HIGH SCHOOL
- ACT Tutoring
- SAT Tutoring
- PSAT Tutoring
- ASPIRE Tutoring
- SHSAT Tutoring
- STAAR Tutoring

GRADUATE SCHOOL
- MCAT Tutoring
- GRE Tutoring
- LSAT Tutoring
- GMAT Tutoring
- AIMS Tutoring
- HSPT Tutoring
- ISAT Tutoring
- SSAT Tutoring
Search 50+ Tests
Loading Page
math tutoring
- Elementary Math
- Pre-Calculus
- Trigonometry
science tutoring
Foreign languages.
- Mandarin Chinese
elementary tutoring
- Computer Science
Search 350+ Subjects
- Video Overview
- Tutor Selection Process
- Online Tutoring
- Mobile Tutoring
- Instant Tutoring
- How We Operate
- Our Guarantee
- Impact of Tutoring
- Reviews & Testimonials
- About Varsity Tutors
Trigonometry : Solving Word Problems with Trigonometry
Study concepts, example questions & explanations for trigonometry, all trigonometry resources, example questions, example question #1 : solving word problems with trigonometry.

You can draw the following right triangle using the information given by the question:

Since you want to find the height of the platform, you will need to use tangent.

You can draw the following right triangle from the information given by the question.
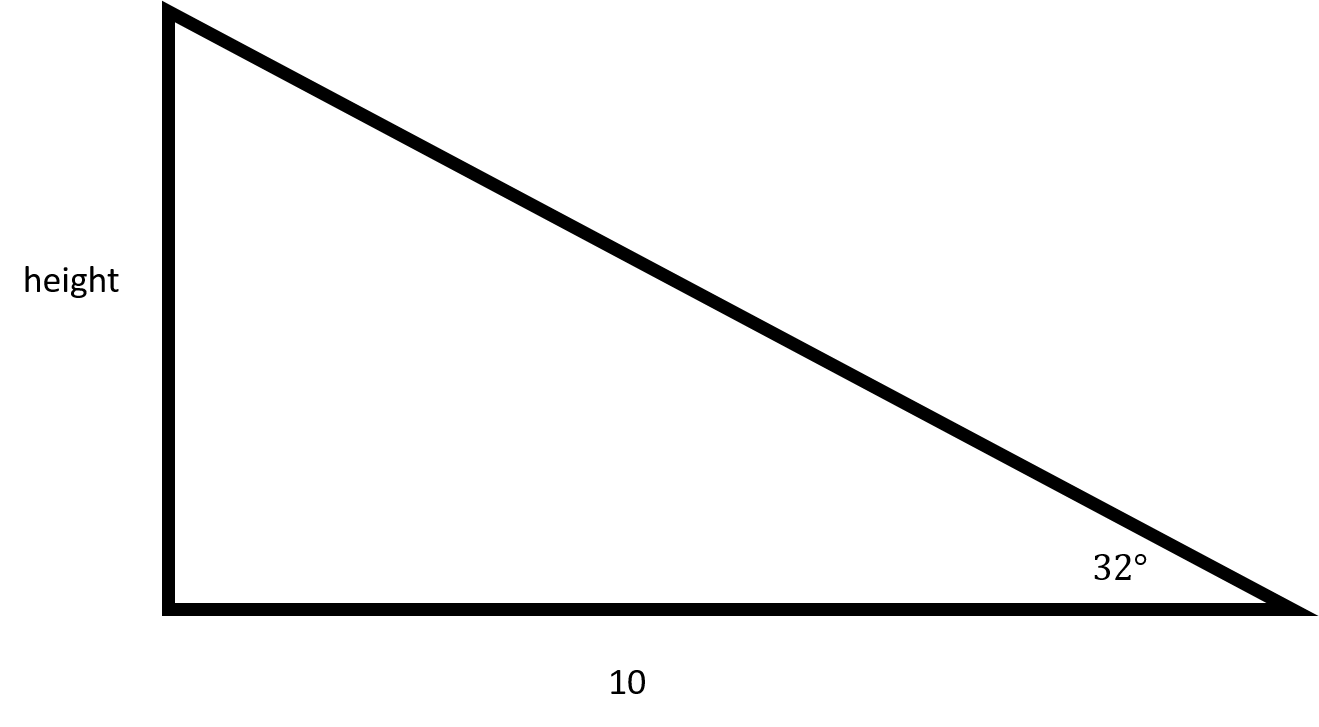
In order to find the height of the flagpole, you will need to use tangent.

You can draw the following right triangle from the information given in the question:
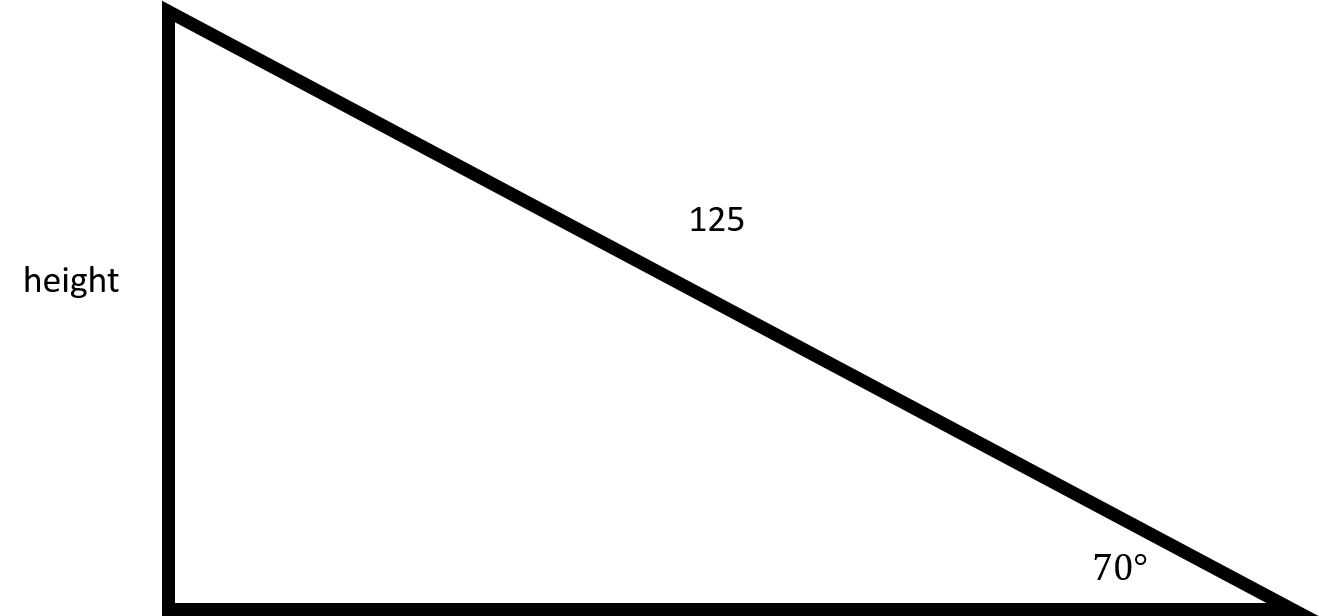
In order to find out how far up the ladder goes, you will need to use sine.

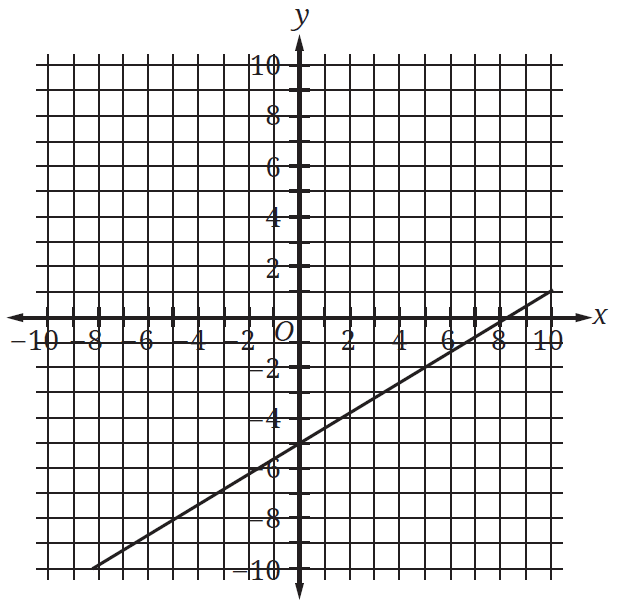
In right triangle ABC, where angle A measures 90 degrees, side AB measures 15 and side AC measures 36, what is the length of side BC?

This triangle cannot exist.

Example Question #5 : Solving Word Problems With Trigonometry
A support wire is anchored 10 meters up from the base of a flagpole, and the wire makes a 25 o angle with the ground. How long is the wire, w? Round your answer to two decimal places.
23.81 meters

28.31 meters
21.83 meters
To make sense of the problem, start by drawing a diagram. Label the angle of elevation as 25 o , the height between the ground and where the wire hits the flagpole as 10 meters, and our unknown, the length of the wire, as w.
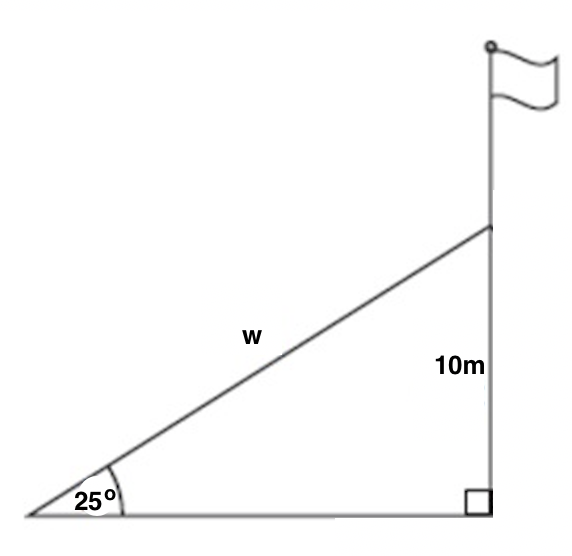
Now, we just need to solve for w using the information given in the diagram. We need to ask ourselves which parts of a triangle 10 and w are relative to our known angle of 25 o . 10 is opposite this angle, and w is the hypotenuse. Now, ask yourself which trig function(s) relate opposite and hypotenuse. There are two correct options: sine and cosecant. Using sine is probably the most common, but both options are detailed below.
We know that sine of a given angle is equal to the opposite divided by the hypotenuse, and cosecant of an angle is equal to the hypotenuse divided by the opposite (just the reciprocal of the sine function). Therefore:

To solve this problem instead using the cosecant function, we would get:

The reason that we got 23.7 here and 23.81 above is due to differences in rounding in the middle of the problem.

Example Question #6 : Solving Word Problems With Trigonometry
When the sun is 22 o above the horizon, how long is the shadow cast by a building that is 60 meters high?
To solve this problem, first set up a diagram that shows all of the info given in the problem.
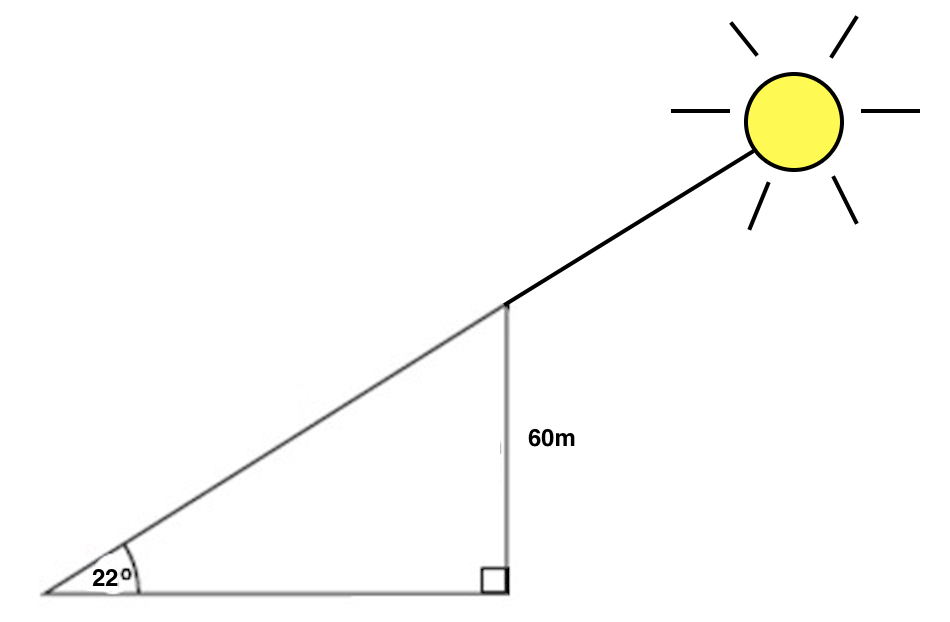
Next, we need to interpret which side length corresponds to the shadow of the building, which is what the problem is asking us to find. Is it the hypotenuse, or the base of the triangle? Think about when you look at a shadow. When you see a shadow, you are seeing it on something else, like the ground, the sidewalk, or another object. We see the shadow on the ground, which corresponds to the base of our triangle, so that is what we'll be solving for. We'll call this base b.

Therefore the shadow cast by the building is 150 meters long.
If you got one of the incorrect answers, you may have used sine or cosine instead of tangent, or you may have used the tangent function but inverted the fraction (adjacent over opposite instead of opposite over adjacent.)
Example Question #7 : Solving Word Problems With Trigonometry
From the top of a lighthouse that sits 105 meters above the sea, the angle of depression of a boat is 19 o . How far from the boat is the top of the lighthouse?
423.18 meters
318.18 meters
36.15 meters
110.53 meters
To solve this problem, we need to create a diagram, but in order to create that diagram, we need to understand the vocabulary that is being used in this question. The following diagram clarifies the difference between an angle of depression (an angle that looks downward; relevant to our problem) and the angle of elevation (an angle that looks upward; relevant to other problems, but not this specific one.) Imagine that the top of the blue altitude line is the top of the lighthouse, the green line labelled GroundHorizon is sea level, and point B is where the boat is.
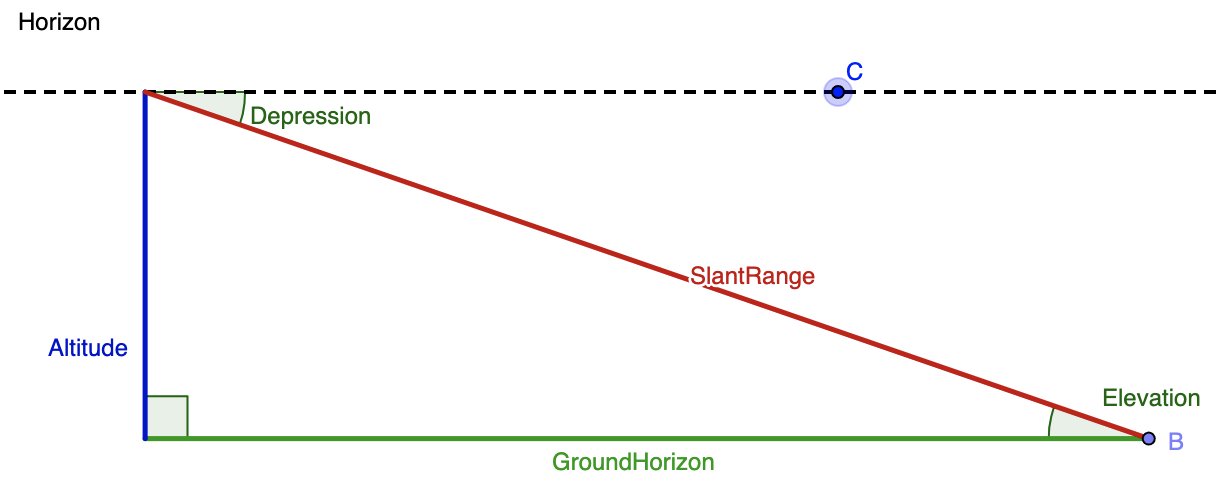
Merging together the given info and this diagram, we know that the angle of depression is 19 o and and the altitude (blue line) is 105 meters. While the blue line is drawn on the left hand side in the diagram, we can assume is it is the same as the right hand side. Next, we need to think of the trig function that relates the given angle, the given side, and the side we want to solve for. The altitude or blue line is opposite the known angle, and we want to find the distance between the boat (point B) and the top of the lighthouse. That means that we want to determine the length of the hypotenuse, or red line labelled SlantRange. The sine function relates opposite and hypotenuse, so we'll use that here. We get:

