rather than being spent in one hit.
When you decide to make a major business purchase, such as a new vehicle, also think about taking out a short-term loan.
3. Take your bookkeeping seriously
As a small business owner, it’s vital you record and structure everything correctly when keeping the books.
For your sake, your accountant’s sanity, and to satisfy the tax department, you’ll want to build an accurate and reliable picture of your business’s health. Not only are there laws to be met, but you’ll be able to determine how well (or how poorly) your business performed over a certain period.
The advantages of keeping your books clean and up-to-date include:
- Paying your bills on time and gaining a good credit score.
- Less chance of becoming a victim of fraud – because you’ll be able to keep a close eye on stock levels and help prevent staff theft.
- Saving money – if your accounts are accurate when you meet your accountant at the end of the year.
These days, many small business owners use online accounting software like Receipt Bank to keep an electronic record of their receipts and invoices in the cloud. Take a look at the online accounting options that could enhance your bookkeeping accuracy.
4. Reconcile accounts with your bank feed
To reduce the chance of inaccuracies, it’s important you reconcile your business’s accounts with your bank feed regularly.
As a small business owner, online accounting software can be vitally helpful when it comes to reconciling your accounts. An online banking feed will help you ensure all transactions are accounted for. Reconciling accurately can save your business time and money.
Going through this process on a fairly regular basis will help you track your business’s financial situation. After all, with your mind mainly focused on the day-to-day running of your business, it’s possible that smaller expenses could get forgotten and go unrecorded.
5. Keep up-to-date with your accounting records
Keeping accurate records of all your business’s transactions (even the seemingly insignificant ones) is essential to running a successful business. Assigning a few minutes a day to sorting your invoices and receipts will help you avoid having to untangle a web of neglected records come tax time.
By staying on top of your smaller transactions, it will be a lot easier to manage the larger ones. You’ll be able to consistently manage your books and continue growing your business in confidence as the numbers of transactions increase.
6. Separate your business expenses from your personal ones
One of the most widespread accounting errors involves mixing up personal and business expenses. Keeping all your business finances in one place will make tax time much more bearable.
Ideally, you’ll want to be able to browse your business’s accounts at the end of each month and be sure no personal expenses are included. Some methods you can put in place to achieve this are:
- Using an online invoicing and billing system – where you can access the data from anywhere and record purchases with your phone while on the go.
- Getting a dedicated business credit card – to ensure all relevant purchases can easily be accounted for.
If you do get a business credit card, just remember to only use it for work expenses.
These six tips can go a long way to solving typical accounting problems. Keep on top of your records, reconcile often, and ensure your personal expenses are separate from your business ones.
- Talk to your accountant about how you’re going about record keeping.
- Speak to your bank manager about opening up a business bank account.
Complementary Discovery Session
This is our way for each of us to get to know each other a little bit better so we can map out a strategy that will help you meet your goals
- Phone This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
The global body for professional accountants
- Search jobs
- Find an accountant
- Technical activities
- Help & support
Can't find your location/region listed? Please visit our global website instead
- Middle East
- Cayman Islands
- Trinidad & Tobago
- Virgin Islands (British)
- United Kingdom
- Czech Republic
- United Arab Emirates
- Saudi Arabia
- State of Palestine
- Syrian Arab Republic
- South Africa
- Africa (other)
- Hong Kong SAR of China
- New Zealand
- Our qualifications
- Getting started
- Your career
- Apply to become an ACCA student
- Why choose to study ACCA?
- ACCA accountancy qualifications
- Getting started with ACCA
- ACCA Learning
- Register your interest in ACCA
- Learn why you should hire ACCA members
- Why train your staff with ACCA?
- Recruit finance staff
- Train and develop finance talent
- Approved Employer programme
- Employer support
- Resources to help your organisation stay one step ahead
- Support for Approved Learning Partners
- Becoming an ACCA Approved Learning Partner
- Tutor support
- Computer-Based Exam (CBE) centres
- Content providers
- Registered Learning Partner
- Exemption accreditation
- University partnerships
- Find tuition
- Virtual classroom support for learning partners
- Find CPD resources
- Your membership
- Member networks
- AB magazine
- Sectors and industries
- Regulation and standards
- Advocacy and mentoring
- Council, elections and AGM
- Tuition and study options
- Study support resources
- Practical experience
- Our ethics modules
- Student Accountant
- Support for students in Australia and New Zealand
- ACCA Approved Learning Partners Australia and New Zealand
- Campus Ambassador Program
- Regulation and standards for students
- Your 2024 subscription
- Completing your EPSM
- Completing your PER
- Apply for membership
- Skills webinars
- Finding a great supervisor
- Choosing the right objectives for you
- Regularly recording your PER
- The next phase of your journey
- Your future once qualified
- Mentoring and networks
- Advance e-magazine
- Affiliate video support
- About policy and insights at ACCA
- Meet the team
- Global economics
- Professional accountants - the future
- Supporting the global profession
- Download the insights app
Can't find your location listed? Please visit our global website instead
- The joys of problem solving
- Student e-magazine
Many accountants enjoy problem solving more than number crunching. So what typical problems can you look forward to cracking at work? Iwona Tokc-Wilde reports

Problem solving is something that accountants and finance professionals deal with virtually every working day. In fact, a recent survey by Robert Half shows it is this part of working in the profession that they like best: 41% of accountants say solving problems gives them the most job satisfaction, compared to just 22% who prefer working with numbers.
‘Accountants are usually excellent at dealing with detail and spotting patterns, which makes them good at – and enjoy – problem solving,’ comments Andi Lonnen, founder and director of Finance Training Academy.
If you are at the beginning of your journey into the profession and enjoy tackling problems, you have a head start. Problem solving is also a skill that is one of the 10 most sought-after trainee skills globally (see 'Related links').
Why problem-solving skills are so important
‘The role of accountancy and finance has shifted from a pure focus on fiscal control to one where it has an impact on the business,’ says Phil Sheridan, managing director at Robert Half.
‘The requirement for problem-solving skills is part of this transition as, by mining data and analysing trends, accountants are now translating numbers into actionable insights for the business and are increasingly being seen as strategic partners.’ By putting their data skills and their problem-solving skills to work together, they also help uncover potential areas for concern.
It is vital for accountants in practice to correctly identify, analyse and solve problems too.
‘As trusted advisers, it’s our role to look at everything in detail to pick-up anomalies, patterns and correlations in order to advise our clients on how to take things forward,’ says Shahzad Nawaz of AA Accountants. If they fail to pick up and analyse problems correctly, the accounts could be wrong.
‘This means the business owner would be relying on incorrect data, which could have a detrimental effect on the future of the business. And, of course, if external stakeholders are relying on the data, then we could potentially be misleading them too.’
Incorrect accounts could also have other serious knock-on effects.
‘If the accounting figures are incorrect, then the tax payments relating to the company will be incorrect too. Later on, the client could find themselves with additional tax to pay – with interest,’ says Tanya Addy of BHP Chartered Accountants.
‘Inaccurate accounting can also land businesses in serious commercial difficulties especially if, as a result, directors/owners have been taking more salary or dividends from the business than they were entitled to. In the worst case scenario, it could even lead to closure of the business.’
Problem solving at work
There are many areas where trainee and new accountants can practise solving problems, depending on the job you are doing.
‘If it’s accountancy, you’ll be looking at helping a business with cash flow, debtors and improving their record-keeping,’ says Nawaz.
At the nitty-gritty level, you will be reconciling control accounts, trying to understand why an account might not be balancing and investigating and clearing old items on reconciliations.
‘The work to balance an account involves finding out what the problem is and then resolving it, for example identifying and correcting transposition errors,’ says Lodden.
If you work in tax, you’ll be involved in advising a client on how much tax they will need to pay (and how much tax they can save) in a particular year.
‘This will require a review of the information provided by the client, such as bank statements and expenses, analysing which expenses incurred are allowable and disallowable for taxation, quantifying the results and communicating them to the client and to tax authorities,’ explains Carolyn Napier, senior ACCA tutor at London School of Business and Finance.
You will also be dealing with tax implications, and tax cost for both employer and employee, of providing benefits.
‘You will need to ascertain which benefits are taxable and which are tax-free, and then you’ll need to "solve the problem" of which tax or taxes are due and payable, and by what date,’ says Napier.
In industry, you may be given the opportunity to help analyse projects, and communicate your findings to various parts of the business.
‘This is where new and trainee accountants will need to be prepared to utilise their problem-solving skills – noting anomalies and seeking clarification on areas of uncertainly will ensure that a clearer picture can be obtained,’ says Sheridan.
Deborah Adigun-Hameed is an accountant and junior financial analyst at BlueBay Asset Management. By utilising her problem-solving aptitude and skills, she has been involved in major decisions that shape the company she works for.
‘I’ve contributed to key strategic discussions about which market and products are profitable, what we should be selling and how we compare with our competitors,’ says Adigun-Hameed.
‘I may be newly qualified, but my informed opinions and advice are really valued by the management.’
Both in practice and in industry, accountants are also increasingly called upon to help solve technology problems – for example, when a business intends to implement new business software solutions. They help with the evaluation and selection of a solution, and with planning and execution of the implementation process. They also assist in testing the new system and facilitate going live when the system is ready.
Hone your problem-solving skills
Problem solving is about using logic and your technical expertise to assess a situation and to come up with a workable solution. It is connected to other skills such as level-headedness and resilience, analytical skills and good teamworking skills.
It also requires creativity, which is best learnt through collaboration – brainstorming with others to clarify the problem, generate ideas and create as many potential solutions as possible. When putting forward ideas, be confident in your contributions.
‘Everyone, including those newly-qualified, has something to offer,’ says Adigun-Hameed. ‘Always think outside of the box, as cliché as that may sound. No new idea is insignificant. Innovation can be incremental; change can be small or radical.’
Improving your listening and communication skills will also make you a better problem solver.
‘Learning to communicate well is vital as you need to build rapport with clients. If you have a good rapport with someone, you are confident to ask questions, which is how you can pin down problems and find answers to those problems,’ says Nawaz.
Above all else, getting practical on-the-job experience is how you can get really good at problem solving.
‘The first control account a trainee tends to tackle and perfect is the bank control account; every trainee accountant has had to look for that 1p difference – as painful as that sounds, it certainly helps you learn,’ says Lauren Burt, client manager at EST Accountants and Tax Advisers.
"Everyone, including those newly-qualified, has something to offer. Always think outside of the box, as cliché as that may sound. No new idea is insignificant. Innovation can be incremental; change can be small or radical" Deborah Adigun-Hameed - BlueBay Asset Management
Related Links
- Top 10 global in-demand skills
- Student Accountant hub
Advertisement
- ACCA Careers
- ACCA Career Navigator
- ACCA Learning Community
Useful links
- Make a payment
- ACCA-X online courses
- ACCA Rulebook
- Work for us
Most popular
- Professional insights
- ACCA Qualification
- Member events and CPD
- Supporting Ukraine
- Past exam papers
Connect with us
Planned system updates.
- Accessibility
- Legal policies
- Data protection & cookies
- Advertising
- User Manager
- Saved for Later

Developing your problem-solving skills
Problem Solving has emerged as one of the key skills that accountants will need in the future. As we are increasingly called upon to help solve problems, both in business and in practice, so it's vital that we hone our skills in this area so that we can continue to add value to our organisations in the future. In this extract from his new course, Problem Solving for Accountants , Alan Nelson describes how we can develop our problem-solving skills.
Before we elaborate on why accountants should be interested in developing their problem-solving skills, let's go back to basics.
The most obvious sign of a problem is that something is not working as well as you would like it to be.
What is a problem?
What are the signs that there is a problem? A downturn in reported sales for the period?
Whether it is a financial reporting issue, a timing issue, a sales issue or a business performance problem, the most obvious sign of a problem is that something is not working as well as you would like it to be.
What are examples of typical accounting problems?
Accountants and finance professionals deal with problems on a daily basis. You might:
- Spot that some creditors are taking longer to pay
- Reconcile accounts
- Notice that an important KPI is off target
- Identify an increase in production costs
- Uncover errors in tax returns
- Foresee a cash shortage before it becomes critical
As accountants, it's vital that you notice the finer details, meaning you are able to spot errors and patterns with figures. Not only do you have the skills to identify these kinds of problems, but you have the technical knowledge to make the numbers right.
How is the nature of problem-solving changing in accounting?
Emerging technologies are causing the accounting industry to change. Computer programmes are starting to rectify the nitty-gritty numbers issues that accountants traditionally dealt with, meaning you will be faced with new problems to solve.
As those of you in practice attempt to move towards becoming trusted business advisers, and those in business towards being finance business partners, rather than being asked to solve problems to do with the accounts, you will be asked to seek out � and provide solutions to � issues in the wider business.
How will I need to develop my problem-solving skills then?
With the rise of automation, accountants of the future will be required to focus less on highlighting these sorts of issues with the numbers, and become much better at thinking up alternative solutions to a range of issues across the organisation.
Your job will be to bring problems to senior management and highlight how they present an opportunity for the business to improve � provide a better service, make better products, satisfy more customers, make more money... the list goes on.
And there are two different sets of skills that you can develop to help you do this.
Traditionally, the strategies used to get to the cause of a problem can be seen as being either creative or analytical. So it's developing your problem-solving skills in these areas that the new course focuses on.
Alan Nelson is an author for accountingcpd. To see his courses, click here .
You need to sign in or register before you can add a contribution.

