- Aptitude Tests
- Cognitive Ability Test

Cognitive Ability Test - Prepare with Free Practice Cognitive Questions & Tips
Employer? Recruit top talent with ATS - AI Recruitment
What is a Cognitive Ability Test?
Cognitive ability tests are widely used by employers to predict job performance and serve as an indicator of general cognitive ability. Cognitive tests may differ in format, but they typically contain 20-50 multiple-choice questions that measure core elements of cognitive ability and must be answered under a tight time limit.
On this page, you will find accurate examples of cognitive ability test questions that represent the questions you could find in some of the industry's leading cognitive ability tests, including ASVAB , PI , Wonderlic , CCAT , WorkKeys , NOCTI , Bryq , Raven's and P&G . Each question is followed by a full answer with useful information and tips for you to learn from, just like what you would find in JobTestPrep's many cognitive ability preparation packs.
Looking to practice a specific test? Check out our exams below:
Free IBEW Test | PI Cognitive Assessment | Indeed Assessments Test | Free Police Written Exam | Free Civil Service Exam | Free TSA CBT Test | Free CritiCall Test | Free WorkKeysTest | Firefighter Test USPS Postal Exam (474 - 477) | Free NYPD Exam | Watson Glaser Test | FEAST I Air Traffic Test | ATSA Test | HireVue | Free Pymetrics Practice Test
Get the most accurate practice for any SHL test with our All-Inclusive SHL Test preparation pack .

David , Psychometric Testing Expert at JobTestPrep .
What do Cognitive Ability Tests Measure?
By combining questions of varying complexity from several fields with a stressful time limit , the cognitive ability test challenges the candidate's problem solving and processing speed abilities, and provides the employer with a measurement of general cognitive ability - a central component of intelligence.
Cognitive testing is such a popular hiring process tool because it is one of the most valid predictors of job success . By giving the employer a preview of a candidate’s cognitive abilities, the cognitive ability test increases the chances that the hiring process will be successful – to the benefit of the organization as well as the candidate.
What Topics are Included in Cognitive Ability Tests ?
Although there is a wide variety of cognitive ability tests that differ in format and difficulty, they generally all set out to measure the same fields:
- Numerical Reasoning – this is the broad term for number-based cognitive skill tests that range from basic math problems to complex numerical problem solving.
- Verbal Reasoning – these cognitive tests evaluate your language comprehension through a range of English language skills, such as vocabulary, grammar, reading comprehension, and critical reasoning.
- Deductive Reasoning – questions where you must deduce from certain rules given in a statement or argument in order to reach conclusions.
- Logical Reasoning – these questions assess your ability to understand complicated texts and, most importantly, to utilize critical thinking skills to draw conclusions and recognize important facts.
- Abstract Reasoning – these cognitive tests measure your ability to draw conclusions based on hidden information in symbols or matrices. You are asked to identify a missing item that completes a certain pattern of logic that you must recognize in a sample given to you.

Applying for a different test? Check out our designated free practice pages: HireVue | IBEW | TSA | ASVAB | Criticall | Watson Glaser | EIAT
Create Your Own Assessment Prep Kit!
Job-seeking can be a long and frustrating process that can take several months. As part of this journey, you'll have to take a number of pre-employment tests or video interviews.
We've designed our Premium Membership to guide you through the entire journey:
Mix & match 3 PrepPacks of your choice at a 50% discount for 1 month / 3 months / 6 months.
Cognitive Test Example Questions
In this section, you will find 20 cognitive ability example questions simulating those you would find in the most respected cognitive ability tests in use today. Read each question carefully and select the answer you think is correct, and then read the full answer that follows. Good luck!
1. Verbal Analogy: find the relationship between the pair of words below, and identify the most similar relationship in the answer options.
REPLETE is to FAMISHED as:
The answer is C.
REPLETE means “full with,” and FAMISHED means “very hungry.” If a person is FAMISHED, they are not REPLETE with food. In a specific context, these two adjectives directly contradict one another.
If something is BLATANT it is very obvious, while if something is MASKED it is hidden. If something is MASKED, it is not BLATANT – these two words also directly contradict each other, and is, therefore, the correct answer.
Incorrect Answers A – SHROUD means “to cover,” and HASTEN means “to do something quickly.” These two words do not have a strong relationship.
B – PLAUSIBLE means “reasonable,” and PLACATE means “try to please.” These two words do not have a strong relationship.
D – COMMENCE means to begin, and a person GRADUATEs upon completing a course of study. Often, GRADUATION ceremonies are referred to as COMMENCEment ceremonies. These two words are related but do not contradict one another.
E – A person who is DEPRESSED may not be SUCCESSFUL, but these two words do not directly contradict each other.
2. Number Series: identify the hidden pattern in the series of numbers below, and use it to predict the next / missing number:
8 | 3 | 9 | 10 | 17 | ?
The answer is: 25.
Answer explanation: This series is a variation of the famous Fibonacci sequence: each term equals the sum of the two previous terms minus 2.
3. Abstract Reasoning - the numbers in the figures below have the same mathematical relationship to one another.
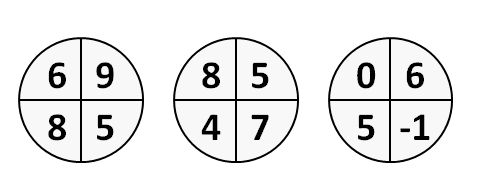
What number should replace the question mark in the figure below?
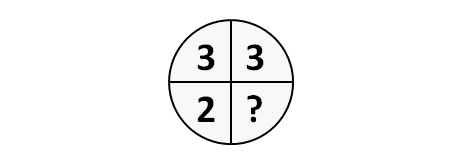
The correct answer is: 2.
When solving this type of question it is important to understand the pattern that the three circles exhibit and the numerical relationship between them.
Focus on the quarter that the question mark appears in and check to see if there is a common relationship that repeats itself between that quarter and the other quarters of each of the circles.
In this example, the circles share the following pattern: (Top cell) minus (Diagonal-bottom-cell) = 1.
e.g. left circle: 6 (top-left) – 5 (bottom-right) = 1, 9 (top-right) – 8 (bottom-left) = 1; right circle: 0 (top-left) – (-1) (bottom-right) = 1.
According to the reasoning above the (top-left) cell – (bottom-right) cell = 1. Therefore, the (bottom-right) cell = 2.
4. Deductive Reasoning - These cognitive test questions measure your ability to analyze sentences and reach a logical conclusion. Some of the questions are numerical, and some are verbal, and the conclusion is generally reached by applying general rules.
If the first two statements are true, is the final statement true?
Most snakes are green. Most snakes are quick.
At least one snake is both green and quick.
The correct answer is A - Yes.
The way to solve this type of question is to examine the ratios and see if there could be an overlap between the two groups - if most of the snakes are green and most of the snakes are quick, we can deduce that there has to be at least one green snake that is also quick.
This happens because the subgroups of "green" and "quick" each constitute more than 50% of the entire snake population (most of the snakes means more than 50%) and consequently must overlap.
5. Numerical Reasoning: Percentages and Word Problems. Percentage problems can take the form of word problems and are usually structured in the following way: "(this) is (a percentage) of (that)", which translates to = (to a decimal) × (that)".
If there are 32 students in the classroom and 12.5% of them own at least one pet, how many students do not own any pets?
The correct answer is 28.
It helps to memorize the most common fractions that represent each type of percentages/decimals.
For example: 1\4 = 0.25 = 25% 1\8 = 0.125 = 12.5%
If there are 32 students in the class and only 12.5% of them own at least one pet then all that is left is to divide 32\8 to know that 4 students own a pet and 28 do not.
6. Verbal Reasoning: Vocabulary
Clout most closely means -
The correct answer is prestige. The word clout has two meanings: (1) A heavy blow, especially with the hand (2) The power to influence, usually regarding politics or business. Prestige is close in meaning to the second definition of clout and is therefore the correct answer.
7. Numerical Reasoning: Word Problems
Shelley has 7 dresses, 8 pairs of shoes, and 7 necklaces. If she wears one combination of clothes per day. How many days can she go without wearing the same outfit?
The answer is 392.
This is a classic combinations question. In order to solve the problem, you must figure the correct number of choices in each category. We have 3 categories: Dresses= a choice between 7 options. Shoes = a choice between 8 options. Necklaces = a choice between 7 options.
The overall number of combinations equals to a multiplication of the number of options within each category: 7*7*8=392
8. Verbal Reasoning: Synonym / Antonym
IMPERIOUS is the opposite of:
The correct answer is subservient.
Imperious means "domineering in a haughty manner; dictatorial; overbearing," so the antonym is subservient. Arrogant is a similar word but not a synonym. Quiet, stormy, and gloomy are not related.
Therefore, the correct answer is subservient.
Questions 2-8 are the type of cognitive questions you will face in the Wonderlic Test . For a full length Wonderlic practice test, click here .
9. Abstract Reasoning - Spatial
Which of the following boxes should replace the question mark (?) to complete the pattern?
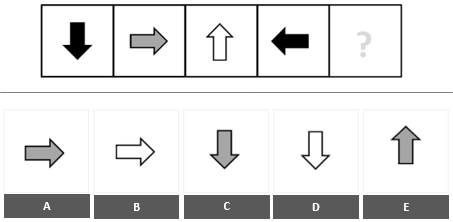
The arrows move 90 degrees counterclockwise, and the colors change between black, grey and white in cycles of three.
Based on the progression of the arrows, the following arrow in the series must be gray and pointing downwards.
10. Logical Reasoning - Syllogisms are a type of deductive reasoning where a conclusion is drawn from two premises provided to you in the question.
Assume the first two statements are true:
All athletes are hard workers.
Alice is not an athlete.
Alice is not a hard worker.
Is the final statement:
You can deduce from the first statement that all athletes are hard workers, but you do not have any information about non-athletes.
Therefore, according to the second statement, you cannot conclude anything regarding Alice, who is not an athlete.
The final statement is uncertain.
11. Numerical reasoning - Word Problems
In a popular music station, songs are played fully and uninterrupted (i.e., no commercial breaks). The popular music broadcast "Hits All Around Us" lasts 2 hours and 15 minutes, in which two-song lengths are played – songs that last 3 minutes and songs that last 6 minutes.
How many songs will be played during the broadcast?
Two hours and 15 minutes are 135 minutes in total.
The most songs that can be played are 45 (45 songs X 3 minutes each = 135 minutes).
The last songs that can be played are 23 (22 songs X 6 minutes each + 1 song X 3 minutes = 132 + 3 = 135)
12. Verbal Reasoning - sentence completion. Choose the word that, when inserted in the sentence to replace the blank, best fits the meaning of the sentence.
Electronic information and automated systems are essential to ____ all major federal operations.
The sentence refers to electronic information that is fundamental to (something) all major federal operations. The sentence's general idea implies that electronic information is essential to practically / nearly / almost all primary federal operations.
Therefore, the only word accurately reflecting that meaning in the sentence's context is "virtually".
13. Abstract Reasoning - these types of cognitive questions require finding hidden patterns or rules in shapes. There are many types of abstract reasoning questions in cognitive tests, in which you need to pay attention to different elements. In the following question, you must pay attention to shape and movement.
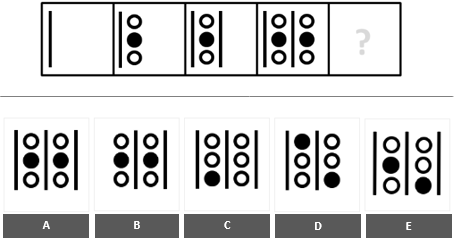
In this series, alternating vertical lines or vertical chains of circles are added to each figure, depending on the previous figure.
The middle circle in the vertical chain is always black. Since the last figure in the series contained an additional vertical chain of circles, the next figure should include an additional vertical line.
The figure appearing in answer option A is the only one that fits.
14. Letter Series - What would be the next group of letters in the following series?
zone --> ynnd --> xmnc --> wlnb --> ?
The pattern in this question is that all the letters move one letter backward in the alphabet except the letter "n" which stays constant. Therefore the answer is vkna.
Tip - at first glance, this type of cognitive ability question seems confusing. It is in fact no different than a number series! To help you solve these questions quickly, write down the ABC with a corresponding number beneath each letter (A-1, B-2 etc.). This will help you identify the pattern.
Cognitive question examples 9-14 are the type of questions you will encounter in the CCAT Test . To practice more questions, try our Free CCAT Practice Test.
15. Logical Reasoning - In the following question you will be presented with a fact and a pursuant conclusion. It is up to you to decide if the conclusion can be proven or not.
FACTS: If Jason is late to the meeting, Kevin will have to work late. Lois will not cook dinner for Kevin unless Kevin gets home from work on time. If Lois does not cook dinner for Kevin, Kevin will order pizza for dinner. Lois cooked dinner for Kevin.
CONCLUSION: Jason was late to the meeting.
The facts disprove the conclusion
If Jason is late to the meeting then Kevin will not get home from work on time because he will have to work late. Lois will cook dinner for Kevin only if Kevin gets home from work on time Thus, if Lois cooked dinner for Kevin, Jason could not have come late to the meeting.
16. Verbal Reasoning - Odd One Out. In this type of cognitive question, you need to select the word that stands out in regard to its meaning.
Which word does not belong on this list?
The correct answer is archaic
Archaic is a word used to describe something that belongs to an earlier period of time, while the other words are used to describe sad and gloomy states of mind or facial expressions.
17. Abstract Reasoning - Odd One Out
Choose the odd one out:
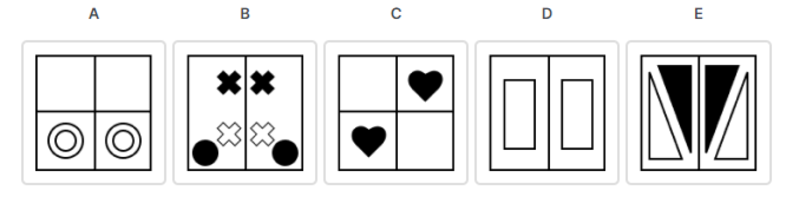
The correct answer is C.
The logic: In all of the options except for option three, there is a vertical line which separates these boxes into two, equal, symmetrical halves which mirror one another. If these boxes were pieces of paper which were folded vertically, the items in the boxes would be matching and perfectly identical. The right and left halves are mirror-images of one another. This is not the case for option three. In option 3, there is no mirroring effect between the halves. Both hearts have to be either on the top or on the box's bottom for there to be symmetry.
You have probably noticed that the amount, shape and color of the items are insignificant features and are simply distracters.
18. Numerical Reasoning - Word Problems
When a smartphone is connected to a charger the battery charge increases by 4.5% per minute. When applications are in use the battery decreases by 3% per 2.5 minutes.
What is the percentage of charging rate per minute if the phone is connected to a charger while several applications are in use?
The correct answer is 3.3%.
In order to tackle this question we will first need to understand that there are two opposite "forces" in this question - charging and discharging (i.e. application usage) of the battery. The charger works in a "positive direction" and the applications in a "negative direction". Now we can address the given information: Charger's work rate: 4.5/1 (4.5% charge per minute) Applications' work rate: -3/2.5 = -1.2/1 (1.2% discharge per minute) Thus, the total charging rate ("sum of forces"): 4.5/1 – 1.2/1 = 3.3/1, meaning: 3.3% per minute.
19. Logical Reasoning
Assumptions:
Most technicians work on the first floor. All accountants work on the second floor. No secretaries work on the third floor.
Conclusion: Rose, a technician, works on the third floor.
If the assumptions are true, is the conclusion:
According to the first assumption, most technicians work on the first floor. This means that there is at least one technician who does not work on the first floor. Thus, Rose may or may not work on the third floor.
Therefore, the conclusion Cannot be determined based on the information
20. Abstract Reasoning - Next in Series
Which block completes the following sequence:
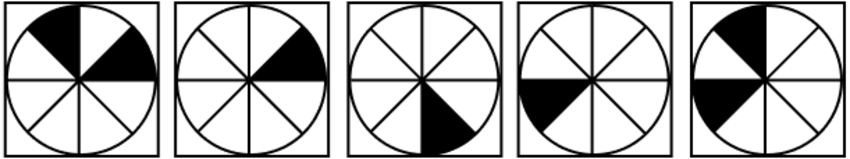
The correct answer is D.
The two black sections of the circle move around it clockwise in a different pattern: the section on the upper left side of the circle moves two sections each step. The second section (upper right side in the first frame) stays in the same spot for a step and then moves two sections in the next two steps. When the two sections land on the same spot, they appear as one, such as in the third frame.
In the next frame of the sequence, the first section should appear on the upper right side of the circle, so answers (A), (B), and (E) can be ruled out. The second section should stay where it is, which leaves the answer (D).
Cognitive questions 15-20 are the types of questions commonly found in the PI cognitive assessment . To practice more questions like these, try our free Predictive Index Practice Test.
Prepare for your Cognitive Ability Test
Cognitive tests present two major obstacles: short time frames, and questions that include known tricks and distracters . Luckily, you can overcome these two obstacles with the right practice.
JobTestPrep's cognitive test preparation packs offer a comprehensive review of all the question types seen on contemporary employers' cognitive ability tests. Practicing the full range of numerical, verbal, deductive, spatial, and logical reasoning questions under strict time frames can greatly assist in improving your scores.
We also provide detailed answer explanations, helping you to understand the logic behind each question. Furthermore, our insightful score reports can help you assess your own cognitive abilities, strengths, and weaknesses.
Start preparing today with one of our specialized prep packs!
Tips to Help You Pass Your Cognitive Test
Cognitive tests can be daunting, and the stress that accompanies them due to the high stakes that are involved can make them even more so. However, there are a number of tips and hacks that can help you improve your cognitive test score before even beginning to practice!
- Don't waste too much time on one question. There will always be a question that you don't get and find yourself wasting time on. You've been asked what placate means and you don't remember? The best option is to guess and move on. Good time management is one of the most vital tools you will gain with our cognitive ability practice.
- Read the instructions carefully. Reading the instructions for each cognitive test question will help ensure you are not missing any important details, and keep you from missing out on points you had in the bag.
Given that an incorrect answer yields the same 1-point reduction from your cognitive ability score, it is best to not leave any questions unanswered and try guessing instead. This strategy is great in helping you earn as many points as you can, rather than losing points for leaving questions blank.
Use scrap paper.
The questions in cognitive tests are built to overload your brain. Using a piece of scrap paper to make calculations or visualize a tricky abstract reasoning question can make a big difference.
Types of Cognitive Ability Tests
While cognitive ability tests generally measure similar fields, they can vary significantly in length, time limit, and difficulty. Below are some of the most popular cognitive tests being used today, click on the link to learn more about how each one measures cognitive abilities:
- Wonderlic – also known as the Wonderlic Personnel Test-Revised (WPT-R), this cognitive test pits you against 50 multiple-choice questions that must be completed in 12 minutes - meaning processing speed and time management are particularly important.
- Criteria Cognitive Aptitude Test (CCAT) – a cognitive test that measures a candidate's cognitive aptitude , problem-solving abilities, skill-learning capabilities, and critical thinking. It consists of 50 questions and has a 15-minute time limit.
- Predictive Index (PI) Cognitive Assessment – formerly known as the Professional Learning Indicator (PLI), this is a 12-minute cognitive test comprised of 50 questions. The PLI is given to potential hires to test for skills not easily found on a resume or during an interview and measures your capacity to solve problems, learn, and adapt in the workplace.
- The Universal Cognitive Aptitude Test (UCAT) is a job application assessment that measures your critical thinking, problem-solving, analytical, and mathematical abilities. It consists of 40 questions, and you are given 20 minutes to complete it. Unlike the CCAT exam, the UCAT excludes verbal reasoning and verbal ability sections.
- The Revelian Cognitive Ability Test (RCAT) , previously known as Onetest, assesses three areas: verbal, numerical, and abstract reasoning. The test's difficulty increases as you proceed. You have 20 minutes to answer its 51 questions.
- SHL Tests - SHL is a longtime giant of psychometric testing, with a set of recognized, well-validated assessments. Most common among them are the SHL Numerical , SHL Verbal , SHL Inductive , and SHL Deductive tests. These four are sometimes grouped together to create the SHL General Ability Test . Other cognitive assessments include the SHL Calculation Test , SHL Checking Test , and SHL Mechanical Comprehension .
- The Caliper Assessment , commonly referred to as the Caliper Profile, is a pre-employment test designed to measure the alignment of your personality traits and cognitive skills with the demands of the job you're seeking. It's frequently used for senior, managerial, and leadership positions. Try free Caliper test questions .
- Procter and Gamble Assessment - this cognitive abilities test is adaptive (changes in difficulty based on your answers) and fully interactive. It measures a number of cognitive abilities such as spatial orientation and memory, as well as personality traits through a personality test a situational judgment test.
- Pymetrics - The Pymetrics games test comprises a set of twelve activities crafted to evaluate your personality traits and cognitive abilities. The primary hurdle of the Pymetrics assessment lies in grasping the intended result of each test, along with the aspects being gauged and rated.
- Free IBEW Practice - The IBEW Aptitude Test stands as a notably demanding cognitive assessment, mandatory for aspiring licensed electricians to successfully clear.
- The Hogan Business Reasoning Inventory - a cognitive test, typically used to assess reasoning and decision-making skills for senior positions.
- Aon Assessments - Aon’s assessment tests are unique in their interface, gamified assessments, and their particular ways of evaluating your competencies, abilities, characteristics, and behavioral tendencies required in the workplace.
Mercer Mettl Test - assessing cognitive abilities, technical skills, and personality traits. With adaptive testing, it adjusts question difficulty based on your responses, offering precise insights for job applications and personal development.
Many tests include cognitive ability sections along with other topics. You can find army-related cognitive ability sample questions on our Free ASVAB Practice and Free AFOQT Practice Test .
While not a cognitive test, interviews play a significant part in the hiring process for most employers. The most notorious one is the pre-recorded video interview .
Cognitive Ability Test Scores
Cognitive tests measure your cognitive abilities - but how are the scores used to decide which candidate gets the job?
There are two main scoring methods to compare cognitive ability scores:
Relative score - your score is placed on a bell curve along with the scores of other candidates so that your score is compared to theirs and a certain cutoff point is decided. For example, an employer might decide that only the top 10% of the scores move on to the next step of the hiring process.
Absolute score - a threshold is set by the employer in advance, and your cognitive ability score needs to pass it. For example, getting more than 30 questions right in the Wonderlic Test .
For more scoring methods, you can observe our ASVAB Scores guide.
- What's on this page
- Cognitive Example Questions
- List of Cognitive Ability Tests
- Free Cognitive Ability Practice Tests
- CCAT Practice Test
- SHL Practice Test
- Wonderlic Practice Test
- P&G Practice Test
- PI Cognitive Assessment Practice Test
- Raven's Progressive Matrices Practice Test
Cognitive ability test
Article author: Dr. Edwin van Thiel , updated July 6, 2022
What is a cognitive ability test?
A cognitive ability test , or a cognitive test in general, is simply put a measurement of a mental performance. This can be a very specific one, such as solving a mathematical sum, or a very broad measurement such as determining someone's general intelligence .
Cognitive ability tests ...
- Call upon logical reasoning, either through induction or deduction, and general problem solving
- Measure abilities that will vary in the extent to which they are innate or learnable
- Deal with sensory perception, memory, learning and applying (acquired) knowledge
What are cognitive ability tests used for in assessments?
Ability test practice.
Score higher on ability assessment tests.
The promise a cognitive test holds is that it predicts future job performance. It goes without saying that the better a cognitive test resembles tasks that need to be performed in a job, the better the prediction will be.
In general though, most cognitive tests will to some degree also predict other cognitive skills. So even when the cognitive abilities assessed seem somewhat inappropriate for a given job, chances are they still are valid predictors for it.
Do I need to practice ability tests?
Absolutely! Cognitive assessment tests are almost always learnable to a degree. Even aspects that are rather innate, such as processing speed, can be improved by practicing. When you understand the tactics, strategies, styles and instructions used in ability tests, you will score higher.
Would you like to try cognitive ability tests? We have many specific free ability assessment tests you can use to practice. Here are free examples of the ten most frequently used cognitive tests:
- Numerical reasoning test
- Verbal reasoning test
- Logical reasoning test
- Diagrammatic reasoning test
- Spatial reasoning test
- Inductive reasoning test
- Deductive reasoning test
- Mechanical reasoning test
- Critical thinking test
- Error checking test
Often used commercial cognitive ability tests
- CCAT - Criteria Cognitive Aptitude Test - (primarily US)
- WPT - Wonderlic Personnel Test - (primarily US)
- PLI - Predictive Index Learning Indicator
- RCAT - Revelian Cognitive Ability Test - (primarily Australia)
- MMAT - McQuaig Mental Agility Test
- Cubiks Logiks
- GIA - Thomas International General Intelligence Assessment
- HBRI - Hogan Business Reasoning Inventory
Let someone else know about this article
If you think reading this article would benefit someone you know, you can easily share it through the medium of your choice.
Share article:
- Practice Tests
- Predictive Index
- Firefighter
- Hogan Assessments
- Leadership Assessment
- Ramsay Technician Assessments
- Watson-Glaser
- Raven's Progressive Matrix
- NEO Personality Inventory
- Texas Success Initiative
- Birkman Personality Test
- TSA Prep Booster™ Course
- TSA Practice Test
- TSA Written Skills Assessment
- TSA CBT X-Ray Object Recognition Test
- TSA Connect the Dots
- SHL Assessment Prep Course
- Practice Test & Answers
- SHL Practice Tests
- SHL Test Answers
- SHL Inductive Reasoning Test
- SHL Numerical Reasoning Test
- SHL Verbal Reasoning Test
- SHL Verify G+ Test
- SHL Mechanical Comprehension Test
- SHL Situational Judgment Test
- SHL OPQ Personality Test
- Predictive Index Master (Cognitive & Behavioral)
- Predictive Index Cognitive Assessment
- Predictive Index Behavioral Assessment
- Predictive Index Practice Test
- Predictive Index Results
- Caliper Course
- Caliper Test Prep With Real Practice Test
- USPS Postal Exam
- Postal Exam 474
- Postal Exam 475
- Postal Exam 476
- Postal Exam 477
- USPS Postal Exam Prep
- Pass the 2024 Postal Exam With Practice Tests
- Virtual Entry Assessment (VEA)
- General Police Prep Course
- Police Situational Judgement Test
- Police Psychological Exam Course
- Massachusetts State Police Exam
- Pennsylvania Police Exam
- Philadelphia Police Exam
- Nassau County Police Exam Course
- Suffolk County Police Exam
- Correctional Officer Exam
- MTA Police Exam
- New York State Police Exam Prep Course
- School Safety Agent Course
- Police Officer NYPD Exam
- Police Fitness Prep Course
- Exam Formats
- EB Jacobs Law Enforcement Aptitude Battery
- CJBAT Study Guide
- DELPOE Police Exam
- Texas LEVEL Test With Expert Guides
- PELLETB Course
- FBI Test Phase 1 (Special Agent Exam): Guide with Practice Test [2024]
- Police Test Preparation Suite
- Pass a Polygraph Test (Lie Detector): Expert Tips & Questions – 2024
- Firefighter Test
- FDNY Firefighter Prep Course
- Firefighter Psych Test
- NFSI Firefighter Prep Course
- FCTC Firefighter Prep Course
- Firefighter Aptitude and Character Test
- FireTeam Prep Course
- Master Course
- Hogan Assessments Master Course
- Personality Courses
- Hogan Personality Inventory (HPI)
- Hogan Development Survey (HDS)
- Hogan Motives, Values & Preferences Inventory (MVPI)
- Busines Reasoning Course
- Hogan Business Reasoning Inventory (HBRI)
- Leadership Assessment Test
- GardaWorld Pre Board Primer
- Bennett Mechanical Comprehension Test II (BMCT-II) Success Prep Course
- Beat the 2024 BMCT With Industry Expert Guides & Realistic Practice Tests
- 911 Dispatcher
- CHP Dispatcher
- Exam Format
- Criticall Dispatcher
- Criticall Dispatcher Test
- Criteria Cognitive Aptitude Test - CCAT Course
- Universal Cognitive Aptitude Test - UCAT Course
- CCAT Practice Test
- Criteria Pre-employment Testing: Personality, Aptitude & Skill Tests
- Korn Ferry Course
- Ace the 2024 Korn Ferry Assessment With Practice Test & Expert Guides
- Ramsay Electrical Assessment
- Ramsay Maintenance Assessment
- Ramsay Mechanical Assessment
- Ramsay Multicraft Assessment
- Ramsay Electrical Practice Test
- Ramsay Maintenance Practice Test
- Ramsay Mechanical Practice Test
- Ramsay Multicraft Practice Test
- Ramsay Test Prep
- AFOQT Study Guide
- ASTB Study Guide
- SIFT Study Guide
- Watson-Glaser Critical Thinking Course
- Beat the Watson Glaser and Upgrade Your Career
- Raven's Advanced Progressive Matrices
- Texas Success Initiative Course
- TSI Practice Test 2024: Math, Reading & Writing
- TSI Reading Practice Test: 15 Q&A with Explanations
- Pass our Free TSI Math Practice Test (2024 Update)
- Take our Free TSI Writing Practice Test (2024)
- Birkman Personality Course
- How it Works
Cognitive Ability Test Guide: Take Free Practice Tests Online
What is the cognitive ability test.
Cognitive tests measure a candidate’s thinking abilities, including, reasoning, perception, memory, problem-solving skills, and verbal reasoning. They are usually used by potential employers to assess an applicant’s thinking abilities.
The questions featured in these tests tend to include verbal analogies, arithmetic calculations, spatial relations number series puzzles, comprehension, and reading comprehension. Cognitive ability tests are notoriously tricky, as they often come with harsh time-limits and specific question types. Yet, rest assured, through practice it is possible to familiarize yourself with the types of questions featured on these tests and to improve your speed.
Here’s our 3-step easy to follow formula to ace any cognitive ability test:
- Read this short guide to learn everything related to cognitive ability tests.
- Take our online practice tests to assess your knowledge.
- Take our Rapid Cognitive Ability Course Online to increase your score.
Take the Free Cognitive Ability Practice Test
Quick facts on cognitive ability tests.
- Cognitive Ability tests mainly have multiple-choice format.
- Cognitive tests usually consist of verbal, numerical, abstract and logical tests.
- Questions from many topics will be included in the test, for example verbal, logical, etc.
- A single question may not be about one single topic.
- There are typically many questions that need to be answered in a very short time.
- Applicants are not required to complete these exams in their entirety.
- The content of the tests is generally not hard, however, the time constraints and the changing between subjects makes the tests difficult.
That’s why Prepterminal’s Cognitive Ability Test Prep Course is designed to get you top results in no time. With the course, you’ll benefit from learning the following: time management, a detailed strategy, question preparation and tips on approaching the test with confidence.
What topics are included in Cognitive Ability Tests?
In this part, you’ll learn about what topics are included in most of the cognitive ability tests.
Numerical Reasoning
- Basic Numeracy: Undertaker basic math – 4 operations (subtraction, addition, division, multiplication), averages, fractions, and ratios.
- Word problems: Study and solve mathematical questions given in text format.
- Number series: Discover and follow patterns in a specific list of numbers.
Verbal Reasoning
- Vocabulary: Show your knowledge of the definitions and usages of various words.
- Analogies: Discover relationships between two words and apply this relationship to an additional word.
Abstract Reasoning
- Odd One Out: Choose which shape doesn’t fit in a specific set.
- Next in Series: Discover a progression pattern of shapes and find out which shape is next.
- Matrices: Similar to ‘next in series’, but rather in a two-dimensional matrix format.
- Analogies: Discover the relationship between a certain pair of shapes and apply this knowledge to another shape.
Logical Reasoning
- Syllogisms: Come up with a conclusion from a certain number of premises.
- Deduction and Conclusions: ‘Syllogisms’ in reverse – use the necessary information to form a certain conclusion.
- Seating Arrangements: Discover the order of various elements in keeping with a given set of rules.
Sometimes test takers confuse Cognitive Ability tests with Cognitive Skills tests. Cognitive Ability tests mesure your general intelegence, your ability to learn and apply new skills. And Cognitive Skills tests are designed to find out if math and verbal career training programmes are necessary for entry-level roles. This exam will inform your future employer about where best to put you within the company structure.
Cognitive Ability Test Scores
Let’s take a look at cognitive ability test scores terminology:
1. Raw score
2. subscores, 3. percentile score, 4. stanine score.
| Stanine | Percentile Rank | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1-3 | Very Low |
| 2 | 4-10 | Below Average |
| 3 | 11-22 | Below Average |
| 4 | 23-39 | Average |
| 5 | 40-59 | Average |
| 6 | 60-76 | Average |
| 7 | 77-88 | Above Average |
| 8 | 89-95 | Above Average |
| 9 | 96-99 | Very High |
5. Norm group
A norm group is a sample of pre-tested candidates who have a specific characteristic in common and whose scores were aggregated to develop a benchmark. Norm groups can be divided by industry, geography, profession and the like. An example of a norm group could be the population of employed managers.
Is there a cut-off score for all cognitive ability tests? In short, no. Firstly, all test providers have unique score distributions. Thus, when you are looking to find a cut-off score for your own test, ensure that you are examining the data that relates to your own assessment.
Secondly, a cut-off score or target score varies according to the employer’s recruiting decisions and thus the job position you are applying for.
6. Negative scoring
Most cognitive ability tests do not take off points for incorrect answers or blank answers. It is thus better to take an educated guess, than to leave a question blank.
Make sure you get a top score on your cognitive ability test. Maximize your test score PrepTerminal’s cognitive ability prep course today!
Rapid Cognitive Ability Course
- Word Problems – Video Guide
- Word Problems – Written Guide
- Word Problems Practice Questions
- 2 BONUS Interview Prep Video Guide Buy this Course: Get full access to all lessons, practice tests and guides.
- Practice Test 1
- Practice Test 2
- Practice Test 3
- Tables - Written Guide
- Tables Questions
- Ratio - Written Guide
- Ratios Questions
- Percentages - Written Guide
- Percentages Questions
- Currency Exchange
- Currency Exchange Questions
- 1/2/3/4 Operations - Video Guide
- 1/2/3/4 Operations - Written Guide
- 1/2/3/4 Operations Questions
- Synonyms - Written Guide
- Reading Comprehension – Written Guide
- Reading Comprehension Questions
- 11 Spatial Awareness Buy this Course: Get full access to all lessons, practice tests and guides.
- Non-Verbal Analogies – Video Guide
- Non-Verbal Analogies – Written Guide
- Non-Verbal Analogies Practice Questions
- Lowest Values – Video Guide
- Lowest Values – Written Guide
- Lowest Values Practice Questions
- Inductive Reasoning – Video Guide
- Inductive Reasoning – Written Guide
- Inductive Reasoning Practice Questions
- Formal Logic – Video Guide
- Formal Logic – Written Guide
- Formal Logic Practice Questions
- Antonyms Video Guide
- Antonyms – Written Guide
- Antonyms Practice Questions
- Analogies - Video Guide
- Analogies – Written Guide
- Analogies Practice Questions
- 18 Introduction Buy this Course: Get full access to all lessons, practice tests and guides.
- 19 Number Series Buy this Course: Get full access to all lessons, practice tests and guides.
Most Popular Cognitive Ability Tests Employers Usually Use
There are several Cognitive Ability Tests, that employers might require to pass. Here we have collected the most popular Cognitive Ability Tests. Take a look at our separate guides to be aware of each test in detail:
- The Wonderlic Test
- Criteria Cognitive Aptitude Test (CCAT)
- Cubiks Logic
Frequently Asked Questions
Can i bring and use a calculator.
While some exams let you use a calculator for numerical questions, the majority of cognitive ability tests don’t.
Bear this in mind when you practice, and try to do the calculations in your head.
Should I just guess if I don’t know an answer?
Skipping a question depends on the manner in which the exam is scored. It depends if points are taken off for incorrect answers.
If they are deducted – you shouldn’t guess, and just skip the question. If they aren’t – you should take a guess and then move on to the subsequent question.
Can I go back and answer a question that I missed?
This changes from test to test. Make sure you read the instructions well on your test day. The instructions will tell you if you can go back and answer a question you skipped.
If you read that you can’t go back then you need to address each question as they are presented.
If you are allowed to go back, you can choose, for example, to answer all the questions you know best first, and only then go back and answer the questions you are not sure about.
Will I have enough time to answer all the exam questions?
Most people don’t complete the entire test in the given amount of time. This is primarily due to the fact that typically there are a lot of questions that need to be answered in a short time frame.
It is very rare for applicants to not only answer all of the questions, but also to answer them accurately. Make sure you focus on quality and not quantity.