Example Question #8 : Solving Word Problems With Trigonometry
Angelina just got a new car, and she wants to ride it to the top of a mountain and visit a lookout point. If she drives 4000 meters along a road that is inclined 22 o to the horizontal, how high above her starting point is she when she arrives at the lookout?
9.37 meters
1480 meters
3708.74 meters
10677.87 meters
1616.1 meters
As with other trig problems, begin with a sketch of a diagram of the given and sought after information.
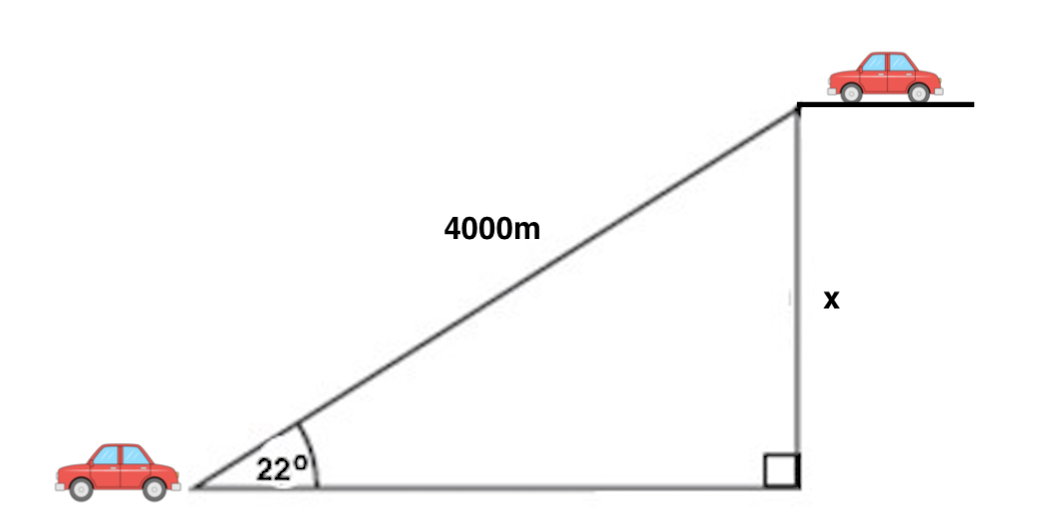
Angelina and her car start at the bottom left of the diagram. The road she is driving on is the hypotenuse of our triangle, and the angle of the road relative to flat ground is 22 o . Because we want to find the change in height (also called elevation), we want to determine the difference between her ending and starting heights, which is labelled x in the diagram. Next, consider which trig function relates together an angle and the sides opposite and hypotenuse relative to it; the correct one is sine. Then, set up:

Therefore the change in height between Angelina's starting and ending points is 1480 meters.
Example Question #9 : Solving Word Problems With Trigonometry
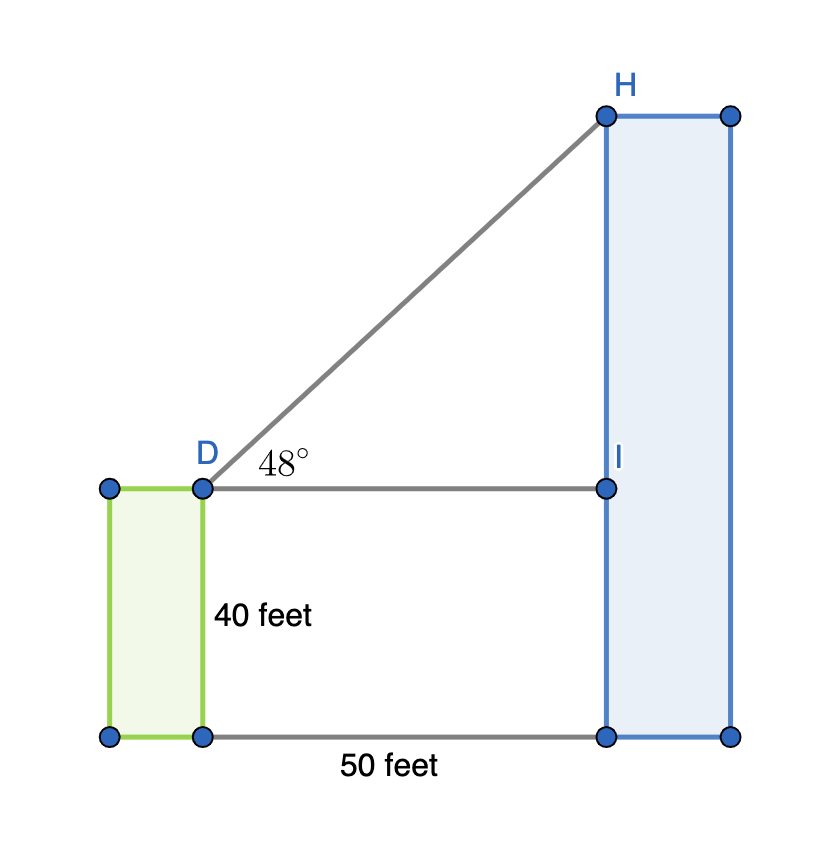
Two buildings with flat roofs are 50 feet apart. The shorter building is 40 feet tall. From the roof of the shorter building, the angle of elevation to the edge of the taller building is 48 o . How high is the taller building?
To solve this problem, let's start by drawing a diagram of the two buildings, the distance in between them, and the angle between the tops of the two buildings. Then, label in the given lengths and angle.
Example Question #10 : Solving Word Problems With Trigonometry
Two buildings with flat roofs are 80 feet apart. The shorter building is 55 feet tall. From the roof of the shorter building, the angle of elevation to the edge of the taller building is 32 o . How high is the taller building?
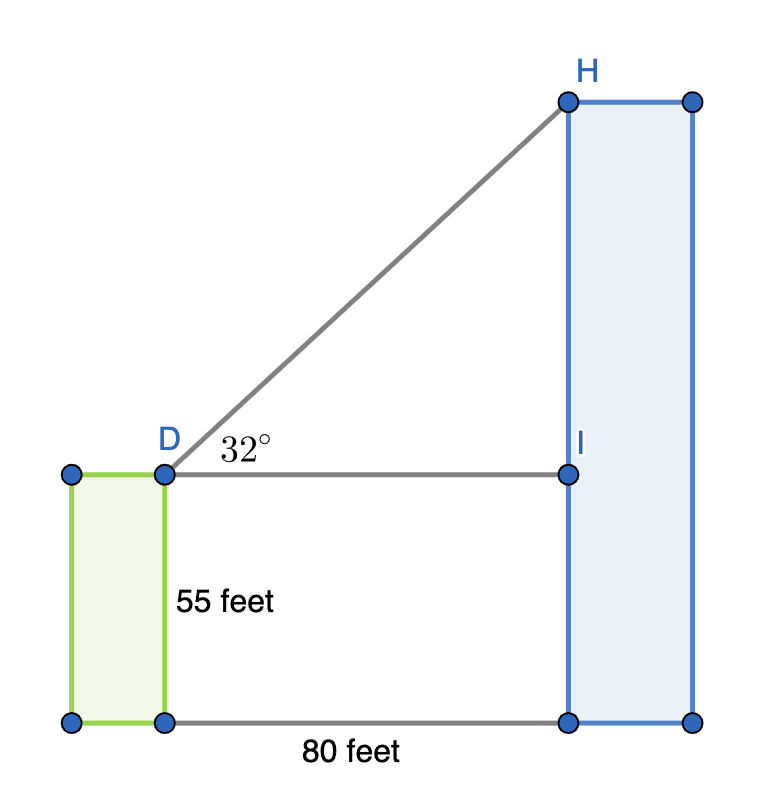
Report an issue with this question
If you've found an issue with this question, please let us know. With the help of the community we can continue to improve our educational resources.
DMCA Complaint
If you believe that content available by means of the Website (as defined in our Terms of Service) infringes one or more of your copyrights, please notify us by providing a written notice (“Infringement Notice”) containing the information described below to the designated agent listed below. If Varsity Tutors takes action in response to an Infringement Notice, it will make a good faith attempt to contact the party that made such content available by means of the most recent email address, if any, provided by such party to Varsity Tutors.
Your Infringement Notice may be forwarded to the party that made the content available or to third parties such as ChillingEffects.org.
Please be advised that you will be liable for damages (including costs and attorneys’ fees) if you materially misrepresent that a product or activity is infringing your copyrights. Thus, if you are not sure content located on or linked-to by the Website infringes your copyright, you should consider first contacting an attorney.
Please follow these steps to file a notice:
You must include the following:
A physical or electronic signature of the copyright owner or a person authorized to act on their behalf; An identification of the copyright claimed to have been infringed; A description of the nature and exact location of the content that you claim to infringe your copyright, in \ sufficient detail to permit Varsity Tutors to find and positively identify that content; for example we require a link to the specific question (not just the name of the question) that contains the content and a description of which specific portion of the question – an image, a link, the text, etc – your complaint refers to; Your name, address, telephone number and email address; and A statement by you: (a) that you believe in good faith that the use of the content that you claim to infringe your copyright is not authorized by law, or by the copyright owner or such owner’s agent; (b) that all of the information contained in your Infringement Notice is accurate, and (c) under penalty of perjury, that you are either the copyright owner or a person authorized to act on their behalf.
Send your complaint to our designated agent at:
Charles Cohn Varsity Tutors LLC 101 S. Hanley Rd, Suite 300 St. Louis, MO 63105
Or fill out the form below:
Contact Information
Complaint details.

| Email address: | |
| Your name: | |
| Feedback: |
Trigonometry Word Problems
Contextual use of triangle properties, ratios, theorems, and laws..
- Assign Practice
- Assign to Class
- Create Assignment
- Add to Library
- Share with Classes
- Add to FlexBook® Textbook
- Edit Edit View Latest Customize Customize help icon
- PDF Most Devices
- mobi Kindle
- ePub iPad and Android
Notes/Highlights
| Color | Highlighted Text | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Show More | |||
Image Attributions
Show hide details, description, learning objectives, difficulty level, date created:, last modified:, other details, concept nodes:, show hide resources.

- English Language Arts
- Graphic Organizers
- Social Studies
- Teacher Printables
- Foreign Language
Home > Math Worksheets > Word Problems > Trigonometry
These types of problems focus on the lengths of sides and angles within a triangle. After all that is what trigonometry is all about. Start to approach these problems by focusing on understanding the figures that are involved and model this by drawing diagrams. On the diagram highlight all the information that we know about each stage of the diagram. Make sure that if a unit of measure is attached to that information that you show that as well. We then start to analyze the system and identify if Pythagorean Theorem comes into play or if we can apply various trigonometric functions to determine the angle of elevation or depression.
In these worksheets, your students will solve word problems involving trigonometry. Diagrams are included to accompany some problems. These are moderately complex problems and a sound understanding of trigonometry is required in order for students to be successful with these worksheets. There are six worksheets in this set. This set of worksheets contains lessons, step-by-step solutions to sample problems, and both simple and more complex problems. It also includes ample worksheets for students to practice independently. Students may require extra paper on which to do their calculations. Most worksheets contain between eight and eleven problems. When finished with this set of worksheets, students will be able to solve word problems that involve trigonometry. These worksheets explain how to solve word problems by using trigonometry. Sample problems are solved and practice problems are provided.
Get Free Worksheets In Your Inbox!
Trigonometry word problems worksheets, click the buttons to print each worksheet and answer key., trigonometric word problem lesson.
This worksheet explains how to solve word problems by using trigonometry. A sample problem is solved, and two practice problems are provided.
You are stationed at a radar base and you observe an unidentified plane at an altitude h = 2000 m flying towards your radar base at an angle of elevation = 30o. After exactly one minute, your radar sweep reveals that the plane is now at an angle of elevation = 60o maintaining the same altitude. What is the speed (in m/s) of the plane?
A fisherman drops a boat anchor and pays out 93 meter of anchor rope. The rope makes an angle of depression of 59.5 degrees with the horizontal. Assuming a level bottom, how deep in the water?
Review and Practice
What is the measure of the diagonal of the rectangle ABHG ?
A tree in a back yard is to be cut down. The base of the tree from the house is 23 meters away, and the angle of elevation from the house to the top of the tree is 45.5 degrees. Could the tree hit the house when it is cut down?
An aerial 30 meter tail is to be supported by 2 guy wires each 50 meter from its base. How long will each guy wire be?

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

4.1.7: Trigonometry Word Problems
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 14875
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Contextual use of triangle properties, ratios, theorems, and laws.
Angle of Depression and Angle of Elevation
One application of the trigonometric ratios is to find lengths that you cannot measure. Very frequently, angles of depression and elevation are used in these types of problems.
Angle of Depression: The angle measured down from the horizon or a horizontal line.