The Art of Effective Problem Solving: A Step-by-Step Guide
Author: Daniel Croft
Daniel Croft is an experienced continuous improvement manager with a Lean Six Sigma Black Belt and a Bachelor's degree in Business Management. With more than ten years of experience applying his skills across various industries, Daniel specializes in optimizing processes and improving efficiency. His approach combines practical experience with a deep understanding of business fundamentals to drive meaningful change.
Whether we realise it or not, problem solving skills are an important part of our daily lives. From resolving a minor annoyance at home to tackling complex business challenges at work, our ability to solve problems has a significant impact on our success and happiness. However, not everyone is naturally gifted at problem-solving, and even those who are can always improve their skills. In this blog post, we will go over the art of effective problem-solving step by step.
You will learn how to define a problem, gather information, assess alternatives, and implement a solution, all while honing your critical thinking and creative problem-solving skills. Whether you’re a seasoned problem solver or just getting started, this guide will arm you with the knowledge and tools you need to face any challenge with confidence. So let’s get started!
Problem Solving Methodologies
Individuals and organisations can use a variety of problem-solving methodologies to address complex challenges. 8D and A3 problem solving techniques are two popular methodologies in the Lean Six Sigma framework.
Methodology of 8D (Eight Discipline) Problem Solving:
The 8D problem solving methodology is a systematic, team-based approach to problem solving. It is a method that guides a team through eight distinct steps to solve a problem in a systematic and comprehensive manner.
The 8D process consists of the following steps:

- Form a team: Assemble a group of people who have the necessary expertise to work on the problem.
- Define the issue: Clearly identify and define the problem, including the root cause and the customer impact.
- Create a temporary containment plan: Put in place a plan to lessen the impact of the problem until a permanent solution can be found.
- Identify the root cause: To identify the underlying causes of the problem, use root cause analysis techniques such as Fishbone diagrams and Pareto charts.
- Create and test long-term corrective actions: Create and test a long-term solution to eliminate the root cause of the problem.
- Implement and validate the permanent solution: Implement and validate the permanent solution’s effectiveness.
- Prevent recurrence: Put in place measures to keep the problem from recurring.
- Recognize and reward the team: Recognize and reward the team for its efforts.
Download the 8D Problem Solving Template
A3 Problem Solving Method:
The A3 problem solving technique is a visual, team-based problem-solving approach that is frequently used in Lean Six Sigma projects. The A3 report is a one-page document that clearly and concisely outlines the problem, root cause analysis, and proposed solution.
The A3 problem-solving procedure consists of the following steps:
- Determine the issue: Define the issue clearly, including its impact on the customer.
- Perform root cause analysis: Identify the underlying causes of the problem using root cause analysis techniques.
- Create and implement a solution: Create and implement a solution that addresses the problem’s root cause.
- Monitor and improve the solution: Keep an eye on the solution’s effectiveness and make any necessary changes.
Subsequently, in the Lean Six Sigma framework, the 8D and A3 problem solving methodologies are two popular approaches to problem solving. Both methodologies provide a structured, team-based problem-solving approach that guides individuals through a comprehensive and systematic process of identifying, analysing, and resolving problems in an effective and efficient manner.
Step 1 – Define the Problem
The definition of the problem is the first step in effective problem solving. This may appear to be a simple task, but it is actually quite difficult. This is because problems are frequently complex and multi-layered, making it easy to confuse symptoms with the underlying cause. To avoid this pitfall, it is critical to thoroughly understand the problem.
To begin, ask yourself some clarifying questions:
- What exactly is the issue?
- What are the problem’s symptoms or consequences?
- Who or what is impacted by the issue?
- When and where does the issue arise?
Answering these questions will assist you in determining the scope of the problem. However, simply describing the problem is not always sufficient; you must also identify the root cause. The root cause is the underlying cause of the problem and is usually the key to resolving it permanently.
Try asking “why” questions to find the root cause:
- What causes the problem?
- Why does it continue?
- Why does it have the effects that it does?
By repeatedly asking “ why ,” you’ll eventually get to the bottom of the problem. This is an important step in the problem-solving process because it ensures that you’re dealing with the root cause rather than just the symptoms.
Once you have a firm grasp on the issue, it is time to divide it into smaller, more manageable chunks. This makes tackling the problem easier and reduces the risk of becoming overwhelmed. For example, if you’re attempting to solve a complex business problem, you might divide it into smaller components like market research, product development, and sales strategies.
To summarise step 1, defining the problem is an important first step in effective problem-solving. You will be able to identify the root cause and break it down into manageable parts if you take the time to thoroughly understand the problem. This will prepare you for the next step in the problem-solving process, which is gathering information and brainstorming ideas.
Step 2 – Gather Information and Brainstorm Ideas

Gathering information and brainstorming ideas is the next step in effective problem solving. This entails researching the problem and relevant information, collaborating with others, and coming up with a variety of potential solutions. This increases your chances of finding the best solution to the problem.
Begin by researching the problem and relevant information. This could include reading articles, conducting surveys, or consulting with experts. The goal is to collect as much information as possible in order to better understand the problem and possible solutions.
Next, work with others to gather a variety of perspectives. Brainstorming with others can be an excellent way to come up with new and creative ideas. Encourage everyone to share their thoughts and ideas when working in a group, and make an effort to actively listen to what others have to say. Be open to new and unconventional ideas and resist the urge to dismiss them too quickly.
Finally, use brainstorming to generate a wide range of potential solutions. This is the place where you can let your imagination run wild. At this stage, don’t worry about the feasibility or practicality of the solutions; instead, focus on generating as many ideas as possible. Write down everything that comes to mind, no matter how ridiculous or unusual it may appear. This can be done individually or in groups.
Once you’ve compiled a list of potential solutions, it’s time to assess them and select the best one. This is the next step in the problem-solving process, which we’ll go over in greater detail in the following section.
Step 3 – Evaluate Options and Choose the Best Solution
Once you’ve compiled a list of potential solutions, it’s time to assess them and select the best one. This is the third step in effective problem solving, and it entails weighing the advantages and disadvantages of each solution, considering their feasibility and practicability, and selecting the solution that is most likely to solve the problem effectively.
To begin, weigh the advantages and disadvantages of each solution. This will assist you in determining the potential outcomes of each solution and deciding which is the best option. For example, a quick and easy solution may not be the most effective in the long run, whereas a more complex and time-consuming solution may be more effective in solving the problem in the long run.
Consider each solution’s feasibility and practicability. Consider the following:
- Can the solution be implemented within the available resources, time, and budget?
- What are the possible barriers to implementing the solution?
- Is the solution feasible in today’s political, economic, and social environment?
You’ll be able to tell which solutions are likely to succeed and which aren’t by assessing their feasibility and practicability.
Finally, choose the solution that is most likely to effectively solve the problem. This solution should be based on the criteria you’ve established, such as the advantages and disadvantages of each solution, their feasibility and practicability, and your overall goals.
It is critical to remember that there is no one-size-fits-all solution to problems. What is effective for one person or situation may not be effective for another. This is why it is critical to consider a wide range of solutions and evaluate each one based on its ability to effectively solve the problem.
Step 4 – Implement and Monitor the Solution

When you’ve decided on the best solution, it’s time to put it into action. The fourth and final step in effective problem solving is to put the solution into action, monitor its progress, and make any necessary adjustments.
To begin, implement the solution. This may entail delegating tasks, developing a strategy, and allocating resources. Ascertain that everyone involved understands their role and responsibilities in the solution’s implementation.
Next, keep an eye on the solution’s progress. This may entail scheduling regular check-ins, tracking metrics, and soliciting feedback from others. You will be able to identify any potential roadblocks and make any necessary adjustments in a timely manner if you monitor the progress of the solution.
Finally, make any necessary modifications to the solution. This could entail changing the solution, altering the plan of action, or delegating different tasks. Be willing to make changes if they will improve the solution or help it solve the problem more effectively.
It’s important to remember that problem solving is an iterative process, and there may be times when you need to start from scratch. This is especially true if the initial solution does not effectively solve the problem. In these situations, it’s critical to be adaptable and flexible and to keep trying new solutions until you find the one that works best.
To summarise, effective problem solving is a critical skill that can assist individuals and organisations in overcoming challenges and achieving their objectives. Effective problem solving consists of four key steps: defining the problem, generating potential solutions, evaluating alternatives and selecting the best solution, and implementing the solution.
You can increase your chances of success in problem solving by following these steps and considering factors such as the pros and cons of each solution, their feasibility and practicability, and making any necessary adjustments. Furthermore, keep in mind that problem solving is an iterative process, and there may be times when you need to go back to the beginning and restart. Maintain your adaptability and try new solutions until you find the one that works best for you.
- Novick, L.R. and Bassok, M., 2005. Problem Solving . Cambridge University Press.
Was this helpful?

Daniel Croft
Daniel Croft is a seasoned continuous improvement manager with a Black Belt in Lean Six Sigma. With over 10 years of real-world application experience across diverse sectors, Daniel has a passion for optimizing processes and fostering a culture of efficiency. He's not just a practitioner but also an avid learner, constantly seeking to expand his knowledge. Outside of his professional life, Daniel has a keen Investing, statistics and knowledge-sharing, which led him to create the website www.learnleansigma.com, a platform dedicated to Lean Six Sigma and process improvement insights.

8D (8 Disciplines)
What is the (PDCA) Plan, Do, Check, Act Cycle?
Free lean six sigma templates.
Improve your Lean Six Sigma projects with our free templates. They're designed to make implementation and management easier, helping you achieve better results.

5S Floor Marking Best Practices
In lean manufacturing, the 5S System is a foundational tool, involving the steps: Sort, Set…
How to Measure the ROI of Continuous Improvement Initiatives
When it comes to business, knowing the value you’re getting for your money is crucial,…
8D Problem-Solving: Common Mistakes to Avoid
In today’s competitive business landscape, effective problem-solving is the cornerstone of organizational success. The 8D…
The Evolution of 8D Problem-Solving: From Basics to Excellence
In a world where efficiency and effectiveness are more than just buzzwords, the need for…
8D: Tools and Techniques
Are you grappling with recurring problems in your organization and searching for a structured way…
How to Select the Right Lean Six Sigma Projects: A Comprehensive Guide
Going on a Lean Six Sigma journey is an invigorating experience filled with opportunities for…
- User Roles & Access
- FAQ’s
oboloo Articles
Mastering accounting practice problems: tips and tricks for success, introduction.
Are you ready to dive into the world of accounting practice problems ? Whether you’re a seasoned accountant or just starting out in your financial journey, these practice problems are an essential tool for sharpening your skills and expanding your knowledge. But don’t worry, we’ve got you covered! In this blog post, we’ll explore what accounting practice problems are all about and share some valuable tips and tricks that will help you conquer them with confidence. So grab your calculator and let’s get started on the path to mastering accounting practice problems!
What are accounting practice problems?
What are accounting practice problems ?
Accounting practice problems are exercises or scenarios that are designed to test your understanding and application of accounting principles and concepts. These problems typically involve analyzing financial data, preparing financial statements, and applying various accounting methods and techniques.
Solving accounting practice problems is an essential part of mastering the subject. They help you develop critical thinking skills, improve your problem-solving abilities, and enhance your overall understanding of accounting principles.
These problems can cover a wide range of topics, such as journal entries, adjusting entries, trial balances, income statements, balance sheets, cash flow statements , inventory valuation methods, depreciation calculations, and more. They require you to apply the rules and guidelines set forth by generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) or international financial reporting standards (IFRS).
By solving these practice problems regularly and effectively engaging with them through analysis and interpretation of financial data sets or case studies will enable you to gain confidence in tackling real-world accounting challenges. So don’t shy away from embracing these opportunities for growth!
Tips for solving accounting practice problems
Tips for Solving Accounting Practice Problems:
1. Understand the question: Before diving into solving accounting practice problems, it is crucial to fully comprehend what is being asked. Take your time to read and analyze the problem carefully. Look for keywords or specific instructions that can guide you in finding the appropriate solution.
2. Review relevant concepts: Accounting practice problems often require a solid understanding of fundamental accounting principles and concepts. Make sure you are familiar with topics such as balance sheets , income statements, debits and credits, and financial analysis techniques. If needed, refer back to your textbooks or online resources to refresh your knowledge.
3. Break down complex problems: Sometimes accounting practice problems may appear overwhelming due to their complexity or lengthiness. To tackle these challenges effectively, break them down into smaller manageable tasks . Identify each step required to reach the final answer and approach them one at a time.
4. Utilize real-world examples: Linking theoretical concepts with practical examples can enhance your understanding of accounting principles while solving practice problems . Try relating the given scenario with real-life situations or business operations to grasp how different transactions impact financial statements.
5. Practice regularly: The key to mastering any skill is consistent practice! Set aside dedicated study sessions where you solve various types of accounting practice problems regularly. The more exposure you have to different scenarios and calculations, the better equipped you will be during exams or when facing actual accounting challenges in professional settings.
Remember that solving accounting practice problems requires both technical knowledge and critical thinking skills. Stay patient, focused, and determined throughout the process as mastery comes through continuous efforts rather than overnight success!
Tricks for solving accounting practice problems
Tricks for Solving Accounting Practice Problems
When it comes to mastering accounting practice problems, having a few tricks up your sleeve can make all the difference. These tricks can help you approach complex scenarios with confidence and accuracy. Here are some tips to help you solve accounting practice problems more effectively .
1. Break it Down: When faced with a challenging problem, break it down into smaller, manageable parts . This will not only make the problem seem less daunting but also allow you to focus on each component individually.
2. Use Visual Aids: Sometimes, visualizing the problem can provide clarity and help identify patterns or relationships. Utilize charts, graphs, or diagrams to organize information visually and gain a better understanding of the situation at hand.
3. Apply Concepts: Always refer back to fundamental accounting concepts when solving practice problems. Understanding how different principles apply in specific scenarios will guide your decision-making process and ensure accurate solutions.
4. Practice Time Management: Time management is crucial when tackling accounting practice problems that have time constraints attached to them (such as exams). Allocate appropriate time for each question based on its complexity so that you can complete all tasks within the given timeframe.
5. Develop Problem-Solving Strategies: Over time, develop your own problem-solving strategies by analyzing past mistakes and learning from them. Identify common pitfalls or areas where you tend to get stuck and devise techniques specifically tailored to overcome these challenges.
6. Collaborate with Peers: Engaging in group study sessions or collaborating with peers who are also studying accounting can be beneficial for problem-solving skills development. Through discussions and sharing insights, you may discover alternative approaches or perspectives that enhance your abilities.
Remember that becoming proficient at solving accounting practice problems takes time and effort—there’s no substitute for regular practice! By implementing these tricks into your study routine, you’ll increase your efficiency in handling complex scenarios while building a solid foundation of knowledge in procurement accounting practices .
Resources for accounting practice problems
Resources for Accounting Practice Problems
When it comes to mastering accounting practice problems, having access to the right resources can make all the difference. Luckily, there are plenty of tools and materials available that can help you sharpen your skills and improve your problem-solving abilities. Here are a few resources worth exploring:
1. Online Tutorials: There are numerous websites and platforms that offer comprehensive tutorials on various accounting topics. These tutorials often include detailed explanations of concepts, step-by-step solutions to practice problems, and interactive quizzes to test your understanding.
2. Textbooks and Study Guides: Investing in a good accounting textbook or study guide can provide you with a wealth of practice problems. Look for books that offer clear explanations along with worked-out examples so you can learn from both correct and incorrect approaches.
3. Accounting Forums: Participating in online forums dedicated to accounting can be incredibly helpful when it comes to solving practice problems. You can post questions, seek guidance from experienced professionals or students, and engage in discussions about different problem-solving strategies.
4. Practice Exam Prep Books: Many publishers release specialized exam preparation books tailored specifically for accounting exams such as the CPA or CMA exams. These books typically include sets of practice problems designed to mimic real exam questions.
5. Educational Apps: Mobile apps have become increasingly popular tools for learning and practicing accounting concepts on-the-go. Look for apps that offer a wide range of practice problems with varying levels of difficulty.
Remember, consistently working through practice problems is essential if you want to excel in accounting . By utilizing these resources effectively , you’ll be well-equipped on your journey towards mastering accounting principles and becoming a proficient problem solver!
Mastering accounting practice problems is an essential skill for any aspiring accountant. By following the tips and tricks outlined in this article, you can improve your problem-solving abilities and gain confidence in tackling complex accounting scenarios.
Remember to start by understanding the basics of accounting principles and concepts. This foundation will provide you with a solid framework to approach any practice problem. Practice regularly using real-life examples or online resources specifically designed for accounting practice problems.
When solving these problems, be systematic and organized. Break down the question into smaller parts, identify relevant information , apply appropriate formulas or techniques, and double-check your work for accuracy. Utilize shortcuts and time-saving strategies where applicable to streamline your problem-solving process .
Additionally, take advantage of various resources available to enhance your learning experience. Online tutorials, textbooks, video lectures, and study groups can all contribute to sharpening your skills in solving accounting practice problems.
By adopting these strategies consistently over time, you will notice significant improvement in your ability to tackle even the most challenging accounting practice problems confidently.
So don’t let these problems intimidate you! Embrace them as opportunities for growth and mastery of this fundamental aspect of the field. With dedication and persistence, you’ll soon find yourself acing those tricky accounting questions with ease!
Happy problem-solving!

- Onsite training
3,000,000+ delegates
15,000+ clients
1,000+ locations
- KnowledgePass
- Log a ticket
01344203999 Available 24/7

What is Problem Solving? A Comprehensive Guide
In this blog, we will explore "What is Problem Solving?" In detail. From defining the nature of Problem Solving to understanding the key process in resolving issues, this blog covers it all. So, wait no more; let’s go deeper into this fundamental concept.

Exclusive 40% OFF
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Share this Resource
- Introduction to Management
- Personal & Organisational Development
- Workforce Resource Planning Training
- Supervisor Training
- Introduction to Managing Budgets

Table of contents
1) What is Problem Solving definition?
2) The process of Problem Solving
3) Key skills for effective Problem Solving
4) Strategies for enhancing Problem Solving abilities
5) Problem Solving tools and techniques
6) Conclusion
What is Problem Solving definition?