Created by: Matthew Appleyard
Psychometric tutor, prepterminal test expert, 1826 students, 4.6 , 268 reviews.
I’m Matthew Appleyard, Prepterminal’s Cognitive Ability Expert. Any questions about the course? Let me know at [email protected]
Get 25% off all test packages.
Get 25% off all test packages!
Click below to get 25% off all test packages.
Cognitive Ability Tests
- 456 questions
Cognitive ability tests are predictors of general intelligence. Like IQ tests, they examine your ability to solve problems and think logically, via verbal, numerical, mechanical, spatial and logical questions.
Cognitive tests are popular with employers, as the broad range of aptitudes covered can give a good overview of each candidate’s strengths and weaknesses, and indicate whether they have what it takes to succeed in the role.
What is a cognitive ability test?
Cognitive ability tests were first created at the end of the 19th century and are used as a measure of someone’s general mental ability .
Unlike more targeted aptitude tests (such as verbal or numerical reasoning) the cognitive ability test covers a range of aptitudes – often mechanical reasoning and spatial awareness – to assess an individual’s overall intelligence.
The shift between subjects can be challenging, especially if your strengths lie in one area, and the tight time limit makes it even harder. Practice and preparation is the key, especially for those aptitudes where you often get lower scores.
On a typical cognitive ability test, you might answer questions on any of these topics:
- Numerical reasoning
- Verbal reasoning
Logical reasoning
- Mechanical reasoning
- Spatial awareness
Getting familiar with the different styles of questions, the shift between topics and the speed in which you need to answer each question will really help when it comes to tackling the cognitive ability test as part of a job application.
Which employers use them, and why?
The cognitive ability test is recognised as one of the best indicators of a potential employee’s ability for the job they’re applying for.
Assessing not just your general aptitude, but your ability to work under pressure and shift between different styles of questions and challenges, the test can prove to an employer that you’ll make smart decisions, that you can think on your feet and that you know how to keep calm under pressure — all invaluable skills.
As a result, the cognitive ability test is used by a wide range of employers in industries as diverse as finance and the armed forces. However, it’s particularly useful when hiring for jobs that are known to require complex decision-making; roles such as pilot, doctor, lawyer and engineer, because the relationship between a strong cognitive ability test score and overall job performance here is considered to be closely linked.
Implementing a cognitive ability test can yield numerous benefits for employers, including improved hiring outcomes, reduced training periods, and various financial advantages. Considering the modest cost associated with administering and analyzing the test results, it’s no surprise that it has emerged as one of the most prevalent recruitment tools in use today.
Types of cognitive ability test
When you take a cognitive ability test you’ll cover a range of different subjects and questions that can be practised in greater detail as full tests.
In particular, you should aim to prepare for:
Numerical Ability Tests
Numerical ability tests are designed to examine your aptitude for numbers. The questions cover mathematical problems such as ratios and percentages, fractions, data interpretation and even financial analysis .
This type of test is particularly challenging as the questions are complex and the tight time limits don’t leave much more than a minute for you to answer each question.
Practising as many numerical reasoning tests as you can, particularly if this is an area you’re weaker at, will help you to perform better at the cognitive ability test, and will prove to an employer that you’re able to work with numbers quickly and accurately.
Verbal Ability Tests
Verbal ability tests evaluate your comprehension and communication skills.
You’ll read through dense passages of text and then be faced with a series of questions on what you’ve just read, to which you’ll have to select a multiple-choice answer (usually ‘true’, ‘false’ or ‘cannot say’).
No prior knowledge of the subject matter is needed. In fact, it’s important that you answer based just on what you’ve read, paying particular attention to what’s actually been stated, and what’s merely been inferred.
Scoring well at the verbal ability section of the cognitive ability test shows an employer that you’re able to assimilate lots of information quickly, that you have good comprehension skills and that you’re able to differentiate between fact and fiction.
Logical Ability Tests
Logical ability tests use pattern- and shape-based puzzles to assess your problem solving and logical thinking skills.
You’ll be required to look at a series of different shapes or patterns and use your logical abilities to work out the rule that connects them all, in order to finish the sequence.
The questions might be unlike anything you’ve ever seen before. And you won’t have long to answer each question — so practising as many of these tests as you can before taking a general cognitive ability test will help to improve both your speed and accuracy.
Mechanical Ability Tests
Mechanical ability tests assess your ability to understand different mechanical and electrical principles. Covering everything from energy and transformation, to levers, pulleys and pressure, these tests are commonly used when hiring for engineers and the armed forces .
The knowledge you’re being tested on here is very specific; it really does require prior reading rather than guesswork on the day.
Practising a few mechanical reasoning tests before taking a cognitive ability test will help you to brush up on your understanding of mechanical and electrical principles. It will also ensure you’re used to the question style and the speed at which you’ll need to answer every question.
Spatial Awareness Tests
Spatial awareness tests are an opportunity for you to demonstrate your ability to manipulate images and shapes into their two- and three-dimensional forms, and draw conclusions from limited amounts of information.
Typically set by architecture and engineering firms, the spatial awareness test helps an employer to see how good you are at working with shapes, as well as your problem-solving skills and time management.
Again, this style of question isn’t something you’ll necessarily have come across, which makes practising past tests all the more important.
Publishers of cognitive ability tests
There are numerous publishers who administer cognitive ability tests. If you can find out which organisation is publishing the test you’re taking, it means you can prepare using past tests from that publisher, and get used to the specific style and format of questions.
Here are a few of the most popular publishers used in the UK:
Revelian — An Australian test provider that uses tests created by psychologists for employers across the world.
SHL — One of the biggest test providers, offering assessments for 150 countries in 30 different languages.
Predictive Index — A popular pre-employment assessment provider that specialises in cognitive and behavioural tests.
Prepare yourself for leading employers