Angle of Elevation: The angle measured up from the horizon or a horizontal line.
What if you placed a ladder 10 feet from a haymow whose floor is 20 feet from the ground? How tall would the ladder need to be to reach the haymow's floor if it forms a \(30^{\circ}\) angle with the ground?
Example \(\PageIndex{1}\)
A math student is standing 25 feet from the base of the Washington Monument. The angle of elevation from her horizontal line of sight is \(87.4^{\circ}\). If her “eye height” is 5 ft, how tall is the monument?
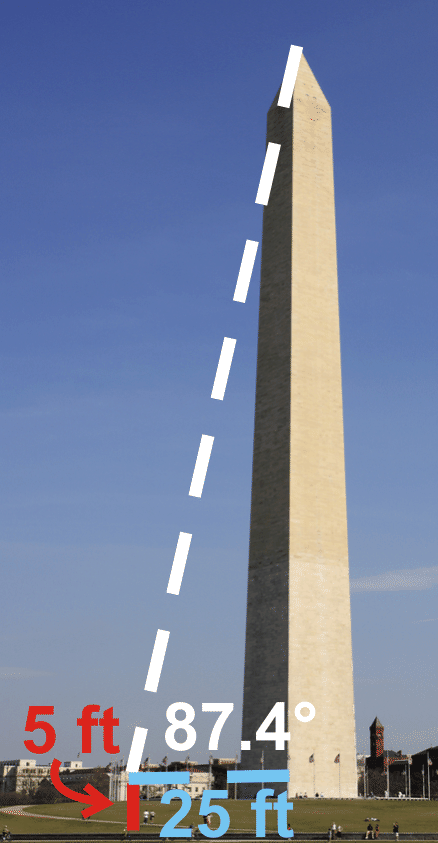
We can find the height of the monument by using the tangent ratio.
\(\begin{aligned} \tan 87.4^{\circ} &=\dfrac{h}{25} \\ h&=25\cdot \tan 87.4^{\circ}=550.54 \end{aligned}\)
Adding 5 ft, the total height of the Washington Monument is 555.54 ft.
Example \(\PageIndex{2}\)
A 25 foot tall flagpole casts a 42 foot shadow. What is the angle that the sun hits the flagpole?
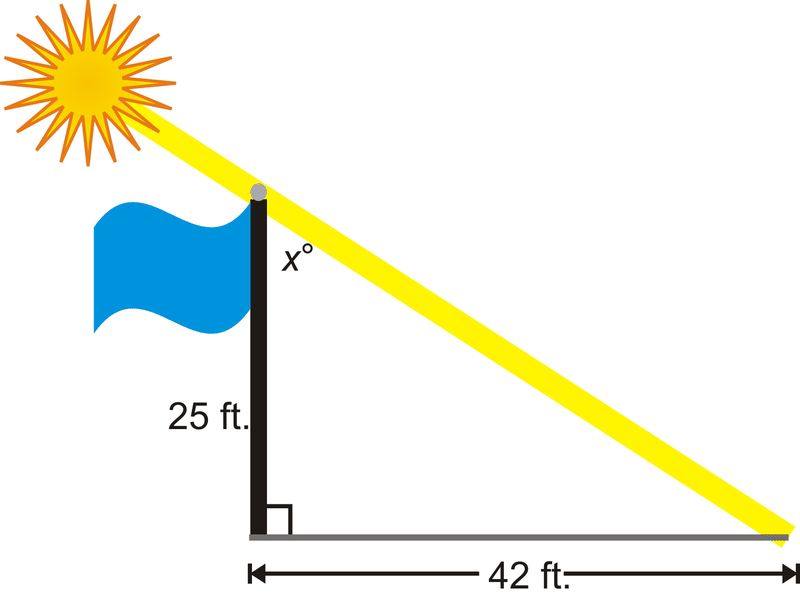
Draw a picture. The angle that the sun hits the flagpole is \(x^{\circ}\). We need to use the inverse tangent ratio.
\(\begin{aligned} \tan x &=\dfrac{42}{25} \\ \tan^{−1} \dfrac{42}{25}&\approx 59.2^{\circ}=x \end{aligned}\)
Example \(\PageIndex{3}\)
Elise is standing on top of a 50 foot building and sees her friend, Molly. If Molly is 30 feet away from the base of the building, what is the angle of depression from Elise to Molly? Elise’s eye height is 4.5 feet.
Because of parallel lines, the angle of depression is equal to the angle at Molly, or \(x^{\circ}\). We can use the inverse tangent ratio.
\(\tan^{−1} \left(\dfrac{54.5}{30}\right)=61.2^{\circ}=x\)
Example \(\PageIndex{4}\)
Mark is flying a kite and realizes that 300 feet of string are out. The angle of the string with the ground is \(42.5^{\circ}\). How high is Mark's kite above the ground?
It might help to draw a picture. Then write and solve a trig equation.
\(\begin{aligned} \sin 42.5^{\circ} &=\dfrac{x}{300}\\ 300\cdot \sin 42.5^{\circ} &=x \\ x&\approx 202.7\end{aligned}\)
The kite is about 202.7 feet off of the ground.
Example \(\PageIndex{5}\)
A 20 foot ladder rests against a wall. The base of the ladder is 7 feet from the wall. What angle does the ladder make with the ground?
It might help to draw a picture.
\(\begin{aligned} \cos x &=\dfrac{7}{20}\\ x&=\cos ^{−1}\dfrac{7}{20}\\ x&\approx 69.5^{\circ}\end{aligned}\)
Use what you know about right triangles to solve for the missing angle. If needed, draw a picture. Round all answers to the nearest tenth of a degree.
- A 75 foot building casts an 82 foot shadow. What is the angle that the sun hits the building?
- Over 2 miles (horizontal), a road rises 300 feet (vertical). What is the angle of elevation?
- A boat is sailing and spots a shipwreck 650 feet below the water. A diver jumps from the boat and swims 935 feet to reach the wreck. What is the angle of depression from the boat to the shipwreck?
- Standing 100 feet from the base of a building, Sam measures the angle to the top of the building from his eye height to be \(50^{\circ}\). If his eyes are 6 feet above the ground, how tall is the building?
- Over 4 miles (horizontal), a road rises 200 feet (vertical). What is the angle of elevation?
- A 90 foot building casts an 110 foot shadow. What is the angle that the sun hits the building?
- Luke is flying a kite and realizes that 400 feet of string are out. The angle of the string with the ground is \(50^{\circ}\). How high is Luke's kite above the ground?
- An 18 foot ladder rests against a wall. The base of the ladder is 10 feet from the wall. What angle does the ladder make with the ground?
Review (Answers)
To see the Review answers, open this PDF file and look for section 8.9.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| The angle of depression is the angle formed by a horizontal line and the line of sight down to an object when the image of an object is located beneath the horizontal line. | |
| The angle of elevation is the angle formed by a horizontal line and the line of sight up to an object when the image of an object is located above the horizontal line. | |
| ASA, angle-side-angle, refers to two known angles in a triangle with one known side between the known angles. | |
| The law of cosines is a rule relating the sides of a triangle to the cosine of one of its angles. The law of cosines states that c2=a2+b2−2abcosC, where C is the angle across from side c. | |
| The law of sines is a rule applied to triangles stating that the ratio of the sine of an angle to the side opposite that angle is equal to the ratio of the sine of another angle in the triangle to the side opposite that angle. | |
| The tangent of an angle in a right triangle is a value found by dividing the length of the side opposite the given angle by the length of the side adjacent to the given angle. | |
| Ratios that help us to understand the relationships between sides and angles of right triangles. |
Additional Resources
Interactive element.
Video: Trigonometry Word Problems Principles - Basic
Activities: Trigonometry Word Problems Discussion Questions
Practice: Trigonometry Word Problems
Real World: Measuring Mountains
TRIGONOMETRY WORD PROBLEMS WITH SOLUTIONS
Problem 1 :
The angle of elevation of the top of the building at a distance of 50 m from its foot on a horizontal plane is found to be 60 °. Find the height of the building.
Draw a sketch.
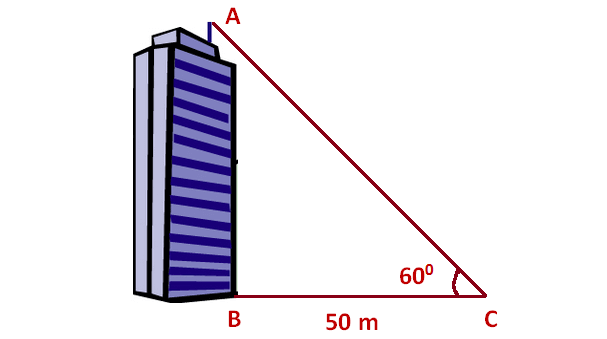
Here, AB represents height of the building, BC represents distance of the building from the point of observation.
In the right triangle ABC, the side which is opposite to the angle 60° is known as opposite side (AB), the side which is opposite to 90° is called hypotenuse side (AC) and the remaining side is called adjacent side (BC).
Now we need to find the length of the side AB.
tanθ = Opposite side/Adjacent side
tan60° = AB/BC
√3 x 50 = AB
Approximate value of √3 is 1.732
AB = 50 (1.732)
AB = 86.6 m
So, the height of the building is 86.6 m.
Problem 2 :
A ladder placed against a wall such that it reaches the top of the wall of height 6 m and the ladder is inclined at an angle of 60 ° . Find how far the ladder is from the foot of the wall.
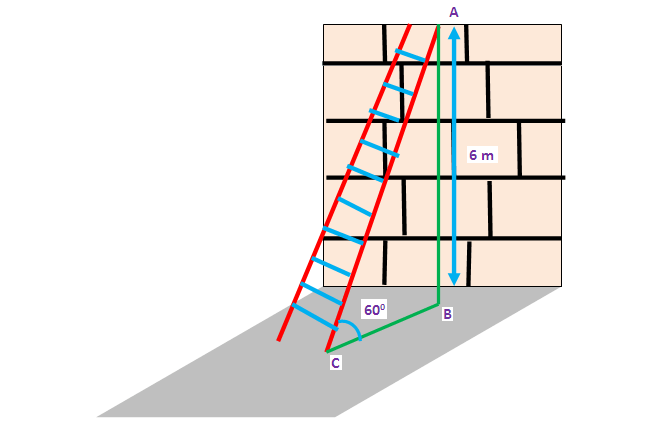
Here AB represents height of the wall, BC represents the distance between the wall and the foot of the ladder and AC represents the length of the ladder.
In the right triangle ABC, the side which is opposite to angle 60° is known as opposite side (AB), the side which is opposite to 90° is called hypotenuse side (AC) and remaining side is called adjacent side (BC).
Now, we need to find the distance between foot of the ladder and the wall. That is, we have to find the length of BC.
tanθ = opposite side/adjacent side
BC = (6/√3) x (√3/√3)
BC = (6√3)/3
Approximate value of √3 is 1.732.
BC = 2 (1.732)
BC = 3.464 m
So, the distance between foot of the ladder and the wall is 3.464 m.
Problem 3 :
A string of a kite is 100 meters long and t he inclination of the string with the ground is 60°. Find the height of the kite, assuming that there is no slack in the string.
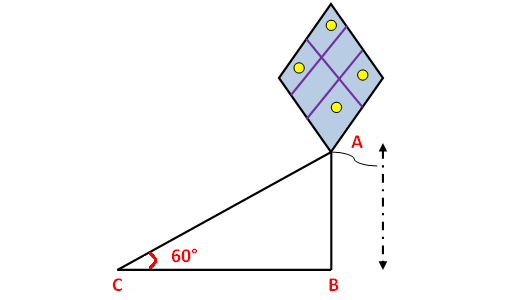
Here AB represents height of kite from the ground, BC represents the distance of kite from the point of observation.
In the right triangle ABC the side which is opposite to angle 60° is known as opposite side (AB), the side which is opposite to 90° is called hypotenuse side (AC) and remaining side is called adjacent side (BC).
Now we need to find the height of the side AB.
sinθ = opposite side/hypotenuse side
sinθ = AB/AC
sin60° = AB/100
√3/2 = AB/100
(√3/2) x 100 = AB
AB = 50√3 m
So, the height of kite from the ground 50√3 m.
Problem 4 :
From the top of the tower 30 m height a man is observing the base of a tree at an angle of depression measuring 30 ° . Find the distance between the tree and the tower.
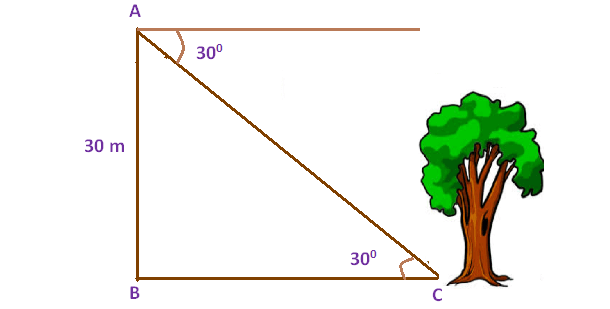
Here AB represents height of the tower, BC represents the distance between foot of the tower and the foot of the tree.
Now we need to find the distance between foot of the tower and the foot of the tree (BC).
tan30° = AB/BC
1/√3 = 30/BC
BC = 30(1.732)
BC = 51.96 m
So, the distance between the tree and the tower is 51.96 m.
Problem 5 :
A man wants to determine the height of a light house. He measured the angle at A and found that tan A = 3/4. What is the height of the light house if A is 40m from the base?
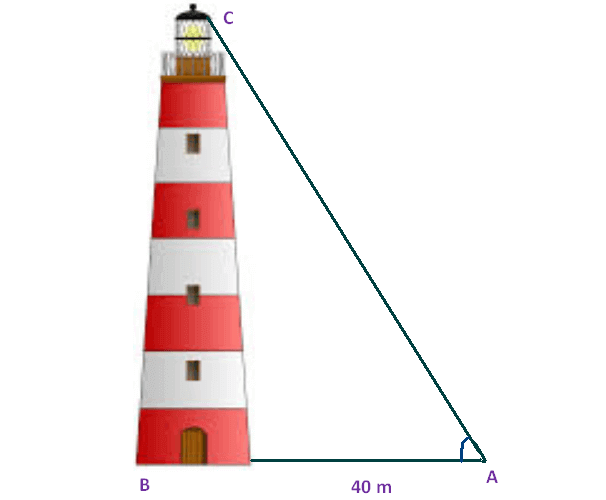
Here BC represents height of the light house, AB represents the distance between the light house from the point of observation.
In the right triangle ABC the side which is opposite to the angle A is known as opposite side (BC), the side which is opposite to 90° is called hypotenuse side (AC) and remaining side is called adjacent side (AB).
Now we need to find the height of the light house (BC).
tanA = opposite side/adjacent side
tanA = BC/AB
Given : tanA = 3/4.
3/4 = BC/40
Multiply each side by 40.
So, the height of the light house is 30 m.
Problem 6 :
A ladder is leaning against a vertical wall makes an angle of 20° with the ground. The foot of the ladder is 3 m from the wall. Find the length of ladder.
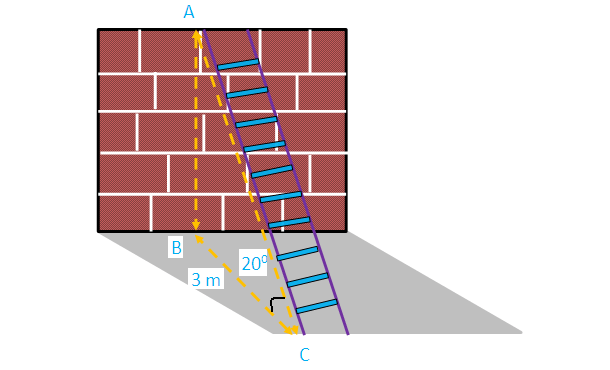
Here AB represents height of the wall, BC represents the distance of the wall from the foot of the ladder.
In the right triangle ABC, the side which is opposite to the angle 20° is known as opposite side (AB),the side which is opposite to 90° is called hypotenuse side (AC) and remaining side is called adjacent side (BC).
Now we need to find the length of the ladder (AC).
cosθ = adjacent side/hypotenuse side
Cosθ = BC/AC
Cos 20° = 3/AC
0.9397 = 3/AC
AC = 3/0.9396
So, the length of the ladder is about 3.193 m.
Problem 7 :
A kite is flying at a height of 65 m attached to a string. If the inclination of the string with the ground is 31°, find the length of string.
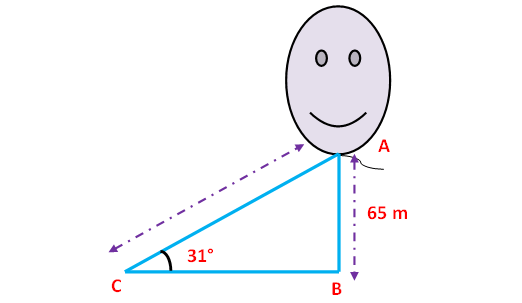
Here AB represents height of the kite. In the right triangle ABC the side which is opposite to angle 31° is known as opposite side (AB), the side which is opposite to 90° is called hypotenuse side (AC) and the remaining side is called adjacent side (BC).
Now we need to find the length of the string AC.
sin31° = AB/AC
0.5150 = 65/AC
AC = 65/0.5150
AC = 126.2 m
Hence, the length of the string is 126.2 m.
Problem 8 :
The length of a string between a kite and a point on the ground is 90 m. If the string makes an angle θ with the ground level such that tan θ = 15/8, how high will the kite be ?
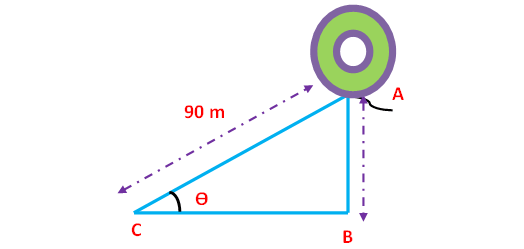
Here AB represents height of the balloon from the ground. In the right triangle ABC the side which is opposite to angle θ is known as opposite side (AB), the side which is opposite to 90° is called hypotenuse side (AC) and remaining side is called adjacent side (BC).
tanθ = 15/8 ----> cotθ = 8/15
cscθ = √(1+ cot 2 θ)
cscθ = √(1 + 64/225)
cscθ = √(225 + 64)/225
cscθ = √289/225
cscθ = 17/15 ----> sinθ = 15/17
But, sinθ = opposite side/hypotenuse side = AB/AC.
AB/AC = 15/17
AB/90 = 15/17
So, the height of the tower is 79.41 m.
Problem 9 :
An airplane is observed to be approaching a point that is at a distance of 12 km from the point of observation and makes an angle of elevation of 50°. Find the height of the airplane above the ground.
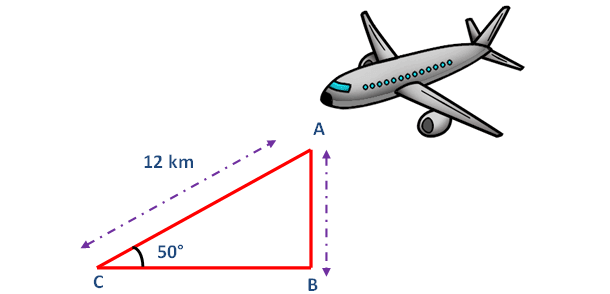
Here AB represents height of the airplane from the ground. In the right triangle ABC the side which is opposite to angle 50° is known as opposite side (AB), the side which is opposite to 90° is called hypotenuse side (AC) and remaining side is called adjacent side (BC).
From the figure given above, AB stands for the height of the airplane above the ground.
sin50° = AB/AC
0.7660 = h/12
0.7660 x 12 = h
So, the height of the airplane above the ground is 9.192 km.
Problem 10 :
A balloon is connected to a meteorological station by a cable of length 200 m inclined at 60 ° angle with the ground. Find the height of the balloon from the ground. (Imagine that there is no slack in the cable)
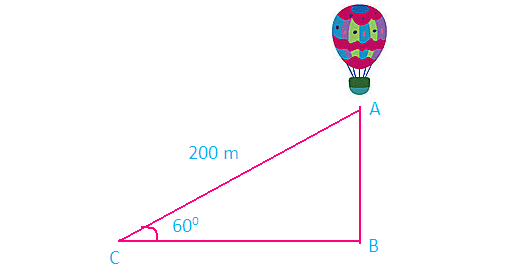
Here AB represents height of the balloon from the ground. In the right triangle ABC the side which is opposite to angle 60° is known as opposite side (AB), the side which is opposite to 90° is called hypotenuse (AC) and the remaining side is called as adjacent side (BC).
From the figure given above, AB stands for the height of the balloon above the ground.
sin60° = AB/200
√3/2 = AB/200
AB = (√3/2) x 200
AB = 100(1.732)
AB = 173.2 m
So, the height of the balloon from the ground is 173.2 m.
Kindly mail your feedback to [email protected]
We always appreciate your feedback.
© All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com
- Sat Math Practice
- SAT Math Worksheets
- PEMDAS Rule
- BODMAS rule
- GEMDAS Order of Operations
- Math Calculators
- Transformations of Functions
- Order of rotational symmetry
- Lines of symmetry
- Compound Angles
- Quantitative Aptitude Tricks
- Trigonometric ratio table
- Word Problems
- Times Table Shortcuts
- 10th CBSE solution
- PSAT Math Preparation
- Privacy Policy
- Laws of Exponents
Recent Articles
SAT Math Videos (Part - 17)
Jul 10, 24 09:42 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions
Jul 10, 24 09:39 AM
Pre Calculus Problems and Solutions (Part - 4)
Jul 09, 24 06:52 PM
Want Better Math Grades?
✅ Unlimited Solutions
✅ Step-by-Step Answers
✅ Available 24/7
➕ Free Bonuses ($1085 value!)
On this page
- Search IntMath
- Math interactives
- About (site info)
- Uses of Trignometry
- ASCIIMath input, KaTeX output
- ASCIIMath input, LaTeX and KaTeX output
- Send Math in emails
- Syntax for ASCIIMathML
- Math Display Experiments
- Scientific Notebook
- Math Problem Solver
Related Sections
Math Tutoring
Need help? Chat with a tutor anytime, 24/7.
Trigonometry Problem Solver