The process of Problem Solving
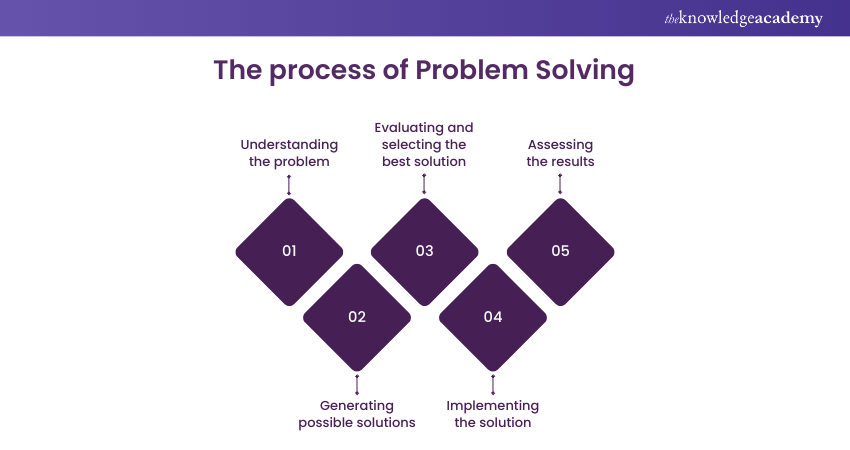
Understanding the problem
The first step in Problem Solving is gaining a clear understanding of the issue at hand. Take the time to thoroughly analyse the problem and gather relevant information. Ask yourself questions like:
1) What is the nature of the problem?
2) What are the factors contributing to the problem?
3) What are the desired outcomes?
4) Are there any constraints or limitations to consider?
By gaining a comprehensive understanding of the problem, you lay a solid foundation for finding an effective solution.
Generating possible solutions
Once you have a clear grasp of the problem, it's time to brainstorm potential solutions. Encourage creativity and think outside the box. Consider all possible options without judgment or criticism. The goal at this stage is to generate a variety of ideas and alternatives.
Evaluating and selecting the best solution
After generating a list of possible solutions, it's important to evaluate each option based on its feasibility, effectiveness, and alignment with the desired outcome. Consider the advantages and disadvantages of each and every solution. Assess its practicality and the resources required for implementation.
Additionally, take into account the potential risks and benefits associated with each solution. Consider any potential consequences or impacts on other aspects. Based on this evaluation, select the solution that appears most viable and promising.
Implementing the solution
Once you have chosen the best solution, it's time to put it into action. Develop a detailed plan outlining the necessary steps and allocate the required resources. Determine responsibilities and deadlines to ensure a smooth implementation process.
During implementation, monitor progress and make any necessary adjustments or adaptations. Stay proactive and address any challenges or obstacles that may arise along the way. Effective communication and collaboration with others involved in the process can greatly contribute to successful implementation.
Assessing the results
After implementing the solution, it's essential to assess the results. Evaluate whether the problem has been properly resolved or if further adjustments are required. Analyse the outcomes and compare them against the desired goals and expectations.
Consider whether the chosen solution has brought about the intended benefits and if any unexpected consequences have emerged. Reflect on the overall effectiveness of the Problem Solving process and identify any lessons learned for future reference.
Remember, Problem Solving is an iterative process, and it's not uncommon to revisit and refine solutions based on ongoing evaluation and feedback. Embrace a continuous improvement mindset and be open to seeking alternative approaches if necessary.
By following this Problem Solving process, you can approach challenges systematically and increase your chances of finding effective solutions. Remember that practice and experience play a vital role in honing your skills.
Master the art of solving problems and become a catalyst for innovation and success with our Problem Solving Training – sign up now!
Key skills for effective Problem Solving
What one must do to become an effective problem solver is to develop key skills that enhance your Problem Solving abilities. The skills give you the ability to tackle challenges with a strategic mind and find the needed solutions. Below is a dive into the most important of them:
Critical thinking
Critical thinking is a skill that includes the objective analysis of information, considering different viewpoints, and being able to arrive at a sensible judgment. This helps you to assess problems with the right accuracy in judgment and also find suitable solutions.
It means that creativity is the ability of a person to think outside the box and come up with innovative solutions. It includes pressing the mind toward new possibilities and viewing the problem in different ways.
Analytical skills
In this ability, there is the aspect of breaking down a problem into subunits that helps in identifying the patterns, relationships, and causes within the problem.
Decision-making
Sound skills in decision making call for the assessment of the pros and cons of all solutions provided and thus choosing the best alternative. Risks must always be considered with the benefits any alternative might bring.
Strategies for enhancing Problem Solving abilities
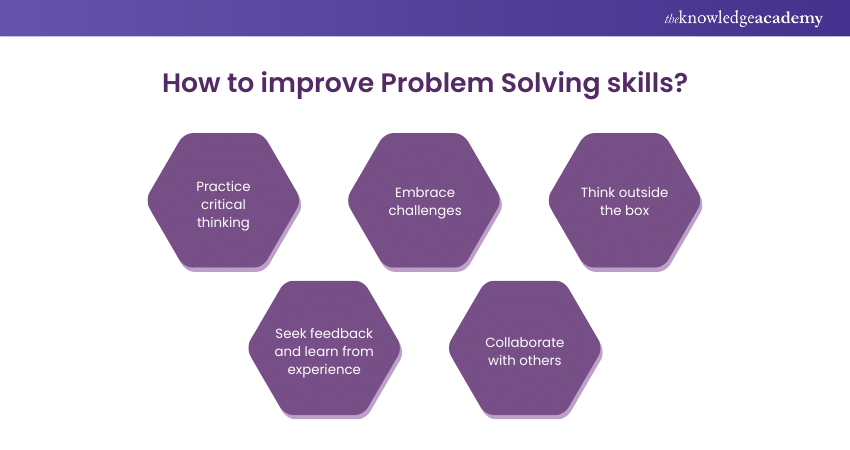
Practice critical thinking
Engage yourself in activities which require critical thinking, including solving puzzles, complex discussion, challenging all assumptions. This will increase your ability to enhance sharpening of your analytical skills and let you think critically at a time when problems are in your way.
Seek feedback and learn from experience
Seek responses from your mentors, course peers, and Problem Solving experts. From the successes and failures, reflect on the reasons for the occurrences over previous experiences and point out what could be improved. Treat the opportunity of Problem Solving as one of the chances that shall be given to you to grow and develop each time you make it through a problem.
Embrace challenges
You can redesign your problematic issues and take every challenge coming across as an opportunity for growth. Hence, it paves the way for the ability of resilience and strengthens your Problem Solving abilities.
Collaborate with others
In Problem Solving, collaboration is embraced by pooling different perspectives and ideas. Work with others in activities that involve groups to discuss issues and seek input from others, listening actively to various viewpoints. Working collaboratively with others helps expand your knowledge of various ways of Problem Solving and encourages innovation.
Think outside the box
Encourage creative thinking by exploring unconventional ideas and solutions. Challenge every assumption and all its related alternatives. Shift to this kind of mindset, and it can drive innovative Problem Solving strategies, letting you uncover newer ways to solve age-old complex problems.
Problem Solving tools and techniques
When faced with complex problems, utilising specific tools and techniques can help facilitate the solving process and lead to more effective solutions. Here are some commonly used Problem Solving tools and techniques:
Root cause analysis
Root cause analysis is a methodology used to detect the underlying causes of a problem. It involves investigating the problem's symptoms and tracing them back to their fundamental causes. By addressing the root causes, Problem Solvers can prevent the issue from recurring.
Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats (SWOT) analysis
SWOT analysis is a planning tool that strategically helps measure the weaknesses and internal strengths of a situation. Moreover, it can find external opportunities and threats. By assessing these factors, Problem Solvers can gain insights into the current state and make informed decisions about potential solutions.
Fishbone diagrams
Fishbone diagrams, also known as cause-and-effect diagrams or Ishikawa Diagrams, visually represent the possible causes contributing to a problem. By organising causes into categories (such as people, process, equipment, and environment), Problem Solvers can systematically analyse the problem's potential sources.
Decision matrices
Decision matrices are used to evaluate and compare different options based on multiple criteria. This tool helps Problem Solvers weigh the importance of various factors and objectively assess each alternative, leading to an informed decision.
Six Thinking Hats
Six Thinking Hats is a technique initially developed by Edward de Bono that encourages parallel thinking by exploring different perspectives. Each "hat" represents a different thinking approach (e.g., logical, creative, emotional), allowing Problem Solvers to consider diverse viewpoints and generate innovative solutions.
These are just a few examples of Problem Solving tools and techniques. Depending on the nature of the problem, other methods, such as brainstorming, mind mapping, flowcharts, or Pareto analysis, can also be applied. Choosing the appropriate tool or technique depends on the specific problem and the desired outcome.
Navigate conflicts with finesse and foster collaboration with our transformative Conflict Management Training – sign up today!
Conclusion
We hope you read and understand everything about What is Problem Solving? Developing effective skills is crucial for overcoming challenges, making informed decisions, and achieving success. By embracing problems as opportunities and applying strategic approaches, individuals can become proficient Problem Solvers in various domains of life.
Unlock your management potential and elevate your skills to new heights with our cutting-edge Management Courses – sign up now!
Frequently Asked Questions
There are two major types of Problem Solving: Reflective and Creative. Regardless of the type, it focuses on understanding the issues, considering all factors and finding a solution.
Problem Solving in the workplace refers to an individual’s ability to manage difficult situations and find solutions to complex business issues.
The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs , videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA .
The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass , a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
The Knowledge Academy offers various Management Courses including Business Process Improvement Training, Performance Management Training and Introduction to Managing People. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Resource Planning Template .
Our Business Skills Blogs cover a range of topics related to musical instruments, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your skills as a Music Producer, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Fri 23rd Aug 2024
Fri 11th Oct 2024
Fri 13th Dec 2024
Get A Quote
WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
My employer
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry
- Business Analysis
- Lean Six Sigma Certification
Share this course
Our biggest spring sale.

We cannot process your enquiry without contacting you, please tick to confirm your consent to us for contacting you about your enquiry.
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry.
We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Or select from our popular topics
- ITIL® Certification
- Scrum Certification
- Change Management Certification
- Business Analysis Courses
- Microsoft Azure Certification
- Microsoft Excel Courses
- Microsoft Project
- Explore more courses
Press esc to close
Fill out your contact details below and our training experts will be in touch.
Fill out your contact details below
Thank you for your enquiry!
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go over your training requirements.
Back to Course Information
Fill out your contact details below so we can get in touch with you regarding your training requirements.
* WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
Preferred Contact Method
No preference
Back to course information
Fill out your training details below
Fill out your training details below so we have a better idea of what your training requirements are.
HOW MANY DELEGATES NEED TRAINING?
HOW DO YOU WANT THE COURSE DELIVERED?
Online Instructor-led
Online Self-paced
WHEN WOULD YOU LIKE TO TAKE THIS COURSE?
Next 2 - 4 months
WHAT IS YOUR REASON FOR ENQUIRING?
Looking for some information
Looking for a discount
I want to book but have questions
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go overy your training requirements.
Your privacy & cookies!
Like many websites we use cookies. We care about your data and experience, so to give you the best possible experience using our site, we store a very limited amount of your data. Continuing to use this site or clicking “Accept & close” means that you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about our privacy policy and cookie policy cookie policy .
We use cookies that are essential for our site to work. Please visit our cookie policy for more information. To accept all cookies click 'Accept & close'.

Effective Problem-Solving Techniques in Business
Problem solving is an increasingly important soft skill for those in business. The Future of Jobs Survey by the World Economic Forum drives this point home. According to this report, complex problem solving is identified as one of the top 15 skills that will be sought by employers in 2025, along with other soft skills such as analytical thinking, creativity and leadership.
Dr. Amy David , clinical associate professor of management for supply chain and operations management, spoke about business problem-solving methods and how the Purdue University Online MBA program prepares students to be business decision-makers.
Why Are Problem-Solving Skills Essential in Leadership Roles?
Every business will face challenges at some point. Those that are successful will have people in place who can identify and solve problems before the damage is done.
“The business world is constantly changing, and companies need to be able to adapt well in order to produce good results and meet the needs of their customers,” David says. “They also need to keep in mind the triple bottom line of ‘people, profit and planet.’ And these priorities are constantly evolving.”
To that end, David says people in management or leadership need to be able to handle new situations, something that may be outside the scope of their everyday work.
“The name of the game these days is change—and the speed of change—and that means solving new problems on a daily basis,” she says.
The pace of information and technology has also empowered the customer in a new way that provides challenges—or opportunities—for businesses to respond.
“Our customers have a lot more information and a lot more power,” she says. “If you think about somebody having an unhappy experience and tweeting about it, that’s very different from maybe 15 years ago. Back then, if you had a bad experience with a product, you might grumble about it to one or two people.”
David says that this reality changes how quickly organizations need to react and respond to their customers. And taking prompt and decisive action requires solid problem-solving skills.

What Are Some of the Most Effective Problem-Solving Methods?
David says there are a few things to consider when encountering a challenge in business.
“When faced with a problem, are we talking about something that is broad and affects a lot of people? Or is it something that affects a select few? Depending on the issue and situation, you’ll need to use different types of problem-solving strategies,” she says.
Using Techniques
There are a number of techniques that businesses use to problem solve. These can include:
- Five Whys : This approach is helpful when the problem at hand is clear but the underlying causes are less so. By asking “Why?” five times, the final answer should get at the potential root of the problem and perhaps yield a solution.
- Gap Analysis : Companies use gap analyses to compare current performance with expected or desired performance, which will help a company determine how to use its resources differently or adjust expectations.
- Gemba Walk : The name, which is derived from a Japanese word meaning “the real place,” refers to a commonly used technique that allows managers to see what works (and what doesn’t) from the ground up. This is an opportunity for managers to focus on the fundamental elements of the process, identify where the value stream is and determine areas that could use improvement.
- Porter’s Five Forces : Developed by Harvard Business School professor Michael E. Porter, applying the Five Forces is a way for companies to identify competitors for their business or services, and determine how the organization can adjust to stay ahead of the game.
- Six Thinking Hats : In his book of the same name, Dr. Edward de Bono details this method that encourages parallel thinking and attempting to solve a problem by trying on different “thinking hats.” Each color hat signifies a different approach that can be utilized in the problem-solving process, ranging from logic to feelings to creativity and beyond. This method allows organizations to view problems from different angles and perspectives.
- SWOT Analysis : This common strategic planning and management tool helps businesses identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats (SWOT).
“We have a lot of these different tools,” David says. “Which one to use when is going to be dependent on the problem itself, the level of the stakeholders, the number of different stakeholder groups and so on.”
Each of the techniques outlined above uses the same core steps of problem solving:
- Identify and define the problem
- Consider possible solutions
- Evaluate options
- Choose the best solution
- Implement the solution
- Evaluate the outcome
Data drives a lot of daily decisions in business and beyond. Analytics have also been deployed to problem solve.
“We have specific classes around storytelling with data and how you convince your audience to understand what the data is,” David says. “Your audience has to trust the data, and only then can you use it for real decision-making.”
Data can be a powerful tool for identifying larger trends and making informed decisions when it’s clearly understood and communicated. It’s also vital for performance monitoring and optimization.
How Is Problem Solving Prioritized in Purdue’s Online MBA?
The courses in the Purdue Online MBA program teach problem-solving methods to students, keeping them up to date with the latest techniques and allowing them to apply their knowledge to business-related scenarios.
“I can give you a model or a tool, but most of the time, a real-world situation is going to be a lot messier and more valuable than what we’ve seen in a textbook,” David says. “Asking students to take what they know and apply it to a case where there’s not one single correct answer is a big part of the learning experience.”
Make Your Own Decision to Further Your Career
An online MBA from Purdue University can help advance your career by teaching you problem-solving skills, decision-making strategies and more. Reach out today to learn more about earning an online MBA with Purdue University .
If you would like to receive more information about pursuing a business master’s at the Mitchell E. Daniels, Jr. School of Business, please fill out the form and a program specialist will be in touch!
Connect With Us