Free Practice Cognitive Ability Test Questions
As mentioned, the cognitive ability test covers a huge variety of topics and question styles.
Most people will naturally be stronger at some areas and have to work a little harder on others, so it’s important to try your hand at all the various different types of questions as part of your preparation.
Below are five practice cognitive ability questions for you to try out. All answers are below.
Numerical Reasoning

What was the total power in gigawatts generated by thermal power over the full year?
Verbal Reasoning

Statement : A derivative could be used by an airline to secure the price of oil now, which it won’t use until six months time.
Logical Reasoning

Which of the given shapes would complete the sequence?
Mechanical Reasoning

How much force is required to lift the weight?
Spatial Reasoning

Which of the given shapes is the unfolded net of the 3D shape?
Numerical reasoning : Q1 = 10 GW Q2 = 10 GW Q3 = 14 GW Q4 = 13 GW
So the total is C) 47 GW produced by thermal power.
Verbal reasoning : True – “to secure the price of a commodity which is to be “bought” at a future date, but at a price that is set today.”
Logical reasoning : The shapes are moving around the points of the polygon. The circle and arrow are both moving anti-clockwise 2 points, and the square is moving 4 spaces in a clockwise direction. So the answer is C.
Mechanical reasoning : There is only 1 load-bearing section of rope, which means that the force needed to lift the weight is the same as the weight itself. So the answer is 10kg.
Spatial reasoning : If you look at the two ends, you can see that the only correct answer could be C.
Sample Cognitive Ability Tests question Test your knowledge!
A sequence of statements is given below. Which statement logically follows from the given statements? 1. No manager is a leader. 2. All directors are managers. 3. Some leaders are directors.
- Some directors are not leaders.
- No directors are leaders.
- All leaders are directors.
- Some managers are not directors.
All roses are flowers. Some flowers fade quickly. Therefore:
- Some roses fade quickly.
- Roses are the only flowers that do not fade quickly.
- No roses fade quickly.
- It is possible that some roses fade quickly.
If it takes 5 minutes to drill a half-inch hole, how long will it take to drill a two-inch hole?
A researcher compiled data over several years and found that for Company X, employee productivity increases by 2% for every 1% increase in salary. If an employee's salary is increased by 10%, by how much can the researcher expect their productivity to increase?
Which word is a synonym for 'evanescent'?
Start your success journey
Access one of our Cognitive Ability tests for FREE.
I’ve practiced hundreds of numerical questions and still have plenty more to try.
Ellen used Practice Aptitude Tests to prepare for her upcoming interview at HSBC.

Hire better talent
At Neuroworx we help companies build perfect teams

Cognitive Ability Tests Tips
1 try out each of the different test types.
We recommend working through the different types of tests we’ve listed that sit within the overall cognitive ability test. This will help you identify your stronger and weaker areas.
2 Work harder on your weaker areas
It’s tempting to spend more time on the areas you enjoy, but ignoring this urge in favour of working on your weaker spots will pay dividends when it counts. So whether it’s logic slowing you down or verbal reasoning causing you a little uneasiness, spend the extra time on the topics you find more challenging.
3 Practice in a suitable environment
Practically speaking, there’s no substitute for a quiet environment when taking mock tests. Try to find as peaceful an area as possible when you’re taking a mock test, and ensure you have everything you need before you start.
4 Put the timer on
It’s essential to time yourself while doing any practice tests, so you can see how well you fare against the clock. At the end, go over your answers and spend time evaluating your score, and if there were mistakes, why they happened.
Cognitive Ability Video Tutorials

Graph Interpretation
Prepare for your cognitive ability assessments.
Immediate access. Cancel anytime.
- 20 Aptitude packages
- 59 Language packages
- 110 Programming packages
- 39 Admissions packages
- 48 Personality packages
- 315 Employer packages
- 34 Publisher packages
- 35 Industry packages
- Dashboard performance tracking
- Full solutions and explanations
- Tips, tricks, guides and resources
- Access to free tests
- Basic performance tracking
- Solutions & explanations
- Tips and resources
Cognitive Ability Tests FAQs
What is this test used for.
Cognitive ability tests are a common tool used by employers to gauge a job seeker’s potential in various skill areas. They serve as a quantifiable method to assess problem-solving and logical thinking capacities, which are essential across numerous jobs and industries.
What do these tests involve?
These tests are a series of questions designed to evaluate your problem-solving abilities and logical reasoning. Covering a range of topics, from verbal to spatial understanding, they effectively measure how you process information and confront complex situations.
What do these tests measure?
Our cognitive ability tests focus on precise evaluation of your analytical skills, adaptability, and problem-solving prowess. Utilizing state-of-the-art adaptive technology, our test questions constantly evolve to maintain up-to-date with industry trends and standards, offering a true measure of your cognitive strengths.
Where can I practice these tests?
You can dive into a variety of practice cognitive ability tests right here at Practice Aptitude Tests. We provide a deep library of simulations that closely mimic real test environments, giving you the best preparation for your upcoming assessments.
Which employers use these tests?
A wide range of employers across various fields leverage cognitive ability tests as part of their hiring process. These assessments help them identify candidates who have the necessary mental acuity and agility that complement their specific job roles and organizational needs.
Reviews of our Cognitive Ability tests
What our customers say about our Cognitive Ability tests
United States of America
October 14, 2023
Challenging
I found the test challenging and very exciting. I really had to slow down to think through the logic.
Preeti Borra
October 10, 2023
I like the test it's very difficult to solve in one attempt. It is very good test for practice the exam. But they are almost same type of questions still it is very difficult to solve. I would like to attempt more questions like this for practice. I try to understand the pattern.
Christopher Christopher Ward
United Kingdom
October 03, 2023
This required a thoughtful anyalysis of all information presented and required cross referencing of evidence provided.
Obialo Egwim
September 06, 2023
The test was challenging
The test was difficult to understand for the last few questions but decently easy to understand for the first few . But I understood the questions .
Pamela Almeida
July 24, 2023
Shapes and Positions
Interesting series of questions. Sometimes the answers come easier by visual review, sometimes by comparative review.
July 05, 2023
This Was Fun
This test seems t only be focused on spatial awareness and pattern recognition. Although, because I have not yet seen the results of the test I'm unfamiliar just how much these two skills play a role in the bigger picture.
Vladimir Nicolescu
June 29, 2023
Pretty Balanced
It was my first cognitive ability test. seems pretty balanced. Some harder but I managed to find some logic even in the toughest ones
Dylan Kovacevich
June 28, 2023
Good, like to see more.
Thought there would of been a mix of numerical and verbal reasoning, rather than just abstract reasoning.
Sayantani Halder
June 22, 2023
Best GCA questions to practice
I liked the way the questions slowly progressed toward increasing difficulty levels. It helps in getting a grip on the logical reasoning skills
Busi Mongwe
South Africa
June 21, 2023
Pay attention
There instructions were at the beginning of the test which made me panic and anxious so I just clicked on anything but caught on in the middle of the test
By using our website you agree with our Cookie Policy.

A List of Cognitive Ability Tests available for Practice in 2024
History of cognitive ability tests, why are cognitive ability tests used and by whom, how are cognitive tests administered, how to prepare for a cognitive ability test in 2024, final thoughts, what are cognitive ability tests (2024 guide).
Updated November 18, 2023

- Cognitive Ability Test
- Revelian Cognitive Ability Test (RCAT)
Cognitive ability tests are a form of psychometric test to measure and assess intelligence. They are commonly used in pre-employment screening as a way to give an overview of a candidate’s strengths and weaknesses over a broad range of aptitudes – to predict the success of the candidate in a role.
Measuring general intelligence or cognitive ability through a range of tests that include logic, reasoning and problem-solving is simple and easy for a recruiter to administer to a large number of candidates and can reduce the hiring pool to a more manageable size.
Cognitive ability tests are most often used in hiring alongside resumes and qualifications, but they can also be used once an employee is in post as a training tool or for promotion.
Depending on the industry, a cognitive ability test can include questions about numerical ability, vocabulary, logic, spatial awareness, recognizing patterns and mechanical reasoning.
Common Characteristics of Cognitive Ability Tests
Although every test publisher may create a slightly different cognitive ability test battery, they do share some characteristics.
Variety of Topics and Abilities
In a cognitive ability test, the questions are likely to move from one topic or subject (and back again) throughout the test, so there are no defined ‘sections’ dealing with one aspect of ability.
This can happen from question to question, and there may be certain questions that are actually testing more than one ability at a time.
Time Constraints Make the Tests Difficult
The timing of the tests tends to be the most challenging aspect – cognitive ability tests are meant to put pressure on you and get you thinking and reacting quickly, so they offer a relatively short time to answer quite a few questions.
The Questions Are Not Hard... but the Test Is
Cognitive ability tests are meant to be assessments of general intelligence, and as such, they require no specialist or job-related knowledge.
Instead, they are looking for inherent aptitude to predict whether a candidate would be a suitable hire, would learn well and would perform well in the role.
The questions in a cognitive ability test, therefore, are not hard. It is the pressure from the timing and the unfamiliar circumstances that make them difficult. This is why practice is so important.
Cognitive ability, or general intelligence, was first tested for in the early 19th century. While these early tests sought to find a correlation between intelligence and performance, they were often highly inaccurate and didn’t stand up to scientific scrutiny. Trained psychologists were needed to create something more standardized.
In 1904, Charles Spearman began stating that there was a correlation between good performance in one aptitude and good performance in another. He described a ‘general mental ability’, which is essentially what we think of as intelligence.
Another founding father of the cognitive ability test is William Stern who, in 1912, developed the Intelligence Quotient (IQ) to measure a child’s mental age.
Since then, many assessments described as ‘cognitive ability tests’ have been developed throughout the world. They are considered an almost necessary part of the sifting process for roles in many industries – from entry-level and graduate schemes to management and C-suite roles.
Commonly Used Cognitive Ability Tests
Throughout the world, cognitive ability tests are used in pre-employment screening, role training and promotion decisions.
There are a few companies that make some of the most well-known tests of this type.
Predictive Index Test
Predictive Index makes a number of tests, but the Predictive Index Cognitive Assessment (PICA) is the one most often used to make an unbiased assessment of abstract intelligence.
Fifty multiple-choice questions are available to answer in just 12 minutes.
The objective results are used in the recruitment process for a number of companies such as:
Practice Cognitive Ability Test with JobTestPrep
McQuaig Mental Agility Test
The McQuaig Mental Agility Test measures general intelligence and the speed of thought processes.
Fifty questions are available to answer in just 15 minutes. It assesses reaction speed in answering questions on mathematics, reasoning and verbal understanding.
Employers that use the McQuaig Mental Agility Test include:
- Highland Spring
Try a McQuaig Mental Agility Test
Wonderlic created the Wonderlic Personnel Test (WPT-R) .
This is the most popular one in its battery because it is very quick and can be used in the early part of the recruitment process, usually for graduate-level roles.
The full test asks 50 questions in 12 minutes, while the Quicktest asks 30 questions in just eight minutes, based on fact, logic, pattern recognition, verbal reasoning and word problems.
This test is used by employers like:
- MENSA International
- Apple Chevrolet
- Gulf Coast Commercial Group
Try a Wonderlic Personnel Test
Revelian is an Australian testing publisher that has produced a number of tests for cognitive ability, reasoning, personality and work preferences.
The Revelian Cognitive Test (RCT) has up to 51 questions of increasing difficulty to be answered in 20 minutes.
It also offers two game-based cognitive ability assessments that use role-playing and puzzle-solving to measure cognitive ability.
As this is an Australian publisher, RCTs can typically be found as part of the recruitment process all over Australia but, in particular, the following organizations use them:
- The Australian Government
Try a Revelian Cognitive Test
Through extensive psychological research, it is understood that cognitive ability is an excellent indicator of great performance in work. This makes it an effective way to screen potential candidates, especially for graduate and managerial roles where situations are likely to call for confident decision-making and abstract thinking.
Although cognitive ability tests are not meant to be hard in themselves, they are difficult due to the time pressures and the number of abilities that are being tested.
Practice will help to make sure that you get through to the next round of the application process. However, a good recruiter will use the tests in combination with other factors – like a great resume and cover letter, as well as qualifications and experience – to make a hiring decision.
Each cognitive ability test will have a different scoring range, and the pass marks will depend entirely on the business and its standards – so there is no ‘one size fits all’ score that will land you the role.
Instead, aim high and answer as many questions as you can to give yourself the best chance.
If you need to prepare for a number of different employment tests and want to outsmart the competition, choose a Premium Membership from JobTestPrep . You will get access to three PrepPacks of your choice, from a database that covers all the major test providers and employers and tailored profession packs.
Get a Premium Package Now
What Does Scoring Highly on Cognitive Ability Tests Mean?
There are several skills and qualities that a cognitive ability test can measure.
Those who score highly on them are likely to be:
- Good at adapting to new working environments
- Able to make intelligent and difficult decisions
- Able to apply new knowledge
- Easier to train
- Able to work well under pressure
- Able to quickly shift from one thought process to another
- More capable of abstract and lateral thinking
- Better at planning and organization
What Does a Cognitive Ability Test Measure?
Each cognitive ability test will ask questions on a number of subjects, measuring the ability of candidates in various areas. These are not subjects that require specific knowledge or revision, just a basic understanding – so they test the candidate’s general intelligence.
Verbal Reasoning
Verbal reasoning questions involve a passage of text that may or may not be relevant to the job role you have applied for. You will be asked questions about this passage of text and will need to quickly read, understand and analyze the text to find the relevant answer(s).
The verbal reasoning questions are often multiple-choice format, with a statement that you must decide is either true or false, or that there isn’t enough information to make a decision.
Here the most common verbal reasoning questions you might come across:
- Comprehension – Comprehension questions test your understanding of the text provided. Questions might ask about the argument made in the text.
- Vocabulary – In vocabulary questions, you might be asked to find the definition of a word or provide synonyms and antonyms.
- Analogies – Analogies in verbal tests are looking for the specific relationships between words. They ask candidates to find logical connections.
“In Australia, timber flooring is a popular flooring option, especially in the Queensland area. Timber offers a natural finish to a room that lends itself to both modern and traditional styles, and with the right upkeep (including regular sanding and polishing) it can look as good as new even many years later. However, for many renovators and home builders, the opportunity to purchase timber-look tiles gives even more value for money as they need no maintenance and are easier to use in conjunction with options like underfloor heating and cooling systems. The tiles now offer a level of realism that would have been unimaginable just ten years ago – and this means timber-look tiles are growing in popularity.”
Is the following statement about this passage true, false, or is there not enough information to decide?
'Timber flooring needs no upkeep.'
a) True b) False c) Not enough information
Try a Verbal Reasoning Test
Numerical Reasoning
In the numerical reasoning questions, you will be presented with some numerical data – like a table, graph or problem, and need to read, understand and analyze the information before solving the problem.
You do not need a degree in mathematics for numerical ability tests, just a basic understanding of functions like percentages, fractions and ratios.
- Mathematical word problems – Word problems can seem complicated because of the way they are written, but they usually require an uncomplicated sum that shouldn’t need too much consideration.
- Number series – You might be asked to find a pattern to work out the next number in a series. It might be a missing number in the middle of a pattern, or at the end.
- Basic mathematics – A rudimentary knowledge of math should be sufficient for success in the mathematical questions of the cognitive ability test. In almost all of these tests, you will not be allowed a calculator during the assessment so practicing quick mental arithmetic will help you make the most of your time.
Find the next number in this series:
3 | 16 | 29 | 42 | ……
a) 56 b) 52 c) 55 d) 49
Try a Numerical Reasoning Test
Logical Reasoning
Logical reasoning can be presented in many forms, but each one is testing the same thing – your ability to draw logical conclusions from limited information.
They can be shapes, pictures or word-based, and will often need you to find patterns and rules to make logical decisions.
- Deductions – Deductive questions are often posed in the form of a word problem, detailing a series of stated facts. These can be answered as true/false/cannot say.
- Syllogisms – You may be presented with two statements of truth and need to logically deduce if a third statement is true, given the provided information. There is a major premise and a minor premise, which should lead to a conclusion.
All cats are animals. All animals have teeth. All cats have teeth.
Given the first two statements, is the third statement:
a) True b) False c) Cannot say
It is worth mentioning here that at no point in the cognitive ability test should you bring any outside information in. The questions should be answered based only on the data you are given in the question.
Try a Logical Reasoning Test
Abstract Reasoning
Like other reasoning questions, you are expected to understand and analyze information to answer questions. In abstract reasoning, these are usually shapes or images rather than words or numbers.
- Matrix – Patterns or shapes may be presented in matrices, and you are required to find the missing item in each matrix.
- Next in series – A series of shapes or images are presented, and you need to find the pattern in order to work out what comes next out of the provided multiple-choice answers.
- Odd one out – Several different images or shapes are presented, and you need to choose which one is the odd one out.
Which image is the next in this pattern?
Try an Abstract Reasoning Test
Spatial Awareness
Spatial awareness questions are often used in pre-employment screening assessments for technical roles, and they tend to relate to the manipulation of space and shapes in both 2D and 3D.
Example Spatial Awareness Question
Try a Spatial Awareness Test
Mechanical Reasoning
Mechanical tests allow candidates to demonstrate their knowledge and the application of mechanical concepts and physics like pulleys and gravity, levers and electrical circuits.
These are usually only used in assessments for positions that require some mechanical knowledge, like an engineering position.
How many switches need to be closed to light up one bulb?
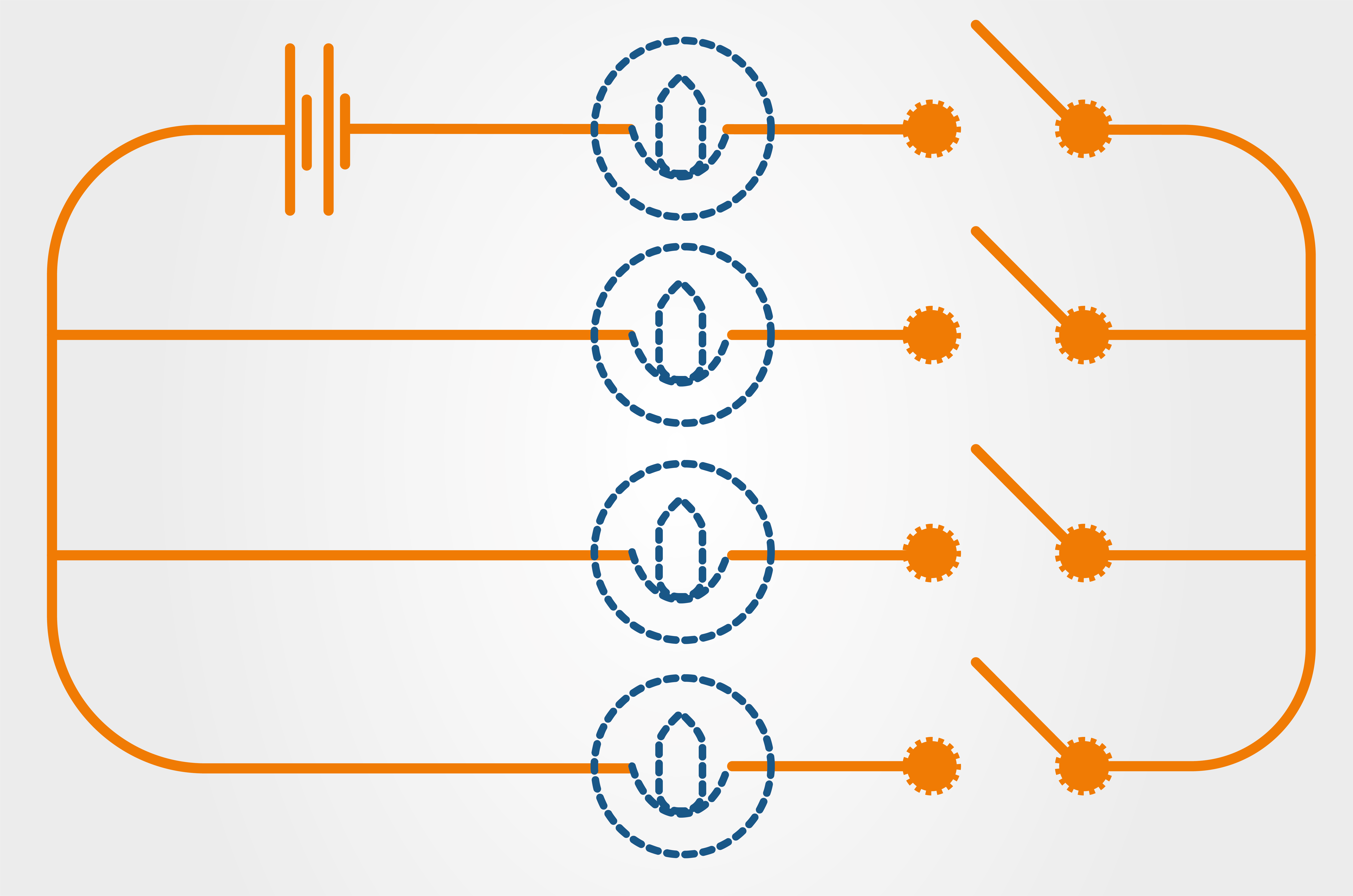
(Source: WikiJob
A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4
Try a Mechanical Reasoning Test
Most cognitive ability tests are administered online and are sent to candidates to be completed at home in their own time. In some cases, you may be required to complete them at an assessment center, or before or after a face-to-face interview at the company.
Cognitive ability tests are usually produced by a test publisher, and although the business may have a bespoke package of pre-employment assessments, it is usually the third-party publisher that administers the tests, collates the results and feeds back to the employer.
This means there is a range of cognitive ability tests that you might take.
Although they share similarities, they will also have notable differences. If you can find out your test publisher, you can familiarize yourself with the structure, time limit and format of the assessment to make your practice sessions more effective.
Although no previous knowledge is needed for a cognitive ability test, it is still important to practice thoroughly and efficiently.
With the often-heavy time pressure in these assessments, familiarity will help you perform well, as will finding the most efficient way to deal with the questions.
Step 1 . Practice
If you can find out the publisher of the test you will be taking, then you can find online practice papers that are the same format, type of questions and timings of the real thing.
Prep packs such as those at JobTestPrep simulate the test that you will take, offering multiple practice papers as well as strategies to help you pass.
Of course, if you cannot find out the publisher through contacting the recruiter or by an online search, then practice papers will help. You can find free online papers and tests for all types of questions, which is especially useful if you know that you have a specific weakness that needs extra work.
Step 2 . Familiarity Is Important
The more familiar you become with the structure, format and timings of the test, the less apprehensive you will feel in the real assessment.
It will help you to know how the questions should be answered and how fast you need to move on from each one.
Step 3 . Practice Under Test Conditions
A recognized pressure in cognitive ability tests is the timing. For almost all test publishers, time constraints mean that you will not have much time to answer each question and you want to make sure that you give yourself the opportunity to answer as many as possible.
If your practice tests are not timed, it might be a good idea to use a stopwatch.
Take the number of questions and work out how much time you can spend on each during your practice – you will probably find that you have much less time than you originally thought.
Make sure that your practice time is spent somewhere quiet where you will not be disturbed. Practice should mimic what the actual test will be like as much as possible to be effective.
Step 4 . Work on Your Weaknesses
As the cognitive ability tests will move from one subject to another throughout the test, you are likely to come across more than one question that will test you on areas where you might not be as strong.
You can (in some assessments) skip questions and come back to them later. However, with the time constraint, it is a safer bet to answer every question to the best of your ability as you go along.
If, during your practice, you realize there are questions that you do need to become faster or stronger on, try and focus your practice on them.
Find solving strategies that allow you to work out the answers quickly, like elimination or targeted reading.
Step 5 . Read Every Question Carefully
Although you might find that the question seems obvious, wasting the opportunity for a correct answer by rushing is never a good idea.
Make sure you read the question carefully so that you understand what it is asking before you try and answer. Don’t allow the time pressure to rush you when you need to consider details.
Step 6 . Don't Apply Outside Knowledge
All the information you need to answer correctly is provided in the question, and that means you need to take what you are presented with as the truth – even if you know differently.
Basic knowledge of language and vocabulary, math and mechanical principles (if necessary) will be enough to give you the tools to answer cognitive ability questions.
How to Improve Cognitive Ability in 2024
There are some steps that you can take to improve your cognitive ability in day-to-day life outside of practicing for a test.
Some of them are simple, basic changes to your outlook and routine that can really make a difference.
Health and Wellbeing
Your body is a biomechanical machine, and as such, it needs the right fuel to perform well. This means that, for best results, focus on what you are putting into your body.
Eat well (and regularly), focusing on oily fish and leafy green vegetables, and make sure you stay hydrated.
Sleep is so important to cognitive ability. It helps to give you energy and improve your memory.
Minimize stress, as cortisol produced by stressful situations can actually impair brain function.
Don’t forget to exercise. Aerobic exercise is great for improving oxygen circulation around the body and to the brain – great for a healthy mind. The endorphins from an exercise session can also help battle stress and aid sleep.
Cultivate a Growth Mindset
Getting into a development phase can be difficult but cultivating a growth mindset can help you believe that you can achieve anything.
Your brain is always developing – that is not something that stops in childhood – so get out of your comfort zone and learn something new. This could be a new language, for example, or a new hobby like playing a musical instrument.
Practice Brain Exercises
Brain exercises don’t need fancy equipment or a gym. You can practice working more with your brain by completing crosswords and sudoku puzzles or playing strategy-based board games.
Reading books will expand your vocabulary and help you think critically about passages of text, and if you need to grow your logic skills, then chess is a great game to play.
Think outside the box and play strategy video games, or write a novel, poetry or song lyrics.
Develop Your Ability to Focus
Focus is a skill that is really important and often overlooked – but if you can hone your focus on the task at hand, you will find that you can work through cognitive ability tests quickly and efficiently without distractions.
However you choose to focus, such as by wearing headphones to shut out extraneous noise, keep practicing. Try and use more senses to increase your understanding – read aloud, make notes or listen to audio clips.
Cognitive ability tests are quick and simple pre-employment assessment tools. They can be used to cut down a potential hiring pool in a way that removes unconscious bias and offers an objective snapshot of the general intelligence of the candidate.
Although tests vary according to publisher and industry, they all cover a number of subjects in a short space of time, needing fast reactions and quick calculations to be successful.
Although they do not need any specific knowledge, it is always a good idea to thoroughly practice before a cognitive ability test so that you are familiar with the layout and to ensure that you have efficient strategies for answering questions.
Cognitive ability tests are not the only way a candidate’s suitability for a role is assessed, but good performance in them will help to show you are a good fit.
You might also be interested in these other Psychometric Success articles:

Or explore the Aptitude Tests / Test Types sections.
Outdated browser detected
We recommend upgrading to a modern browser.
If you choose to continue with your current browser we cannot guarantee your experience.
Latest browser options
- Practice Tests
- English (Global)
- English (India)
- English (Middle East & North Africa)
- English (South Africa)
SHL Cognitive Assessments
Measure potential to learn, adapt, and perform in any role with shl verify interactive cognitive assessments ..
Speak With Our Team
SHL Insights
2500+ clients use our cognitive assessments as part of their talent acquisition strategies.
Understand candidates’ learning potential and adaptability..
- SHL combines interactive numerical, deductive reasoning, and reasoning ability assessments with data gathered from decades of global experience.
- Gain insight into each candidate’s ability to learn—and, combined with behavioral assessments, their willingness to try.
Quickly and accurately assess candidates at scale.
- SHL’s cognitive assessments are automated, remotely proctored, and ask fewer questions thanks to our unique partial-scoring methodology.
- Assess high candidate volumes faster and more reliably, so your teams can make confident, efficient hiring decisions.
Provide all candidates with truly engaging experiences.
- Our immersive assessments upgrade button clicking with “drag-and-drop" and gamified interactions without compromising professional assessment standards.
- This helps your teams keep applicants engaged, while meeting their expectation of being taken seriously with job-relevant, real-world tasks.
Understand candidate learning potential before making hiring decisions.
Shl's cognitive assessments.
Our pre-employment cognitive assessment starts by asking candidates a series of interactive questions organized around a central principle linked to something they are likely to encounter in the role.
Verify G+ Test
Measures general mental ability , or G, and effectively measures candidates’ problem-solving and critical reasoning capabilities.
SHL Verify Deductive Reasoning
Measures candidates’ ability to draw logical conclusions and complete scenarios based on the information provided. Tasks include reading statements, then determining which subsequent options cannot be true or must be true.
SHL Verify Interactive – Inductive Reasoning
Measures candidates’ ability to draw inferences from, and understand relationships between, various concepts. Tasks include working out the pattern in a set of images and identifying the correct next image.
SHL Verify Interactive – Numerical Reasoning
Measures candidates’ ability to work with numbers and use appropriate mathematics in different situations. Tasks include solving word problems, performing numerical calculations, and interpreting charts and graphs.
Our Assessment Science
SHL's Verify Interactive delivers precise scores indicating candidates' cognitive ability. These scores, along with other SHL talent acquisition data such as behavior and personality assessments, culminate in a well-rounded job score for each candidate. SHL's cognitive assessments aim to empower your teams to make fair and efficient talent choices, leading to business success.
Hear from Our Customers

SHL is helping us to find top talent to create and manage the professional, motivated, and resilient teams we need to deliver excellent customer service. We use SHL assessments to match the competency profiles of our managers and specialists with business needs and thereby focus our development activities.
Head of Recruiting and HR Development
Brüder Schlau
Power Your People’s Journey with SHL Talent Solutions.

Graduate Hiring
Strengthen your workforce by converting diverse, top-quality graduates with meaningful hiring experiences, fair assessment tools and unrivalled science.

Technology Hiring
Reboot your technology hiring process to draw in top-quality developers through immersive experiences and AI-powered virtual hiring tools.

Competency Fit
Boost the performance of your people with detailed workforce analytics that identify specific opportunities to develop their capability and potential.

SHL Mobilize
Drive smarter talent mobility, succession planning, HIPO identification, and workforce development decisions with actionable talent insights.
Explore SHL’s Wide Range of Solutions
With our platform of pre-configured talent acquisition and talent management solutions, maximize the potential of your company’s greatest asset—your people.
See Our Solutions
About Cookies on this site
This site uses Cookies to improve your online experience. By continuing to use this site without changing your cookie preferences we will assume that you are agreeing to our use of cookies. For more information, or to change your cookie preferences, visit our cookie policy .
CogniFit - Brain Training
Sign up on here if you don't have your mobile handy
You are going to create a patient management account. This account is designed to give your patients access to CogniFit evaluations and training.
You are going to create a research account. This account is specially designed to help researchers with their studies in the cognitive areas.
You are going to create a student management account. This account is designed to give your students access to CogniFit evaluations and training.
You are going to create a family account. This account is designed to give your family members access to CogniFit evaluations and training.
You are going to create a company management account. This account is designed to give your employees access to CogniFit evaluations and training.
For personal use
I'm a health professional
For my family
I'm an educator
I'm a researcher
Employee Wellbeing
You are going to create a personal account. This type of account is specially designed to help you evaluate and train your cognitive skills.
You are going to create a developer account. This account is designed to integrate CogniFit’s products within your company.
For users 16 years and older. Children under 16 can use CogniFit with a parent on one of the family platforms.
Send assessments and training programs to patients
Send assessments and training programs to students
Send assessments and training programs to your children or other family members.
Send assessments and training programs to research participants.
By clicking Sign Up or using CogniFit, you are indicating that you have read, understood, and agree to CogniFit's Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policy .
Scan the below QR with your phone to register through our mobile app for the ultimate convenience and access on-the-go!

If you don't have your mobile handy sign up on here
Download our app to enjoy a good experience on this device