This tool combines the power of mathematical computation engine that excels at solving mathematical formulas with the power of artificial intelligence large language models to parse and generate natural language answers. This creates a math problem solver that's more accurate than ChatGPT, more flexible than a math calculator, and provides answers faster than a human tutor.
Sign up for free here .
Problem Solver Subjects
Our math problem solver that lets you input a wide variety of trigonometry math problems and it will provide a step by step answer. This math solver excels at math word problems as well as a wide range of math subjects.
- Math Word Problems
- Pre-Algebra
- Geometry Graphing
- Trigonometry
- Precalculus
- Finite Math
- Linear Algebra
Here are example math problems within each subject that can be input into the calculator and solved. This list is constanstly growing as functionality is added to the calculator.
Basic Math Solutions
Below are examples of basic math problems that can be solved.
- Long Arithmetic
- Rational Numbers
- Operations with Fractions
- Ratios, Proportions, Percents
- Measurement, Area, and Volume
- Factors, Fractions, and Exponents
- Unit Conversions
- Data Measurement and Statistics
- Points and Line Segments
Math Word Problem Solutions
Math word problems require interpreting what is being asked and simplifying that into a basic math equation. Once you have the equation you can then enter that into the problem solver as a basic math or algebra question to be correctly solved. Below are math word problem examples and their simplified forms.
Word Problem: Rachel has 17 apples. She gives some to Sarah. Sarah now has 8 apples. How many apples did Rachel give her?
Simplified Equation: 17 - x = 8
Word Problem: Rhonda has 12 marbles more than Douglas. Douglas has 6 marbles more than Bertha. Rhonda has twice as many marbles as Bertha has. How many marbles does Douglas have?
Variables: Rhonda's marbles is represented by (r), Douglas' marbles is represented by (d) and Bertha's marbles is represented by (b)
Simplified Equation: {r = d + 12, d = b + 6, r = 2 �� b}
Word Problem: if there are 40 cookies all together and Angela takes 10 and Brett takes 5 how many are left?
Simplified: 40 - 10 - 5
Pre-Algebra Solutions
Below are examples of Pre-Algebra math problems that can be solved.
- Variables, Expressions, and Integers
- Simplifying and Evaluating Expressions
- Solving Equations
- Multi-Step Equations and Inequalities
- Ratios, Proportions, and Percents
- Linear Equations and Inequalities
Algebra Solutions
Below are examples of Algebra math problems that can be solved.
- Algebra Concepts and Expressions
- Points, Lines, and Line Segments
- Simplifying Polynomials
- Factoring Polynomials
- Linear Equations
- Absolute Value Expressions and Equations
- Radical Expressions and Equations
- Systems of Equations
- Quadratic Equations
- Inequalities
- Complex Numbers and Vector Analysis
- Logarithmic Expressions and Equations
- Exponential Expressions and Equations
- Conic Sections
- Vector Spaces
- 3d Coordinate System
- Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors
- Linear Transformations
- Number Sets
- Analytic Geometry
Trigonometry Solutions
Below are examples of Trigonometry math problems that can be solved.
- Algebra Concepts and Expressions Review
- Right Triangle Trigonometry
- Radian Measure and Circular Functions
- Graphing Trigonometric Functions
- Simplifying Trigonometric Expressions
- Verifying Trigonometric Identities
- Solving Trigonometric Equations
- Complex Numbers
- Analytic Geometry in Polar Coordinates
- Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
- Vector Arithmetic
Precalculus Solutions
Below are examples of Precalculus math problems that can be solved.
- Operations on Functions
- Rational Expressions and Equations
- Polynomial and Rational Functions
- Analytic Trigonometry
- Sequences and Series
- Analytic Geometry in Rectangular Coordinates
- Limits and an Introduction to Calculus
Calculus Solutions
Below are examples of Calculus math problems that can be solved.
- Evaluating Limits
- Derivatives
- Applications of Differentiation
- Applications of Integration
- Techniques of Integration
- Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates
- Differential Equations
Statistics Solutions
Below are examples of Statistics problems that can be solved.
- Algebra Review
- Average Descriptive Statistics
- Dispersion Statistics
- Probability
- Probability Distributions
- Frequency Distribution
- Normal Distributions
- t-Distributions
- Hypothesis Testing
- Estimation and Sample Size
- Correlation and Regression
Finite Math Solutions
Below are examples of Finite Math problems that can be solved.
- Polynomials and Expressions
- Equations and Inequalities
- Linear Functions and Points
- Systems of Linear Equations
- Mathematics of Finance
- Statistical Distributions
Linear Algebra Solutions
Below are examples of Linear Algebra math problems that can be solved.
- Introduction to Matrices
- Linear Independence and Combinations
Chemistry Solutions
Below are examples of Chemistry problems that can be solved.
- Unit Conversion
- Atomic Structure
- Molecules and Compounds
- Chemical Equations and Reactions
- Behavior of Gases
- Solutions and Concentrations
Physics Solutions
Below are examples of Physics math problems that can be solved.
- Static Equilibrium
- Dynamic Equilibrium
- Kinematics Equations
- Electricity
- Thermodymanics
Geometry Graphing Solutions
Below are examples of Geometry and graphing math problems that can be solved.
- Step By Step Graphing
- Linear Equations and Functions
- Polar Equations
Looking for the old Mathway Calculator? We've moved it to here .
Tips, tricks, lessons, and tutoring to help reduce test anxiety and move to the top of the class.
Email Address Sign Up
Math Plane
---->>>FLIGHT DELAYS!!
Recently, Mathplane has been experiencing slow page loads.
Sorry for the delays. We are working on the traffic and server issues.
Thank you for your patience and persistence!
- Welcome message
- Did you know?
- Airport Terminal
- 3rd Grade Worksheets
- Greatest Common Factor & Least Common Multiple
- Decimals Puzzle
- Fractions Exercises
- Mixed Numbers
- Percentages
- Converting Fractions Decimals Percentages
- Word Problems
- Angles & Triangles Exercise
- Middle School Geometry
- Conversions
- Negative Numbers
- Mean Median Mode
- Scientific Notation
- Pre-Algebra Review 1
- Pre-Algebra Review 2
- Pre-Algebra Review 3
- Algebra Preview
- Algebra Preview 2
- Exponents & Roots and Order of Operations
- Negative Exponents and Variables
- Exponents and Exponential Equations
- Inequalities and Number Line
- Absolute Value and Inequalities
- Absolute Value and Inequalities Videos
- Linear Equations
- Linear Equations 2
- Linear Systems
- Linear Systems 2
- Slope & Linear Equations Videos
- Linear Programming (Optimization)
- Story Graphs
- Inverse Functions
- Average Midpoint Distance Test
- Intro to Polynomials
- Factoring Quadratics
- Simplifying Rational Polynomials
- Simplifying Rational Expressions
- f(x) and Piecewise functions
- Probability
- Word Problems 2
- Algebra Word Problem Videos
- Algebra Word Problem Videos 2
- Domain, Range, Functions, & Relations
- Algebra Review 1
- Algebra Review 2
- Algebra Review 3
- Algebra Review 4
- Algebra Review 5
- Geometry Introduction
- Angle Properties
- Triangle Characteristics
- Triangle Restrictions
- Special Quadrilaterals 1
- Special Quadrilaterals 2
- Logic and Reasoning
- Always Sometimes Never
- Congruent Triangles Topics
- Proofs & Postulates 0
- Proofs & Postulates 1
- Proofs & Postulates 2
- Diagramless and Detour Proofs
- Indirect Proofs
- Equidistance Theorem
- Parallel Lines Cut by Transversals
- Planes Properties and Proofs
- Triangle Median Altitude Bisectors
- Midpoint and Distance
- Similarity and Proportions 1
- Similarity and Proportions 2
- Similarity and Proportions 3
- Similarity and Proportions 4
- Means Extremes and Right Triangles
- Pythagorean Theorem & Distance
- Pythagorean Theorem 2 (more questions)
- Area and Perimeter of Polygons 1
- Area and Perimeter of Polygons 2
- Area and Perimeter of Complex Shapes
- Area of Shapes (Honors)
- Surface Area
- Surface Area and Volume (Advanced)
- Circles Introduction
- Circles and Geometry
- Circles and Inscribed Figures
- Circles Review (Honors)
- Circles Review (Advanced)
- Circles Practice Test
- Coordinate Geometry 1
- Coordinate Geometry 2
- Coordinate Geometry 3 Drawing Exercise
- Coordinate Geometry 4 - Advanced
- Locus of Points
- Geometry Construction Videos 1 - Intro
- Geometry Construction Videos 2- Intermediate
- Geometry Construction Videos 3- Advanced
- Geometry Review 1
- Geometry Review 2
- Geometry Review 3
- Geometry Review 4
- Geometry Review 5 Midterm
- Angle Measurement
- Arc Length & Sector Area
- Right Triangle Review
- Trigonometry Introduction
- Unit Circle and Trigonometry Functions
- Inverse Trig Values
- Law of Sines and Cosines I
- Law of Sines and Cosines II
- Law of Sines and Cosines III
- Periodic Functions I - Sine (Graphs)
- Periodic Functions II - Cosine
- Periodic Functions III - Tangent
- Periodic Functions IV - Reciprocals
- Periodic Inverse Functions
- Periodic Trig Function Models
- Trig Identities I - Introduction
- Trig Identities II - Double Angles
- Trig Identities III - Solving and Graphing
- Trig Identities IV - Review Test
- Trig Identities V - Honors
- Polar Coordinates and Complex System
- Polar Equations and Graphs
- Trigonometry Extras
- Trigonometry Review 1
- Trigonometry Review 2
- Trigonometry Review 3
- Trigonometry Review 4
- Algebra I/Geometry Review
- Algebra II Preview
- Graphing I - Parent Functions & Transformations
- Graphing II - Translation, Reflection, & Rotation
- Graphing III Identifying Functions
- Graphing Functions Videos
- Absolute Value Graphing Topics
- Double Absolute Values
- Composite Functions Topics
- Quadratics Overview
- Completing the Square & Quadratic Formula
- Identifying Quadratic Equations from Points
- Quadratics Practice Test
- Comparing Equations
- Modeling Word Problems
- Polynomials: Factors, Roots & Theorems I
- Polynomials: Factors, Roots, & Theorems II
- Polynomials: Factors, Roots, & Theorems III (Honors)
- Solving Rational Equations
- Sketching Rational Expressions I
- Sketching Rational Expressions II
- Reciprocal Functions
- Direct and Inverse Variation
- Conics I - Circles & Ellipses
- Conics II - Hyperbolas and Parabolas
- Conics III - Review Properties
- Conics IV - Systems
- Conics V - More Advanced
- Conics VI - Honors Topics
- Rotation of Axes
- Analytic Geometry
- Semicircles
- Transformations of Functions (Advanced)
- Matrix I Examples
- Matrix II and Determinants
- Matrix III Coordinate Geometry
- Imaginary and Complex Numbers
- Rational Exponents & Radical Equations
- Variable Exponents and Higher Roots
- Exponents and Exponential Equations (Honors)
- Logarithms and Exponents I
- Logarithms and Exponents II
- Logarithms and Exponents III (Advanced)
- Growth Decay Interest & Half-Life
- Logarithms Practice Test
- Combinations, Permutations, & Counting
- Sequences & Series I
- Sequences & Series II
- Sequences & Series III
- Binomial Expansion Theorem
- Math Induction
- Parametric Equations
- 3 Dimensional Space and Vectors
- 3-Dimensional Space and Sketches
- Partial Fractions
- Algebra II Notation & Operations Puzzle
- Algebra II review 1
- Algebra II review 2
- Algebra II review 3
- Algebra II review 4
- Algebra II review 5
- Algebra II review 6
- Algebra II review Equations and Inequalities
- Pre-Calculus Advanced Questions
- Algebra II/Trig Practice Exam
- Limits and Asymptotes
- Definition of Instantaneous Rate of Change
- Continuity & Differentiability
- Intro to Derivatives
- Derivative Rules: Product/Quotient, Chain & Power
- Derivative Rules: Trigonometry Functions
- Derivative Rules: Log, Exponents, & Trig functions
- Applications of derivatives
- Mean Value Theorem
- Derivative max/min word problems
- Critical Values from Derivatives
- Sketching Graphs 1: 1st and 2nd derivatives
- Sketching Graphs 2: anti-derivatives
- Position Velocity Speed Acceleration
- Implicit Differentiation
- Related Rates of Change
- Using Derivatives in Economics
- Intro to Integrals
- Antiderivatives and Integrals
- Fundamental Theorem of Calculus (Part 1)
- Trapezoid Rule
- Definite Integrals & Fundamental Theorem of Calculus (Part 2)
- Definite Integrals Concepts and Applications
- Definite Integrals and Area Between Curves
- Natural log and e
- Improper Integrals
- Volumes of Solids 1
- Volumes of Solids 2
- Trig Substitutions
- Separable Differential Equations
- Using Integrals in Economics
- Series Convergence and Divergence
- Calculus Extras
- Calculus Review 1
- Calculus Review 2
- Calculus Review 3 AP Multiple Choice
- Calculus Review 4 AP Free Response
- Calculus Review 5 AP Multiple Choice 2
- Probability 1 Introduction
- Probability 2 Random Questions
- Venn Diagrams
- Permutations and Combinations
- Regressions and Models
- Normal Distributions
- Statistics Puzzle
- Statistics Review 1
- Airport Terminal 2
- Math Resources: Definitions
- Math Resources: Community Help
- Math Resources: Calculators
- TI nspire cx cas calculator tutorial 0
- TI nspire cx cas calculator tutorial 1
- TI nspire cx cas calculator tutorial 2
- TI nspire cx cas calculator tutorial 3
- TI nspire cx cas calculator tutorial 4
- TI nspire cx cas calculator tutorial 5
- TI nspire cx cas calculator questions
- TI nspire cx cas calculator project 1
- TI nspire cx cas calculator project 2
- TI nspire cx cas calculator project 3
- TI nspire cx cas calculator project 4
- TI nspire cx cas calculator project 5
- TI nspire cx cas calculator project 6
- ACT subjects to know
- SAT subjects to know
- ACT/SAT Quick Quiz 1
- ACT/SAT Quick Quiz 2
- ACT/SAT Quick Quiz 3
- ACT/SAT Quick Quiz 4*
- Mental Math Speed Drills
- ACT Practice Test 1
- ACT Practice Test 2
- ACT Practice Test 3
- ACT Practice Test 4
- ACT Practice Test 5
- ACT Geometry Practice Test 1
- ACT Trigonometry Practice Test 1
- SAT Practice Test 1
- SAT Practice Test 2
- SAT Practice Test 3
- SAT Practice Test 4*
- SAT Practice Test 5
- Challenging ACT/SAT practice test 1
- Challenging ACT/SAT practice test 2
- ACT Hidden Message Puzzle 1
- ACT Hidden Message Puzzle 2
- Overview & Random Suggestions
- SAT Subject Test Level 2 Topics to know
- SAT Math Level 2 Practice Test A
- SAT Math Level 2 Practice Test B
- SAT Math Level 2 Practice Test C
- SAT Math Level 2 Practice Test D
- SAT Math Level 2 Practice Test E
- SAT Math Level 2 Practice Test F
- SAT 2 Hidden Message Puzzle
- Math Places: Knowledge
- Math Places: Games
- Math Places: Humor
- 10 Math Place Recommendations
- Math Resources: Lessons
- Math Resources: Free Worksheets
- Math Resources: Video
- Math Resources: Standardized Test Prep
- Math Comics Archive (Fall 2011)
- Math Comics Archive (Winter 2012)
- Math Comics Archive (Spring 2012)
- Math Comics Archive (Summer 2012)
- Math Comics Archive (Fall 2012)
- Math Comics Archive (Winter 2013)
- Math Comics Archive (Spring 2013)
- Math Comics Archive (Summer 2013)
- Math Comics Archive (Fall 2013)
- Math Comics Archive (Winter 2014)
- Math Comics Archive (Spring 2014)
- Math Comics Archive (Summer 2014)
- Math Comics Archive (Fall 2014)
- Math Comics Archive (Winter 2015)
- Math Comics Archive (Spring 2015)
- Math Comics Archive (Summer 2015)
- Math Comics Archive (Fall 2015)
- Math Comics Archive (Winter 2016)
- Math Comics Archive (Spring 2016)
- Math Comics Archive (Summer 2016)
- Math Comics Archive (Fall 2016)
- Math Comics Archive (Winter 2017)
- Math Comics Archive (Spring 2017)
- Math Comics Archive (Summer 2017)
- Math Comics Archive (Fall 2017)
- Math Comics Archive (Winter 2018)
- Math Comics Archive (Spring 2018)
- Math Comics Archive (Summer 2018)
- Math Comics Archive (Fall 2018)
- Math Comics Archive (Winter 2019)
- Math Comics Archive (Spring 2019)
- Math Comics Archive (Summer/Fall 2019)
- Math Comics Archive (Winter/Spring 2020)
- Travel Checklist
- Featured Destination math enrichment
- Random Places to Visit
- 2012 Puzzle
- Super Bowl XLVI
- I (Heart) Symmetry
- When in Rome
- Live at the Mobius Strip
- Trick Shots in the Pool Hall
- 2013 Puzzle
- 8 - wonder of the world
- In the Dog house
- parallelogram parking
- slice of pi
- April 15th Tax Relief
- Math Photos
- 2014 Puzzle
- 2015 Puzzle
- What are the odds?
- In-Flight Entertainment (Videos)
- spare parts 24
- spare parts 23
- spare parts 22
- spare parts 21
- spare parts 20
- spare parts 19
- spare parts 18
- spare parts 17
- spare parts 16
- spare parts 15
- spare parts 14
- spare parts 13
- spare parts 12
- spare parts 11
- spare parts 10
- spare parts 9
- spare parts 8
- spare parts 7
- spare parts 6
- spare parts 5
- spare parts 4
- spare parts 3
- spare parts 2
- spare parts 1
- Thirty Useful Math Topics to Review
- Hidden Message Math Puzzles
- ACT SAT Math Strategies
- 200 SAT ACT Math Questions
- 200 (MORE) SAT ACT Practice Questions
- Cartesian Coordinate Cartoons
- Math Enrichment Archives
- 150 SAT Math Level 2 Questions
- Algebra Chain Letters
- Geometry Chain Letters
- 2013 US Road Trip with Oscar the Dog
- 2013 US Road Trip with Oscar (Part II)
- 2014 US South Road Trip with Oscar
- 2014 US Summer Road Trip with Oscar (East)
- 2014 US Summer Road Trip with Oscar (South)
- 2015 Summer Road Trip with Oscar (Canada West)
- 2015 Summer Road Trip with Oscar (Canada East)
- 2017 Summer Road Trip with Norway the Husky (US - Canada East)
- 2017 Summer Road Trip with Norway the Husky (Canada - US West)
- 2018 Summer Road Trip with Norway the Husky (US - Canada East)
- 2018 Summer Road Trip with Norway the Husky (Canada - US West)
- 2019 US South Road Trip with Norway the Husky
- 2019 Summer Road Trip with Norway the Husky (around Lake Michigan)
- 2021 Summer Road Trip with Norway the Husky (The Heartland)
- 2022 Winter Road Trip with Norway the Husky (Route 66)
- 2023 Winter Road Trip with Norway the Husky (Route 66)
- Terms of Use
- Advertising
- Spread the Word
- Bring Oscar
Trigonometry Word Problems
Applications of Right Triangles and Trigonometric Functions are in the questions and links below.
Click right corner to select larger image.
Right click to view or save to desktop.
___________________________________________
Download Free Complete Trigonometry Word Problems .pdf file