What is Problem Solving? (Steps, Techniques, Examples)
By Status.net Editorial Team on May 7, 2023 — 5 minutes to read
What Is Problem Solving?
Definition and importance.
Problem solving is the process of finding solutions to obstacles or challenges you encounter in your life or work. It is a crucial skill that allows you to tackle complex situations, adapt to changes, and overcome difficulties with ease. Mastering this ability will contribute to both your personal and professional growth, leading to more successful outcomes and better decision-making.
Problem-Solving Steps
The problem-solving process typically includes the following steps:
- Identify the issue : Recognize the problem that needs to be solved.
- Analyze the situation : Examine the issue in depth, gather all relevant information, and consider any limitations or constraints that may be present.
- Generate potential solutions : Brainstorm a list of possible solutions to the issue, without immediately judging or evaluating them.
- Evaluate options : Weigh the pros and cons of each potential solution, considering factors such as feasibility, effectiveness, and potential risks.
- Select the best solution : Choose the option that best addresses the problem and aligns with your objectives.
- Implement the solution : Put the selected solution into action and monitor the results to ensure it resolves the issue.
- Review and learn : Reflect on the problem-solving process, identify any improvements or adjustments that can be made, and apply these learnings to future situations.
Defining the Problem
To start tackling a problem, first, identify and understand it. Analyzing the issue thoroughly helps to clarify its scope and nature. Ask questions to gather information and consider the problem from various angles. Some strategies to define the problem include:
- Brainstorming with others
- Asking the 5 Ws and 1 H (Who, What, When, Where, Why, and How)
- Analyzing cause and effect
- Creating a problem statement
Generating Solutions
Once the problem is clearly understood, brainstorm possible solutions. Think creatively and keep an open mind, as well as considering lessons from past experiences. Consider:
- Creating a list of potential ideas to solve the problem
- Grouping and categorizing similar solutions
- Prioritizing potential solutions based on feasibility, cost, and resources required
- Involving others to share diverse opinions and inputs
Evaluating and Selecting Solutions
Evaluate each potential solution, weighing its pros and cons. To facilitate decision-making, use techniques such as:
- SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats)
- Decision-making matrices
- Pros and cons lists
- Risk assessments
After evaluating, choose the most suitable solution based on effectiveness, cost, and time constraints.
Implementing and Monitoring the Solution
Implement the chosen solution and monitor its progress. Key actions include:
- Communicating the solution to relevant parties
- Setting timelines and milestones
- Assigning tasks and responsibilities
- Monitoring the solution and making adjustments as necessary
- Evaluating the effectiveness of the solution after implementation
Utilize feedback from stakeholders and consider potential improvements. Remember that problem-solving is an ongoing process that can always be refined and enhanced.
Problem-Solving Techniques
During each step, you may find it helpful to utilize various problem-solving techniques, such as:
- Brainstorming : A free-flowing, open-minded session where ideas are generated and listed without judgment, to encourage creativity and innovative thinking.
- Root cause analysis : A method that explores the underlying causes of a problem to find the most effective solution rather than addressing superficial symptoms.
- SWOT analysis : A tool used to evaluate the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to a problem or decision, providing a comprehensive view of the situation.
- Mind mapping : A visual technique that uses diagrams to organize and connect ideas, helping to identify patterns, relationships, and possible solutions.
Brainstorming
When facing a problem, start by conducting a brainstorming session. Gather your team and encourage an open discussion where everyone contributes ideas, no matter how outlandish they may seem. This helps you:
- Generate a diverse range of solutions
- Encourage all team members to participate
- Foster creative thinking
When brainstorming, remember to:
- Reserve judgment until the session is over
- Encourage wild ideas
- Combine and improve upon ideas
Root Cause Analysis
For effective problem-solving, identifying the root cause of the issue at hand is crucial. Try these methods:
- 5 Whys : Ask “why” five times to get to the underlying cause.
- Fishbone Diagram : Create a diagram representing the problem and break it down into categories of potential causes.
- Pareto Analysis : Determine the few most significant causes underlying the majority of problems.
SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis helps you examine the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats related to your problem. To perform a SWOT analysis:
- List your problem’s strengths, such as relevant resources or strong partnerships.
- Identify its weaknesses, such as knowledge gaps or limited resources.
- Explore opportunities, like trends or new technologies, that could help solve the problem.
- Recognize potential threats, like competition or regulatory barriers.
SWOT analysis aids in understanding the internal and external factors affecting the problem, which can help guide your solution.
Mind Mapping
A mind map is a visual representation of your problem and potential solutions. It enables you to organize information in a structured and intuitive manner. To create a mind map:
- Write the problem in the center of a blank page.
- Draw branches from the central problem to related sub-problems or contributing factors.
- Add more branches to represent potential solutions or further ideas.
Mind mapping allows you to visually see connections between ideas and promotes creativity in problem-solving.
Examples of Problem Solving in Various Contexts
In the business world, you might encounter problems related to finances, operations, or communication. Applying problem-solving skills in these situations could look like:
- Identifying areas of improvement in your company’s financial performance and implementing cost-saving measures
- Resolving internal conflicts among team members by listening and understanding different perspectives, then proposing and negotiating solutions
- Streamlining a process for better productivity by removing redundancies, automating tasks, or re-allocating resources
In educational contexts, problem-solving can be seen in various aspects, such as:
- Addressing a gap in students’ understanding by employing diverse teaching methods to cater to different learning styles
- Developing a strategy for successful time management to balance academic responsibilities and extracurricular activities
- Seeking resources and support to provide equal opportunities for learners with special needs or disabilities
Everyday life is full of challenges that require problem-solving skills. Some examples include:
- Overcoming a personal obstacle, such as improving your fitness level, by establishing achievable goals, measuring progress, and adjusting your approach accordingly
- Navigating a new environment or city by researching your surroundings, asking for directions, or using technology like GPS to guide you
- Dealing with a sudden change, like a change in your work schedule, by assessing the situation, identifying potential impacts, and adapting your plans to accommodate the change.
- How to Resolve Employee Conflict at Work [Steps, Tips, Examples]
- How to Write Inspiring Core Values? 5 Steps with Examples
- 30 Employee Feedback Examples (Positive & Negative)