Cognitive Assessment
Digital assessments validated for scientific accuracy and optimized for operational efficiency.
2,545,080 unique test-takers
4,821 professionals
Discover the ultimate cognitive testing revolution: our state-of-the-art digital self-administered assessment, available for both in-clinic and at-home use. Say hello to a new era of convenience, accuracy, and flexibility in cognitive testing.
With our groundbreaking digital cognitive testing tool, you have the power to assess and monitor cognitive functions like never before. Whether you prefer the comfort of your own home or the convenience of an in-clinic setting, our tool adapts to your needs, providing a seamless and user-friendly experience.
Experience the freedom to take control of your cognitive assessments with our self-administered feature. No more scheduling appointments or relying on external assistance. Our tool empowers you to evaluate your cognitive abilities independently, at your own pace, and in the comfort of your preferred environment.
Whether you're a healthcare professional, a researcher, or an individual seeking cognitive insights, our digital tool offers unparalleled accuracy and reliability. Rest assured that your cognitive assessments are conducted with scientific rigor, ensuring precise and meaningful results.
Embrace the future of cognitive testing and unlock a new level of convenience and accessibility. Experience the ease of in-clinic or at-home assessments with our cutting-edge digital tool, designed to empower you on your cognitive journey. Discover a world of possibilities and gain invaluable insights into your cognitive health like never before.
Each CogniFit cognitive assessment battery is intended for use as a cognitive assessment aid to determine the level of cognitive functioning. It is intended to be used as an aid for physicians to design and monitor each patient's intervention and cognitive rehabilitation process.*
Assessments available
General Cognitive Assessment (CAB) The General Cognitive Assessment is a complete battery made up of neuropsychological tests that were designed to assess the cognitive profile of users with and without pathologies. It allows the user to identify possible cognitive deficits and detect possible cognitive deterioration. The assessment is made up of 17 tasks that measure a total of 22 cognitive skills, which are the following: Working memory, Short-term memory, Naming, Non-verbal memory, Visual short-term memory, Phonological short-term memory, Contextual memory, Divided attention, Focus attention, Inhibition, Updating, Spatial perception, Recognition, Visual scanning, Visual perception, Auditory perception, Estimation, Hand-eye coordination, Response time, Processing speed, Planning, and Shifting.
The general cognitive assessment provides you with a full assessment of a large number of cognitive skills such as your short-term memory, your hand-eye coordination, your focus and planning. In total, more than 15 cognitive skills are measured by the general cognitive assessment.
By completing your full cognitive assessment, you will gain different insights about your cognition and will understand what are your stronger skills and which ones could need some training.
65 and Over Cognitive Assessment (CAB-AG) COGNIFIT_PRODUCT_DESCRIPTION_Over55 Assessment
The 65 and Over Cognitive Assessment (CAB-AG) provides you with a precise assessment of relevant cognitive skills, such as your visual short-term memory, your hand-eye coordination, your divided attention and shifting. In total 7 cognitive skills are measured by this cognitive assessment.
By completing your cognitive assessment, you will gain different insights about your cognition and will understand what are your stronger skills and which ones could need some training.
Academic Cognitive Assessment (CAB K-12)
Every child is unique, with their own set of abilities and challenges. We've developed a specialized Cognitive Assessment tailored for K-12 students, designed to understand and enhance every child's cognitive abilities to pave the way for academic success and overall well-being.
Concentration Cognitive Assessment (CAB-AT) COGNIFIT_PRODUCT_DESCRIPTION_Concentration Assessment
The Concentration Cognitive Assessment (CAB-AT) provides you with a precise assessment of relevant cognitive skills, such as focus attention, inhibition and updating. In total 4 cognitive skills are measured by the concentration cognitive assessment.
By completing the cognitive assessment, you will gain different insights about your cognition and will understand what are your stronger skills and which ones could need some training.
Coordination Cognitive Assessment (CAB-CO) COGNIFIT_PRODUCT_DESCRIPTION_Coordination Assessment
The Coordination Cognitive Assessment (CAB-CO) provides you with a precise assessment of relevant cognitive skills, such as inhibition, hand-eye coordination and processing speed. In total 4 cognitive skills are measured by the coordination cognitive assessment.
Driving Cognitive Assessment (DAB) The Driving Cognitive Assessment (DAB) from CogniFit is a set of cognitive tests prepared to assess the user's driving abilities. It measures a total of 10 cognitive abilities throughout 12 tasks. The cognitive skills that the Driving Assessment Battery measures are: Visual short-term memory, Divided attention, Focus, Inhibition, Width of field-of-view, Visual scanning, Estimation, Hand-eye coordination, Response time, and Shifting.
The Cognitive Driving Assessment provides you with an assessment of a large number of cognitive skills which you use when driving. In total, more than 10 cognitive skills are measured such as the ability to estimate distances, focus, shifting, visual scanning, and response time.
By completing your driving assessment, you will gain important insights about your cognition and will understand what are your stronger skills while driving and which ones may benefit from additional training.
Memory Cognitive Assessment (CAB-ME) COGNIFIT_PRODUCT_DESCRIPTION_Memory Assessment
The Memory Cognitive Assessment (CAB-ME) provides you with a precise assessment of relevant cognitive skills, such as your short-term memory, working memory, naming and recognition. In total, more than 5 cognitive skills are measured by the memory cognitive assessment.
Perception Cognitive Assessment (CAB-PC) COGNIFIT_PRODUCT_DESCRIPTION_Perception Assessment
The Perception Cognitive Assessment (CAB-PC) provides you with a precise assessment of relevant cognitive skills, such as your visual perception, estimation and recognition. In total, more than 5 cognitive skills are measured by the perception cognitive assessment.
Reading Comprehension Cognitive Assessment (CAB-RC) COGNIFIT_PRODUCT_DESCRIPTION_Mentalarithmetic Assessment
The Reading Comprehension Cognitive Assessment (CAB-RC) provides you with an assessment of the following cognitive skills: working memory, phonological short-term memory, and visual short-term memory.
Reasoning Cognitive Assessment (CAB-RS) COGNIFIT_PRODUCT_DESCRIPTION_Reasoning Assessment
The Reasoning Cognitive Assessment (CAB-RS) provides you with a precise assessment of relevant cognitive skills, such as your working memory, your processing speed, updating and planning. In total, more than 5 cognitive skills are measured by the reasoning cognitive assessment.
Useful Field of View Test
This test was inspired by the Useful Field of Vision test (UFOV) and on other neuropsychological batteries that measure field of view. This test assesses the amount of visual information that one receives when looking at a single point. This makes it possible to precisely measure field of view.
Trail Making Test (TMT)
The CogniFit's Trail Making Test (TMT) is a digitized replica of the task of the same name (Reitan, 1955; Reitan, 1958). This task tests processing speed, shifting, the ability to make an effective visual scan, as well as other underlying executive functions.
Eriksen's Flanker Test
The CogniFit's Eriksen's Flanker Test is a digitized replica of the task of the same name (Eriksen and Eriksen, 1974). This task seeks to measure how much interference is generated by the presentation of adjacent incongruent and irrelevant visual information.
The CogniFit's Simon Test is a digitized replica of the task of the same name (Simon and Wolf, 1963). The performance of the task will allow identifying the difference between the reaction time between incongruent and congruent trials that have been answered correctly, which is known as the Simon Effect.
Deary-Liewald Test
The Deary-Liewald CogniFit Test is a digitized replica of the Deary-Liewald task (Deary et al., 2010). The performance of the task will allow measuring the user's reaction time in simple situations (a single button response) and in more complex situations (four alternative responses).
Tower of Hanoi Test
The CogniFit's Tower of Hanoi Test (TOH) is a digitized replica of the task of the same name (Hinz, 1989). This task seeks to measure high-order cognitive problem solving and learning of complex cognitive procedures, providing information about the cognitive abilities mainly related to executive functions such as planning, visual imagery, abstract thinking, working memory and self-monitoring.
Inhibition of Return Test
The CogniFit inhibition of return (IOR) test is a digitized replica of the homonymous task (Posner & Cohen, 1984). This task allows the assessment of the phenomenon known as "inhibition of return", which consists of people responding more slowly to stimuli located in the position where at least 300 milliseconds before a task-irrelevant stimulus was shown.
Visual Episodic Memory Test MemTrax
The CogniFit Visual Episodic Memory Test is a version of the Memtrax memory assessment task (Ashford, 2005). This task seeks to measure episodic memory through items of a visual nature, identifying only whether the displayed image has been previously displayed or not.
Progressive Matrices Test
The CogniFit Progressive Matrices Test (PM) is based on the Raven's Standard Progressive Matrices Test (RSPM; Raven, 1936; Raven, 1938). This task allows for the assessment of abstract reasoning, which is an elementary component of intelligence.
Selective Attention Test
The CogniFit Selective Attention Test is based on the classic d2 Test (Brickenkamp, 1962). This task is specifically aimed at measuring the user's selective attention.
Sustained Attention to Response Test
The CogniFit Sustained Attention Response Test is based on the classic task of the same name (SART; Robertson et al., 1977). This task is specifically aimed at measuring the user's sustained attention.
Tapping Test
The Speed Test REST-HECOOR exercise was inspired by the classic test of Fingertip tapping from the assessment battery NEPSY (Korkman et al., 1998). The test-taker is required to keep on clicking for 10 seconds and as rapidly as possible with the mouse, or finger if using a touch-screen device, in a defined area on the screen. Data is collected as the number of clicks during the allocated time, number of clicks inside the defined area and number of clicks outside it.
Psychomotor Vigilance Test
The Resolution Test REST-SPER was inspired by the classic paradigms Go/No Go Task (Gordon & Caramazza, 1982), Continuous Performance Test (Conners, 1989; Epstein et al., 2001), and the Psychomotor Vigilance Task (Dinges & Powell, 1985). The test-taker is required to rapidly press on circles which appear on the screen and to ignore hexagons should they also appear. Embedded in the task are 16 circles-only items and 8 circles-and-hexagons items. For each item data is collected on response time, response accuracy and cursor distance from target center.
Visual Search Test
The Exploration Test SCAVI-REST was inspired by the Hooper Visual Organization Task (VOT) test by Hooper (1983). This cognitive assessment is responsible for measuring visual scanning and response time in order to find a stimulus that is surrounded by other, less important stimuli. Initially, it requires an investigation of the context on a general level, in order to later perform a more specific scan.
Stop-Signal Test
The Inattention Test FOCU-SHIF is based on the classic Conners (CPT) test. The user will have to react quickly to the changing colors, which makes it possible to assess inhibition, shifting, and focused attention.
Visual Organization Test
The CogniFit Visual Organization Test is based on Hooper's classic task of the same name (VOT; Hooper, 1983; Merten, 2004). This task is specifically aimed at measuring the user's visual organization and visual perception.
CogniFit's IQbe test is based on the Raven's Standard Progressive Matrices test (RSPM; Raven, 1936; Raven, 1938). This task assesses abstract reasoning in a manipulative manner in a 3D environment and provides an estimate of the manipulative-executive intelligence quotient (IQ). This score is validated for men and women between 18 and 55 years of age.
Ace Detector Test
The CogniFit Ace Detector Test is composed of a set of four CogniFit tasks that have been modified to be shorter and more demanding: Tapping Test (Halstead, 1947), Visual Search Test (Treisman & Gelade, 1980), Selective Attention Test (Brickenkamp, 1962), Sustained Attention to Response Test (Robertson et al., 1997). The purpose of this task is to quickly identify the most cognitively sharp and active elite players, particularly in bench sports environments.
Verbal Fluency Test
The CogniFit Verbal Fluency Test is a digitized replica of the classic F-A-S task (Spreen & Benton, 1977). This task will allow to know the user's verbal fluency, i.e. the ability to evoke valid and distinct exemplars of a particular category. This task requires a device with a microphone and permissions to use it.
Vocabulary Test
The CogniFit Vocabulary Test is a digitized reinterpretation of the classic Boston Naming Test (Kaplan et al., 1983) and by the vocabulary test from the WAIS-III (Wechsler, 1997). This task will allow us to know the user's level of vocabulary and naming, i.e. the ability to access the person's verbal lexicon.
Reading Test
The CogniFit Reading Test is based on classic reading comprehension tests, such as the Woodcock Reading Mastery Test (Woodcock, 2011). This task seeks to measure the user's speed, accuracy, and reading comprehension through reading a text aloud and the answers given to a series of questions about the read text.
Verbal Description Test
The CogniFit Verbal Description Test is based on the cookie theft image description task from the Boston Diagnostic Aphasia Examination (BDAE; Goodglass & Kaplan, 1972). To complete this activity it will be necessary to pay visual attention to all the things that happen or are shown in the image, understand them and name them out loud.
Auditory Comprehension Test
The CogniFit Auditory Comprehension Test is based on the Sentence Comprehension Test, included in the Verb and Sentence Test (VAST; Bastiaanse et al., 2003). This task provides an assessment of the user's ability to understand a series of auditory descriptions and to identify the visual representation of each description among a series of three images.
Face Working Memory Span Test
Face Working Memory Span Test is a version of the Corsi Cubes Test (Corsi, 1972; Kessels et al., 2000; Wechsler, 1945) to which visual information (faces) and verbal information (Names). The objective of this task is to assess the span of working memory using stimuli similar to those that people handle in their daily lives.
Number-Size Congruency Test
The Processing Test REST-INH was inspired by the classic Stroop test (Stroop, 1935). The test-taker is required to press on the larger of two circles, regardless of the number inscribed in each circle, while ignoring the text that could appear on the top-middle part of the screen. They are then required to press on the higher number regardless of the size of the circle in which the number is inscribed.
Digit Span Test
The Sequencing Test WOM-ASM is based on the classic direct and indirect digit test of the WAIS-III (Wechsler, 1997). The test-taker is required to remember and reproduce increasingly longer number sequences, which appear, each in its turn, on the screen. The task will begin with a two- -number sequence.
Time Estimation Test
The Estimation Test EST-II is based on the Duration Pattern Test (DPT) (Frota & Pereira, 2003). The test-taker is asked to interrupt an ongoing auditory stimulus so as to reproduce the exact length of time of the previously presented one. In the first part of the task an animated drawing accompanies the stimulus. During the second part of the task, the drawing remains still.
Eye-Hand Coordination Test Fixed Trajectory and Predictable Direction
The Synchronization Test UPDA-SHIF is based on the Vienna Test System (VST) (Whiteside, 2002). In this task the test-taker is required to carefully and precisely track a ball which moves along a path. The distance in pixels between the center of the ball and the cursor moved by the user is considered to calculate the accuracy score.
The Programming Test VIPER-PLAN took as a reference the classic Porteus Maze Test (Porteus, 1950), and the Route finding (NEPSY) (Korkman et al., 1998). The test-taker is presented with several mazes with dead-ends and is required to successfully go through it, from start to end, in the smallest possible number of steps, and as fast as possible.
Visual Memory Test
The Recognition Test WOM-REST is based on the classic tests of Symbol search (WAIS) (Wechsler, 1997), Wisconsin Card Sorting Test (WCST) (Heaton, 1981) and Raven's Progressive Matrices Test (Raven, 1936). In this task, a trio-sequence of objects is presented in the center of the screen. The test-taker is required to memorize these stimuli in a first screen, and to recognize it from among four trio-sequences in a second screen. The number of correct answers is considered to calculate an accuracy percentage.
Stroop Test
The Equivalencies Test INH-REST was based on the classic Stroop test (Stroop, 1935). The test-taker is asked to press on the spacebar (go action) only if the color names on the screen are printed in the matching color and to refrain from pressing (no-go) if the color of the letters does not match the printed color name.
Eye-Hand Coordination Test Multidirectional and Unpredictable Direction
The Coordination Test HECOOR was inspired by the classic Trail Making Test (Reitan, 1955), and by the Vienna Test System (Whiteside, 2002). The test-taker is required to track, with the mouse (or on-screen digital joystick, if using a mobile device), a ball moving in an undetermined itinerary.
Visual Working Memory Span Test
The Concentration Test VISMEM-PLAN took as a reference the Corsi block-tapping test (Corsi, 1972; Kessels et al., 2000; Wechsler, 1945). In the first part of the task, some circles, within a fixed array of circles, light up. The test-taker is required to memorize which circles, within the array, have lit up and then try to reproduce the sequence in the right order. In the second part of the task, a delay of 4 secs is added between the first screen and the playback screen, in order to increase the time the user must retain the information.
Naming Test
The Decoding Test VIPER-NAM was inspired by the Boston Naming Test (Kaplan et al., 1983) and by the vocabulary test from the WAIS-III (Wechsler, 1997). The test-taker is required to click on the first letter, among four of them, that spells the name of the object depicted on the screen. For example, for the picture of an apple, the test-taker should click on the letter “A” but not on the three incorrect responses (C, P, M) also present on the screen.
Multimodal Lexical Memory Test
The Identification Test COM-NAM is based on the Boston Naming Test (Kaplan et al., 1983) and by the vocabulary test from the WAIS-III (Wechsler, 1997). For each object shown, the test-taker must choose from three possibilities: 1) the item is presented for the first time in the task or 2) the last time it appeared the item was spoken or 3) the last time it appeared the item was presented as a picture.
Lexical Memory Test
The Inquiry Test REST-COM took as a reference the classic Boston Naming Test (Kaplan et al., 1983), the vocabulary test from WAIS-III (Wechsler, 1997), the Test of Variables of Attention (Greenberg et al., 1996), and the Rey Auditory Verbal Learning Test (Schmidt, 1994). A series of objects are shown. In a new series of objects, the test-taker must then recognize only those objects that were previously displayed. This new series could be presented as images or as spoken words.
Speed Estimation Test
The Estimation Test EST-I was inspired by the Biber Cognitive Estimation Test (Goldstein et al., 1996). In the first part, the test-taker is required to determine which of two balls moves faster. In the second part, another ball is added. In the third part, a fourth ball is added and it should be indicated which ball moves twice as fast as a designated ball (the red one). In the fourth part, while watching four balls moving in four separate itineraries, the test- -taker must determine as quickly as possible which ball will arrive at a given point first.
Distance Estimation Test
The Estimation Test EST- III is based on the Biber Cognitive Estimation Test (Goldstein et al., 1996). The first part consists of indicating which of the objects on the screen is farther away from the user. The second part consists of indicating which of the objects is farther away from a pink ball, also located on the screen. The third part consists of indicating which two objects are at the same distance from the pink ball. The fourth part consists of indicating which object is not at the same distance from the pink ball. Finally, the fifth part is to indicate which of the images has the objects spatially arranged differently from the model.
Divided Attention Test
The Simultaneity Test DIAT-SHIF stems from the classic Stroop test (Stroop, 1935), the Vienna Test System (Whiteside, 2002), and the Test of Variables of Attention (Greenberg et al., 1996). The test-taker is required to accurately follow a ball moving and turning in all directions on the screen while, at the same time, performing a variant of the Stroop test.
CogniFit App
Brain Science
- The Human Brain
- Brain and Mind
- Parts of the Brain
- Brain Plasticity
- Brain Fitness
- Memory Loss
- Intellectual Disabilities
- Brain Functions
- Executive Functions
- Coordination
- Digital Therapeutics Validation
- Computer Games
- Healthy Older Adults Trial
- Navy Pilots
- Senior Wellness
- Healthy Seniors
- Senior Cognitive Training
- Cognitive state in adults
- Systematic review
- SG4D taxonomy
- Brain Games
- Chess Online
- Mini Crossword
- Fruit Frenzy
- Crystal Miner
- Robo Factory
- Treasure Island
- Neon Lights
- Drive me crazy
- Visual Crossword
- Space Rescue
- Math Madness
- Marble Race
- Melodic Tennis
- Find Your Pet
- Melody Mayhem
- 3D Art Puzzle
- Happy Hopper
- Candy Line Up
- Penguin Explorer
- Bee Balloon
- Cube Foundry
- Fresh Squeeze
- Minus Malus
- Mouse Challenge
- Perfect Tension
- Slice and Drop
- Water Lilies
- Reaction Field
- Words Birds
- See More Games...
- For Families
- For Clinicians
- For Researchers
- Babybright®
- Exercises for Children
- Cognitive Development
- Brain Exercise
- Individualized Training System
- Cognitive Stimulation Therapy
- Mind Exercises
- Personalized Brain Training
- Mental Exercise
- Online Memory Games
- Cool Math Games
- Brain Battles
* Every CogniFit cognitive assessment is intended as an aid for assessing cognitive wellbeing of an individual. In a clinical setting, the CogniFit results (when interpreted by a qualified healthcare provider), may be used as an aid in determining whether further cognitive evaluation is needed. CogniFit’s brain trainings are designed to promote/encourage the general state of cognitive health. CogniFit does not offer any medical diagnosis or treatment of any medical disease or condition. CogniFit products may also be used for research purposes for any range of cognitive related assessments. If used for research purposes, all use of the product must be in compliance with appropriate human subjects' procedures as they exist within the researchers' institution and will be the researcher's obligation. All such human subject protections shall be under the provisions of all applicable sections of the Code of Federal Regulations.
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
- Management Team
- CogniFit Newsroom
- Become an Affiliate
Please type your email address
- Brain Development
- Childhood & Adolescence
- Diet & Lifestyle
- Emotions, Stress & Anxiety
- Learning & Memory
- Thinking & Awareness
- Alzheimer's & Dementia
- Childhood Disorders
- Immune System Disorders
- Mental Health
- Neurodegenerative Disorders
- Infectious Disease
- Neurological Disorders A-Z
- Body Systems
- Cells & Circuits
- Genes & Molecules
- The Arts & the Brain
- Law, Economics & Ethics
- Neuroscience in the News
- Supporting Research
- Tech & the Brain
- Animals in Research
- BRAIN Initiative
- Meet the Researcher
- Neuro-technologies
- Tools & Techniques
- Core Concepts
- For Educators
- Ask an Expert
- The Brain Facts Book

Test Your Problem-Solving Skills
Personalize your emails.
Personalize your monthly updates from BrainFacts.org by choosing the topics that you care about most!
Find a Neuroscientist
Engage local scientists to educate your community about the brain.
Image of the Week
Check out the Image of the Week Archive.

SUPPORTING PARTNERS
- Privacy Policy
- Accessibility Policy
- Terms and Conditions
- Manage Cookies
Some pages on this website provide links that require Adobe Reader to view.

- Critical thinking
- Problem solving skills
- Verbal knowledge
- Ability to learn new information
Recommended for:
- Any mid- to high-level jobs that require problem solving and attention to detail.
Test Description
Cognify® is an award-winning game-based assessment that measures cognitive aptitude, one of the best predictors of job success. By combining innovative game design with proven cognitive assessment methods, Cognify emphasizes a world-class candidate experience that delivers rich insights about each applicant. The assessment features three highly engaging and interactive games that measure a candidate’s ability to solve problems, work with numbers, and correctly interpret and edit written text.
Candidates can take Cognify on any device, and the assessment takes just 10 minutes to complete, plus tutorials.
Score Reports
Each candidate is given a percentile ranking to demonstrate how the individual scored in relation to others who have taken the test. An overall percentile is provided, along with percentiles for the three categories of problem solving, numerical reasoning, and verbal knowledge.
Engaging the Candidate
Cognify combines rigorous validation and assessment science with an emphasis on an engaging, brand-positive candidate experience. Game-based assessments, unlike traditional assessments, take more into account than just the correct answer, providing richer insight into a candidate’s strengths and abilities. The fun and immersive games engage candidates and cultivate a positive image for your employer brand.
Award-Winning Game Design
An independent judging panel of I/O psychologists awarded Cognify a Workplace Excellence Award in 2018. And in 2016, Cognify won the Serious Games Showcase and Challenge.

Validity Information
Cognify has been extensively validated, demonstrating that the test is highly predictive of job performance for a wide variety of jobs. Cognify has also been independently validated by two major studies, one conducted by a multinational tech company, and another by globally recognized psychologist Dr. Richard Landers.
A six-game version is also available on request.
Languages Offered:
- English (US) - Default
- For more languages, visit UCognify , the language-independent version of Cognify
Learn About Pricing
More about the TestGorilla Problem Solving test
Discover the science behind this test and check out the recommended tests you may find useful alongside it in an assessment.
Scroll down for the latest validity study and suggested additional tests.
Back to the Problem Solving test page
Available languages: English, Dutch, French, German, Spanish, Portuguese (Brazil), Japanese, Italian, Swedish, Danish, Norwegian, and Polish

Test type:
Cognitive ability
Administration time:
Difficulty level:
Intermediate
Number of questions:
12 questions per test, 97 in the test bank

Scoring benchmarks
Benchmarks are available for various education levels (ranging from some high school education to Master’s degree or higher), business functions (from administrative to software development), and seniority levels (junior to senior).
Psychometric properties of the Problem Solving test
The metrics reported below are based on a sample size (N) of at least 1,000 candidates unless indicated otherwise.
Reliability: Cronbach’s alpha coefficient = .72
Face validity: Candidates rated this test as accurately measuring their skills (average score of 3.88 out of 5.00).
Criterion-related validity: Candidates with higher scores on this test received higher average ratings from the hiring team during the selection process (r = .30).
For an in-depth look at interpreting test results, please take a look at our Science series articles: How to interpret test fact sheets (part 1): Reliability , and How to interpret test fact sheets (part 2): Validity.
For an explanation of the various terms, please refer to our Science glossary .
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
Reliability | ✔ | ✔ | Acceptable |
Content validity | ✔ | ✔ | Acceptable |
Face validity | ✔ | ✔ | Acceptable |
Construct validity | ✔ | ✔ | Acceptable |
Criterion-related validity | ✔ | ✔ | Acceptable |
| |||
Age differences | Pending | Pending | Pending |
Gender differences | ✔ | ✔ | Acceptable |
Ethnicity differences | Pending | Pending | Pending |
Use these tests with the Problem Solving test
We believe that multi-measure testing is essential in a holistic hiring process because it examines the candidate as a whole, including technical skills, soft skills, and personality. Below are some tests we recommend using alongside the Problem Solving test.
Attention to Detail (Textual)
Understanding instructions, big 5 (ocean).