Connections

Right Triangle Word Problems|Angle of Elevation lesson at purplemath.com
__________________________________________
'Franklin's Kite Experiment'

Webcomic #33 " Ye Olde Trig Homework " by Lance Friedman
In the comic, what is the height of the kite?
____________________________________

Information
- Trigonometry Functions
- Applications of the Right Triangle
- Angles of Elevation and Depression
- Steps and Illustrations
- Diagonals of a Rhombus
Were you looking for more advanced word problems?
Then, check out law of sine and cosine word problems and periodic trig function word problems in other parts of the Trig section

Mathplane Express for mobile and tablets

Copyright 2010 The Math Plane. All rights reserved.
Lesson Word problems on Trigonometric functions
Math, Science, Test Prep, Music Theory
Easy Video Tutorials For Your Class
Home » Angles » Trigonometric Functions WORD problems
- Absolute Value (2)
- Absolute Value Equations (1)
- Absolute Value Inequalities (1)
- ACT Math Practice Test (2)
- ACT Math Tips Tricks Strategies (25)
- Addition & Subtraction of Polynomials (2)
- Addition Property of Equality (2)
- Addition Tricks (1)
- Adjacent Angles (2)
- Albert Einstein's Puzzle (1)
- Algebra (3)
- Alternate Exterior Angles Theorem (1)
- Alternate Interior Angles Theorem (2)
- Alternating Series (1)
- Altitude of a Triangle (2)
- Angle Addition Postulate (1)
- Angle Angle Side Theorem (1)
- Angle Angle Similarity Postulate (1)
- Angle Bisector Theorem (2)
- Angle Side Angle Theorem (1)
- Angles (28)
- Angles Parallel Lines Transversals (1)
- Application of Differentiation (6)
- Application of Integration (8)
- Arc Addition Postulate (1)
- Arc Length of a Curve Integration (1)
- Area as a Function of Length (1)
- Area between Curves Integration (2)
- Arithmetic & Geometric Sequence (1)
- Asymptotes of Rational Functions (1)
- Atoms Molecules Ions (2)
- Avogadro Gas Law (2)
- Balancing Chemical Equations (2)
- Base Angles Theorem (1)
- Binary Ionic Compound Formulas (2)
- Binomial Distribution (4)
- Binomial Theorem (2)
- Bounded Sequence (1)
- Boyle Gas Law (2)
- Business Calculus (1)
- Calorimetry (1)
- CASTC Theorem (1)
- Central Angle (2)
- Centroid (1)
- Chain Rule of Derivatives (1)
- Charles Gas Law (2)
- Chemical Reactions in Aqueous Solutions (5)
- Chemistry Matter and Measurement (2)
- Circles (3)
- Circumcenter (1)
- Combined Gas Law (2)
- Combined Variation and Proportion (1)
- Combining Like Terms in Polynomials (1)
- Commutative Property of Multiplication (1)
- Comparison Test (1)
- Completing the Square (2)
- Complex and Imaginary Numbers (2)
- Composition of Functions (2)
- Compound Interest (1)
- Conditional Expectation (1)
- Conditional Probability (2)
- Confidence Intervals (1)
- Conic Sections (1)
- Consecutive Exterior Angles Theorem (1)
- Consecutive Interior Angles Theorem (2)
- Continuity (3)
- Continuous Random Variable (8)
- Converse of Base Angles Theorem (1)
- Corresponding Angles Theorem (1)
- Covariance (1)
- CPCTC Theorem (1)
- CSSTP Theorem (1)
- Cumulative Distribution (1)
- Curve Sketching with Differentiation (2)
- Cylindrical Coordinates (1)
- Cylindrical Shell Integration Method (2)
- Decimal and Rational Number Operations (1)
- Derivative of Exponential Functions (3)
- Derivative of Hyperbolic & Inverse Hyperbolic Functions (3)
- Derivative of Inverse Functions (3)
- Derivative of Inverse Trigonometric Functions (3)
- Derivative of Logarithmic Functions (3)
- Differential Equations (10)
- Differentials (1)
- Dilation (1)
- Direct Variation and Proportion (1)
- Discrete Mathematics and Combinatorics (4)
- Discrete Random Variable (7)
- Disk Integration Method (2)
- Distributive Property of Multiplication (1)
- Division Property of Equality (2)
- Division Tricks (1)
- Domain and Range of a Function (1)
- Double Integrals (4)
- Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors (1)
- Ellipse (1)
- Empirical and Molecular Formula (2)
- Enthalpy Change (2)
- Equilateral Triangles (1)
- Expected Value (5)
- Exponential Distribution (1)
- Exponential Equations (3)
- Exponents (3)
- Exterior Angle Theorem (1)
- Exterior Angles (1)
- Factoring Polynomials (3)
- Financial Math (6)
- First Law of Thermodynamics (2)
- Fourier Series (1)
- Fraction Multiplication Rule (1)
- Fractions (7)
- Fundamental Theorem of Calculus (2)
- Gas Pressure (2)
- Gases in Chemistry (7)
- GED Math (4)
- Geometric Distribution (1)
- Geometric Formula as a Function (1)
- Geometric Formula Proof with Integration (2)
- Geometric Series (1)
- Geometry (14)
- Graph of Trigonometric Functions (2)
- GRE Math (4)
- Greatest Common Factor (1)
- Harmonic Series (1)
- Hydrostatic Force & Work (3)
- Hyperbola (1)
- Hypergeometric Distribution (2)
- Hypotenuse Leg Theorem (1)
- Hypothesis Testing (1)
- Ideal Gas Law (2)
- Identity Property of Multiplication (1)
- Implicit Differentiation (7)
- Improper Integrals (7)
- Incenter (1)
- Increasing or Decreasing Sequence (1)
- Independent Events Probability (1)
- Infinite Sequences (8)
- Infinite Series (19)
- Infinite Series Derivative (1)
- Inscribed Angle (1)
- Integral Test (1)
- Integration by Partial Fraction Decomposition (6)
- Integration by Parts (6)
- Integration by Trigonometric Substitution (5)
- Integration of Exponential Functions by Substitution (5)
- Integration of Functions with Roots & Fractions (5)
- Integration of Hyperbolic & Inverse Hyperbolic Functions by Substitution (5)
- Integration of Inverse Trigonometric Functions by Substitution (5)
- Integration of Logarithmic Functions by Substitution (5)
- Integration of Trigonometric Functions by Substitution (5)
- Integration with Reduction Formula (1)
- Interior Angles (2)
- Inverse Functions (2)
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions (1)
- Inverse Variation and Proportion (1)
- Isosceles Triangles (1)
- Joint Distribution (1)
- Joint Moment Generating Functions (1)
- Joint Variation and Proportion (1)
- Lattice Multiplication (1)
- Law of Combining Volumes (2)
- Law of Cooling (1)
- Law of Cosines (1)
- Law of Sines (1)
- Laws of Chemical Combination (2)
- Least Common Multiple (1)
- Limit Comparison Test (1)
- Limit Definition of Derivative (3)
- Limiting Reactants (2)
- Limits (10)
- Line Segments (1)
- Linear Algebra (6)
- Linear Approximation (2)
- Linear Equations (3)
- Linear Functions (1)
- Linear Measure (1)
- Linear Pair Angles Theorem (2)
- Locus of Points (1)
- Logarithmic Differentiation (2)
- Logarithmic Equations (1)
- Logarithms (4)
- Maclaurin Series (1)
- Mass Percent Composition from Chemical Formulas (2)
- Math Puzzles (2)
- Math Tricks (7)
- Matrices (5)
- Mean Value Theorem for Integrals (1)
- Means-Extremes Property of Proportions (2)
- Median of a Triangle (1)
- Midsegment Theorem (1)
- Molar Mass (2)
- Molarity of Compounds and Ions (2)
- Mole and Avogadro's Number (2)
- Molecular and Formula Mass (2)
- Moment Generating Function (2)
- Multiple Integrals (2)
- Multiplication Property of Equality (2)
- Multiplication Tricks (1)
- Multivariable Calculus (5)
- Music Theory (3)
- Negative Binomial Distribution (1)
- Negative Exponents (1)
- NonLinear Equations (8)
- NonLinear Inequalities (2)
- Normal Approximation (1)
- Normal Distribution (3)
- Nth Term Test (1)
- Number Line (5)
- Optimization (4)
- Orthocenter (2)
- Oxidation and Reduction in Chemical Reactions (2)
- P Series (1)
- Parabola (3)
- Parametric Equations and Curves (2)
- Partial Derivatives (2)
- Partial Fraction Decomposition (1)
- Particle Motion (1)
- Pascal's Triangle (1)
- Percentage Probability (1)
- Perimeter as a Function of Area (1)
- Permutations and Combinations (1)
- Perpendicular Bisector Theorem (1)
- Physics (1)
- Piecewise Probability Distribution Functions (4)
- Poisson Distribution (2)
- Polar Coordinates (2)
- Polynomial Multiplication (1)
- Power Rule of Derivatives (5)
- Power Series (1)
- Precalculus (2)
- Precipitate Formation in Chemical Reactions (2)
- Principle of Mathematical Induction (1)
- Probability & Statistics (25)
- Probability of Outcomes (1)
- Product Rule of Derivatives (1)
- Projectile Motion (3)
- Puzzles (6)
- Quadratic Equations (3)
- Quadratic Formula (1)
- Quadratic Functions (2)
- Quadratic Inequalities (1)
- Quotient Rule of Derivatives (1)
- Radians Degrees Minutes Seconds (2)
- Radicals (1)
- Rational and Radical Expressions (3)
- Rational Equations (1)
- Rational Inequalities (1)
- Rational Numbers (2)
- Reactions of Acids and Bases (2)
- Reciprocal Rule of Division (1)
- Rectangles (1)
- Reference Angles (1)
- Reflection (2)
- Reflexive Property (1)
- Related Rates (3)
- Riemann Sum (20)
- Right Triangles (1)
- Rotation (2)
- Rotation of Axes (1)
- Rule of Product (1)
- Russian Peasant Multiplication (1)
- SAT Math Practice Test #1 (59)
- SAT Math Practice Test #2 (59)
- SAT Math Practice Test #3 (59)
- SAT Math Practice Test #4 (59)
- SAT Math Practice Test #5 (30)
- SAT Math Practice Test #6 (25)
- SAT Math Practice Test #7 (12)
- SAT Math Practice Test #8 (3)
- Scientific Notation (2)
- Segment Addition Postulate (1)
- Side Angle Side Theorem (1)
- Side Side Side Theorem (1)
- Sidelight Division (1)
- Significance Tests (1)
- Significant Figures (2)
- Similarity of Triangles (1)
- SOA Exam P (4)
- Solve for X (2)
- Specific Heat (1)
- Spherical Coordinates (1)
- Square Number (1)
- Squares (1)
- Standard Deviation (3)
- Stoichiometry Chemical Calculations (8)
- Substitution Property of Equality (2)
- Subtraction Property of Equality (2)
- Summation Formulas (2)
- Supplementary Angle Theorem (1)
- Surface Area Integration (2)
- Symmetric Property (2)
- Symmetry Tests (1)
- Synthetic and Long Division of Polynomials (1)
- System of NonLinear Equations (1)
- Systems of Linear Equations (1)
- T Distribution (1)
- Table Data (3)
- Table of Ordered Pairs (1)
- Taylor Series (1)
- Telescoping Series (1)
- Theoretical & Proofs (5)
- Thermochemistry (3)
- Titrations in Chemical Reactions (2)
- Transformation (5)
- Transitive Property (2)
- Translation (1)
- Trapezoid (1)
- Tree Diagram Probability (1)
- Triangles (22)
- Trigonometric Angle Sum Difference Multiple Half-Angle Formulas (3)
- Trigonometric Equations (4)
- Trigonometric Form of Complex Numbers (1)
- Trigonometric Functions (4)
- Trigonometric Identity Proofs (1)
- Trigonometry (19)
- Triple Integrals (1)
- Truth Tables (1)
- Two Column Proofs (2)
- Two Way Table (1)
- Uniform Distribution (1)
- Unit Circle (5)
- Unit Conversions (2)
- Variance (2)
- Variation and Proportion (4)
- Vectors (1)
- Vectors in the Plane (2)
- Venn Diagram (1)
- Vertex Form of a Parabola (1)
- Vertical Angles Theorem (2)
- Volume of the Solid of Revolution (2)
- Washer Integration Method (2)
- Whole Number Operations (3)
- World's HARDEST Easy Geometry problems (1)
- Wronskian (1)
- Yield of Chemical Reactions (2)
Trigonometric Functions WORD problems
Ferris wheel trigonometry word problem.
The Ferris wheel at Navy Pier has a diameter of 140 feet. It stands 10 feet off the ground. The wheel has 40 gondolas that seat six passengers each. It takes about 6 minutes for the Navi Pier Ferris wheel to complete one rotation.
Draw a diagram of the Navy Pier Ferris wheel and the boarding platform. Fill in the necessary information. Sketch the graph. Write a cosine equation for your curve. Write a sine equation for your curve.
Answer the following questions:
i. What is the circumference of the wheel?
ii. At what speed is the wheel traveling? Please answer in feet / second.
iii. If you begin your ride at the base of the wheel, what is the height after 1 minute? 4 minutes?
iv. At what approximate time(s) will you reach the following heights?
v. What is the length of the arc traveled by the Navy Pier Ferris wheel from the 4 o’clock to the 7 o’clock position?
Solution to this Trigonometric Function word practice problem is provided in the video below!
Roller Coaster trigonometry problem
A portion of a roller coaster is to be built in the shape of a sinusoid. You have been hired to calculate the lengths of the horizontal and vertical timber supports to be used.
a. The high and low points on the track are separated by 50 meters horizontally and 30 meters vertically. The low point is 3 meters below the ground. Letting y be the number of meters the track is above the ground and x the number of meters horizontally from the high point, write an equation expressing y in terms of x .
b. How long is the vertical timber at the high point? At x = 4 m? At x = 32 m?
c. Where does the track first go below ground?
Solution to this Trigonometric Function example practice problem is provided in the video below!
Steamboat trigonometry example word problem
Mark Twain sat on the deck of a river steamboat. As the paddlewheel turned, a point on the paddle blade moved in such a way that its distance, d , from the water’s surface was a sinusoidal function of time. When his stopwatch read 4 seconds, the point was at its highest, 16 feet above the water’s surface. The wheel’s diameter was 18 feet, and it completed a revolution every 10 seconds.
a. Sketch a graph of the sinusoid
b. Write the equation of the sinusoid
c. How far above the surface was the point when Mark’s stopwatch read:
i. 5 seconds
ii. 17 seconds
d. What is the first positive value of time at which the point was at the water’s surface? At that time, was it going into or coming out of the water? Explain.
Solution to this Trigonometric Function example word problem is provided in the video below!
Temperature trigonometry word problem
The max temperature in Buenos Aires is on January 15 and is 33 degrees Celsius. The minimum temperature is on July 16 (day 197) and is 9 degrees Celsius. (Assume the period is 365 days).
a) Sketch the temperature as a function of time
b) Find the equation for the temperature, T, as a function of time, t.
c) What is the temperature on Mother’s Day, May 10?
d) Give the dates during a one year period when the temperature is below 18 degrees Celsius.
Tags: trigonometric application problems , trigonometric function example word problems , trigonometric functions word problems and solutions , trigonometry application problems , trigonometry application word problems , trigonometry word problems , unit circle word problems , word problems trigonometry
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Recent Posts
- Angular Speed and Linear Speed problems March 13, 2024
- Converting Repeating Decimals to Fractions problems February 29, 2024
- Geometry Puzzles and Brain Teasers December 18, 2023
- VERIFYING Whether Given Two Functions are Inverses December 15, 2023
- Trigonometric Functions WORD problems December 11, 2023
- Null Hypothesis Testing statistics problems February 9, 2021
- Variance problems February 9, 2021
- Confidence Interval statistics problems December 9, 2020
- Greatest Common Factor and Least Common Multiple problems December 3, 2020
- Translation Geometry problems December 1, 2020
- March 2024 (1)
- February 2024 (1)
- December 2023 (3)
- February 2021 (2)
- December 2020 (4)
- November 2020 (4)
- October 2020 (12)
- September 2020 (10)
- August 2020 (2)
- July 2020 (9)
- June 2020 (2)
- May 2020 (22)
- April 2020 (5)
- November 2019 (1)
- May 2019 (409)
- April 2019 (62)
- March 2019 (63)
Recent Comments
- Elliott Danielle on Pigeonhole Principle problems – Discrete Math
- Kava on Permutations & Combinations problems
- Sonya on Greatest Common Factor and Least Common Multiple problems
- Demetra on Geometric Formula Proof Double Integral problems
- Clarisa on Maclaurin & Taylor Infinite Series problems
| S | M | T | W | T | F | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 |
| 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 |
| 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | |||
MathCabin.com 2019-2024 © All Rights Reserved.
- MathCabin.com
- 📕 Perfect Score SAT Math eBook
- ✅ Live Online SAT Math Practice Test
- 🎵 Relaxation Music
- ⏰ Timed SUDOKU Games
- Online Math Tutoring
Powered by WordPress / Academica WordPress Theme by WPZOOM
Find Study Materials for
- Explanations
- Business Studies
- Combined Science
- Computer Science
- Engineering
- English literature
- Environmental Science
- Human Geography
- Macroeconomics
- Microeconomics
- Social Studies
- Browse all subjects
- Textbook Solutions
- Read our Magazine
Create Study Materials
- Flashcards Create and find the best flashcards.
- Notes Create notes faster than ever before.
- Study Sets Everything you need for your studies in one place.
- Study Plans Stop procrastinating with our smart planner features.
- Trigonometry Word Problems
Trigonometry word problems involve applying the principles of trigonometric ratios —sine, cosine, and tangent—to solve real-world scenarios such as determining heights, distances, and angles . Mastery of these problems requires a thorough understanding of right-angle triangles and the Pythagorean theorem. By practising, students can enhance their problem-solving skills and effectively use trigonometry in practical situations.