Accounting Problems (& Answers): How to Avoid Accounting Issues
Keeping up with technology and regulatory changes are significant concerns of 51% and 24%, respectively, of CPA and accounting firm survey participants, according to Accounting Today’s survey, The Year Ahead: 2022 in Numbers .
Delays in advanced software technology adoption and failures in regulatory compliance can lead to accounting challenges and problems for businesses. These accounting issues include errors in financial statements, fraud and security risks, and the potential for massive fines and imprisonment for regulatory non-compliance.
Trained business finance teams using advanced software technology that also automates regulatory compliance can overcome typical (and new) accounting problems.
What are Accounting Problems?
Accounting problems are issues resulting in material financial statement errors, undetected fraud due to inadequate internal control, misapplication of generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP accounting standards), regulatory noncompliance, and cybersecurity risks. Accounting problems may have unfavorable cash flow impacts and misstate business profitability.
What Causes Accounting Problems?
Some accounting problems are caused by using outdated software technology for accounting. Intentional fraud due to greed and poor internal control causes other financial issues. Low staffing levels can cause accounting problems. Not training the financial team causes accounting problems related to improperly applying GAAP.
The business must defend itself against cybersecurity attacks and stay up-to-date on changing regulatory compliance issues.
How do Businesses Solve Accounting Problems?
Financial professionals in businesses should use software with advanced technology capable of handling current accounting standards, including revenue recognition and lease accounting, and regulatory requirements to avoid or solve significant accounting problems.
Requiring CPA employees and accountants to take relevant continuing education courses regularly can also help businesses solve accounting problems. Adequate staffing levels help accountants solve accounting issues.
Top management must communicate an ethical tone, corporate values, employee empowerment, and key expectations.
11 Common Accounting Problems
In its fiscal year 2021, the SEC received 1,913 whistleblower complaints relating to corporate disclosures and financials, signaling possible accounting problems in these publicly-held businesses. The SEC also received whistleblower complaints related to the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act.
11 common accounting problems are:
- Revenue recognition
- Lease accounting
- Missing impairment write-downs
- Payroll errors
- Cash flow statement
- Outdated accounting software technology
- Not enough financial analysis
- Inadequate internal control
- Regulatory non-compliance
- Inadequate security
1. Revenue Recognition
Improperly applying GAAP revenue recognition standards, creating fraudulent revenue schemes, including improper accounting for consignments and third-party inventory shipments beyond the level of possible usage, and using unreasonable estimates, are revenue recognition problems.
CFODive published an article on August 20, 2020 (based on an Accounting Today analysis) titled Improper revenue recognition tops SEC fraud cases . This article highlights the significance of revenue recognition as an accounting problem.
Find an accounting software or ERP solution that helps your company achieve proper revenue recognition. Your accounting and finance teams need adequate training on FASB accounting standards to comply with GAAP revenue recognition. Excel spreadsheets are popular. But spreadsheets are error-prone and inefficient. If possible, seek a different software solution.
2. Lease Accounting
Changes to GAAP lease accounting standards require lessee companies to capitalize their operating leases with tenant right of use (ROU) and a term of over twelve months. Shorter operating leases (including office space leases) can still be recorded monthly as rent expenses. The leases are amortized over time.
Accounting standards are codified by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB). Accountants must also follow other changes to the Lease accounting standard.
Business accounting teams need adequate training to follow the latest GAAP standards on Lease accounting. And they will benefit greatly by using specialized lease accounting software.
3. Impairment Write-downs and Fair Market Valuation
Accountants may miss making impairment write-downs or required adjustments for recording required assets or liabilities at a fair market valuation.
Changing economic and business conditions require accountants to periodically assess whether asset valuations have been impaired (to recognize the loss of value). Accountants must also consider adjustments to the fair value of certain assets and liabilities. Accounting professionals make adjustments through journal entries and financial statement disclosures when GAAP requires.
Supply chain backlogs and economic conditions resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic triggered accounting issues to watch for, including impairment and fair value accounting, according to EY, a top-tier accounting firm.
Examples of asset impairment include:
- Assessing goodwill from M&A transactions annually for impairment
- Considering capitalized lease asset impairment
- Recording inventory at the lower of cost or market (LCM), where market value is constrained by an upper range not exceeding net realizable value and a lower range of net realizable value less a normal profit margin.
Examples of fair market valuation include:
- Trading securities (debt and equity) held as short-term investments; gains or losses on trading securities flow to Net Income on the income statement
- Available-for-sale securities (debt and equity) held as investments to be sold before maturity; net gains or losses are included in Shareholders’ Equity as Other Comprehensive Income (Loss), listed below Retained Earnings
- Liabilities measured under ASC 820 Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures
Accountants must have adequate training to properly record asset impairments and fair market valuation when required by GAAP and make necessary financial statement disclosures. Research financial statement areas subject to accounting issues with impairment.
4. Payroll Errors
If a small business decides to calculate its own payroll, payroll taxes, and benefits, it’s possible that payment errors and accounting problems will occur. Payroll problems like miscalculating paychecks for salary expenses and hourly wages hurt employee morale and productivity.
Outsource payroll to a very experienced company providing those services, like ADP or Paychex. If the right number of hours and payroll information is provided, payments and taxes withheld should be correctly computed and compliant with tax laws. You can expect accurate reports to account for those items. Your business can make payroll tax remittances on time when due.
5. Cash Flow Statement
The cash flow statement may include errors in classification by activity type and may not include restricted cash, a newer GAAP requirement.
Cash flow statement classification errors may include misclassifying the type of activity for interest and dividends received and paid. Interest received and paid is an operating activity in the cash flow statement. Dividends received are an operating activity, and dividends paid are a financing activity in the cash flow statement.
The CPA firm, RSM, summarizes U.S. GAAP (vs IFRS) classification for certain items in the cash flow statement, including interest and dividends and restricted cash.
Cash flow statement problem solving requires keeping up to date with FASB updates and training topics related to cash flow statement preparation to understand the basics.
6. Outdated Accounting Software Technology
Outdated accounting software technology isn’t efficient, doesn’t provide real-time results for visibility in managing the company or its sales & marketing processes, relies on manual data entry and paper documents for business transaction processing and recording, and doesn’t automate regulatory compliance.
Outdated ERP systems may not be cloud-based. On-premises software systems cause inefficiencies in accessing the software and require more IT department resources to update the system and address software and hardware problems at the company’s location. These ERP systems not deployed on the cloud aren’t ideal for the changed reality of remote or hybrid work situations.
Upgrade outdated software technology in accounting software or ERP systems by changing to modern cloud-based software. If you don’t have the budget for an ERP system overhaul, consider integrating third-party add-on software to meet your needs for:
- AP automation and global mass payments software, also automating regulatory compliance
- Subscription billing (applicable to a SaaS , publishing, or utilities business model)
- Forecasting, planning, and cash management software
- Customer relationship management (CRM) software to increase efficiency and better track the sales and marketing process
- Lease accounting specialty software
- Revenue recognition software functionality, if not included in your ERP
- Data visualization software for data analytics and business intelligence
7. Not Enough Financial Analysis
An accounting team without efficient accounting systems is spending too much time closing the books, leaving less time for value-added work. Financial analysis adds value by calculating ratios, spotting and managing business trends, and providing decision support for new opportunities.
Use enhanced cloud-based ERP systems and third-party add-on software with built-in artificial intelligence/machine learning that automates accounting processes and financial analysis to the extent possible. You need real-time dashboards with your company’s KPIs (key performance indicators), including trend analysis that all functional areas with authorization privileges can access.
Supplement these systems with data visualization software like Tableau or Microsoft Power BI for data analytics with real-time capabilities and periodic automated report runs for data your company follows as timeline trends. Data visualization software embeds machine learning tools to deliver business intelligence.
8. Inadequate Internal Control
Small businesses may not have enough staffing to attain the separation of duties needed for adequate internal control. Their accounting systems may be inadequate to prevent fraud and duplicate payment errors.
When segregation of duties isn’t being achieved, get the business owner involved in the approval process as a matched vendor invoice document reviewer and second signature.
The finance and accounting department needs the human capital and software resources required to perform its duties and achieve results. Is the accounting department getting its fair share of company resources?
Custody of Assets
Custody of assets includes recorded balance sheet assets and assets not yet recorded in the books like undeposited cash.
Inventory needs controls for proper receiving, custody, secured storage with controlled access, and physical inventory in full annually and via periodic cycle counts. Office equipment should also be tagged upon receipt and subject to a physical inventory. As stated earlier, inventory should be tested for any loss in value requiring a write-down.
Discrepancies in the balance of fixed assets may result from a physical fixed asset count. Set a proper cutoff for recording fixed asset purchases.
If a fixed asset isn’t recorded, look for the purchase documents and invoice to record it. If another fixed asset isn’t counted, investigate where it may be or if it was sold. For accounting purposes, record the difference between the book value of fixed assets net of accumulated depreciation and sale proceeds, computing gain or loss on the sale of fixed assets. Write off missing fixed assets if necessary after your investigation.
Fraud, including embezzlement, may result from inadequate internal control and employee collusion.
Use modern cloud-based automation software that helps you find fraud and errors like duplicate payments. Use variance analysis and followup on significant differences for budget vs actual expenses. Review vendor master files, perform 3-way document matching for invoices, and validate vendors for authenticity before paying them.
Strive to achieve adequate segregation of duties with employee task assignments. Control or custody of assets and recording transactions in the books need to be performed by different employees.
10. Regulatory Non-Compliance
Regulatory compliance covers different areas, including taxation, data privacy and security, sanctions lists like OFAC, and the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA).
The Foreign Corrupt Practices Act covers not making bribes in foreign countries. And the FCPA’s scope goes far beyond preventing bribes.
Violations of the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act and other regulations could result in:
- Massive fines for companies and convicted individuals
- Imprisonment
- Tarnishing a company’s and convicted individual’s business reputation and ethics
Familiarize your company, including the financial and accounting staff, with regulatory issues applying to your industry and company. Perform a project to document regulatory concerns and distribute the results widely. Hold a training session for company employees. Emphasize company values that include being ethical and empowering employees to act as the “conscience of the company.”
Find an automation software solution handling regulatory compliance. Tipalti AP automation software includes automated regulatory compliance features.
11. Inadequate Security
Cybersecurity is a significant issue that can compromise business intellectual property and customer data and employee records in your system.
Implement the most advanced cybersecurity software. Create and distribute an up-to-date company policy on required steps for achieving adequate cybersecurity. Train employees on how to avoid email and other scans that can result in hacks compromising company security.
Using Automation to Solve Accounting Problems
You can solve some accounting problems and become more efficient by applying accounting automation software. AP automation will provide significant benefits for your business.
Accounting Automation Software Applications
Businesses can deploy accounting automation in several areas to improve accounting processes and results. Accounting systems automation includes efficient financial technology (FinTech) applied to vendor invoice processing and payments and customer billing and accounts receivable.
Automate subscription billing, if applicable to your business model. Use automated customer credit decision solutions to decide which customers will be offered accounts receivable instead of requiring cash payments upfront.
Integrate CRM and marketing automation software like Salesforce and Marketo to improve sales & marketing processes and convert more new customers.
Automate forecasting, budgeting, business planning, and cash flow management.
AP Automation Software Benefits
Gain time to perform financial analysis by closing the books sooner. You can accomplish this by automating routine accounting processes like accounts payable and global mass payments with add-on AP automation software accessed via ERP integration.
Automated systems provide outsized benefits in the areas of payables automation and global mass payments to suppliers, vendors, and payouts to independent contractors, including freelancers and affiliates, and royalty recipients. Automated systems improve cash flow . They increase efficiency to let your company process vendor invoices and pay in time to take lucrative early payment discounts .
The best add-on AP automation and global mass payments software:
- Automates supplier onboarding and tax compliance
- Scans with OCR technology or uploads invoices and supporting documents electronically
- Improves your company’s expense management
- Makes efficient batch payments using a choice of payment methods
- Automates payments reconciliation and adds more accounts payable reports
- Lets your company close its books faster during the accounting cycle
- Reduces fraud and errors
- Automates regulatory compliance
Using electronic documents instead of paper-based documents:
- Ends paper-based data entry, invoice matching, and processing costs
- Creates a relevant document repository through the supplier portal
- Creates an audit trail
- Enables automatic approvals with notifications and follow-up
- Makes efficient batch payments (or single payments)
- Ends the inefficient, unsafe, and costly use of paper checks
- Automatically reconciles batch payments
The level of resources required in accounting and bookkeeping can be leveraged by efficiencies provided by AP automation software. Efficiency is improved by up to 80%. Books are closed much more quickly, letting the finance team spend more time on value-added financial analysis and decision support.
Cloud-based AP automation software using AI/ML and RPA and tools for regulatory compliance work in combination with ERP systems.
Real-time SaaS automation software and ERP systems with modern technology can prevent or solve several types of accounting problems and issues, including fraud, accounting errors related to vendor invoices and payments, GAAP compliance in financial reporting, and regulatory compliance.
And adequate training of the finance and accounting team prevents or solves accounting problems.
About the Author
Barbara Cook
RELATED ARTICLES
Top Accounting Problems & Solutions in 2024
Accounting problems have never been an easy issue to solve, but today presents some unique challenges. The IRS is ramping up its compliance and audit efforts while cross-border trade and transactions increase complexity for firms of all sizes. Although the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) claims to be trying to keep GAAP accounting requirements nimble and less burdensome, those at the tail end of their decisions often feel differently.
But today’s era in accounting offers new solutions to old and ongoing problems in accounting. Artificial intelligence, finance automation software , and streamlined data analytics combine with simpler payment processing methods and other next-gen tech to make your accounting team’s lives easier.
Still, though some issues in accounting are new based on shifting times, others are constant and have plagued executives for decades. Work with your team to understand some of today’s top accounting problems - and how to best address them.
What Are Accounting Problems?
Accounting problems range in severity, complexity, and frequency. But, while the details vary, the core definition of accounting problems doesn’t. Accounting problems are any identifiable, preventable accounting factor that contributes directly to a tangible negative outcome within your business, including:
- Inaccurate financial statements and regulatory filings.
- Physical and digital security risks, including fraud.
- Outdated accounting standards usage.
- Negative audit outcomes.
The keyword in our definition is preventable . Other factors, unforeseen and unpredictable, can impact your business negatively. The trick with managing accounting problems is that each of them is avoidable - if you have the knowledge, foresight, and tools to combat them,
What Causes Accounting Problems?
The root cause of every accounting problem is implied above - if you don’t have the knowledge, foresight, or tools to fight accounting problems, you’re not equipped to deal with them before they arise.
Beyond conceptual causes, though, material causes include (among many others):
- Lacking internal controls contributing to unnoticed human error and fraud.
- Financial teams not conducting regular training or keeping abreast of changing regulations and reporting standards.
- “Single points of failure,” where your financial and accounting cycle relies on a sole individual whether due to staffing concerns, competency, or training.
- Ethical causes that contribute to fraud, or even “soft fraud” wherein employees creatively interpret information to paint an artificially rosy picture.
The Top Ten Accounting Problems
No organization is perfect, and chances are high that your firm needs improvement within at least one of these domains. That isn’t bad, though - what’s bad is identifying an issue and not acting upon it. Remember, the first step in addressing your accounting problems is developing the knowledge to identity and act upon them, so understanding where your firm falls short kickstarts the process of optimizing your enterprise.
The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) is ramping up its enforcement efforts and prosecuted 9% more enforcement violations in 2022 than last year. Remember, the SEC won’t accept ignorance as an excuse for mismanaging accounting problems, and neither should you.
1. Human Error and Inaccurate Data Entry
Human error is the most common accounting problem, costing corporations millions of dollars annually. Manually managing thousands of lines of transactional accounting isn’t easy, and time pressure coupled with exhaustion can create sloppiness that creates a catastrophic snowball effect over time. These problems range from simple, such as double vendor payments , to far more difficult to untangle, like inadvertently missing payroll.
Solution: Accounting automation tools with baked-in validation checks and error notifications go a long way towards removing human error elements from the equation but aren’t a final solution. You’ll still need to implement robust staff training, both during onboarding and on an ongoing refresher basis. Third-party or automated audits , reviews, and reconciliation also help as a set of fresh eyes might catch errors those with skin in the game (or simple stat exhaustion) cannot.
2. Cash Flow Management and Statement Accuracy
Your income statement might paint a rosy picture, but if you can’t manage your cash flow, you’re in trouble - especially as higher rates increase borrowing costs and make credit management a trickier proposition.
Even if your physical cash management strategies are solid, keeping your cash flow statement compliant is another matter. Rules change often, and the SEC notes that “preparers and auditors may not always apply the same rigor and attention to the statement of cash flows as they do to other financial statements.”
Solution: The solution to this accountancy issue is double-pronged: First, ensure your accounting team is as diligent with your cash flow statement as other filings. Matching cash flow across all three categories is tough, especially if overseas transactions and currency exchange affect your bottom line, but many accounting tools can help serve as a vital assistant in the process. Second, develop a system like a third-party auditor to check your cash flow statement from an external, unbiased perspective.
3. Strategic Financial Analysis
One of today’s top commodities is data, but many companies don’t leverage the depths of data they generate when it comes to financial analysis. Even firms digging into granular aspects of marketing and productization often overlook the benefit that rigorous and objective strategic financial analysis offers.
Solution: Your financial platform likely offers tools to mine existing data. Some also offer analytics dashboards, while others require migrating to a third-party service, but extracting data from value is a two-fold process. Pulling the data tends to be the easy part, whereas consolidating it into a digestible and accessible dashboard to deliver insight can be elusive.
Remember, not everyone has the time or inclination to study reams of accounting documentation. To best derive effective and actionable insight from your data, it needs to be delivered in a format that helps stakeholders identify trends to shape decision-making with a quick glance.
4. Fraud, Waste, and Abuse
While we’d like to think employees, and even managers, wouldn’t defraud a company, the fact stands that human nature creates incentives that can send even the most honest workers down a bad path. Even in cases where fraud never happens, sloppy financial management can create significant wastage and unnecessary expense.
Solution: You should have a robust series of checks on expense management , with particular attention paid to approval workflows and order matching. Furthermore, you should schedule recurring reviews of your workflow processes, even if you manage a robust automated expensing and procurement system .
Maintaining an internal veil between departments and even individual employees while ensuring a sole staffer doesn’t have exclusive access also helps prevent payment fraud .
5. Account Reconciliation
If you don’t reconcile accounts properly , you’re in for a world of pain. Unreconciled accounts can paint a rosy picture on paper but leave you holding the bag when your real-world balances don’t match. At the same time, slipping slightly can compound rapidly as a missed reconciliation on a single account in one period can snowball into a six-figure error a year later.
Solution: This accounting problem is easy - reconcile your accounts often and accurately. Make sure your accounting team’s access runs the gamut of credit, banking, and other accounts to make sure nothing slips under the radar. Centralizing your account management on a single database tends to be a good practice, especially if your company juggles many accounts at once.
6. Security and Internal Controls
Too often, companies face one of two accountancy challenges related to internal controls . They either rely too much on just a few employees without external validation checks or outsource everything to software and adopt a “hands-off” approach. Both significant accounting challenges can bring a well-run company to its knees.
Solution: If you can’t keep a substantial separation between employees, i.e., running a small operation, you’ll need to set aside time to validate approvals as they route personally. It’s burdensome and time-consuming, but the effects of not doing so are far worse. If you can use automated accounting software to implement controls, ensure you’re still conducting regular reviews of the workflows to ensure they remain accurate and useful.
7. Misaligned Revenue Recognition
Properly recognizing revenue is tough, especially for subscription-based firms like SaaS companies. Worse yet, there’s an incentive to improperly time revenue recognition, as “borrowing” revenue today from tomorrow’s earnings can artificially inflate current reports and help boost a company’s image. But that short-lived boost tends to collapse quickly once the bill comes due.
Other misaligned revenue recognition includes channel stuffing, where companies push products to distributors without the necessary demand signal to pump sales stats. Some companies can even falsify revenue, particularly in cash-based businesses, but the trick doesn’t usually go unnoticed for long.
Solution: Ensure your accounting platform has accurate revenue recognition controls, and develop your operating procedure to address circumstances in which there’s a degree of uncertainty or room for interpretation. You’ll also need to ensure your accounting staff is up-to-date on changing accounting requirements and standards to maintain compliance as regulatory guidance evolves.
8. Non-Cash Expenses
Any time financial engineers, no matter how experienced, begin working with non-cash expenses, room for error multiplies. In some cases, the rules supporting non-cash expenses are unclear; in others, they’re open enough to interpretation that one accountant might generate a very different series of figures for the same circumstance.
Remember, non-cash expenses include:
- Depreciation and amortization
- Depletion
- Asset impairment
- Stock-based compensation
Asset impairment is one of the most common non-cash expense accounting problems. Determining value via mark-to-market accounting demands nuanced market understanding, accurate outlook, and honesty. For example, valuing assets like real estate requires a close look at local market factors, current condition, and how long the company has held the real estate asset. Depending on an individual accountant’s perspective, a real estate asset could be “worth” much more or less than another’s assessment of the same property. Inaccurate non-cash expensing can, therefore, create an artificially inflated balance sheet and cause concern that your company is misleading investors.
Solution: The best way to mitigate accounting issues associated with non-cash expenses is to have a comprehensive standard operating procedure for common items. Even straightforward non-cash expenses, like depreciation, should be meticulously prescribed to your financial team (i.e., whether an item depreciates along a straight line, via units of production, etc.). If you’re a smaller firm, your CFO or financial controller should prioritize codifying an SOP that addresses all non-cash expenses to save time and prevent legal entanglement later.
9. Payroll Errors or Inefficiencies
Smaller companies can’t usually afford to outsource their payroll, retirement benefits, and tax management requirements. This is understandable since third-party firms are costly and often unnecessary for companies with just a handful of employees. But, when you rely on less experienced internal assets to manage payroll, you open the door to significant problems in accounting. Certain benefit and tax structures are complex to navigate solo, but even basic salary payments are prone to miscalculation and error.
Solution: Remember - your employees are your greatest asset, and payroll errors are a great way to create dissatisfied staff. If you can’t afford to wholly outsource your payroll management, find a software solution that effectively serves your company’s payment and compensation structure. You may also want to spend the cash up front for consulting to get a solid system in place and pay for recurring audits along the way to ensure you remain on track.
10. Technology Challenges
Not all of us are digital natives and certain sectors of the workforce struggle to adapt as accounting tech evolves. At the same time, your company might be totally dependent on outdated manual tools to balance the books and manage supplier payment accounts. While those systems and tools might have worked well in the past, shifting trends point to an imminent need to ditch outdated financial software in favor of something cloud-based and easily integrated within your existing workflow.
Solution: Training, no matter your platform of choice, is the first step to ensuring everyone understands the tools they’re given. Beyond that, depending on your company’s circumstances, you can solve this accounting problem by exploring tools that offer:
- Payment management across a spectrum of methods ( ACH , check, card, etc.)
- BI and data analytics (see the third accounting problem)
- Recurring bill management
- AP automation and automated customer billing solutions
We’ve referenced it a lot in relation to solving your accounting issues, but automated financial and accounting tools go a long way toward solving problems in accounting. At their baseline, effective automated accounting tools free up untold amounts of time compared to manually managing your finances, freeing your team up to focus on business growth and operational optimization.
At the same time, these tools help prevent catastrophic results - in the event of fraud or regulatory noncompliance - while keeping vendors and customers happy by offering timely and accessible payment options. They also bundle a suite of security services to manage documentation long-term and keep your (and your customers’) information safe.