Use TestGorilla to discover top candidates
Unlock the power of successful hiring! Streamline your hiring process, make informed decisions, and build a team that drives success. Begin your journey to a stronger team – use our Problem Solving test in your assessment and find your future top performers.
An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- A–Z Index
- Operating Status

Resources For
- New / Prospective Employees
- Federal Employees
- HR Professionals
Cognitive Ability Tests
Table of contents.
- Assessment Method Considerations
- Accomplishment Records
- Assessment Centers
- Cognitive Ability
- Emotional Intelligence
- Integrity/Honesty Tests
- Job Knowledge Tests
- Personality Tests
- Reference Checking
- Situational Judgment Test
- Structured Interviews
- Training and Experience
- Work Samples
Related Methods
- Background Evaluation/Investigation
- Job Fit Measures
- Physical Ability Tests
- Realistic Job Previews
Related Information
- See an example of a cognitive ability test item.
Cognitive ability tests assess abilities involved in thinking (e.g., reasoning, perception, memory, verbal and mathematical ability, and problem solving). Such tests pose questions designed to estimate applicants' potential to use mental processes to solve work-related problems or to acquire new job knowledge.
Traditionally, the general trait measured by cognitive ability tests is called "intelligence" or "general mental ability." However, an intelligence test often includes various item types which measure different and more specific mental factors often referred to as "specific mental abilities." Examples of such items include arithmetic computations, verbal analogies, reading comprehension, number series completion, and spatial relations (i.e., visualizing objects in three-dimensional space).
Some cognitive ability tests sum up the correct answers to all of the items to obtain an overall score that represents a measure of general mental ability. If an individual score is computed for each of the specific types of abilities (e.g., numeric, verbal, reasoning), then the resulting scores represent measures of the specific mental abilities.
Traditional cognitive tests are well-standardized, contain items reliably scored, and can be administered to large groups of people at one time. Examples of item formats include multiple choice, sentence completion, short answer, or true-false. Many professionally developed cognitive tests are available commercially and may be considered when there is no significant need to develop a test that refers specifically to the particular job or organization.
Considerations
- Validity - Tests of general cognitive ability are good predictors of job performance and training success for a wide variety of jobs (i.e., they have a high degree of criterion-related validity ); The more complex the job or training demands, the better these tests work; Other predictors may add only small amounts of incremental validity over cognitive tests
- Face Validity/Applicant Reactions - Tests developed to refer explicitly to specific jobs or types of jobs within the hiring organization may be viewed as more highly related to the job (i.e., high face validity) than commercially developed tests
- Administration Method - Can be administered via paper and pencil or electronically
- Subgroup Differences - Cognitive ability tests typically produce racial and ethnic differences larger than other valid predictors of job performance such as biodata , personality tests , and structured interviews ; The use of other assessment methods (e.g., interviews, biodata instruments) in combination with cognitive ability tests is recommended to lower any potential adverse impact
- Development Costs - Cost of purchasing a cognitive test is typically less expensive than developing a customized test
- Administration Costs - Generally inexpensive, requires few resources for administration, and does not require skilled administrators
- Utility/ROI - High return on investment if you need applicants who possess particular cognitive abilities or have high potential to acquire job knowledge or benefit from training; Cost effectiveness of developing own test over purchasing a commercial test is lower when face validity is not an issue
- Common Uses - Best used for jobs requiring particular cognitive abilities for effective job performance and for more complex jobs
(See Section VI for a summary of each article)
Hunter, J. E. (1986). Cognitive ability, cognitive aptitude, job knowledge, and job performance. Journal of Vocational Behavior, 29 (3), 340-362.
Murphy, K. R., Cronin, B. E., & Tam, A. P. (2003). Controversy and consensus regarding the use of cognitive ability testing in organizations. Journal of Applied Psychology, 88 (4), 660-671.
Outtz, J. L. (2002). The role of cognitive ability tests in employment selection. Human Performance, 15 (1-2), 161-172.
Ree, M. J., Earles, J. A., & Teachout, M. S. (1994). Predicting job performance: Not much more than g. Journal of Applied Psychology, 79 (4), 518-524.
Schmidt, F. L., & Hunter, J. (2004). General mental ability in the world of work: Occupational attainment and job performance. Journal of Personality & Social Psychology, 86 (1), 162-173.
The Society for Industrial and Organizational Psychology (SIOP) website contains information on Cognitive Ability Tests.
Back to Top

Cognitive Ability Tests - Guide & Tips
Cognitive ability tests are assessments designed to measure a person's mental capabilities, such as their aptitude or speed of cognition. These tests evaluate an individual's capacity for problem-solving, critical thinking, and information processing.
One important aspect of cognitive ability tests is their ability to measure an individual's fluid intelligence. Fluid intelligence refers to a person's ability to solve novel problems, think abstractly, and adapt to new situations. Assessing fluid intelligence is important for individuals as it can help them identify their strengths and weaknesses and make informed decisions about their career and personal development. For organisations, measuring fluid intelligence can aid in selecting the most qualified candidates and predicting job performance. In this guide, we will explore the different types of cognitive ability tests and their applications in various settings
What is a cognitive ability test?
A cognitive ability test is an assessment that measures an individual's mental capabilities and potential. These tests evaluate a person's intelligence, problem-solving skills, and decision-making abilities. They provide insights into how individuals process and use information, make decisions, and solve problems.
Cognitive ability tests typically comprise different types of tests, including numerical reasoning tests that assess a person's ability to work with numbers and mathematical concepts. Verbal reasoning tests measure a person's ability to understand and use language. Logical reasoning tests evaluate a person's capacity to analyse information and draw conclusions based on it. Mechanical reasoning tests measure an individual's ability to understand and solve mechanical problems. Finally, spatial awareness tests assess a person's ability to visualise objects and manipulate them in space.
Numerical reasoning
Numerical reasoning is the ability to work with numbers, understand numerical concepts, and use them to solve problems. It is a critical component of cognitive ability tests as it evaluates an individual's quantitative aptitude and problem-solving skills. Numerical reasoning questions can come in various formats, including arithmetic problems, data interpretation, and logical reasoning.
To approach numerical reasoning questions, it is important to read the questions carefully, identify the key information, and apply the appropriate mathematical concepts or formulas. It is also helpful to check the units of measurement and ensure that the answer makes sense. To improve numerical reasoning, practise mental maths techniques regularly, review mathematical concepts and formulae, and ensure you manage your time effectively during the test to ensure that all questions are answered within the given time limit.
Verbal reasoning
Verbal reasoning is the ability to understand and analyse written or spoken language and draw logical conclusions from it. It is a crucial component of cognitive ability tests as it assesses an individual's ability to comprehend and reason with language. Verbal reasoning questions can come in various formats, including analogies, comprehension, and critical reasoning.
To approach verbal reasoning questions, it is essential to read the text carefully, identify the key information, and analyse the relationships between the different elements. It is also helpful to consider the context and the intended meaning of the words or phrases used. To improve verbal reasoning, read widely and regularly, expand your vocabulary and practice comprehension and critical reasoning exercises.
Logical reasoning
Logical reasoning is the ability to draw conclusions from information presented in a structured and organised manner. Logical reasoning assessments test an individual's ability to reason and think critically. Logical reasoning questions can come in various formats, including syllogisms, deductive reasoning, and inductive reasoning.
To approach logical reasoning questions, it is essential to understand the relationship between the different elements presented, identify any patterns or rules, and use this information to draw logical conclusions. It is also helpful to consider the context and the intended meaning of the information presented. Practice, using visual aids to represent information, and breaking complex problems into simpler components can all aid performance on logical reasoning tests.
Mechanical reasoning
Mechanical reasoning is the ability to understand and solve problems related to mechanical systems and processes. Mechanical reasoning questions can come in various formats, including pulleys and gears, levers and simple machines, and electrical circuits.
To approach mechanical reasoning questions, it is essential to understand the mechanics involved, identify any patterns or rules, and use this information to solve the problem presented. It is also helpful to consider the context and the intended purpose of the mechanical system or process. Regular practice, developing a strong understanding of mechanical concepts and principles, and using diagrams or visual aids to represent information can all improve performance on mechanical reasoning tests.
Spatial awareness
Spatial reasoning is the ability to visualise and manipulate objects in three-dimensional space. Spatial reasoning questions can come in various formats, including shape rotations, spatial visualisation, and pattern recognition. To approach spatial reasoning questions, it is essential to visualise the objects and their relationship to each other in three-dimensional space, identify any patterns or rules, and use this information to solve the problem presented. It is also helpful to consider the intended purpose of the objects. Seeking feedback and guidance from experts or mentors can be helpful in identifying areas for improvement and developing effective strategies for approaching spatial reasoning questions.
Are cognitive ability tests reliable?
Cognitive ability tests have been shown to be reliable and valid measures of mental abilities. Research studies have consistently found high test-retest reliability and internal consistency for cognitive ability tests across a range of populations and contexts. For example, a study by Schmidt and Hunter (1998) found that cognitive ability tests had an average test-retest reliability of .86, indicating strong consistency over time. Moreover, cognitive ability tests have been shown to predict various outcomes such as academic achievement, job performance, and leadership potential, demonstrating their validity.
However, some criticisms of cognitive ability tests have been raised. These include concerns about cultural bias, test anxiety, and potential adverse impacts on marginalised populations. It is important to acknowledge these concerns and take steps to mitigate any potential biases in the administration and interpretation of cognitive ability tests. For example, using multiple measures and considering contextual factors in the interpretation of test results can help reduce the impact of any biases . Overall, cognitive ability tests remain valuable tools for assessing and predicting mental abilities and potential, but it is important to use them judiciously and with a clear understanding of their strengths and limitations .
Why are cognitive ability tests used by employers?
Using cognitive ability tests in the recruitment process can offer several benefits for employers, including increased accuracy, improved candidate selection, and reduced bias. These tests can help assess a candidate's ability to think critically, solve problems, and adapt to new situations, which are essential skills for many job roles. By using standardised tests, employers can obtain objective and comparable results across candidates, leading to more accurate and reliable evaluations. Furthermore, cognitive ability tests can help reduce biases in the recruitment process, such as the influence of personal characteristics or demographics, by focusing on skills and abilities rather than background or experience.
Several case studies demonstrate the benefits of using cognitive ability tests in recruitment. For example, the Tangerine Bank introduced cognitive ability tests as part of their recruitment process to identify candidates with the skills and aptitude needed by the firm. The tests helped improve the quality of candidates and cut the number of interviews needed by a third during the training process.
Another example is software company Canonical , which introduced cognitive ability tests as part of their recruitment process to identify candidates with the potential for success in a standardised way across their international operations. The tests helped identify individuals with high potential and reduce subjectivity and bias in the selection process. These examples demonstrate how cognitive ability tests can improve the accuracy and efficiency of the recruitment process and lead to better candidate selection.
Tips for practicing for cognitive ability tests
Practice different types of test.
To improve cognitive ability test performance, there are several practical tips and strategies to consider. Firstly, familiarise yourself with different test types and formats, such as numerical reasoning, verbal reasoning, logical reasoning, mechanical reasoning, and spatial awareness tests, and practice with sample questions. This will help you identify your strengths and weaknesses and develop targeted strategies for improving your performance.
Work on your weaknesses
Secondly, focus on improving your weaker areas by practicing regularly, reviewing relevant concepts and principles, and seeking feedback and guidance from experts or mentors.
Practice properly
Thirdly, practice proper test-taking techniques, such as managing time effectively, reading questions carefully, and checking your answers.
To prepare for cognitive ability tests, it is also essential to manage test anxiety. This can be achieved through various techniques such as deep breathing, visualisation, and positive self-talk. Setting realistic expectations, getting enough sleep, and maintaining a healthy diet and exercise routine can also help manage stress levels and promote mental clarity. Lastly, it is important to approach the test with a positive and confident attitude, believing in your ability to succeed.
Request reasonable adjustments if appropriate
To ensure that candidates with disabilities or protected characteristics are not unfairly disadvantaged in the recruitment process, employers are legally required under the Equality Act 2010, to make reasonable adjustments for protected characteristics, such as neurodiversity , visual impairments, and other factors that could affect a candidate's performance on a cognitive ability test.
For instance, candidates with dyslexia may require additional time or specialised software to complete a verbal reasoning test, while candidates with visual impairments may require assistive technology or alternative test formats. Making reasonable adjustments helps to ensure that all candidates have an equal opportunity to demonstrate their skills and abilities and promotes diversity and inclusion in the workplace.
Cognitive ability tests in summary
In conclusion, cognitive ability tests provide valuable insights into an individual's mental capabilities and potential, making them essential tools for recruitment and personal development programs. Assessing how quickly someone learns new information can inform recruitment decisions and help identify candidates with the skills and aptitude needed for specific job roles. Additionally, understanding an individual's cognitive abilities can help identify areas for development and create tailored training programs that meet their needs.
The Thomas Aptitude assessment (GIA) is an online test that comprises five different types of tests, including reasoning, perceptual speed, number speed and accuracy, word meaning, and spatial visualisation. By adopting the Thomas Aptitude assessment in recruitment, you can gain valuable insights into candidates’ cognitive abilities in the areas required by a role, as well as the speed with which they will learn new information, factors that have been shown to be more predictive of success than experience. The assessment provides these insights in minutes, helping you accelerate the hiring process whilst making informed and objective recruitment decisions. The assessment has also been shown to predict leadership potential and trainability, essential information for informing senior hires, succession planning and development programmes.
If you're interested in learning more about the Thomas Aptitude assessment and how it can help you better understand the learning speed and trainability of your people, speak to one of our team today .
Please select which Thomas product you would like to sign in to

- Doctors, Clinics & Locations, Conditions & Treatments
- Patients & Visitors
- Medical Records
- Support Groups
- Help Paying Your Bill
- COVID-19 Resource Center
- Locations and Parking
- Visitor Policy
- Hospital Check-in
- Video Visits
- International Patients
View the changes to our visitor policy
View information for Guest Services
New to MyHealth?
Manage Your Care From Anywhere.
Access your health information from any device with MyHealth. You can message your clinic, view lab results, schedule an appointment, and pay your bill.
ALREADY HAVE AN ACCESS CODE?
Don't have an access code, need more details.
Learn More about MyHealth Learn More about Video Visits
MyHealth for Mobile
Get the iPhone MyHealth app Get the Android MyHealth app
WELCOME BACK
Cognitive and neuropsychological tests.
Cognitive and neuropsychological tests measure memory, language skills, math skills, visual and spatial skills, and other abilities related to mental functioning to help them diagnose a patient's condition accurately. For example, people with Alzheimer's disease often show changes in so-called executive functions (such as problem-solving), memory, and the ability to perform once-automatic tasks.
Detailed neuropsychological testing is time-consuming and requires special training, and it usually occurs during a separate appointment with a neuropsychologist. However, during a regular neurology doctor visit, tests such as the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) or Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) provide a quick way to assess cognitive skills in people with suspected deficits.
These tests examine orientation, memory, and attention, as well as the ability to name objects, follow verbal and written commands, and copy a complex shape. Doctors also use a variety of other tests and rating scales to identify specific types of cognitive problems and abilities.

Condition Spotlight

Clinical Trials
Clinical trials are research studies that evaluate a new medical approach, device, drug, or other treatment. As a Stanford Health Care patient, you may have access to the latest, advanced clinical trials.
Open trials refer to studies currently accepting participants. Closed trials are not currently enrolling, but may open in the future.
- Transitions of Care 650-723-1303
Warning: The NCBI web site requires JavaScript to function. more...
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Browse Titles
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.