Create learning materials about Trigonometry Word Problems with our free learning app!
- Instand access to millions of learning materials
- Flashcards, notes, mock-exams and more
- Everything you need to ace your exams
Millions of flashcards designed to help you ace your studies
- Cell Biology
What is Trigonometry?
What are the main steps to solve trigonometry word problems?
What is the value of the height of a tree if it casts a shadow of 10 metres and the angle of elevation of the sun is 30 degrees?
How would you find the distance from the base of the ladder to the wall if the ladder is 5 metres long and the angle between the ladder and the ground is 60 degrees?
What is the height of a building if viewed from a distance of 50 metres with an angle of elevation of 45 degrees?
Given triangle ABC with sides a = 8, b = 6, and angle C = 60 degrees, how do you find side c?
What is one everyday application of trigonometry for measuring heights?
How can trigonometry be used in astronomy?
What is the law of cosines formula used in engineering?
What is the correct ratio for the sine function?
How do you find the height of a tree if you stand 30 metres away and the angle of elevation is 45 degrees?
Convert documents into flashcards for free with AI!

- Applied Mathematics
- Decision Maths
- Discrete Mathematics
- Logic and Functions
- Mechanics Maths
- Probability and Statistics
- ASA Theorem
- Absolute Convergence
- Absolute Value Equations and Inequalities
- Absolute Values
- Abstract algebra
- Addition and Multiplication of series
- Addition and Subtraction of Rational Expressions
- Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication and Division
- Algebra of limits
- Algebra over a field
- Algebraic Expressions
- Algebraic Fractions
- Algebraic K-theory
- Algebraic Notation
- Algebraic Representation
- Algebraic curves
- Algebraic geometry
- Algebraic number theory
- Algebraic topology
- Analyzing Graphs of Polynomials
- Angle Conversion
- Angle Measure
- Angle Of Depression
- Angle Of Elevation
- Angles in Polygons
- Angular geometry
- Approximation and Estimation
- Area and Perimeter of Quadrilaterals
- Area of Triangles
- Argand Diagram
- Arithmetic Sequences
- Associative algebra
- Average Rate of Change
- Banach algebras
- Bearing In Trigonometry
- Bijective Functions
- Bilinear forms
- Binomial Expansion
- Binomial Theorem
- Bounded Sequence
- C*-algebras
- Category theory
- Cauchy Sequence
- Cayley Hamilton Theorem
- Central Angles
- Circle Theorems
- Circles Maths
- Clifford algebras
- Cofunction Identities
- Cohomology theory
- Combinatorics
- Common Factors
- Common Multiples
- Commutative algebra
- Compact Set
- Completing the Square
- Complex Numbers
- Composite Figures
- Composite Functions
- Composition of Functions
- Compound Interest
- Compound Units
- Congruence Equations
- Conic Sections
- Connected Set
- Construction and Loci
- Continuity and Uniform convergence
- Continuity of derivative
- Continuity of real valued functions
- Continuous Function
- Convergent Sequence
- Converting Metrics
- Convexity and Concavity
- Coordinate Geometry
- Coordinates in Four Quadrants
- Cosecant Ratios
- Cosine Ratios
- Cotangent Ratios
- Coupled First-order Differential Equations
- Cubic Function Graph
- Cyclic Quadrilaterals
- Data Transformations
- De Moivre's Theorem
- Deductive Reasoning
- Definite Integrals
- Derivative of a real function
- Deriving Equations
- Determinant Of Inverse Matrix
- Determinant of Matrix
- Determinants
- Diagonalising Matrix
- Differentiability of real valued functions
- Differential Equations
- Differential algebra
- Differentiation
- Differentiation Rules
- Differentiation from First Principles
- Differentiation of Hyperbolic Functions
- Direct and Inverse proportions
- Direct variation
- Discontinuity
- Disjoint and Overlapping Events
- Disproof By Counterexample
- Distance formula
- Distance from a Point to a Line
- Divergent Sequence
- Divisibility Tests
- Division algebras
- Double Angle and Half Angle Formulas
- Drawing Conclusions from Examples
- Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors
- Elliptic curves
- Equation of Line in 3D
- Equation of a Perpendicular Bisector
- Equation of a circle
- Equations and Identities
- Equations and Inequalities
- Equicontinuous families of functions
- Estimation in Real Life
- Euclidean Algorithm
- Evaluating and Graphing Polynomials
- Even Functions
- Exponential Form of Complex Numbers
- Exponential Rules
- Exponentials and Logarithms
- Expression Math
- Expressions and Formulas
- Faces Edges and Vertices
- Factoring Polynomials
- Factoring Quadratic Equations
- Factorising expressions
- Fermat's Little Theorem
- Field theory
- Finding Maxima and Minima Using Derivatives
- Finding Rational Zeros
- Finding The Area
- First Fundamental Theorem
- First-order Differential Equations
- Forms of Quadratic Functions
- Fourier analysis
- Fractional Powers
- Fractional Ratio
- Fractions and Decimals
- Fractions and Factors
- Fractions in Expressions and Equations
- Fractions, Decimals and Percentages
- Function Basics
- Functional Analysis
- Fundamental Counting Principle
- Fundamental Theorem of Algebra
- Generating Terms of a Sequence
- Geometric Sequence
- Gradient and Intercept
- Gram-Schmidt Process
- Graphical Representation
- Graphing Rational Functions
- Graphing Trigonometric Functions
- Graphs And Differentiation
- Graphs Of Exponents And Logarithms
- Graphs of Common Functions
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions
- Greatest Common Divisor
- Grothendieck topologies
- Group Mathematics
- Group representations
- Growth and Decay
- Growth of Functions
- Gröbner bases
- Harmonic Motion
- Hermitian algebra
- Higher Derivatives
- Highest Common Factor
- Homogeneous System of Equations
- Homological algebra
- Homotopy theory
- Hopf algebras
- Ideal theory
- Imaginary Unit And Polar Bijection
- Implicit differentiation
- Indirect variation
- Inductive Reasoning
- Inequalities Maths
- Infinite geometric series
- Injective functions
- Injective linear transformation
- Instantaneous Rate of Change
- Integrating Ex And 1x
- Integrating Polynomials
- Integrating Trigonometric Functions
- Integration
- Integration By Parts
- Integration By Substitution
- Integration Using Partial Fractions
- Integration of Hyperbolic Functions
- Interest calculations
- Invariant Points
- Inverse Hyperbolic Functions
- Inverse Matrices
- Inverse and Joint Variation
- Inverse functions
- Inverse of a Matrix and System of Linear equation
- Invertible linear transformation
- Irrational numbers
- Isosceles Triangles Trigonometry
- Iterative Methods
- Jordan algebras
- Knot theory
- L'hopitals Rule
- Lattice theory
- Law Of Cosines In Algebra
- Law Of Sines In Algebra
- Laws of Logs
- Leibnitz's Theorem
- Lie algebras
- Limits of Accuracy
- Linear Algebra
- Linear Combination
- Linear Expressions
- Linear Independence
- Linear Systems
- Linear Transformation
- Linear Transformations of Matrices
- Linear graphs
- Location of Roots
- Logarithm Base
- Lower and Upper Bounds
- Lowest Common Denominator
- Lowest Common Multiple
- Math formula
- Matrix Addition And Subtraction
- Matrix Calculations
- Matrix Determinant
- Matrix Multiplication
- Matrix inverses
- Matrix operations
- Mean value theorem
- Metric and Imperial Units
- Midpoint formula
- Misleading Graphs
- Mixed Expressions
- Modelling with First-order Differential Equations
- Modular Arithmetic
- Module theory
- Modulus Functions
- Modulus and Phase
- Monoidal categories
- Monotonic Function
- Multiples of Pi
- Multiplication and Division of Fractions
- Multiplicative Relationship
- Multiplicative ideal theory
- Multiplying And Dividing Rational Expressions
- Natural Logarithm
- Natural Numbers
- Non-associative algebra
- Normed spaces
- Number Line
- Number Systems
- Number Theory
- Numerical Methods
- Odd functions
- Open Sentences and Identities
- Operation with Complex Numbers
- Operations With Matrices
- Operations with Decimals
- Operations with Polynomials
- Operator algebras
- Order of Operations
- Orthogonal groups
- Orthogonality
- Parallel Lines
- Parametric Differentiation
- Parametric Equations
- Parametric Hyperbolas
- Parametric Integration
- Parametric Parabolas
- Partial Fractions
- Pascal's Triangle
- Percentage Increase and Decrease
- Perimeter of a Triangle
- Permutations and Combinations
- Perpendicular Lines
- Phase Shift
- Points Lines and Planes
- Pointwise convergence
- Poisson algebras
- Polynomial Graphs
- Polynomial division
- Polynomial rings
- Polynomials
- Powers Roots And Radicals
- Powers and Exponents
- Powers and Roots
- Prime Factorization
- Prime Numbers
- Problem-solving Models and Strategies
- Product Rule
- Product of polynomials
- Product-to-sum Formulas
- Proof and Mathematical Induction
- Proof by Contradiction
- Proof by Deduction
- Proof by Exhaustion
- Proof by Induction
- Properties of Determinants
- Properties of Exponents
- Properties of Riemann Integral
- Properties of dimension
- Properties of eigenvalues and eigenvectors
- Proving an Identity
- Pythagorean Identities
- Quadratic Equations
- Quadratic Function Graphs
- Quadratic Graphs
- Quadratic forms
- Quadratic functions
- Quadrilaterals
- Quantum groups
- Quotient Rule
- Radian Measure
- Radical Functions
- Rates of Change
- Ratio Fractions
- Ratio and Root test
- Rational Exponents
- Rational Expressions
- Rational Functions
- Rational Numbers and Fractions
- Rationalizing denominators
- Ratios as Fractions
- Real Numbers
- Rearrangement
- Reciprocal Graphs
- Recurrence Relation
- Recursion and Special Sequences
- Reduced Row Echelon Form
- Reducible Differential Equations
- Remainder and Factor Theorems
- Representation Of Complex Numbers
- Representation theory
- Rewriting Formulas and Equations
- Riemann integral for step function
- Riemann surfaces
- Riemannian geometry
- Right Triangle Trigonometry
- Ring theory
- Roots Of Unity
- Roots of Complex Numbers
- Roots of Polynomials
- SAS Theorem
- SSS Theorem
- Scalar Products
- Scalar Triple Product
- Scale Drawings and Maps
- Scale Factors
- Scalene Triangles Trigonometry
- Scientific Notation
- Secant Ratios
- Second Fundamental Theorem
- Second Order Recurrence Relation
- Second-order Differential Equations
- Sector of a Circle
- Segment of a Circle
- Sequence and series of real valued functions
- Sequence of Real Numbers
- Sequences and Series
- Series Maths
- Series of non negative terms
- Series of real numbers
- Sigma notation
- Similar Triangles
- Similar and Congruent Shapes
- Similarity and diagonalisation
- Simple Interest
- Simple algebras
- Simplifying Fractions
- Simplifying Radicals
- Simultaneous Equations
- Sine Ratios
- Sine and Cosine Rules
- Sinusoidal Graphs
- Slope formulas
- Slope-intercept form
- Small Angle Approximation
- Solving Linear Equations
- Solving Linear Systems
- Solving Oblique Triangles
- Solving Quadratic Equations
- Solving Radical Inequalities
- Solving Rational Equations
- Solving Right Triangles
- Solving Simultaneous Equations Using Matrices
- Solving Systems of Inequalities
- Solving Trigonometric Equations
- Solving and Graphing Quadratic Equations
- Solving and Graphing Quadratic Inequalities
- Spanning Set
- Special Products
- Special Sequences
- Spherical Trigonometry
- Standard Form
- Standard Integrals
- Standard Unit
- Standard form equations
- Stone Weierstrass theorem
- Straight Line Graphs
- Subsequence
- Substraction and addition of fractions
- Sum and Difference of Angles Formulas
- Sum of Natural Numbers
- Sum-to-product Formulas
- Summation by Parts
- Supremum and Infimum
- Surjective functions
- Surjective linear transformation
- System of Linear Equations
- Tables and Graphs
- Tangent Ratios
- Tangent of a Circle
- Tangent rule
- Taylor theorem
- The Quadratic Formula and the Discriminant
- Topological groups
- Torsion theories
- Transformations
- Transformations geometry
- Transformations of Graphs
- Transformations of Roots
- Translations of Trigonometric Functions
- Transversals
- Triangle Rules
- Triangle trigonometry
- Trigonometric Functions
- Trigonometric Functions of General Angles
- Trigonometric Identities
- Trigonometric Identities Sum Angles
- Trigonometric Proofs
- Trigonometric Ratios
- Trigonometric Ratios Of Complementary Angles
- Trigonometry
- Trigonometry Height And Distance
- Turning Points
- Types of Functions
- Types of Numbers
- Types of Triangles
- Uniform convergence
- Unit Circle
- Universal algebra
- Upper and Lower Bounds
- Valuation theory
- Variable expressions
- Variables in Algebra
- Vector Notation
- Vector Space
- Vector spaces
- Verifying Trigonometric Identities
- Vertex form
- Volume calculations
- Volumes of Revolution
- Von Neumann algebras
- Writing Equations
- Writing Linear Equations
- Zariski topology
- secant lines
- slope formula
- Theoretical and Mathematical Physics
Introduction to Trigonometry Word Problems
Trigonometry word problems apply the principles of trigonometry to real-life scenarios. Understanding these problems helps you see the practical uses of mathematics, from measuring heights to navigating maps.
The Importance of Trigonometry Word Problems
Understanding trigonometry word problems allows you to apply trigonometric concepts to practical situations. This not only enhances your problem-solving skills but also shows how maths is used in various fields such as engineering, physics, and navigation.
Trigonometry: A branch of mathematics that studies relationships between side lengths and angles of triangles.
Key Trigonometric Functions
In trigonometry, three main functions are used to solve problems involving right-angled triangles:
- Sine (sin): The ratio of the length of the opposite side to the hypotenuse.
- Cosine (cos): The ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse.
- Tangent (tan): The ratio of the length of the opposite side to the adjacent side.
Example: Given a right-angled triangle where the opposite side is 3 units , the adjacent side is 4 units, and the hypotenuse is 5 units:
- sin(θ) = 3/5
- cos(θ) = 4/5
- tan(θ) = 3/4
Steps to Solving Trigonometry Word Problems
To tackle trigonometry word problems effectively, follow these steps:
- Understand the problem: Read the problem statement carefully to determine what is being asked.
- Identify the right triangle: Sketch the scenario and highlight the right-angled triangle.
- Choose the correct function: Decide whether to use sine, cosine, or tangent based on the given information.
- Set up the equation: Write the equation using the chosen trigonometric function and solve for the unknown.
- Check your answer: Confirm if the solution is reasonable and correctly answers the problem.
Sometimes, trigonometry word problems may involve more complex scenarios, such as non-right triangles or 3D contexts. In such cases, you might need to use advanced trigonometric principles like the law of sines or the law of cosines. These laws generalise the basic trigonometric functions and can handle various triangle types.
Example Problem
Example: A tree casts a shadow of 10 metres, and the angle of elevation of the sun is 30 degrees. Find the height of the tree.Solution:
- Let the height of the tree be h.
- tan(30) = h / 10
- Since tan(30) = 1/√3, then 1/√3 = h / 10.
- h = 10 / √3 ≈ 5.77 metres.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When solving trigonometry word problems, some common mistakes include:
- Not identifying the right function: Ensure you choose the correct trigonometric function (sine, cosine, or tangent) based on the given information.
- Forgetting to use the correct units : Always keep track of the units and convert them if necessary.
- Not checking your work: Always recheck your calculations and ensure your answer makes sense in the context of the problem.
- Not using a calculator properly: Ensure your calculator is set to the correct mode (degrees or radians ) based on the angle measures used in the problem.