Jeremy is a finance writer experienced with a range of B2B solutions, including accounting, financial automation, and corporate financial management. He lives in Austin, TX with his wife & young son.
Related content

What Are Analytical Skills? Definition and Examples
- Share on Twitter Share on Twitter
- Share on Facebook Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn Share on LinkedIn

Forage puts students first. Our blog articles are written independently by our editorial team. They have not been paid for or sponsored by our partners. See our full editorial guidelines .
Analytical skills help you assess information and facts, problem-solve, and implement the best solutions. According to LinkedIn , they’re one of the top 10 most in-demand soft skills of 2024. So, what are some analytical skills examples and how can you improve yours?
Analytical Skills Definition
Analytical skills are the skills you use to make decisions and find solutions to problems. In the workplace, an analytical person helps the company problem-solve by breaking down information; looking through data and finding patterns, trends, and outliers; brainstorming new ideas; and making decisions on what solutions to implement.
These skills apply to multiple fields, not just in traditional data-heavy or analytics roles. You can use analytical skills in the workplace:
- In marketing , to review traffic to the website and understand what is (and isn’t) driving people to the site
- In data analytics , to identify seasonal trends in a company’s sales to understand the best time to launch a campaign
- In finance , to prepare forecasts of the company’s financial performance for the next year
- In user experience (UX) design , to understand current issues with the company’s UX while interviewing a user
- In sales, to create models to track revenue growth

Oliver Wyman Financial Services: Climate Change
Apply analytical skills in the consulting field to help decrease carbon emissions.
Avg. Time: 4-5 hours
Skills you’ll build: Data analysis, critical thinking, research
Analytical Skills Examples
While analytical skills are a type of soft skill, you may apply hard skills to help you become a better analytical thinker. Analytical skills examples include data analysis, logical thinking, research, creativity, and communication.
>>MORE: Discover the right career for you based on your skills with a career aptitude test .
Data Analytics
Data analytics is a hard skill where you look at data to put numbers behind answers to questions or potential solutions. For example, you might use data analytics to answer what products have had the most success during the summer vs. winter months, or to create charts or graphs that show the company’s recent financial performance.
Examples of data analytics skills include:
- Programming languages (specifically SQL, Python, and R)
- Probability and statistical analysis
- Machine learning
- Microsoft Excel
- Data visualization

Accenture Navigating Numbers
Practice your data modeling and visualization skills — then present your work in a professional scenario.
Avg. Time: 5-6 hours
Skills you’ll build: Data analysis, data modeling, data visualization, presenting, public speaking
Logical Thinking
Logical thinking is when you use reason to analyze a situation and come up with a solution. There are a few different types of logical thinking, including:
- Inference: Assuming an answer based on facts we already know
- Inductive reasoning : Observing a specific pattern, then making a general conclusion
- Deductive reasoning : Observing a general premise, then applying it to a specific situation
For example, as a writer on a marketing team, I might use logical thinking, and specifically inductive reasoning, by taking action based on a specific trend I notice about my company’s audience. I may notice a specific pattern — for instance, that our audience is clicking on stories that have investment banking skills in them. Then, I could make the general conclusion that our audience values investment banking content. I would then test my hypothesis by writing more content on that topic, and hopefully increase our audience in the process.
Analytical people seek all the facts and information before coming to a conclusion. A smart researcher knows where to find those facts and who to ask for help to get more information.
In the workplace, you might apply research skills to discover facts about the company’s history, like conducting a reflective analysis, and showing the company’s progress over the last five years. You could also do more qualitative research , and speak to colleagues in other departments to understand how a problem is affecting their team, or even set up an informational interview with an outside expert to learn from their experience.
Examples of research analytical skills include:
- Report writing
- Data collection and analysis
- Critical thinking
- User interviews
Communication
Analytical skills aren’t just about facts and figures; they also require creativity to brainstorm solutions and possible answers to problems. Creativity helps analytical people move away from the small points and think big picture.
In the workplace, you might use creative thinking to organize a brainstorm with team members, or to propose product improvements based on a client survey. You could also use it to present information to stakeholders in a new, exciting way, or to create a new brand design for your company’s website. Creative thinking can be applied to numerous industries, even in more data-heavy or analytical roles.
Examples of analytical creativity skills include:
- Active listening
- Risk-taking
- Storytelling
Your analytical thinking won’t have an impact unless you share it with the team; however, not everyone can easily understand data or analytical problem-solving. Communication skills help you translate complex analytical ideas into digestible, actionable takeaways for the rest of your team.
For example, you can use communication skills to explain a data visualization to team members and help them understand company performance, or to present high-level findings from a data exercise or statistical analysis.
Examples of analytical communication skills include:
- Verbal communication
- Chart, graph, and data presentation
- Public speaking
How to Show Your Analytical Skills in a Job Application
In a job application, you can show off your analytical skills in two ways: first, by demonstrating the technical analytical tools you know and second, by explaining your problem-solving skills to show your analytical thinking.
Demonstrating Technical Analytical Skills
“For early professionals, definitely showing the tools, the technical skills, and also projects you’ve worked on is important,” Kristen Rice, product manager, website growth at Sprout Social, says. “If you don’t have a particular project in mind or that you can share, showcase ideas that you do have around analytics. If you use a type of code such as SQL, Python, R etc., that is huge because businesses seek to automate analyses a lot quicker and there is an increasing need to connect data that doesn’t always share the same foundation. These different programming languages allow for the ability to do those things.”
You can include hard analytical skills on your resume either in a dedicated “skills” section or in a job explanation (if you used the skill in a specific work experience). For example, if you used your data analytics skills in a finance internship , you could write:
Used SQL queries to extract data and create reports that helped the team decrease surplus spending by 13% MoM.
Explaining Your Analytical Thinking Skills
Yet you don’t need to know multiple coding languages or analytics programs to show off your analytical skills. You can also show analytical thinking through how you describe your problem-solving methods and approach at work.
- What do you first consult when solving a problem? Can you talk about any experience analyzing numerical results, looking at website analytics, etc.?
- What steps do you take to make sense of a problem?
- Who or what do you consult to help you solve the problem?
- How do you test and iterate your solution?
- How do you reflect on your solution? What steps do you take after?
Showing Soft Analytical Skills on Your Resume
On your resume , you can describe your analytical skills in your job descriptions. Even if you’re talking about soft skills, you should include the impact your skills had. For example, as a writer, I might write something like:
- Performed competitive research analysis to identify three key improvement opportunities for our blog, leading to 10% traffic growth in two months
- Led brainstorming sessions to produce 30 new content ideas each month
- Conducted and shared analysis of top-performing content to inform future content strategy, leading to 20% MoM traffic growth
Log in to download a customizable resume template with examples of how to include analytical skills:

Showing Soft Analytical Skills in the Interview
In the interview , use the STAR method to show how you apply analytical skills and the impact your skills had. Again, even if you’re talking about soft skills, get specific about programs, tactics, or methodology you use when solving problems. This will give the interviewer a clear picture of how you work and problem-solve.
For example, you might be asked about your decision-making process at work. You can respond with something like:
My decision-making process usually starts with gathering all the information I know about the problem, whether that’s by researching, collaborating with other teams, or performing data analysis. Once I have a better understanding of the problem, I’ll then share this information with my coworkers and ask them to brainstorm with me. After that, I’ll perform a risk analysis of all of the solutions we brainstormed and make a final decision on the best path forward.
>>MORE: Analytical Skills Interview Questions (and Answers)
How to Improve Your Analytical Skills
Even though some technical skills are involved in analytical thinking, much of analytical thinking relies on your soft skills — which means it’s harder to know how to be a better analytical thinker. However, by understanding your current problem-solving process and asking others about theirs, you’ll start to hone your analytical skills.
Document Your Current Skills
It isn’t easy to assess your current skill level if you don’t know how you currently use analytical thinking, even in your everyday life. The next time you approach a problem, even something like figuring out what to wear to dinner with friends, ask yourself:
- What facts am I considering here?
- What research do I do? Do I ask anyone for help, and who?
- How do I brainstorm solutions?
- How do I make my final decision on how to move forward?
- Do I reflect on my decision-making skills after, and if so, how does that affect my future decisions?
To use the dinner example, maybe you consider factors like the weather and the restaurant’s dress code when deciding what to wear. You might look up the weather using an app and research the restaurant online to see what the vibe is. Then, maybe you pull out a few options and try them on to see what you’re comfortable wearing.
This decision-making process might seem simple, but it’s a true skill! Improving your analytical skills starts with understanding how you uniquely solve problems.
Network With Other Teams
Learning from people around you can help you identify the problems they’re working on and show you how they may solve problems. You might learn about new resources or tools, or even just methods and tricks they use at work.
“ Network with people in roles that you’re interested in,” Rice recommends. “I’ve connected with people on LinkedIn who are resources for me, internally at my organization I’ve had the opportunity to learn from our data science, data engineering, and business analytics team, and I also try to attend events or webinars that are geared towards analytics to build my knowledge and connections as well.”
Create Opportunities for Yourself
An analytical thinker will take in facts, do their research, brainstorm creative solutions, narrow down to the most logical one, and reflect on their solutions after the decision was made to learn for the next time. There’s no better way to improve your skills than to put yourself into situations where you need to exercise your analytical skills — whether that’s doing something simple like logic puzzles, or even putting yourself in a professional’s shoes and pretending you have to make a big company decision. Practice walking through these steps when you problem-solve and make a decision, whether big or small.

Lululemon Omnichannel Marketing
Use analytical thinking and creative thinking to create a marketing plan and product strategy.
Avg. Time: 2-2.5 hours
Skills you’ll build: Strategic and analytical thinking, project management, market research, user research, communication
Analytics at Work: The Bottom Line
Analytical skills help you dig into problems and come out with facts-based solutions. While some technical skills like data analysis and visualization are elements of analytical skills, there are also soft skills like creativity and communication that are essential to being an effective analytical thinker.
No matter what kinds of analytical skills you have, show them off on your resume and in the interview by detailing your unique, informative analytical problem-solving process.
Image Credit: olia danilevich / Pexels

Related Posts
6 negotiation skills to level up your work life, how to build conflict resolution skills: case studies and examples, what is github uses and getting started, upskill with forage.

Top companies are hiring!
- Error of Principle In Accounting: Meaning, Causes & Detection

We all make mistakes, and accountants are no different. An error of principle is simply accounting entries in an incorrect account. The accountant recorded the right amount but recorded it in the wrong account.
For example, suppose you want to enter printing expenses, and instead of recording the cost of refilling the printer ink in revenue expenditure, you record it in capital expenditure. Capital expenditures are for fixed assets such as the printer purchase, while revenue expenditures are for day-to-day expenses.
Why is an Error of Principle Such a Big Deal?

The major problem with errors of principle is that, unlike other types of errors, such as the error of original entry , where the incorrect amount is recorded, they are hard to detect. With errors of principle, the account summary may still be balanced with the right amount of expenses and revenue.
However, if your company wants to review its accounting principles these minor accounting mistakes become a problem. They also undermine the integrity of financial statements and lead to significant financial restatements, damaging your company’s reputation with stakeholders.
How Does Errors of Principle Happen?
An error of principle occurs in accounting when a transaction is recorded in violation of a fundamental accounting principle or established company policy. These errors typically involve the correct amount being recorded but in the wrong account . Unlike clerical errors (math mistakes) or errors of omission (missing entries), errors of principle stem from a misunderstanding of accounting concepts or a failure to follow proper procedures.
- Capital Expenditure vs. Revenue Expenditure: Mistakenly recording the purchase of a new machine (capital expenditure) as an expense (revenue expenditure). This distorts the company’s income statement by overstating expenses and understating assets.
- Inventory Valuation: An improper inventory valuation (e.g. FIFO vs LIFO ) may result in an incorrect cost of goods sold (COS) and influence profitability calculations.
- Depreciation Method: Applying an improper depreciation method to an asset, thereby misrepresenting its value on the balance sheet and impacting reported earnings.
What Is the Difference Between Errors of Principle and Other Accounting Principles
- Clerical Errors: These are mathematical mistakes in recording or calculating transactions, often involving typos or misplaced decimal points. Unlike principle errors, they affect the trial balance (total debits do not equal total credits), making them easy to identify.
- Errors of Omission: These include missing entries or even transactions. They typically affect the trial balance and are easier to identify than errors of principle.
Consequences of Errors of Principle

Errors of principle affect different aspects of your business, such as finance, law, and trust. Let’s look at them in more detail:
A. Financial Errors
Errors of principle can significantly distort financial statements, leading to:
- Misstated Profits: Recording revenue expenditures as capital expenditures overstates expenses and understates assets, resulting in overstated profitability. If the case is reversed, profits would be understated, significantly affecting company budgeting and plans.
- Incorrect Financial Position: Misvalued assets or liabilities provide an inaccurate picture of a company’s financial health. For example, if a company’s profit is understated, the company could go as far as downsizing, while if it’s overstated, it could try to scale when it doesn’t have enough funds.
- Misleading Information for Investors: Inaccurate financial statements can mislead investors and creditors when making financial decisions.
B. Legal and Regulatory Implications
Depending on the severity and intent, errors of principle can lead to legal and regulatory issues:
- Securities Fraud: If the error is intentional and used to manipulate financial results, it can constitute securities fraud punishable by law.
- Loss of Investor Confidence: Repeated errors of principle can erode investor confidence and damage the company’s reputation.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: Regulatory bodies may investigate companies with significant errors of principle, leading to fines or penalties.
C. Repercussions for Businesses
Errors of principle can hurt your businesses in several ways:
- Financial Losses: Incorrect decision-making based on flawed financial statements can lead to wasted resources and missed opportunities.
- Increased Costs: Correcting significant errors of principle can be expensive and time-consuming.
- Difficulty Obtaining Financing: Lenders may be hesitant to provide financing to companies with a history of errors in financial reporting.
Common Causes of Errors of Principle
Errors happen all the time, but knowing why is how we identify the root cause and prevent them from happening again. Here’s a breakdown of frequent causes:
- Misunderstanding of Accounting Principles: This typically happens with new staff or those unfamiliar with specific accounting treatments. For example, an intern could wrongly classify assets and expenses if they don’t understand the subtle distinction between the two.
- Misinterpretation of Accounting Standards: Accounting standards guide your business and help you measure profitability, but they can also be complicated. If you don’t understand how accounting standards work, you may make mistakes, such as undervaluing inventory or undervaluing assets.
- Poor Internal Controls: Poor internal controls lead to an environment where mistakes can slip through the cracks. For example, if you are short-staffed (e.g. transactions and reconciliation are performed by the same person) or there are no or poor review procedures.
Detecting and Correcting Errors of Principle
While most people don’t intentionally make errors of principle, they can happen. So here are some key methods to help detect and rectify them:
- Internal Audit Processes: Regularly scheduled internal audits by qualified professionals to identify errors in accounting practices. I nternal audits provide an independent audit and identify areas where principles may be incorrectly applied.
- Regular Reconciliations: Routinely compare accounts (such as bank statements and inventory records) to identify discrepancies that could indicate errors of principle. For instance, a large discrepancy between a bank statement and a general ledger cash account could indicate an improper accounting for a transaction.
- Using Accounting Software for Accuracy: Accounting software automates a wide range of processes and enforces specific accounting policies, minimizing common accounting errors.
Case Studies: Learning from Errors of Principle

Understanding how errors of principle manifest in real-world scenarios can help prevent them in your practices. Let’s look at some examples:
1. Wages Paid for Office Renovation from the Building Account
In this transaction, wages paid for the office refurbishment are a revenue expenditure and should be debited from the wages account. However, in this case, it is treated as capital expenditure and is debited to the building account, violating the accounting principle.
Implications
Going by the recorded expenses, the company would be led to believe they have more assets than they have. This could lead to incorrect company decisions based on a misconception of financial health.
Always reconcile accounts to ensure there are no accounting errors. This would help guide your company’s decisions, especially for budget allocation.
2. Amount Spent on Machinery Replacement Recorded in Repairs
In this transaction, the amount of replacement is a capital expenditure, not a revenue expenditure. Yes, the new machinery was bought to replace an old one but it was a new asset, it should be debited to the Machinery Account not Repairs.
Non-recognition of an asset in the form of capital expenditure shows that the company has fewer assets than it does. This can have significant legal consequences, especially if it impacts the company’s tax position. It could result in fines and penalties; you would pay these fines and still have to deal with a damaged reputation.
Preventing Errors of Principle in Accounting Practices
Desiderius Erasmus once said “Prevention is better than cure”, a proverb we incorporate in everyday life including accounting. Instead of wading through compliance and legal hoops and risking your company reputation, here are a few ways to prevent errors of principle from happening in your accounting:
- Employee Training and Education
- Provide your employees with an in-depth knowledge of GAAP or the applicable accounting framework in your state.
- Offer ongoing training to update employees on any changes or clarifications to accounting standards.
- Strengthening Internal Controls
- Implement a robust system of internal controls to ensure accurate recording and processing of financial transactions. For example, implementing regular reconciliations, and proper documentation.
- Separate accounting tasks to prevent overburdening staff and common oversights e.g., separating authorization, recording, and custody of assets.
- Regular Review of Accounting Policies:
- Periodically review your company’s accounting policies to ensure they align with current GAAP or relevant standards. This helps identify potential inconsistencies or areas for improvement and reduces the risk of errors.
How Formplus Can Help Accountants Avoid Errors of Principle

Formplus is your go-to for simple and effective solutions to manage your business accounts more effectively. Here are some ways Formplus helps you manage your accounts more effectively and prevent common accounting errors:
- Transaction records : Formplus’s secure payment integration with Paypal, Stripe, Paystack, and other payment platforms lets you have a clear record of your transactions and helps you spot discrepancies when matching your records.
- Workplace Integration : Rather than opening multiple tabs and applications and losing track of some accounts, you can streamline your workflow and reduce the risk of errors of principle. Formplus also integrates seamlessly with accounting software like Quickbooks and Sage ensuring that financial records are automatically updated.
- Multiple Templates for Expenses : Formplus also has a wide library of templates to record purchases, inventory, and sales. This allows you to track expenses and easily reconcile accounts if you spot errors of principle in your accounting
- Survey : You can also use Formplus to create surveys to guide you in making better financial decision-making. For example, you can create post-reconciliation surveys to gain insights into the defects of your current accounting practices and recommendations to mitigate them.
Errors of principle whether intentional or not have serious implications. You could end up neck-deep in fines, reputation damage, lost opportunities, or debt. So accurate accounting is not just a legal requirement; it enables informed decision-making and maintains your company’s financial health.
We hope this guide helps you spot and prevent errors of principle in your accounting. Don’t forget to check out Formplus accounting forms to help you record your expenses and revenue effortlessly.