StatPearls [Internet].
Cognitive assessment.
Ischel Gonzalez Kelso ; Prasanna Tadi .
Affiliations
Last Update: November 7, 2022 .
- Definition/Introduction
The cognitive assessment is useful to test for cognitive impairment—a deficiency in knowledge, thought process, or judgment. Psychiatrists often perform cognitive testing during the Mental Status Exam. However, when cognitive impairment is suspected, the cognitive assessment can obtain a more detailed analysis by surveying the neuropsychological domains. This detailed investigation of cognition can diagnose major cognitive impairment (i.e., dementia) and mild cognitive impairment, evaluate traumatic brain injuries, help determine decision-making capacity, and survey intellectual dysfunction. [1] [2] [3] [4]
There are many established tools used to conduct cognitive assessments. Each is carefully constructed to evaluate neuropsychological domains such as memory, language, executive function, abstract reasoning, attention, and visuospatial skills. Available assessment tools range from those designed to evaluate a single neuropsychological domain, to mental status screens that survey multiple neuropsychological domains, to the most extensive test— a complete neuropsychological exam that assesses each neuropsychological domain. [5]
Most clinicians will use an established mental status screening tool such as the Mini-Mental Status Exam (MMSE) or Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) to determine if cognitive impairment is present. Mental status screens are short, efficient, and well-researched modalities designed to evaluate multiple cognitive domains. A cognitive assessment, along with a good history, physical exam, and appropriate labs and imaging, can establish a diagnosis or decide if further evaluation is necessary. [2] [6]
If a screening test is inconclusive or more information is required, a complete neuropsychological evaluation is an option. A full neuropsychological evaluation would ideally identify the patient’s specific deficits, differentiate between neurological and psychological etiologies, differentiate between Alzheimer’s dementia and other dementias, localize the deficits, and help formulate a personalized management plan. This exam is noninvasive and involves a battery of assessments performed by a trained professional. This comprehensive evaluation can take up to a full day to complete. While a full neuropsychological evaluation is the most detailed assessment, it is unnecessary for all patients who have a diagnosis or suspicion of cognitive impairment. However, it can serve as a helpful resource if there are questions or concerns about a diagnosis or care. [7] [8]
When performing a cognitive assessment, the clinician must take a good patient history and perform a physical exam; this ensures that the patients receive a thorough evaluation while strengthening the caregiver-patient relationship. If the assumption is that the patient has cognitive impairment before considering other diagnoses, the patient may feel that the clinician has dismissed them due to their age, level of education, or other reasons. A thorough examination can also help identify any behavior or personality disorders potentially contributing to the patient’s chief complaints, as mild cognitive impairments or dementia often coexist with behavioral and personality disturbances. Cognitively impaired patients cannot express themselves fully, so it is very beneficial to have someone with a close relationship with the patient present to help establish baseline levels of functioning.
Before deciding upon a particular testing modality, one should compare all of the available tests to find the test that is best suited for both the administrator and the patient. One should be mindful that some institutions may have a preferred testing modality. [9]
A variety of cognitive assessment screens exist, and each has instructions, templates (if applicable), and often their own website. Below is a shortlist of some of the more popular screening tools used and the relative strengths and weaknesses.
Mini-Mental State Exam (MMSE)
The MMSE usually takes less than ten minutes to administer, is easy to use, and has been researched thoroughly since 1975. However, what was once the gold standard in cognitive assessments, the MMSE is now used less frequently due to copyright laws and additional costs.
Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA)
The MoCA is another popular screening tool that takes approximately ten minutes to complete. It evaluates visuospatial skills, attention, language, abstract reasoning, delayed recall, executive function, and orientation. [10] The MoCA covers more domains than the MMSE and, as a consequence, has greater sensitivity and specificity. [6] The associated website includes specific adaptations for different populations, many different languages, printable versions of the test, and training opportunities.
The Mini-Cog is one of the faster cognitive assessment screens used. It consists of two parts: a three-item recall and a clock drawing test. The delayed three-item recall tests memory, while the clock drawing test evaluates cognitive function, language, executive function, and visuospatial skills. The Mini-Cog website also gives detailed instructions for administrators.
Saint Louis University Mental Status Exam (SLUMS)
Initially developed for the veteran population, SLUMS is another tool with an online printable form for testing. Their website has an instructional outline for administrators, training opportunities, and a wide range of language options from which to choose.
Other modalities include but are not limited to the Blessed Orientation-Memory-Concentration Test, Kokmen Short Test of Mental Status, Memory Impairment Screen, Ottawa 3DY, Brief Alzheimer’s Screen, Caregiver-completed AD8, and many other dementia screening scales. [11]
The results of these assessments require review in the context of each patient. Each administrator should remember that a screening test is not a substitute for a diagnostic workup. Lastly, it bears mentioning that no current data support the use of cognitive assessments in asymptomatic patients.
Neuropsychological Domains
Cognitive assessments evaluate for cognitive impairment by assessing the neuropsychological domains. A brief explanation of the frequently tested domains follows.
The language domain involves naming, reading, writing, and repeating words. Some practitioners will evaluate the language by noting the patient’s communication skills throughout the interview. There are many ways to test for language. Two neurocognitive tests include the Boston Naming Test and the Controlled Oral Word Association. [12] It should be noted that there is a part of the language domain that can become mildly impaired with normal aging. Expressive aphasia, which is the inability to find words, can become impaired with normal aging.
Executive Function
This assessment encompasses organizing, planning, working memory, mental flexibility, list-making, and executing tasks. An example of executive function impairment might be a patient who cannot follow recipes or cook as well as they used to. Often, executive function testing is by naming as many categorical items as possible; for example: name as many animals as possible in one minute. Other neuropsychological tests include the Trail Making Tests A and B and the Wisconsin Sorting Test. [12] [6]
Abstract Reasoning
Abstract reasoning refers to analyzing information, detecting patterns and relationships, or solving problems on an intangible, theoretical level. An example of abstract reasoning skills would be the ability to identify patterns and/or relationships between things that do not appear to be similar. Another example would be the ability to solve problems without the knowledge that it would normally take to solve them. [13] [14] Abstract reasoning is often tested by having the patient describe similes, analogies, proverbs, or sayings. For example, recognizing the relationship between an airplane and a bicycle is that they are both modes of transportation. Some neuropsychological abstract reasoning tests include the Shipley-2 Abstract Test, Gorham’s Proverbs Test, Conceptual Level Analogy Test, and Verbal Concept Attainment Test. [15]
Memory is the mechanism that takes information and then encodes, stores, and retrieves it for later use. [16] Different kinds of memory make this domain very complicated.
Memory divides into short-term and long-term memory. Short-term memory is capable of taking small pieces of information and utilizing it for a brief period. Long-term memory subdivides into procedural and declarative, which is further divides into episodic and semantic. Procedural memory is the storing of information used to perform or complete tasks that are done often, like driving a car. Declarative memory is the storing and recall of facts and events such as a family member’s birthday. Episodic memory is contextual information storing or remembering things from a specific experience. An example of episodic memory is the patient remembering what they did for their last birthday. Semantic memory is more general knowledge or factual based memory and would include learned subjects such as math.
Because memory is so complex, it is essential to recognize and document what exactly is under evaluation during this part of the assessment. Memory impairment can be easy to pinpoint from the patient’s history, but it can also masquerade as other things, such as having trouble learning new information. [9] It is also worth noting that normal aging can slightly impair memory. A normal aging patient’s activities of daily living will remain intact.
Attention/Concentration
Testing for attention and concentration often take place together. They are frequently tested by spelling words backward and/or serially subtracting numbers from a large starting point, such as the MoCA, where the examiner asks the patient to subtract seven from 100 in five increments. Some clinicians observe the patient and assess their level of attention throughout the interview. [9] An example of a neuropsychological test that acknowledges attention and concentration is the Connors Continuous Performance Test. [6]
Visuospatial Skills
This concept is a person’s ability to conceptualize and manipulate two- and three-dimensional objects. Testing is often by copying figures, block design, or clock drawings. [17] This skill set may be difficult to assess while taking a history but could present as a patient suddenly having difficulty with parallel parking their car or getting into small accidents. [9] In neuropsychology, an example of a test used for these skills is the Rey-Osterrieth Complex Figure Copy Test. [12]
- Issues of Concern
Having standardized cognitive assessments help create a universal way of diagnosing, but these particular tests are not perfect. Scoring can be subjective, conclusions may be drawn based on assumptions, and screening tests have statistical limitations.
If not done correctly, the scoring of these exams can be very subjective. Each result is administrator specific and accordingly introduces the possibility of human error. Some studies show that scoring leniency can negatively affect the sensitivity of the test. In an effort to control this variable, many of the assessment websites give clear instructions and provide tutorials on how to administer and score their assessment properly. [18] [1] [19]
Some of the cognitive assessment screens are undergoing development with limited testing within a cognitive domain. For example, the Mini-Cog tests for memory; it does not test the semantic of long-term procedural memory. Understanding that most of the available assessments are just screening tests is integral to the assessment’s use. [20] [19]
It is also important to remember the statistics when using screening tests. One must be cognizant of false positives and false negatives that are inevitable when the sensitivity and specificity are not 100%. [21]
Some tests may be better at identifying certain impairments over others—for example, some identifying mild cognitive impairment versus major cognitive impairment. The clinician must understand each test, what the test measures, and the limitations of the test. Lastly, cognitive assessments done in the clinical setting are screening tests and must be used along with clinical judgment as well as in the context of each patient presentation. [21]
- Clinical Significance
With medicine and technology continually improving, people are living longer lives. With a population that is increasing in age, the prevalence of cognitive impairment will inevitably rise as cognitive impairment is often age-related. [22] Thus, the diagnosis, management, and research of cognitive impairments are crucial to managing the needs of an aging population. [23] [2]
Cognitive assessments are fast, easy-to-use, and accurate ways to help diagnose, evaluate progress, and manage many kinds of cognitive impairment. [4] These assessments use questions and tasks that strategically test for impairment of various cognitive domains at once in a matter of minutes, which improves efficiency in the clinic as well as the lives of many individuals affected by this devastating condition.
- Nursing, Allied Health, and Interprofessional Team Interventions
The cognitive assessment is useful in determining a patient’s level of understanding and ability. This evaluation is especially important to nurses in an in-patient setting, as nurses spend a significant amount of time with the patients while they are hospitalized. Some levels of cognitive impairment will require constant monitoring. Other patients may need help communicating if their language domain is impaired. Each patient has a unique circumstance, and it is up to the healthcare team to identify the deficits and develop a healthcare plan addressing the same to provide optimum care. With the help of a cognitive assessment, nurses will not only know that a patient is cognitively impaired, but they will learn which domain may be comprised, thereby allowing the nursing staff to adjust patient approaches and/or care plans accordingly. [24]
- Review Questions
- Access free multiple choice questions on this topic.
- Comment on this article.
Disclosure: Ischel Gonzalez Kelso declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Prasanna Tadi declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
This book is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ ), which permits others to distribute the work, provided that the article is not altered or used commercially. You are not required to obtain permission to distribute this article, provided that you credit the author and journal.
- Cite this Page Gonzalez Kelso I, Tadi P. Cognitive Assessment. [Updated 2022 Nov 7]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.
In this Page
Bulk download.
- Bulk download StatPearls data from FTP
Related information
- PMC PubMed Central citations
- PubMed Links to PubMed
Similar articles in PubMed
- Review American Medical Society for Sports Medicine position statement: concussion in sport. [Br J Sports Med. 2013] Review American Medical Society for Sports Medicine position statement: concussion in sport. Harmon KG, Drezner JA, Gammons M, Guskiewicz KM, Halstead M, Herring SA, Kutcher JS, Pana A, Putukian M, Roberts WO. Br J Sports Med. 2013 Jan; 47(1):15-26.
- Understanding the role of psychiatrists in the diagnosis and management of mild cognitive impairment and mild Alzheimer's disease dementia: a cross-sectional survey. [BMC Psychiatry. 2023] Understanding the role of psychiatrists in the diagnosis and management of mild cognitive impairment and mild Alzheimer's disease dementia: a cross-sectional survey. Gopalakrishna G, Brunton S, Pruzin J, Alford S, Hamersky C, Sabharwal A. BMC Psychiatry. 2023 Oct 4; 23(1):716. Epub 2023 Oct 4.
- Review Screening for Cognitive Impairment in Older Adults: An Evidence Update for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force [ 2013] Review Screening for Cognitive Impairment in Older Adults: An Evidence Update for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Lin JS, O'Connor E, Rossom RC, Perdue LA, Burda BU, Thompson M, Eckstrom E. 2013 Nov
- Measurement of Functional Cognition and Complex Everyday Activities in Older Adults with Mild Cognitive Impairment and Mild Dementia: Validity of the Large Allen's Cognitive Level Screen. [Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2017] Measurement of Functional Cognition and Complex Everyday Activities in Older Adults with Mild Cognitive Impairment and Mild Dementia: Validity of the Large Allen's Cognitive Level Screen. Wesson J, Clemson L, Crawford JD, Kochan NA, Brodaty H, Reppermund S. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2017 May; 25(5):471-482. Epub 2017 Jan 4.
- Relationship between the Montreal Cognitive Assessment and Mini-mental State Examination for assessment of mild cognitive impairment in older adults. [BMC Geriatr. 2015] Relationship between the Montreal Cognitive Assessment and Mini-mental State Examination for assessment of mild cognitive impairment in older adults. Trzepacz PT, Hochstetler H, Wang S, Walker B, Saykin AJ, Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. BMC Geriatr. 2015 Sep 7; 15:107. Epub 2015 Sep 7.
Recent Activity
- Cognitive Assessment - StatPearls Cognitive Assessment - StatPearls
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
Turn recording back on
Connect with NLM
National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894
Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
Help Accessibility Careers
Top 5 Cognitive Ability Assessment Tools
When looking for the ideal candidate, there are so many things to check for. How well can they do the job? Will they get along with their coworkers? How will they react to and approach unexpected problems?
The good news for hiring managers is that there are a lot of tools and tests today at their disposal to help them glean the answers to most of these questions. And at the top of the list is cognitive ability assessment tools.
Starting from the beginning, let’s take a look at what cognitive ability really means, which are the best cognitive screening tools, and finish with some key reasons why you should want to evaluate cognitive ability in the first place.
TL;DR – Key Takeaways
- Cognitive ability refers to all the mental skills required to learn, solve problems, memorize, and perform tasks.
- For example, perception, memory, attention, language understanding, problem-solving, and decision-making are all fully under cognitive domains.
- Cognitive testing is used in hiring for several reasons: predictive validity , efficiency and cost savings, fewer chances of unconscious bias , and more standardized results.
- Best practices for running these tests include using them at the beginning of the hiring process, letting candidates know that they will be tested and why, reviewing and updating them often, and combining them with other tools to make good hiring decisions .
- The 5 best cognitive ability testing tools include Toggl Hire, Pymetrics, The Predictive Index, Talogy, and McQuaig.
- With Toggl Hire, you gain access to a rich library of job-specific and cognitive tests to test a range of hard and soft skills in your prospective candidates. The best bit? Every test is customizable, and you can automate the whole process, too, saving hours of your precious time!

What is cognitive ability?
Cognitive ability (also known as cognitive function or capacity) is the human ability to learn , solve problems, perform tasks, and acquire and use new information. Cognitive ability encompasses many mental skills , such as learning, thinking, concentration, memory, perception, problem-solving, language processing, decision-making, executive function, and others.
These skills can be tested using cognitive ability tests . A popular example is the IQ test, which was developed specifically to measure cognitive ability. Other cognitive ability tests like Raven’s Progressive Matrices, Digit Span Test, Verbal Analogies, Abstract Reasoning, and Spatial Visualization are commonly included in IQ tests.
| Cognitive Ability | Definition | Work Context Example |
|---|---|---|
| The ability to focus on specific information or tasks while ignoring distractions. | Staying focused on a project despite interruptions or a noisy office environment. | |
| The ability to store and retrieve information. | Remembering details from a client meeting to accurately complete a project or task. | |
| The ability to interpret sensory information. | Interpreting data from a report to understand market trends. | |
| The ability to find solutions to complex issues. | Identifying a bottleneck in a production process and devising a strategy to improve efficiency. | |
| The ability to evaluate information and options to make a choice. | Choosing the best vendor for a service based on a comparison of cost, quality, and reliability. | |
| The ability to understand and produce language. | Understanding and drafting a complex legal contract. | |
| The ability to understand and work with numbers. | Analyzing financial data to make budgeting decisions. | |
| The ability to understand and manipulate shapes and spaces. | Designing a productive layout for a new office space. | |
| Higher-order cognitive skills used for planning, organizing, and managing time and resources. | Planning a , delegating tasks, and monitoring progress to ensure timely completion. |
Conversely, cognitive impairment refers to poor memory, forgetfulness, and general cognitive difficulty, such as learning new things or concentrating. It’s more likely to affect people after retirement age. For example, Alzheimer’s is an illness that causes cognitive impairment, affecting a third of Americans aged 85 and above.

Why is cognitive ability important at work?
Pretty much every role requires cognitive ability to perform. However, the importance of strong cognition does vary between roles. Doctors and surgeons, for example, require higher cognitive ability than bartenders and other low-skilled jobs like cleaners and drivers.
If we think of physical jobs like athletes, or technical roles like IT engineers, we can see that other skills and talents may rank higher than cognition, even though we apply the cognitive ability to most situations, both in and outside of work.
Need an example?
Imagine a situation: you’re in an important meeting and need to use your cognitive skills.
- Perception. The person in the meeting should be able to fully understand all of the participants. This means not only catching verbal cues, but also interpreting information from slides, graphs, charts, and more. They should also be able to understand the finer nuances of language: tone of voice and body language.
- Memory. In and after the meeting, this person should use cognition to remember the meeting details and recall past situations and meetings before presenting. They should be able to use past information, remember it, and act based on it in the present.
- Attention. It isn’t easy to stay focused during a meeting, especially when the average human attention span is just over 8 seconds . The person in the meeting should be able to focus on the important details without getting lost or distracted while participating, asking and answering questions, and making decisions.
- Language understanding. This is not in the traditional sense of understanding multiple languages and the ability of verbal expression and comprehension (although that helps, too). It means understanding and using language to communicate thoughts and ideas effectively. More specifically, ideas that are related to the job and the industry you are working in.
- Problem-solving. If a problem ari ses during a meeting, such as covering a month’s worth of work in one week, the ideal candidate needs to use their cognition and executive functions to solve it. What shortcuts can they take? Is it possible to get an extension?
- Decision-making. The ability to make difficult decisions on the spot is crucial. Let’s say the candidate needs to determine future hiring needs right in the meeting—how many people to hire or outsource. That requires not just business understanding but also the ability to quickly analyze and summarize information before making a decision.
In short, all of these are important in a business environment in their own way, and a cognitive ability screening test can be a good way to determine if your ideal candidate has them or not.

Why is cognitive ability testing used in hiring?
Employers like cognitive screening primarily because of the proven link between test results and job performance. In addition to these practical reasons:
1. Predictive validity
Simply put, candidates with great cognitive skills tend to perform better on the job . By using a cognitive assessment tool, you can determine not only if they can learn in general but also if they have what it takes to succeed in their future role. And, of course, if the candidate is a better fit for the job, this means a lower turnover rate too.

2. Efficiency and cost savings
Unlike traditional screening methods and techniques, such as screening resumes , cognitive assessment tools allow you to screen thousands of candidates at once . This also means hundreds of hours saved for you as the employer.
An added bonus to cognitive assessment tools is the cost savings. While running through resumes or cover letters would cost thousands of dollars in HR team time, these tools are much cheaper in comparison. And if you can see that a candidate scores lower than average, it will also save you in the long run.
3. Lower chances for unconscious bias
When you review your applicants’ resumes, unconscious bias can creep in, which is when someone gains an unfair advantage because of their educational background, work experience, or some other identifying factor that is not based on merit or ability.
Cognitive tests give you just that: an unfiltered view of someone’s mental performance.

4. Standardization
It can be pretty difficult to objectively compare candidates with different backgrounds and work experience without an objective measure, like cognitive tests.
With all the candidates taking the same screening tests, you’ll have a more objective way to compare them and find the best one out of the lot.
Cognitive assessment tools have many benefits, but this does not mean that they are the definitive answer to your hiring assessment needs. It is always best to use this testing method in combination with further assessment tools and techniques to get a more comprehensive and balanced view of your applicants.

Different types of cognitive ability testing
Several assessment tools have been developed over the years to test for cognitive ability. Depending on the specific skillset you want to test and what role candidates are applying for, you might choose one of these:
- MMAT – McQuaig Mental Agility Test
- GIA – Thomas International General Intelligence Assessment
- HBRI – Hogan Business Reasoning Inventory
- PLI – Predictive Index Learning Indicator
- RCAT – Revelian Cognitive Ability Tests
- WPT – Wonderlic Personnel Test
- CCAT – Criteria Cognitive Aptitude Test
Although these cognitive assessments are used for different purposes, they have one thing in common – they each test for more than one cognitive ability.
They are not meant to be very difficult, and the candidates usually have a very short time frame to answer many questions. For these reasons, very few candidates answer all of the questions in a single test, which is, of course, deliberate: processing speed is also a measure of cognitive ability. All of these tests are also good for spotting red flags , such as cognitive impairment.
4 Cognitive ability test best practices
Before you start your cognitive evaluation tests, remember some tips and best practices , especially if you’re doing them for the first time.
#1. Set benchmarks and update them frequently
Most cognitive tests allow you to get a precise score for each candidate, expressed in numbers. After your candidates have completed a few screening tests, you’ll have a good idea of what constitutes a good score .
As you hire for different roles, you may discover that the benchmark you set is too high or too low. Make sure to update it as time goes by, as the average score might change after more new applicants.
You can then use that average score as a benchmark for future candidates and set an automated threshold that automatically determines which candidates are moved on to the next stage.
#2. Use cognitive tests at the beginning of the hiring process
The ideal place to ask candidates to complete a cognitive test is at the point when they submit an application . This will allow you to screen thousands of candidates at once, immediately at the point of entry. Combine the test results with their LinkedIn profile and resume, and you can save dozens of hours per applicant.
More importantly, you’ll get to screen the best candidates only and disregard those unfit for the job. It’s definitely worth finding out if someone has a cognitive impairment immediately rather than waiting until the end of the hiring process.
#3. Use test results in combination with other assessment tools
Screening tests for cognitive ability should be considered one piece of the puzzle. Depending on the skills needed for the role, someone could be amazing for the job but bad at cognitive screening tests.
This is why it’s important to consider the test results in combination with other aspects, such as work experience, education, a portfolio, interview performance, and more.
#4. Tell your candidates what you’re testing for and why
In today’s competitive and interconnected environment, the candidate experience is crucial, and your applicants need to understand cognitive screening.
A screening test might discourage candidates and cause them to drop out before you even see their application. Therefore, it is important to openly state what you are testing and why so that candidates are informed beforehand.
5 of the best cognitive assessment tools today
The screening tools for cognitive assessment are plenty, and we prepared some of the very best ones with their top features for you.
#1. Toggl Hire
Toggl Hire is a full-cycle hiring platform with unique pre-employment assessment and screening features. While it includes ATS capabilities and other helpful hiring features, you can also use it to test a wide range of hard and soft skills, including cognitive skills.
With Toggl Hire, as opposed to other recruitment software , the main benefit is that you can vet potential employees for anything from design to sales to development and also for crucial cognitive skills. We’d go as far as to say that it’s the best cognitive function test on the market, but we’re a little biased.
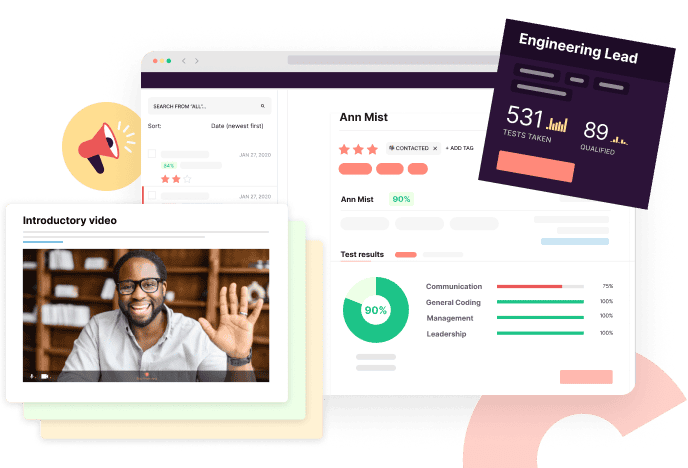
Where Toggl Hire excels, for this use case, is combining job-specific skills with more general cognitive skills in a single assessment test. This allows you to get a full overview of someone’s capabilities to see how they think and how likely they’ll do well in the job.
#2. Pymetrics
Pymetrics is a soft skills assessment platform that lets you test your candidates’ numerical and logical reasoning. You can then get a HiredScore to predict which ones will most likely stay with you. If you have more openings, Pymetrics can show your “silver medalists”, as they call them, to another opening that better suits their cognitive and soft skills and their test scores.