To avoid mistakes, always double-check your chosen trigonometric function and ensure your units are consistent.
Trigonometry Word Problems Examples
Trigonometry word problems involve using trigonometric principles to solve practical problems. These problems can range from understanding heights and distances to complex angle calculations.
Simple Trigonometry Word Problems Examples
Simple trigonometry word problems often involve right-angled triangles and basic trigonometric functions like sine, cosine, and tangent. Let's take a look at an example.
Example: A ladder is leaning against a wall, forming a right-angled triangle with the ground. If the ladder is 5 metres long and the angle between the ladder and the ground is 60 degrees, find the distance from the base of the ladder to the wall.Solution:
- Let the distance from the base of the ladder to the wall be x.
- Using the cosine function, cos(60) = x / 5
- Since cos(60) = 1/2, then 1/2 = x / 5.
- So, x = 5 / 2 = 2.5 metres.
Always start by identifying what is given and what you need to find. This will help you choose the right trigonometric function.
Intermediate Trigonometry Word Problems Examples
Intermediate problems may require you to use multiple trigonometric functions and incorporate more complex geometric shapes. These problems will often involve finding unknown angles or distances.
Example: You are looking at the top of a building from a distance of 50 metres. If the angle of elevation is 45 degrees, find the height of the building.Solution:
- Let the height of the building be h.
- Using the tangent function, tan(45) = h / 50
- Since tan(45) = 1, then 1 = h / 50.
- So, h = 50 metres.
For more complex shapes, you might need to break the problem into smaller right-angled triangles. This approach helps simplify calculations and ensures that you use the correct trigonometric function.
Advanced Trigonometry Word Problems Examples
Advanced problems often involve non-right triangles or three-dimensional geometries. These problems typically require the use of the law of sines or the law of cosines to find unknown measurements.
Law of Sines: \(\frac{a}{\sin A} = \frac{b}{\sin B} = \frac{c}{\sin C}\)
Law of Cosines: \(c^2 = a^2 + b^2 - 2ab \cos C\)
Example: In triangle ABC, you know side a = 8, side b = 6, and angle C = 60 degrees. Find side c.Solution:
- Using the Law of Cosines, \(c^2 = a^2 + b^2 - 2ab \cos C\)
- \(c^2 = 8^2 + 6^2 - 2 \cdot 8 \cdot 6 \cdot \cos(60)\)
- \(c^2 = 64 + 36 - 96 \cdot (1/2) \)
- \(c^2 = 64 + 36 - 48 \)
- \(c^2 = 52 \)
- \(c = \sqrt{52} \)
- \(c \approx 7.21 \) units
Applications of Trigonometry Word Problems
Trigonometry is not just an abstract mathematical concept; it has numerous practical applications in everyday life, science, and engineering. Understanding how to solve trigonometry word problems can help you navigate through various real-world scenarios effectively.
Everyday Applications of Trigonometry Word Problems
Trigonometry is applied in many everyday activities, whether you realise it or not. Here are a few areas where trigonometric calculations are commonly used:
- Navigating Maps: You can use trigonometry to calculate distances and angles between various points on a map.
- Measuring Heights: Determining the height of a tree, building, or any other tall object without climbing it can be done using trigonometric functions.
- Photography: Calculating the ideal angle and distance to take a picture often involves trigonometry.
Example: You want to measure the height of a flagpole. Standing 20 metres away, you measure the angle of elevation to the top of the pole to be 30 degrees. Find the height of the flagpole.Solution:
- Using the tangent function: \( \tan(30) = \frac{ h }{ 20 } \)
- Since \( \tan(30) = \frac{1}{\sqrt{3}} \), then \( \frac{1}{\sqrt{3}} = \frac{ h }{ 20 } \)
- So, \( h = 20 \cdot \frac{1}{\sqrt{3}} \approx 11.55 \) metres.
Always ensure your units are consistent when solving trigonometric problems involving heights and distances.
Applications of Trigonometry Word Problems in Science
In science, trigonometry plays a crucial role in fields such as physics and astronomy. By understanding trigonometric word problems, scientists can make accurate measurements and predictions. Here are some specific applications:
Law of Sines: \( \frac{ a }{ \sin A } = \frac{ b }{ \sin B } = \frac{ c }{ \sin C } \)
- Astronomy: Calculating the distance between celestial bodies often involves using the law of sines and the law of cosines.
- Physics: When studying wave motion or light refraction, trigonometric functions help describe the phenomena accurately.
Example: Astronomers determined the angle between Earth and a distant star is 0.5 degrees, and the distance from Earth to the star is 4 light-years. Find the distance between two observation points on Earth if the angle at the distant star is measured to be 0.001 degrees.Solution:
- Using the law of sines: \( \frac{ 4 \text{ light-years} }{ \sin 0.001 } = \frac{ d }{ \sin 0.5 } \)
- Rearrange to solve for \( d \): \( d = \frac{ 4 \cdot \sin 0.5 }{ \sin 0.001 } \)
- Calculate using the approximate values: \( d \approx 1997.44 \) light-years.
In more complex problems, astronomers and physicists may use spherical trigonometry , which is an extension of trigonometry that deals with spheres rather than planes. This is particularly useful for calculations involving planetary orbits and celestial navigation, where the curvature of space becomes significant.
Applications of Trigonometry Word Problems in Engineering
Engineering makes extensive use of trigonometry, especially in areas such as civil, mechanical and electrical engineering. By applying trigonometric word problems, engineers can design and build structures, machinery, and systems efficiently.
Law of Cosines: \( c^2 = a^2 + b^2 - 2ab \cos C \)
- Structural Engineering: Calculating the forces in various parts of a structure, such as beams and trusses, often involves trigonometric principles.
- Mechanical Engineering: Designing gears, engines, and other mechanical components requires knowledge of angles and distances calculated using trigonometry.
- Electrical Engineering: Analysing AC circuits and waveforms frequently involves trigonometric calculations.
Example: In a truss system, two members join to form a 60-degree angle with each other. If the lengths of the members are 5 metres and 7 metres, find the length of the opposing side.Solution:
- Using the law of cosines: \( c^2 = 5^2 + 7^2 - 2 \cdot 5 \cdot 7 \cdot \cos 60 \)
- So, \( c^2 = 25 + 49 - 35 \)
- \( c^2 = 39 \)
- \( c = \sqrt{39} \approx 6.24 \) metres.
Understanding the law of cosines is crucial for solving problems involving non-right triangles.
Trigonometric Ratios in Word Problems
Trigonometric ratios are pivotal in solving various mathematical problems. They allow you to find unknown angles or distances in different types of triangles . Applying these ratios in word problems helps you understand their real-world functionality.
Using Sine, Cosine, and Tangent in Word Problems
Sine, cosine, and tangent are the primary trigonometric functions used in solving right triangle problems. They help you relate the angles to the lengths of the sides in a triangle. Here’s a quick refresher on these functions:
Example: You are standing 30 metres away from a tree and the angle of elevation to the top of the tree is 45 degrees. Find the height of the tree.Solution:
- Using the tangent function: \( \tan(45) = \frac{\text{height}}{30} \)
- Since \( \tan(45) = 1 \), then \( 1 = \frac{\text{height}}{30} \)
- So, the height is 30 metres.
Always ensure your calculator is in the correct mode (degrees or radians ) based on the given angle.
Right Triangle Trigonometry Word Problems
Right triangle trigonometry involves solving problems where one angle is 90 degrees. The three main trigonometric ratios — sine, cosine, and tangent — are especially useful in these problems.
- Identify the right angle: Determine which angle is 90 degrees to simplify your calculations.
- Choose the appropriate ratio: Decide whether to use sine, cosine, or tangent based on the sides and angles you are dealing with.
Example: A 20-foot ladder is leaning against a wall, making a 60-degree angle with the ground. Find how high up the wall the ladder reaches.Solution:
- Using the cosine function: \( \cos(60) = \frac{\text{adjacent}}{\text{hypotenuse}} \)
- \( \cos(60) = \frac{\text{height}}{20} \)
- Since \( \cos(60) = \frac{1}{2} \), then \( \frac{1}{2} = \frac{\text{height}}{20} \)
- So, the height is 10 feet.
In more complex problems involving right triangles, it might be helpful to use the Pythagorean theorem in conjunction with trigonometric ratios. The Pythagorean theorem states that for a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse (\(c\)) is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides (\(a\) and \(b\)): \( c^2 = a^2 + b^2 \). This theorem can be particularly useful when you have two sides and need to find the third.
Trigonometric Ratios in Non-right Triangle Word Problems
When dealing with non-right triangles, trigonometric ratios can still be utilised, but you may need to employ the law of sines or the law of cosines. These laws help solve for unknown sides or angles.The law of sines states: \[ \frac{a}{\sin A} = \frac{b}{\sin B} = \frac{c}{\sin C} \] While the law of cosines is: \[ c^2 = a^2 + b^2 - 2ab \cos C \]
Example: In triangle ABC, you know that angle A = 30 degrees, angle B = 45 degrees, and side a = 10 units. Find the length of side b.Solution:
- Using the law of sines: \( \frac{a}{\sin A} = \frac{b}{\sin B} \)
- So, \( \frac{10}{\sin 30} = \frac{b}{\sin 45} \)
- Since \( \sin 30 = \frac{1}{2} \) and \( \sin 45 = \frac{\sqrt{2}}{2} \), then \( \frac{10}{0.5} = \frac{b}{0.707} \)
- \( 20 = \frac{b}{0.707} \)
- So, \( b = 20 \times 0.707 \approx 14.14 \) units
In non-right triangle problems, always double-check which law applies to the given sides and angles to avoid mistakes.
Practice Solving Trigonometry Word Problems
Practicing trigonometry word problems sharpens your ability to analyse and solve complex mathematical scenarios. Whether you are preparing for exams or simply looking to enhance your understanding, consistent practice can help build your confidence and proficiency.
Tips for Solving Trigonometry Word Problems
Solving trigonometry word problems effectively requires a step-by-step approach. Here are some tips to help you navigate through these problems with ease:
- Understand the Problem: Carefully read the problem to identify what is being asked and what information is provided.
- Draw a Diagram: Visual representations can simplify complex problems and highlight relationships between different components.
- Choose the Correct Function: Depending on the given information, decide whether to use sine, cosine, or tangent.
- Set Up Equations : Formulate equations using the chosen trigonometric functions and solve for the unknown values.
- Check Your Work: Always review your calculations and ensure that your answers make sense in the context of the problem.
Example: A building casts a shadow of 15 meters, and the angle of elevation of the sun is 30 degrees. Find the height of the building.Solution:
- Using the tangent function: \( \tan(30) = \frac{ h }{ 15 } \)
- Since \( \tan(30) = \frac{1}{\sqrt{3}} \), then \( \frac{1}{\sqrt{3} } = \frac{ h }{ 15 } \)
- So, \( h = 15 \cdot \frac{1}{\sqrt{3}} \approx 8.66 \) meters.
Always draw a diagram to visualise the problem. This can make it easier to see which trigonometric function to use.
Common Mistakes in Solving Trigonometry Word Problems
When working on trigonometry word problems, certain mistakes are frequently made. Recognising and avoiding these can improve your accuracy:
- Choosing the Wrong Function: Ensure you clearly understand whether to use sine, cosine, or tangent based on the sides and angles involved.
- Incorrect Unit Conversion: Make sure all units are consistent, especially when converting between different measurement systems.
- Ignoring Right-Angle Assumptions : If a problem involves a right triangle, leverage the right-angle properties to simplify calculations.
- Calculator Mode Errors: Verify that your calculator is set to the appropriate mode (degrees or radians) as required by the problem.
- Forgetting to Double-Check: Always revisit your steps and calculations to spot any errors.
Keep your work neat and organised. This makes it easier to identify errors and follow your thought process.
Resources for Trigonometry Word Problems Practice
Practicing trigonometry word problems requires access to various resources. Here are some recommended materials to aid your practice:
- Textbooks: Many mathematics textbooks include sections dedicated to trigonometry and related word problems.
- Online Tutorials: Platforms like Khan Academy provide instructional videos and practice problems to help you master trigonometry.
- Practice Worksheets: Printable worksheets that focus on trigonometric word problems can be found on educational websites.
- Math Apps: Apps like Photomath and WolframAlpha offer tools to solve trigonometric problems step-by-step.
- Study Groups: Joining a study group can provide additional support and the opportunity to learn different problem-solving techniques.
Trigonometry Word Problems - Key takeaways
- Trigonometry Word Problems: Utilise trigonometric concepts to solve real-life scenarios, such as measuring heights and navigating maps.
- Key Trigonometric Functions: Sine (sin), Cosine (cos), and Tangent (tan) are ratios used in right-angled triangles to solve word problems.
- Steps to Solving Trigonometry Word Problems: Understand the problem, identify the right triangle, choose the correct function, set up the equation, and check your answer.
- Common Mistakes: Choosing the wrong function, incorrect unit conversion, ignoring right-angle assumptions , calculator mode errors, and not double-checking work.
- Applications of Trigonometry Word Problems: Used in diverse fields like engineering, physics, navigation, and everyday tasks such as photography and measuring heights.
Flashcards in Trigonometry Word Problems 15
A study of the numerical properties and relationships of complex numbers.
Understand the problem, identify the right triangle, choose the correct function, set up the equation, check your answer.
\text{h} = 10 \times \text{tan}(45) \text{, equal to 10 metres exactly}
Use the secant function: \( sec(60) = \frac{x}{5} \) leading to \( x = 0.5 \) metres.
Use the tangent function: \( tan(45) = \frac{h}{50} \) leading to \( h = 50 \) metres.
Use the Pythagorean theorem with adjustment: \( c^2 = a^2 + b^2 + 2ab \cos C \) leading to \( c = 12 \) units.

Learn with 15 Trigonometry Word Problems flashcards in the free Vaia app
We have 14,000 flashcards about Dynamic Landscapes.
Already have an account? Log in
Frequently Asked Questions about Trigonometry Word Problems
Test your knowledge with multiple choice flashcards.

Join the Vaia App and learn efficiently with millions of flashcards and more!
Keep learning, you are doing great.
Discover learning materials with the free Vaia app

Vaia is a globally recognized educational technology company, offering a holistic learning platform designed for students of all ages and educational levels. Our platform provides learning support for a wide range of subjects, including STEM, Social Sciences, and Languages and also helps students to successfully master various tests and exams worldwide, such as GCSE, A Level, SAT, ACT, Abitur, and more. We offer an extensive library of learning materials, including interactive flashcards, comprehensive textbook solutions, and detailed explanations. The cutting-edge technology and tools we provide help students create their own learning materials. StudySmarter’s content is not only expert-verified but also regularly updated to ensure accuracy and relevance.