Connect to Formplus, Get Started Now - It's Free!
- Moradeke Owa

You may also like:
Fishbein’s Model of Attitude In Market Research
Introduction In market research, understanding consumer attitudes is paramount to predicting and influencing buying behaviors. The...

Statistical Analysis Software: A Guide For Social Researchers
Introduction Social research is a complex endeavor. It takes a lot of time, energy, and resources to gather data, analyze and present...
18 Survey & Market Research Certifications To Have by 2024
Introduction Market research is a career that requires a variety of competencies in order to execute the job duties effectively. These...
Unit of Analysis: Definition, Types & Examples
Introduction A unit of analysis is the smallest level of analysis for a research project. It’s important to choose the right unit of...
Formplus - For Seamless Data Collection
Collect data the right way with a versatile data collection tool. try formplus and transform your work productivity today..
Download Chapter
You will receive additional complimentary videos/ updates by email. To complete the process please click the link in the email we will send you.
Download Preview
Welcome back!
Or, sign in with your email
Don’t have an account? Subscribe now

Download The Strategy Journal
What is analytical problem solving.

There are some very common misconceptions and myths about analytical problem solving. Most candidates simply skim over this phrase on consulting profiles without thinking about the meaning. This post will tell you what management consulting firms like McKinsey , Bain and BCG mean by analytical problem solving.
You would be surprised at how many people believe that analytical thinking is something that comes instinctively, letting you do data analysis and pinpoint relevant information to get the key takeaways from complex problems. The truth is, these analytical skills are, more often than not, hard skills that you acquire through years of problem solving and critical thinking. They’re problem-solving skills that help you go from coming up with easy solutions to coming up with creative solutions that go the extra mile.
This is important advice so it is worth reading carefully – we’ll also go over some analytical and problem solving skills examples to help you understand better.
What is analytical problem solving
To be an analytical thinker does not mean you must have a degree in science, engineering, finance, economics or any other quantitative subject. While some subjects, like those listed, imply you could be analytical in your thinking, not having quantitative background does not mean you cannot think analytically. Thousands of candidates with quantitative backgrounds fail to get offers from McKinsey, Bain and BCG every year. Therefore, having a quantitative background can be an advantage, but it does not guarantee analytical problem solving ability.
Being analytical refers to the way you think and not to the problem you solve. This is a very important statement. Lawyers, social scientists, linguists and historians can all be extremely analytical in their thinking. Yet, they are not solving quantitative problems. So the problem is not what determines if you are analytical, it is the way you solve the problem.
Good analyses are grounded in hypotheses. Can you develop hypotheses? It always surprises us how many people do not know what is a hypothesis. A hypothesis is not the problem. It is not a fact. It is not an opinion. It is a statement which captures the observed phenomenon as well as the likely cause of the phenomenon. Both must be present for it to be a hypothesis. A surprising number of candidates do not understand this.
Are you able to reason using only the facts provided? Analytical thinkers are not unemotional. No one is unemotional. However, analytical thinkers are able to separate their emotion from the situation and use the data provided to arrive at a conclusion. Analytical problem solving means reasoning using facts and logic. Past experience or opinions which cannot be substantiated are ignored.
Can you assemble data and facts to develop an argument or line of reasoning? Analytical thinkers can take pieces of information, compare them and decide what the information is saying. They can assemble the information to produce new insight into the problem rather than simply restating the information.
Analytical thinkers do not blurt out answers. Assuming your answer is even correct, the fact that you knew the answer means you did not need to analyse the facts. Therefore, your analytical problem solving skill could not be tested.
Logic has nothing to do with numbers. There is a misconception that if your reasoning lacks numbers then it must be incorrect. That is ridiculous. In many consulting case interviews, you will need to reason based on logical arguments and with very little numbers. Your line of reasoning is more important than your final answer.
Analytical thinkers can show you how they arrived at the answer. This should be obvious, right? After all, it is the foundation of the case interview method. If you followed a path of reasoning to arrive at an answer, you should be able to explain that path to someone. That is why the method is used. The interviewer is more interested in how you arrived at the answer than the answer you developed. How you arrived at the answer shows the strength of your analytical problem solving skill.
Logical thinkers apply MECE , even if they do not know it. I have some impressive friends in the legal profession. Watching them reason and debate is worth doing so. When you ask them how they arrived at an answer or why they eliminated an option, you realize they are applying the rules of MECE perfectly. Yet, they never heard of MECE. Reason and logic is not exclusive to management consulting but is it essential to management consulting.
You do not need to know anything about an income statement, balance sheet or cash-flow statement to develop analytical skills. I should not need to say this but I will say it anyway. The thought process is more important than the topic. You can learn accounting and financial concepts when you need them. It is not very difficult to do so.
Analytical and problem solving skills examples
Below we share with you some examples of analytical and problem solving skills and how analytical skills are being tested during consulting case interviews.
McKinsey case interview examples
- Complex McKinsey Interviewer led profitability case in Pharma (by FIRMSconsulting.com)
- Comprehensive McKinsey hypotheses based case interview example (by FIRMSconsulting.com)
- McKinsey cost-benefit approach complex profit case interview example (by FIRMSconsulting.com)
BCG case interview examples
- Comprehensive BCG interviewer led market entry case interview example (by FIRMSconsulting.com)
General case interview examples
- A comprehensive approach to brainstorming in case interviews (by FIRMSconsulting.com)
- Framework for a Bain, McKinsey, BCG acquisition case (by FIRMSconsulting.com)
Structured case interview analytical and problem solving skills development is needed
If you would like to get help with developing your analytical and problem solving skills, and fast track your case interview preparation, we welcome you to enroll into Premium membership .
There is nowhere else in the world where you can see real candidates trained by former partners from major consulting firms to help them develop analytical and problem solving skills. You will see the candidate’s progression through each step of the case interview preparation process, and how their analytical and problem solving skills are being developed. And you will see candidates receiving real offers from major firms such as Deloitte, McKinsey, or BCG.
SPREAD THE WORD! Like this? Please share it.
Follow us to get the latest updates: Facebook / Twitter / LinkedIn
Image from Trey Ratcliff under cc .
Want to learn more about how FIRMSconsulting can help your organization?
Related articles, management consulting, the good stuff in the sector is in a vault.
The good stuff in the sector is in a vault What could your life be like if for the most important decisions you had to make, you had a trusted advisor that is trained on the thinking and to think like some of the top minds in the world of consulting…
Uncategorized
Senior mckinsey partner on the most important skill you should develop.
Senior McKinsey partner on the most important skill you should develop We trained our AI system on our proprietary information. It’s like having access to our brains 24/7. That said, you might still run into challenges. Maybe you ask a question and don’t get the response you want. This is…
24/7 Personal Strategy & Consulting AI Platform
Business leaders, executives, management consultants, business analysts, internal consultants, and, in fact, everyone in business relies on correct and sound advice to make critical decisions. You must be able to trust the source, and you do not have the time to fact-check. The difference with the field of business, strategy…
Sign up for emails
Never miss an insight. We'll email you when new articles are published on this topic.
All content remains the property of FIRMSconsulting LLC. When using material from this website, including but not limited to tools, frameworks, concepts and methodologies, please provide the proper citations and attributions.
Have you downloaded our free guides?
Case interview resume template used in The Consulting Offer . Offers from McKinsey, BCG, Bain et al.
Overall approach used in well-managed strategy studies PDF guide
More From Forbes
Stumped five ways to hone your problem-solving skills.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Respect the worth of other people's insights
Problems continuously arise in organizational life, making problem-solving an essential skill for leaders. Leaders who are good at tackling conundrums are likely to be more effective at overcoming obstacles and guiding their teams to achieve their goals. So, what’s the secret to better problem-solving skills?
1. Understand the root cause of the problem
“Too often, people fail because they haven’t correctly defined what the problem is,” says David Ross, an international strategist, founder of consultancy Phoenix Strategic Management and author of Confronting the Storm: Regenerating Leadership and Hope in the Age of Uncertainty .
Ross explains that as teams grapple with “wicked” problems – those where there can be several root causes for why a problem exists – there can often be disagreement on the initial assumptions made. As a result, their chances of successfully solving the problem are low.
“Before commencing the process of solving the problem, it is worthwhile identifying who your key stakeholders are and talking to them about the issue,” Ross recommends. “Who could be affected by the issue? What is the problem – and why? How are people affected?”
He argues that if leaders treat people with dignity, respecting the worth of their insights, they are more likely to successfully solve problems.
Best High-Yield Savings Accounts Of 2024
Best 5% interest savings accounts of 2024, 2. unfocus the mind.
“To solve problems, we need to commit to making time to face a problem in its full complexity, which also requires that we take back control of our thinking,” says Chris Griffiths, an expert on creativity and innovative thinking skills, founder and CEO of software provider OpenGenius, and co-author of The Focus Fix: Finding Clarity, Creativity and Resilience in an Overwhelming World .
To do this, it’s necessary to harness the power of the unfocused mind, according to Griffiths. “It might sound oxymoronic, but just like our devices, our brain needs time to recharge,” he says. “ A plethora of research has shown that daydreaming allows us to make creative connections and see abstract solutions that are not obvious when we’re engaged in direct work.”
To make use of the unfocused mind in problem solving, you must begin by getting to know the problem from all angles. “At this stage, don’t worry about actually solving the problem,” says Griffiths. “You’re simply giving your subconscious mind the information it needs to get creative with when you zone out. From here, pick a monotonous or rhythmic activity that will help you to activate the daydreaming state – that might be a walk, some doodling, or even some chores.”
Do this regularly, argues Griffiths, and you’ll soon find that flashes of inspiration and novel solutions naturally present themselves while you’re ostensibly thinking of other things. He says: “By allowing you to access the fullest creative potential of your own brain, daydreaming acts as a skeleton key for a wide range of problems.”
3. Be comfortable making judgment calls
“Admitting to not knowing the future takes courage,” says Professor Stephen Wyatt, founder and lead consultant at consultancy Corporate Rebirth and author of Antidote to the Crisis of Leadership: Opportunity in Complexity . “Leaders are worried our teams won’t respect us and our boards will lose faith in us, but what doesn’t work is drawing up plans and forecasts and holding yourself or others rigidly to them.”
Wyatt advises leaders to heighten their situational awareness – to look broadly, integrate more perspectives and be able to connect the dots. “We need to be comfortable in making judgment calls as the future is unknown,” he says. “There is no data on it. But equally, very few initiatives cannot be adjusted, refined or reviewed while in motion.”
Leaders need to stay vigilant, according to Wyatt, create the capacity of the enterprise to adapt and maintain the support of stakeholders. “The concept of the infallible leader needs to be updated,” he concludes.
4. Be prepared to fail and learn
“Organisations, and arguably society more widely, are obsessed with problems and the notion of problems,” says Steve Hearsum, founder of organizational change consultancy Edge + Stretch and author of No Silver Bullet: Bursting the Bubble of the Organisational Quick Fix .
Hearsum argues that this tendency is complicated by the myth of fixability, namely the idea that all problems, however complex, have a solution. “Our need for certainty, to minimize and dampen the anxiety of ‘not knowing,’ leads us to oversimplify and ignore or filter out anything that challenges the idea that there is a solution,” he says.
Leaders need to shift their mindset to cultivate their comfort with not knowing and couple that with being OK with being wrong, sometimes, notes Hearsum. He adds: “That means developing reflexivity to understand your own beliefs and judgments, and what influences these, asking questions and experimenting.”
5. Unleash the power of empathy
Leaders must be able to communicate problems in order to find solutions to them. But they should avoid bombarding their teams with complex, technical details since these can overwhelm their people’s cognitive load, says Dr Jessica Barker MBE , author of Hacked: The Secrets Behind Cyber Attacks .
Instead, she recommends that leaders frame their messages in ways that cut through jargon and ensure that their advice is relevant, accessible and actionable. “An essential leadership skill for this is empathy,” Barker explains. “When you’re trying to build a positive culture, it is crucial to understand why people are not practicing the behaviors you want rather than trying to force that behavioral change with fear, uncertainty and doubt.”

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Join The Conversation
One Community. Many Voices. Create a free account to share your thoughts.
Forbes Community Guidelines
Our community is about connecting people through open and thoughtful conversations. We want our readers to share their views and exchange ideas and facts in a safe space.
In order to do so, please follow the posting rules in our site's Terms of Service. We've summarized some of those key rules below. Simply put, keep it civil.
Your post will be rejected if we notice that it seems to contain:
- False or intentionally out-of-context or misleading information
- Insults, profanity, incoherent, obscene or inflammatory language or threats of any kind
- Attacks on the identity of other commenters or the article's author
- Content that otherwise violates our site's terms.
User accounts will be blocked if we notice or believe that users are engaged in:
- Continuous attempts to re-post comments that have been previously moderated/rejected
- Racist, sexist, homophobic or other discriminatory comments
- Attempts or tactics that put the site security at risk
- Actions that otherwise violate our site's terms.
So, how can you be a power user?
- Stay on topic and share your insights
- Feel free to be clear and thoughtful to get your point across
- ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ to show your point of view.
- Protect your community.
- Use the report tool to alert us when someone breaks the rules.
Thanks for reading our community guidelines. Please read the full list of posting rules found in our site's Terms of Service.
Instagantt Standalone
Full version of Instagantt. Don't know what Asana is, or don't want to use it with Asana?

Instagantt for Asana
If you need to manage your Asana projects in Instagantt, this is your product.
A Complete Guide to know What is Problem Solving (Updated July 2024)
Everything happening in this world has its problems. This is because no system in this world has 100% efficiency. But this is not a big issue for the people who are prepared to deal with any kind of problem. The field that is heavily affected by the problems in the field of companies and organizations.

This is because a lot of employees are working in different departments under the same name. The problem for one employee or one department can cause issues for others. This is why the employees are given special problem-solving training. Here we will discuss what is problem-solving and some effective steps involved.
What is problem solving?
Problem-solving isa process of solving any kind of problem. This process is acted upon in some steps. These steps start from identifying the problem and determining the cause of the problem. After the problem and its cause are identified, the next step is to select alternatives for the solution and implement the solutions.
All of these steps are collectively known as a problem-solving process.
The basic steps involved in problem-solving.
As the problem-solving process comprises different steps that collectively help in getting id of the problem. So, here we will have a detailed discussion about the steps that are involved in problem-solving.
Defining the problem.
Defining the problem means that you are diagnosing the situation. This helps take the further steps for solving the problem. This is not just as simple as defining the problem. Here you take effective measures to keep track of the situation of the problem. Some of the most effective and easy to implement ways of defining the problem are listed below.
· Flowcharts of the process and the problem init.
· Cause and effect diagram.
With the help of these steps, you can easily identify the root causes of the problem. However, for these ways of defining the problem, you must involve the factual information and then compare the expectations to reality. Apart from this, you also need to stay focused on the root cause of the problem as eradicating this will be your main objective here.
To create a successful deduction for problem-solving in this step, you will first need to review different sectors of your system. Then you will have to evaluate things on the base of how something will affect the system.
Generating the alternatives.
Once you have gone through the first step, the next step will be to get the solution for the problem. It is in our psyche that once we think of an idea or solution, then we keep on thinking that it will be effective. But in reality, this will not happen every time and you will waste a lot of time coming up with another effective solution.
So, here the best thing to do is to come up with more than more solutions at a time. For this, you can do the following things.
· Take ideas from different employees.
· Mold your original idea according to different aspects of the problem.
· Think of other than one effective idea.
When you are going with a set of ideas for the backup, you will be very efficient in solving the problem. This is because if one idea fails, you can implement another one and this can be carried on until you have solved the problem.
Evaluating and selecting alternatives.
So, now you know that you have to come up with more than one idea, but how will you know if the ideas are effective or not. For this, you can easily evaluate the ideas that come up in your mind. This will help in filtering out only the best and the most effective ideas. Here is how this works.
· Will this solution be able to solve the specific problem without causing other problems in the system?
· Will all the people and stakeholders of the system accept the solution?
· Is the solution that I have come up with possible and easy to implement?
· Will the solution and the alternatives be in the constraints of the organization?
When you think of all the ideas and their alternatives, you will be very efficiently filtering out the ideas that do not seem to be working.

Implementing the solutions.
Now you are in the state where you have the ideas, the solutions, and the alternatives of these solutions. The only step left to get the problem solved is to implement the solution. This is also not a very simple step. Here are some things that you must include in this step to increase the efficiency of your solution.
· Involving others.
One of the best things to do is to involve others in the implementation of your solution. This will not only reduce the stress that you will have to bear. But this will also add other innovative ideas that come in their minds. This can be very helpful in making the solution to the problem better.
· Testing and expectations of the solution.
When you are implementing or you have implemented the solution, it is very important to keep constantly monitoring the solution and its working. For this, you can test the solutions’ working at different events. Testing the outcomes and comparing when with the expectations will also give you the idea of how well the solution is performing.
· Feedback system.
When you have implemented the solution, the role that you will play in the future will be lower than the role of other employees. So, you must take feedback after sometime. The feedback system will tell you about the feelings of people about your solution and its working. This will also help in improving the solution.
Some important things to consider in each of the problem-solving steps.
Above in the article, we discussed the significance of each step involved in problem-solving. Here we will discuss some additional things that you must be aware of. This is because they will not only make your problem-solving experience better, but they will also make your problem-solving techniques more efficient.
Knowing your problem in a good way:
If you are thinking about what is problem solving and how important it is to define the problem. Then we will tell you here the importance of defining the problem and some of the best ways to implement it. It is a must for solving any problem that you must know the real cause and the root of the problem.
This is because the smaller problems can be identified and solved easily. But when we are dealing with the problems on the level of different organizations, then it is very important to get rid of the problem from the start. This is because if the problem is not fully identified, then it will never be truly eradicated.
And this will keep on damaging the company in several ways. For the problem identifying methods we mentioned above, the initiative for any of the methods can be taken for different tools. Some of the tools are the 5 W’s, the root cause analysis, and appreciation. This is also very important that you consider each of them carefully from different perspectives.
This is because the cause of the problem could be an unreasonable workload or lack of training but if unidentified, this can be extremely bad.
Knowing about the complexity of the problem.
While you are solving any problem, you must understand that every problem will not have the same scope and the time required for every problem will be different. This is because the complexity of each problem is different. There are a lot of tools and methods to know about the complexity of the problem. Some of them are listed below.
· Affinity diagrams.
· Swim Lane diagram.
· System diagram.
· Flow charts.
· Bottleneck method.
After identifying different factors of the problem, you can implement any of these tools and this will tell you about the complexity of the problem. Sometimes a problem that seems to be a single problem is a collection of different smaller problems.
This is the point where the drill-down technique can be very helpful. It will easily and efficiently breakdown the problem into smaller parts.
Process of solving the problem.
So, there can be a case that the problem is very small, and it can easily be dealt with. But inmost of the cases, the problem is not that simple, and it is a collection of several complex problems related to different departments.
In this case, the head of the problem-solving team must take different members from different departments that will help in solving that problem using the tools, tricks methods, and tips we mentioned above.
With the increasing complexities in different organizations, many people are asking what is problem solving. If you are also uncertain about what is problem solving, then this will be the article that will tell you all about what is problem solving.
This is because it will not only tell you about some of the most effective techniques for solving different problems, but the tips, tools, and methods we mentioned here can also be very helpful for everyone in dealing with complex problems.
We offer monthly and yearly subscriptions. Sign up for free, no credit card required.

Based on 10.000+ reviews on

Make a Gantt Chart Online Now
Start managing your projects efficiently & never struggle with complex tools again.
Ready to simplify your project management?
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
The Supreme Court says cities can punish people for sleeping in public places

Jennifer Ludden
U.S. Supreme Court says cities can punish people for sleeping in public places

A homeless person walks near an elementary school in Grants Pass, Ore., on March 23. The rural city became the unlikely face of the nation's homelessness crisis when it asked the U.S. Supreme Court to uphold its anti-camping laws. Jenny Kane/AP hide caption
In its biggest decision on homelessness in decades, the U.S. Supreme Court today ruled that cities can ban people from sleeping and camping in public places. The justices, in a 6-3 decision along ideological lines, overturned lower court rulings that deemed it cruel and unusual under the Eighth Amendment to punish people for sleeping outside if they had nowhere else to go.
Writing for the majority, Justice Gorsuch said, “Homelessness is complex. Its causes are many.” But he said federal judges do not have any “special competence” to decide how cities should deal with this.
“The Constitution’s Eighth Amendment serves many important functions, but it does not authorize federal judges to wrest those rights and responsibilities from the American people and in their place dictate this Nation’s homelessness policy,” he wrote.
In a dissent, Justice Sotomayor said the decision focused only on the needs of cities but not the most vulnerable. She said sleep is a biological necessity, but this decision leaves a homeless person with “an impossible choice — either stay awake or be arrested.”
The court's decision is a win not only for the small Oregon city of Grants Pass, which brought the case, but also for dozens of Western localities that had urged the high court to grant them more enforcement powers as they grapple with record high rates of homelessness. They said the lower court rulings had tied their hands in trying to keep public spaces open and safe for everyone.

Supreme Court appears to side with an Oregon city's crackdown on homelessness
But advocates for the unhoused say the decision won’t solve the bigger problem, and could make life much harder for the quarter of a million people living on streets, in parks and in their cars. “Where do people experiencing homelessness go if every community decides to punish them for their homelessness?” says Diane Yentel, president of the National Low Income Housing Coalition.
Today’s ruling only changes current law in the 9th Circuit Court of Appeals, which includes California and eight other Western states where the bulk of America’s unhoused population lives. But it will also determine whether similar policies elsewhere are permissible; and it will almost certainly influence homelessness policy in cities around the country.
Cities complained they were hamstrung in managing a public safety crisis
Grants Pass and other cities argued that lower court rulings fueled the spread of homeless encampments, endangering public health and safety. Those decisions did allow cities to restrict when and where people could sleep and even to shut down encampments – but they said cities first had to offer people adequate shelter.
That’s a challenge in many places that don’t have nearly enough shelter beds. In briefs filed by local officials, cities and town also expressed frustration that many unhoused people reject shelter when it is available; they may not want to go if a facility bans pets, for example, or prohibits drugs and alcohol.
Critics also said lower court rulings were ambiguous, making them unworkable in practice. Localities have faced dozens of lawsuits over the details of what’s allowed. And they argued that homelessness is a complex problem that requires balancing competing interests, something local officials are better equipped to do than the courts.
"We are trying to show there's respect for the public areas that we all need to have," Seattle City Attorney Ann Davison told NPR earlier this year. She wrote a legal brief on behalf of more than a dozen other cities. "We care for people, and we're engaging and being involved in the long-term solution for them."
The decision will not solve the larger problem of rising homelessness
Attorneys for homeless people in Grants Pass argued that the city’s regulations were so sweeping, they effectively made it illegal for someone without a home to exist. To discourage sleeping in public spaces, the city banned the use of stoves and sleeping bags, pillows or other bedding. But Grants Pass has no public shelter, only a Christian mission that imposes various restrictions and requires people to attend religious service.
"It's sort of the bare minimum in what a just society should expect, is that you're not going to punish someone for something they have no ability to control," said Ed Johnson of the Oregon Law Center, which represents those who sued the city.
He also said saddling people with fines and a criminal record makes it even harder for them to eventually get into housing.
Johnson and other advocates say today’s decision won’t change the core problem behind rising homelessness: a severe housing shortage, and rents that have become unaffordable for a record half of all tenants. The only real solution, they say, is to create lots more housing people can afford – and that will take years.
- homelessness
- Supreme Court

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This means having a system in place for tracking your progress and keeping your work area tidy. 7. Practice problem solving. One of the best ways to improve your accounting problem solving skills is to practice. This can be done by working on practice problems or by taking on small projects in your personal life. 8.
Accounting Problem-solving in Action. Problem-solving is a term that gets thrown around in interviews and on resumes quite a bit. When the time comes, real problem-solvers like Adam approach things in a specific way. System Upgrades. If you've navigated a system change and survived to tell the tale, some would say you have superpowers.
The rubric assesses learning in an organized way, providing a common framework (criteria) for students to consistently approach problem solving. The criteria include problem identification, analysis, and communication of results. It guides students through a series of problem-solving steps using terms and vocabulary specific to the accounting ...
Developing problem-solving skills will set you apart from your colleagues, as you will be able to help solve these complex problems. For instance, you will be a vital resource for developing the finance function. You'll also become a valued partner to other non-financial managers. You will be able to propose solutions that work for you and them.
Introduction: Problem definition is a crucial step in problem-solving processes across various domains, including accounting and finance. It involves clearly identifying and understanding the nature and scope of the problem at hand. In this guide, we will delve into the concept of problem definition, its importance, and how learners in accounting and finance can effectively […]
Here we outline six ways to solve the majority of your accounting issues. 1. Know the difference between profit and cash flow. If you're a new business owner, it can be easy to spend money on growing your business rather than earning that money back again in profits. You may have a profitable business, but it can still become bankrupt by ...
Problem-solving An accountant can analyse a situation, identify potential issues and evaluate solutions. For example, they can use problem-solving skills to address transactional errors in accounting records. They may also use these skills to handle bank reconciliation challenges. Related: Problem-Solving Skills Examples (With Steps to Develop ...
Problem solving is about using logic and your technical expertise to assess a situation and to come up with a workable solution. It is connected to other skills such as level-headedness and resilience, analytical skills and good teamworking skills. It also requires creativity, which is best learnt through collaboration - brainstorming with ...
How is the nature of problem-solving changing in accounting? Emerging technologies are causing the accounting industry to change. Computer programmes are starting to rectify the nitty-gritty numbers issues that accountants traditionally dealt with, meaning you will be faced with new problems to solve.
Step 1 - Define the Problem. The definition of the problem is the first step in effective problem solving. This may appear to be a simple task, but it is actually quite difficult. This is because problems are frequently complex and multi-layered, making it easy to confuse symptoms with the underlying cause.
Step 3: Organize Your Work Organizing your work is key to solving accounting questions efficiently. Create a neat and well-structured format for your calculations, whether on paper or in a ...
Here are some tips to help you solve accounting practice problems more effectively. 1. Break it Down: When faced with a challenging problem, break it down into smaller, manageable parts. This will not only make the problem seem less daunting but also allow you to focus on each component individually. 2.
Problem Solving refers to the cognitive process of identifying, analysing, and resolving a challenge or obstacle. It involves using logical reasoning, critical thinking, and creativity to find effective solutions. It requires an in-depth analysis to solve problems in many situations, whether simple everyday problems or complex issues.
Problem solving is an increasingly important soft skill for those in business. The Future of Jobs Survey by the World Economic Forum drives this point home. According to this report, complex problem solving is identified as one of the top 15 skills that will be sought by employers in 2025, along with other soft skills such as analytical thinking, creativity and leadership.
Definition and Importance. Problem solving is the process of finding solutions to obstacles or challenges you encounter in your life or work. It is a crucial skill that allows you to tackle complex situations, adapt to changes, and overcome difficulties with ease. Mastering this ability will contribute to both your personal and professional ...
Although problem-solving is a skill in its own right, a subset of seven skills can help make the process of problem-solving easier. These include analysis, communication, emotional intelligence, resilience, creativity, adaptability, and teamwork. 1. Analysis. As a manager, you'll solve each problem by assessing the situation first.
Delays in advanced software technology adoption and failures in regulatory compliance can lead to accounting challenges and problems for businesses. These accounting issues include errors in financial statements, fraud and security risks, and the potential for massive fines and imprisonment for regulatory non-compliance.
BI and data analytics (see the third accounting problem) Recurring bill management; AP automation and automated customer billing solutions; Conclusion. We've referenced it a lot in relation to solving your accounting issues, but automated financial and accounting tools go a long way toward solving problems in accounting. At their baseline ...
For example, you can use communication skills to explain a data visualization to team members and help them understand company performance, or to present high-level findings from a data exercise or statistical analysis. Examples of analytical communication skills include: Verbal communication. Storytelling. Chart, graph, and data presentation.
Separate accounting tasks to prevent overburdening staff and common oversights e.g., separating authorization, recording, and custody of assets. Regular Review of Accounting Policies: Periodically review your company's accounting policies to ensure they align with current GAAP or relevant standards.
No one is unemotional. However, analytical thinkers are able to separate their emotion from the situation and use the data provided to arrive at a conclusion. Analytical problem solving means reasoning using facts and logic. Past experience or opinions which cannot be substantiated are ignored.
"To solve problems, we need to commit to making time to face a problem in its full complexity, which also requires that we take back control of our thinking," says Chris Griffiths, an expert ...
The accounting equation is a fundamental accounting principle that states that the total assets of a business are equal to the sum of its liabilities and owner's equity. It forms the basis of the double-entry accounting system. The accounting equation is based on the double-entry bookkeeping system, which means that for every transaction ...
Problem-solving isa process of solving any kind of problem. This process is acted upon in some steps. These steps start from identifying the problem and determining the cause of the problem. After the problem and its cause are identified, the next step is to select alternatives for the solution and implement the solutions.
The decision will not solve the larger problem of rising homelessness. Attorneys for homeless people in Grants Pass argued that the city's regulations were so sweeping, they effectively made it ...