Vaia Editorial Team
Team Math Teachers
- 14 minutes reading time
- Checked by Vaia Editorial Team
Study anywhere. Anytime.Across all devices.
Create a free account to save this explanation..
Save explanations to your personalised space and access them anytime, anywhere!
By signing up, you agree to the Terms and Conditions and the Privacy Policy of Vaia.
Sign up to highlight and take notes. It’s 100% free.
Join over 22 million students in learning with our Vaia App
The first learning app that truly has everything you need to ace your exams in one place
- Flashcards & Quizzes
- AI Study Assistant
- Study Planner
- Smart Note-Taking

Privacy Overview
Get unlimited access with a free vaia account..
- Instant access to millions of learning materials.
- Flashcards, notes, mock-exams, AI tools and more.
- Everything you need to ace your exams.


Trigonometry Word Problems Videos

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.
- {{subColumn.name}}
STEM Education
- {{newsColumn.name}}
- Share facebook twitter google linkedin

Solving word problems involving triangles and implications on training pre-service mathematics teachers
- William Guo ,
- School of Engineering and Technology, Central Queensland University, North Rockhampton, QLD 4702, Australia
- Academic Editor: Zlatko Jovanoski
- Received: 18 June 2024 Revised: 02 July 2024 Accepted: 05 July 2024 Published: 09 July 2024
- Full Text(HTML)
- Download PDF
Triangles and trigonometry are always difficult topics for both mathematics students and teachers. Hence, students' performance in solving mathematical word problems in these topics is not only a reflection of their learning outcomes but also an indication of teaching effectiveness. This case study drew from two examples of solving word problems involving triangles by pre-service mathematics teachers in a foundation mathematics course delivered by the author. The focus of this case study was on reasoning implications of students' performances on the effective training of pre-service mathematics teachers, from which a three-step interactive explicit teaching-learning approach, comprising teacher-led precise and inspiring teaching (or explicit teaching), student-driven engaged learning (or imitative learning), and student-led and teacher-guided problem-solving for real-world problems or projects (or active application), was summarized. Explicit teaching establishes a solid foundation for students to further their understanding of new mathematical concepts and to conceptualize the technical processes associated with these new concepts. Imitative learning helps students build technical abilities and enhance technical efficacy by engaging in learning activities. Once these first two steps have been completed, students should have a decent understanding of new mathematical concepts and technical efficacy to analyze, formulate, and finally solve real-world applications with assistance from teachers whenever required. Specially crafted professional development should also be considered for some in-service mathematics teachers to adopt this three-step interactive teaching-learning process.
- pre-service mathematics teacher ,
- word problem ,
- triangles ,
- problem-solving ,
- explicit teaching ,
- imitated learning ,
- active applications ,
- professional development
Citation: William Guo. Solving word problems involving triangles and implications on training pre-service mathematics teachers[J]. STEM Education, 2024, 4(3): 263-281. doi: 10.3934/steme.2024016
Related Papers:
| [1] | , 2016, 47(7): 1028-1047. http://doi.org/10.1080/0020739X.2016.1155774 --> Koyunkaya, M.Y., Mathematics education graduate students' understanding of trigonometric ratios. , 2016, 47(7): 1028-1047. http://doi.org/10.1080/0020739X.2016.1155774 doi: |
| [2] | , 2018, 6(1): 58-78. http://doi.org/10.18404/ijemst.328344 --> Koyunkaya, M.Y., An examination of a pre-service mathematics teacher's mental constructions of relationships in a right triangle. , 2018, 6(1): 58-78. http://doi.org/10.18404/ijemst.328344 doi: |
| [3] | , 2019, 14(2): 72-91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.teln.2018.11.004 --> Ngcobo, A.Z., Madonsela, S.P. and Brijlall, D., The teaching and learning of trigonometry. , 2019, 14(2): 72-91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.teln.2018.11.004 doi: |
| [4] | , 2022, 10(2): 208-224. https://doi.org/10.30935/scimath/11716 --> Durmaz, A.B. and Bostan, I.M., Pre-service teachers' knowledge regarding the area of triangle. , 2022, 10(2): 208-224. https://doi.org/10.30935/scimath/11716 doi: |
| [5] | , 2018, 39: 171–196. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13138-017-0123-y --> Rellensmann, J. and Schukajlow, S., Do students enjoy computing a triangle's side? Enjoyment and boredom while solving problems with and without a connection to reality from students' and pre-service teachers' perspectives. , 2018, 39: 171–196. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13138-017-0123-y doi: |
| [6] | , 2017, 5(1): 28-42. https://doi.org/10.30935/scimath/9495 --> Fyhn, A.B., What happens when a climber falls? Young climbers mathematise a climbing situation. , 2017, 5(1): 28-42. https://doi.org/10.30935/scimath/9495 doi: |
| [7] | , 2023, 11(2): 249-258. https://doi.org/10.30935/scimath/12582 --> Guo, W., Solving word problems involving triangles by transitional engineering students: Learning outcomes and implications. , 2023, 11(2): 249-258. https://doi.org/10.30935/scimath/12582 doi: |
| [8] | , 2015, 11(6): 1379-1397. https://doi.org/10.12973/eurasia.2015.1396a --> Dündar, S., Mathematics teacher-candidates' performance in solving problems with different representation styles: The trigonometry example. , 2015, 11(6): 1379-1397. https://doi.org/10.12973/eurasia.2015.1396a doi: |
| [9] | , 2017, 36(3): 273-306. https://doi.org/10.1080/03323315.2017.1327361 --> Walsh, R., Fitzmaurice, O. and O'Donoghue, J., What subject matter knowledge do second-level teachers need to know to teach trigonometry? An exploration and case study. , 2017, 36(3): 273-306. https://doi.org/10.1080/03323315.2017.1327361 doi: |
| [10] | , 2018, 9(1): 169-182. https://doi.org/10.22342/jme.9.2.5261.169-182 --> Nabie, M. J., Akayuure, P., Ibrahim-Bariham, U.A. and Sofo, S., Trigonometric concepts: Pre-service teachers' perceptions and knowledge. , 2018, 9(1): 169-182. https://doi.org/10.22342/jme.9.2.5261.169-182 doi: |
| [11] | , 2021, 53(8): 2004–2025. https://doi.org/10.1080/0020739X.2020.1857858 --> Ubah, I., Pre-service mathematics teachers' semiotic transformation of similar triangles: Euclidean geometry. , 2021, 53(8): 2004–2025. https://doi.org/10.1080/0020739X.2020.1857858 doi: |
| [12] | , 2022, 10(20): 3786. http://doi.org/10.3390/math10203786 --> Guo, W., Exploratory case study on solving word problems involving triangles by pre-service mathematics teachers in a regional university in Australia. , 2022, 10(20): 3786. http://doi.org/10.3390/math10203786 |
| [13] | , 2024, 16(1): 58-68. https://doi.org/10.69721/TPS.J.2024.16.1.07 --> Pentang J.T., Andrade, L.J.T., Golben, J.C., Talua, J.P., Bautista, R.M., Sercenia, J.C., et al., Problem-solving difficulties, performance, and differences among preservice teachers in Western Philippines University. , 2024, 16(1): 58-68. https://doi.org/10.69721/TPS.J.2024.16.1.07 doi: |
| [14] | , 2020, Pearson. --> Christensen, L.B., Johnson, R.B., Turner, L.A. and Christensen, L.B., , 2020, Pearson. |
| [15] | , 2 ed. 2020, Melbourne, Australia: Pearson. --> Guo, W.W., , 2 ed. 2020, Melbourne, Australia: Pearson. |
| [16] | , 2022, 10(16): 2862. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10162862 --> Rézio, S., Andrade, M.P. and Teodoro, M.F., Problem-based learning and applied mathematics. , 2022, 10(16): 2862. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10162862 doi: |
| [17] | , 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13394-023-00468-8 --> Gómez-Chacón, I.M., Bacelo, A., Marbán, J.M. and Palacios, A., Inquiry-based mathematics education and attitudes towards mathematics: tracking profiles for teaching. , 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13394-023-00468-8 doi: |
| [18] | , 1984, 77(6): 351-359. https://doi.org/10.1080/00220671.1984.10885555 --> Darch, C., Carnine D. and Gersten, R., Explicit instruction in mathematics problem solving. , 1984, 77(6): 351-359. https://doi.org/10.1080/00220671.1984.10885555 doi: |
| [19] | , 2004,104(3): 233–251. https://doi.org/10.1086/499751 --> Kroesbergen, E.H., Van Luit, J.E.H. and Maas, C.J.M., Effectiveness of explicit and constructivist mathematics instruction for low-achieving students in The Netherlands. , 2004,104(3): 233–251. https://doi.org/10.1086/499751 doi: |
| [20] | , 2015,115: 303–333. https://doi.org/10.1086/679969 --> Doabler, C.T., Baker, S.K., Kosty, D.B., Smolkowski, K., Clarke, B., Miller, S.J., et al., Examining the association between explicit mathematics instruction and student mathematics achievement. , 2015,115: 303–333. https://doi.org/10.1086/679969 doi: |
| [21] | , 2021, 44(2-3): 267-283. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40614-021-00291-1 --> Gunn, B., Smolkowski, K., Strycker, L.A. and Dennis, C., Measuring Explicit Instruction Using Classroom Observations of Student-Teacher Interactions (COSTI). , 2021, 44(2-3): 267-283. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40614-021-00291-1 doi: |
| [22] | , April 2024. Available from: . --> Evans, T., We need to go back to teacher-led explicit instruction: maths expert. , April 2024. Available from: . |
| [23] | , 2018, 5(6): 2349–5219. --> Magbanua, M.U., Explicit instruction in problem-solving skills, creative and critical thinking skills of the elementary education students. , 2018, 5(6): 2349–5219. |
| [24] | , 2022, 6(5): 7781–7787. --> Joaquin, C.J.A., A guided-discovery approach to problem solving: An explicit instruction. , 2022, 6(5): 7781–7787. |
| [25] | , 2021, 9(14): 1623. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9141623 --> Guo, W., Li, W. and Tisdell, C.C., Effective pedagogy of guiding undergraduate engineering students solving first-order ordinary differential equations. , 2021, 9(14): 1623. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9141623 doi: |
| [26] | , 2024, 12(1): 71-84. https://doi.org/10.30935/scimath/13831 --> Guo, W., Special tutorials to support pre-service mathematics teachers learning differential equations and mathematical modelling. , 2024, 12(1): 71-84. https://doi.org/10.30935/scimath/13831 doi: |
| [27] | , 2022, 2(3): 221-244. https://doi.org/10.3934/steme.2022014 --> Evans, T. and Dietrich, H., Inquiry-based mathematics education: a call for reform in tertiary education seems unjustified. , 2022, 2(3): 221-244. https://doi.org/10.3934/steme.2022014 doi: |
- This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-Share Alike 4.0 Unported License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/ -->
Supplements
Access History
- Corresponding author: Email: [email protected]
Reader Comments
- © 2024 the Author(s), licensee AIMS Press. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0 )
通讯作者: 陈斌, [email protected]
沈阳化工大学材料科学与工程学院 沈阳 110142

Article views( 40 ) PDF downloads( 4 ) Cited by( 0 )
Figures and Tables
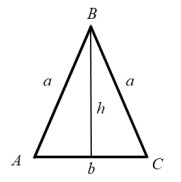
Figures( 5 ) / Tables( 3 )
Associated material
Other articles by authors.
- William Guo
Related pages
- on Google Scholar
- Email to a friend
- Order reprints
Export File

- Figure 1. A sketch of isosceles triangle for the first word problem
- Figure 2. A reworked sketch for the second problem with derived angles (in red)
- Figure 3. The first reworked sketch for solving the second problem through right triangles
- Figure 4. The second reworked sketch for solving the second problem through right triangles
- Figure 5. The third reworked sketch for solving the second problem through right triangles

COMMENTS
Free practice questions for Trigonometry - Solving Word Problems with Trigonometry. Includes full solutions and score reporting.
Trigonometry Word Problems Practice - MathBitsNotebook (Geo) Directions: Carry the full calculator value until rounding the final answer. 1. From a point on the ground 47 feet from the foot of a tree, the angle of elevation of the top of the tree is 35º. Find the height of the tree to the nearest foot. Choose:
TRIGONOMETRY WORD PROBLEMS WORKSHEET WITH ANSWERS 1. The angle of elevation of the top of the building at a distance of 50 m from its foot on a horizontal plane is found to be 60 °. Find the height of the building.
Trigonometry Word Problems. Applications of Right Triangles and Trig FunctionsIncludes angle of elevation and depres. tep-by-step solution. , and more...SOL. TIONS - Thanks for visiting. (Hope it helped!)If you hav. questions, suggestions, or requests, let us know. Also, find mo. e advanced. Also, at TES and TeachersPayTeachers.
Examples, videos, worksheets, solutions, and activities to help Algebra 1 students learn how to solve trigonometry word problems.
Right triangle trigonometry word problems. Bugs Bunny was 33 meters below ground, digging his way toward Pismo Beach, when he realized he wanted to be above ground. He turned and dug through the dirt diagonally for 80 meters until he was above ground. What is the angle of elevation, in degrees, of Bugs Bunny's climb?
How to solve word problems using Trigonometry: sine, cosine, tangent, angle of elevation, calculate the height of a building, balloon, length of ramp, altitude, angle of elevation, with video lessons, examples and step-by-step solutions.
Trigonometry Word Problems A practical application of the trigonometric functions is to find the measure of lengths that you cannot measure. Very frequently, angles of depression and elevation are used in these types of problems.
Trigonometry Applications: How to use trigonometry to solve word problems, examples of solving application of trigonometry word problems, How to Find The Height of a Building using trigonometry, with video lessons, examples and step-by-step solutions.
Learn how to apply trigonometry to real-life situations with these free worksheets. Practice solving problems involving angles of elevation and depression.
This page titled 4.1.7: Trigonometry Word Problems is shared under a CK-12 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by CK-12 Foundation via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the LibreTexts platform. Contextual use of triangle properties, ratios, theorems, and laws.
Trigonometry - Word Problems - MathBitsNotebook (Geo) Trigonometry's connection to measurement places it in the learner's manuals for a wide variety of professions. Carpenters, construction workers, designers, architects, and engineers, to name a few, deal with measurements, and as such, they deal with triangle measures, or trigonometry.
TRIGONOMETRY WORD PROBLEMS WITH SOLUTIONS. Problem 1 : The angle of elevation of the top of the building at a distance of 50 m from its foot on a horizontal plane is found to be 60 °. Find the height of the building. Solution : Draw a sketch.
When I think of trigonometry I think of special trigonometric functions. three main trigoometric functions. We will de ne them using a right angled and the angles within the triangle.
This online Trigonometry solver can tell you the answer for your math problem or word problem, and even show you the steps.
Were you looking for more advanced word problems? Then, check out law of sine and cosine word problems and periodic trig function word problems in other parts of the Trig section. Applications of Right Triangles and Trigonometric Functions are in the questions and links presented. Includes steps and illustration. Free practice Tests.
My other lessons on calculating trig functions and solving trig equations in this site are - Calculating trigonometric functions of angles - Advanced problems on calculating trigonometric functions of angles - Evaluating trigonometric expressions - Solve these trigonometry problems without using a calculator - Finding the slope of the bisector to the angle formed by two given lines in a ...
Basic Word Problems 1) Jimmy is 25' from the base of a tree. The angle of elevation to the top of the tree is 51°. Determine the height of the tree. 2) Jimmy is standing 30m from the base of a tree. He determines the angle of elevation is 31° with a clinometer that he reads 1.5m above the ground. Determine the height of the tree. 3) A ladder is leaning against a wall. It has an angle of ...
Video tutorials on numerous real-life application word problems requiring you to find Trigonometric functions and solve its equations.
Trigonometry Word Problems Trigonometry word problems involve applying the principles of trigonometric ratios —sine, cosine, and tangent—to solve real-world scenarios such as determining heights, distances, and angles. Mastery of these problems requires a thorough understanding of right-angle triangles and the Pythagorean theorem. By practising, students can enhance their problem-solving ...
PRACTICE Trig Word Problems Write the trigonometric equation for the function with a period of 6. The function has a maximum of 3 at x = 2 and a low point of -1.
Trigonometric Functions, How to solve trigonometric word problems, examples and step by step solutions
To solve a problem involving two right triangles using trigonometry, draw and label a diagram showing the given information, and the length or angle measure to be found. identify the two triangles that can be used to solve the problem, and plan how to use each triangle. solve the problem and show each step in your solution.
Triangles and trigonometry are always difficult topics for both mathematics students and teachers. Hence, students' performance in solving mathematical word problems in these topics is not only a reflection of their learning outcomes but also an indication of teaching effectiveness. This case study drew from two examples of solving word problems involving triangles by pre-service mathematics ...
When I press Shift+Space on Word it changes the language I use in the document.How do I stop this feature?Thanks.