#3. The Predictive Index
The Predictive Index is a “talent optimization” platform offering several products to help hire and nurture top talent. They also offer cognitive tests based on “60 years of behavioral science,” so you can hand-pick the best people for the job based on the skills you need in a role.
In addition to their tests, PI are best known for their Behavioral Assessments, having mapped out 17 distinct reference profiles to help organizations build high-performing teams.
With roots going back to 1946, Talogy is an enterprise-level talent management and assessment platform used by organizations such as Coca-Cola and Siemens. One part of Talogy is dedicated to cognitive ability testing, and it is called Mindgage. It has four different sections, called Crunch, Flow, Seek, and Sync, for testing numerical ability, mental rotation ability, perceptual ability, and verbal comprehension ability, respectively.
#5. McQuaig
McQuaig offers a range of different tools for assessing candidates before proceeding further with their applications. Amongst them is a cognitive test to identify and screen for speed of thought, general intelligence and cognitive ability, the ability to process information, and the aptitude for learning and applying that knowledge.
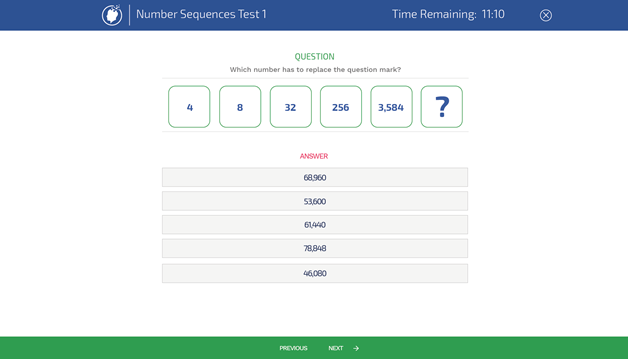
Why combine cognitive skills tests with other tests?
With a combination of job-specific skills tests and cognitive skills tests, you get a whole host of benefits for your hiring process.
Here are our top 3 reasons why you should consider these two test types in combination:
- First, you get a holistic overview of the candidate. You find out if they have the mental ability to learn on the job, adapt, and make their own decisions, plus the skills to excel in their chosen role. Remember, cognitive tests only assess cognition and aren’t a substitute for testing practical, real-world skills.
- Second, you reduce bias as these tests are usually used as the first stage of the hiring process, which means less likelihood of someone on your team being influenced by someone’s gender, work experience, or the university they went to.
- Third, you’ll improve the candidate experience, as they can enjoy a more engaging hiring and evaluation process. Contrary to some expectations, 94% of almost 2,000 candidates who responded to a recent survey answered that they see the value in skills tests as a way to demonstrate their potential to succeed beyond experience.
What’s not to like?
If you’re ready to try it, create a free account to see what it looks like from the inside!

Juste loves investigating through writing. A copywriter by trade, she spent the last ten years in startups, telling stories and building marketing teams. She works at Toggl Hire and writes about how businesses can recruit really great people.
Join 30,000+ subscribers getting the best tips on productivity, work management, hiring and more!
We promise we won't spam you and you can unsubscribe anytime.
You might also like...
Related to Talent Assessments

30 Best Pre-Employment Testing Tools
Top 25 Most In-Demand Skills in 2024 & Beyond

Vervoe vs. Coderbyte vs. Toggl Hire: Choosing a Skills Assessment Tool
Take a peek at our most popular categories:

What are cognitive tests? What can they show? What don't they show?

President Joe Biden is under pressure to undergo cognitive testing even though his physician says he passes an annual neurologic exam. But what can the brief screening tool actually tell about a person’s brain health?
It’s the new chant in Washington politics: “Get a cognitive test!”
Political opponents, armchair pundits and even nervous supporters are demanding that President Joe Biden undergo such testing after his halting debate performance and appearing confused at some events – even though his physician says he passes an annual neurologic exam.
Former President Donald Trump, only a few years younger, has boasted on several occasions about passing cognitive tests. He has made his share of speaking errors that have been pointed out by opponents.
With all the concern, what can cognitive testing actually tell about a person’s brain health – and what can’t they answer? And presidents aside, does the average older adult need one?
What are cognitive tests?
They’re brief screening tools, a 10-minute series of questions to assess different brain functions. Two of the most common are called the MMSE, Mini-Mental State Exam, and the MoCA, Montreal Cognitive Assessment.
Recalling a list of five unrelated nouns or seeing how many words beginning with F you can say in a minute can assess short-term memory and language. Counting backward by 7s tests attention and concentration. Drawing a clock with the correct time is a clue to spatial awareness.
How reliable are cognitive screenings?
They don’t diagnose health problems. A bad score is just a red flag that indicates a need for further testing to see if there is a health problem and uncover what kind, said Dr. James Galvin, a neurologist at the University of Miami.
A good score usually is good news. But the highly educated especially tend to be good test-takers even if cognitive trouble is starting to brew. So if someone scores OK yet they, a family member or the doctor sees some day-to-day concern, more testing still could be warranted.
“We simply use it as a benchmark to determine our suspicion level,” Galvin said.
When and how often should cognitive screenings be done?
"A screening test is exactly a snapshot in time. So it tells you in that moment how someone does on that test,” Galvin stressed. “It doesn’t tell you how a person is functioning in their everyday life.”
Simply reporting a concern is reason enough for a primary care doctor to perform one. But it’s also supposed to be part of the annual Medicare wellness visit for those 65 and older.
Galvin wouldn't discuss Biden or Trump because he hasn't examined them — but said that generally it's a good idea for seniors to get checked yearly to spot changes. It's much like how doctors don’t assume your blood pressure’s still fine; they measure it.
How is a cognitive test different from a neurologic exam?
Cognitive screenings are “pencil and paper tests” usually handled by primary care doctors, while neurologic exams generally are performed by a specialist, Galvin said.
It’s a very detailed physical exam. Doctors watch the patient’s speech patterns and behavior, test how key nerves are functioning, check reflexes that can signal brain diseases and assess muscle tone and function.
If either kind of test signals real cognitive concerns, the next step may be more intensive neuropsychological testing — an exam that often lasts up to three hours.
After an exhaustive interview of the patient and any accompanying family members, the neuropsychologist goes through tests and tasks designed to check specific brain functions – intelligence, memory, verbal ability, problem-solving and reasoning skills, visual and auditory responses, emotion and mood. They may use puzzles, objects to rearrange, or drawing and writing tests.
Blood tests and brain scans also may be ordered. Special types of PET scans can detect Alzheimer’s hallmark amyloid plaques and tau tangles in the brain. An MRI can detect past strokes, helpful in diagnosing vascular dementia.
How can you tell if cognitive concerns are a disease or just getting older?“
Age makes us do things a lot slower,” Galvin said. “We move slower. We think slower. But we’re still moving correctly and we’re still thinking correctly – it just takes us longer.”
Examples of slower cognitive “processing” might be difficulty remembering a name, numbers or specific details under pressure – but they come back to you later.
Galvin noted that sometimes reversible health problems mimic cognitive trouble. For example, urinary tract infections are notorious for causing sudden confusion in older people. Certain medications affect memory, as can thyroid problems, depression, even poorly controlled diabetes.
Anyone who's worried about their memory should talk to their doctor, or seek a specialist, “who can reassure you that everything's OK or develop a treatment plan that's specific for you,” he said.
Copyright 2024 Health News Florida

What cognitive tests can show—and what they can’t

It’s the new chant in Washington politics: “Get a cognitive test!”
Political opponents, armchair pundits and even nervous supporters are demanding that President Joe Biden undergo such testing after his dismal debate performance—even though his physician says he gets, and passes, an annual neurologic exam.
Former President Donald Trump, who’s only a few years younger, makes his own gaffes . He recently bragged about passing a 2018 cognitive test—while calling the doctor who administered it by the wrong name .
With all the concern, what can cognitive testing actually tell about a person’s brain health —and what can’t they answer? And presidents aside , does the average older adult need one?
What are cognitive tests?
They’re brief screening tools, a 10-minute series of questions to assess different brain functions. Two of the most common are called the MMSE, Mini-Mental State Exam, and the MoCA, Montreal Cognitive Assessment.
Recalling a list of five unrelated nouns or seeing how many words beginning with F you can say in a minute can assess short-term memory and language. Counting backward by 7s tests attention and concentration. Drawing a clock with the correct time is a clue to spatial awareness.
How reliable are cognitive screenings?
They don’t diagnose health problems. A bad score is just a red flag that indicates a need for further testing to see if there is a health problem and uncover what kind, said Dr. James Galvin, a neurologist at the University of Miami.
A good score usually is good news. But the highly educated especially tend to be good test-takers even if cognitive trouble is starting to brew. So if someone scores OK yet they, a family member or the doctor sees some day-to-day concern, more testing still could be warranted.
“We simply use it as a benchmark to determine our suspicion level,” Galvin said.
When and how often should cognitive screenings be done?
“A screening test is exactly a snapshot in time. So it tells you in that moment how someone does on that test,” Galvin stressed. “It doesn’t tell you how a person is functioning in their everyday life.”
Simply reporting a concern is reason enough for a primary care doctor to perform one. But it’s also supposed to be part of the annual Medicare wellness visit for those 65 and older.
Galvin wouldn’t discuss Biden or Trump because he hasn’t examined them—but said that generally it’s a good idea for seniors to get checked yearly to spot changes. It’s much like how doctors don’t assume your blood pressure’s still fine, they measure it.
How is a cognitive test different from a neurologic exam?
Cognitive screenings are “pencil and paper tests” usually handled by primary care doctors, while neurologic exams generally are performed by a specialist, Galvin said.
It’s a very detailed physical exam. Doctors watch the patient’s speech patterns and behavior, test how key nerves are functioning, check reflexes that can signal brain diseases and assess muscle tone and function.
If either kind of test signals real cognitive concerns, the next step may be more intensive neuropsychological testing—an exam that often lasts up to three hours.
After an exhaustive interview of the patient and any accompanying family members, the neuropsychologist goes through tests and tasks designed to check specific brain functions—intelligence, memory, verbal ability, problem-solving and reasoning skills, visual and auditory responses, emotion and mood. They may use puzzles, objects to rearrange, or drawing and writing tests.
Blood tests and brain scans also may be ordered. Special types of PET scans can detect Alzheimer’s hallmark amyloid plaques and tau tangles in the brain. An MRI can detect past strokes, helpful in diagnosing vascular dementia.
How can you tell if cognitive concerns are a disease or just getting older?
“Age makes us do things a lot slower,” Galvin said. “We move slower. We think slower. But we’re still moving correctly and we’re still thinking correctly—it just takes us longer.”
Examples of slower cognitive “processing” might be difficulty remembering a name, numbers or specific details under pressure—but they come back to you later.
Galvin noted that sometimes, reversible health problems mimic cognitive trouble. For example, urinary tract infections are notorious for causing sudden confusion in older people. Certain medications affect memory, as can thyroid problems, depression, even poorly controlled diabetes.
Anyone who’s worried about their memory should talk to their doctor, or seek a specialist, “who can reassure you that everything’s OK or develop a treatment plan that’s specific for you,” he said.
Latest in Aging Well

How the ‘Medicare Cliff’ is raising costs and worsening health for many older low-income adults

Menopause stigma is impeding women’s career growth, survey says. Here’s how a lack of support is hampering ambition—and the economy

6 foods that could be making you age faster

Is there a perfect age to be a leader?

What’s happening inside an 80-year-old brain?
Most popular.

3 big changes coming to Medicare in 2025—and what they’ll mean for you

The 5 best supplements for healthy aging, according to a longevity expert

What cognitive tests can show — and what they can't
What can cognitive testing actually tell about a person’s brain health and presidents aside, does the average older adult need one, by lauran neergaard | associated press • published july 10, 2024 • updated on july 10, 2024 at 4:36 pm.
It’s the new chant in Washington politics: “Get a cognitive test!”
Political opponents, armchair pundits and even nervous supporters are demanding that President Joe Biden undergo such testing after his dismal debate performance – even though his physician says he gets, and passes, an annual neurologic exam.
Former President Donald Trump , who’s only a few years younger, makes his own gaffes. He recently bragged about passing a 2018 cognitive test – while calling the doctor who administered it by the wrong name.
24/7 New York news stream: Watch NBC 4 free wherever you are
With all the concern, what can cognitive testing actually tell about a person’s brain health – and what can’t they answer? And presidents aside, does the average older adult need one?
What are cognitive tests?
They’re brief screening tools, a 10-minute series of questions to assess different brain functions. Two of the most common are called the MMSE, Mini-Mental State Exam, and the MoCA, Montreal Cognitive Assessment.
Get Tri-state area news and weather forecasts to your inbox. Sign up for NBC New York newsletters.

Biden refuses to take a cognitive or neurological test in his first post-debate TV interview

The questions about Biden's age and fitness are reminiscent of another campaign: Reagan's in 1984
Recalling a list of five unrelated nouns or seeing how many words beginning with F you can say in a minute can assess short-term memory and language. Counting backward by 7s tests attention and concentration. Drawing a clock with the correct time is a clue to spatial awareness.
How reliable are cognitive screenings?
They don’t diagnose health problems. A bad score is just a red flag that indicates a need for further testing to see if there is a health problem and uncover what kind, said Dr. James Galvin, a neurologist at the University of Miami.
A good score usually is good news. But the highly educated especially tend to be good test-takers even if cognitive trouble is starting to brew. So if someone scores OK yet they, a family member or the doctor sees some day-to-day concern, more testing still could be warranted.
“We simply use it as a benchmark to determine our suspicion level,” Galvin said.
When and how often should cognitive screenings be done?
“A screening test is exactly a snapshot in time. So it tells you in that moment how someone does on that test,” Galvin stressed. “It doesn’t tell you how a person is functioning in their everyday life.”
Simply reporting a concern is reason enough for a primary care doctor to perform one. But it’s also supposed to be part of the annual Medicare wellness visit for those 65 and older.
Galvin wouldn't discuss Biden or Trump because he hasn't examined them — but said that generally it's a good idea for seniors to get checked yearly to spot changes. It's much like how doctors don’t assume your blood pressure’s still fine, they measure it.
How is a cognitive test different from a neurologic exam?
Cognitive screenings are “pencil and paper tests” usually handled by primary care doctors, while neurologic exams generally are performed by a specialist, Galvin said.
It’s a very detailed physical exam. Doctors watch the patient’s speech patterns and behavior, test how key nerves are functioning, check reflexes that can signal brain diseases and assess muscle tone and function.
If either kind of test signals real cognitive concerns, the next step may be more intensive neuropsychological testing — an exam that often lasts up to three hours.
After an exhaustive interview of the patient and any accompanying family members, the neuropsychologist goes through tests and tasks designed to check specific brain functions – intelligence, memory, verbal ability, problem-solving and reasoning skills, visual and auditory responses, emotion and mood. They may use puzzles, objects to rearrange, or drawing and writing tests.
Blood tests and brain scans also may be ordered. Special types of PET scans can detect Alzheimer’s hallmark amyloid plaques and tau tangles in the brain. An MRI can detect past strokes, helpful in diagnosing vascular dementia.
How can you tell if cognitive concerns are a disease or just getting older?
“Age makes us do things a lot slower,” Galvin said. “We move slower. We think slower. But we’re still moving correctly and we’re still thinking correctly – it just takes us longer.”
Examples of slower cognitive “processing” might be difficulty remembering a name, numbers or specific details under pressure – but they come back to you later.
Galvin noted that sometimes, reversible health problems mimic cognitive trouble. For example, urinary tract infections are notorious for causing sudden confusion in older people. Certain medications affect memory, as can thyroid problems, depression, even poorly controlled diabetes.
Anyone who's worried about their memory should talk to their doctor, or seek a specialist, “who can reassure you that everything's OK or develop a treatment plan that's specific for you,” he said.
This article tagged under:
THE BEST TEST PRACTICE
Learn how to pass any reasoning test with my tips, training and free practice tests..

Recommended by:

Free Practice Aptitude Tests
Take 16 free practice aptitude tests . Each test comes with answers and fully explained solutions to each question.
What Is the Saville Wave Test?
The Saville Wave test is a personality questionnaire that comes in different versions to suit all sorts of job roles and levels of seniority.
Created by Saville Assessment, the Wave tests are designed to be the ‘best-in-class predictor of workplace performance and potential’.
They blend digital innovation and science to cover aspects of competency, potential, motivation, talent and preferred company culture in one short assessment.
The Wave tests are usually used in recruitment and selection, but they are also used for talent management and succession planning.
There are two main types of Wave tests used in recruitment:
- The Wave Focus Styles
- The Wave Professional Styles

It is becoming increasingly common for employers to ask potential new employees to complete a variety of assessments as part of their recruitment processes.
One example of this is the Thomas International PPA assessment , which is a personality test commonly used by employers who are looking for individuals with specific personality types or strengths in defined areas.
In this article, you’ll learn what the Thomas International PPA Test is, what you can expect if you are asked to take the assessment and how your test will be scored.
We have also included plenty of helpful tips and free Thomas International PPA sample test questions to help you prepare ahead of taking the Thomas PPA assessment.

The NWEA MAP Growth Test is used in thousands of schools across the US to assess children academically.
The test can be given three times in a school year and helps teachers to plan their lessons so that children can reach their potential and continue to grow throughout their time in education.
In this article, you will learn more about the different levels of the test and the way it is structured to suit different grades, what types of questions are on the tests and how best to prepare your child for success.

If your child is under the age of 12 and aims to get into a gifted school program, they will most likely be required to take the NNAT test to assess their skills.
If you know that your child is expected to take the exam, you can help them prepare for it by letting them know what to expect.
This article contains the most relevant information concerning the NNAT test, including its purpose, scoring system and levels.
You will also receive plenty of helpful tips on how to help your child prepare for the exam by completing a Naglieri Nonverbal Ability Test sample and working on their weaknesses in each question type.

The Hogan Business Reasoning Inventory (HBRI) is a scientifically-based aptitude test.
It is designed to assess cognitive ability and a candidate’s preferences for using qualitative and quantitative reasoning skills.
The HBRI is a popular tool for pre-employment screening, particularly in the management, sales and marketing sectors.
If you have been asked to take the HBRI, your test results will offer prospective employers insight into your decision-making skills, problem-solving abilities, approach to processing information and ability to learn from past experiences.
In this article, you can learn what to expect when taking the Hogan Business Reasoning Inventory HBRI test, see examples of the type of Hogan Business Reasoning Inventory questions you might be faced with and guidance on how to prepare for the assessment.

The MAP Kindergarten Test is a computer-adaptive test that measures your child’s progress throughout their academic career.
The grades K through 2 tests assess mathematics and reading abilities.
The results from these tests allow teachers to identify the gaps in your child’s knowledge and to better understand their ability to learn and retain information.
The MAP test is administered three times in the academic year to ensure your child’s progress is properly recorded.

The Ramsay Mechanical Aptitude Test is used as part of the pre-employment screening process for a number of roles in different industries.
It is an excellent indicator of how well you can learn on the job, as well as your ability to use basic physics principles and mechanical knowledge to solve problems.
In this article, you will learn more about which job roles require completion of the Ramsay MAT as part of the application process, and what different types of tests are available.
The format of the assessment, as well as the number of questions and the time limit, will also be discussed. You’ll also learn how the Ramsay MAT is scored and what happens next.
There will be example questions that are similar to those you are likely to find on the assessment, as well as some top tips for success.

The Saville assessments are used worldwide by companies during the recruitment process to assess a candidate’s suitability for a given role.
This series of tests measures numerical, verbal, spatial and abstract reasoning . You may also be assigned a situational judgement test and a personality questionnaire. Some roles may even require a mechanical reasoning test .

The SHL OPQ32 test is the flagship personality test from SHL.
Used by major organizations all over the world, it is considered to be one of the best psychometric assessment tools currently available on the market.
It is a trait-based personality test that is designed to gauge a candidate’s personality attributes and behavioral preferences in the workplace.
A candidate’s test results are analyzed by recruiters, helping them to decide whether a candidate is a good match for the job role they have applied for.

OLSAT stands for Otis-Lennon School Ability Test.
Children take the test to help schools decide admissions into their gifted-and-talented programs.
Preparing your children for taking the OLSAT is a good idea as it could determine their eligibility and acceptance to extra academic programs that are offered by their schools.

If you are looking for a career working with the emergency services, then becoming a 911 call handler and dispatcher might be just the role for you.
If you can handle working under pressure, helping the public and are able to deal with difficult and uncomfortable situations with a calm head, then you might have what it takes to be the first port of call in an emergency.
Becoming a 911 call handler and dispatcher means you will need to have some very specific skills and abilities, and as part of the recruitment process, you will have the opportunity to demonstrate your suitability by taking the CritiCall 911 dispatch test .
Used throughout the US for recruiting people for 911 roles, the CritiCall test does not assess your previous experience or your knowledge of the role.
Instead, it is designed to assess candidates on the inherent aptitudes that are needed to be successful in the role.
This article will discuss what the CritiCall test is assessing, the types of questions that you are likely to face and what the recruiters will be looking for.
There will be some example questions, as well as details about what mark you will need to achieve to pass the test.
Finally, there are some CritiCall test prep tips to help you prepare for the assessment and what to think about on the day.

The McQuaig Word Survey is a type of personality assessment.
Survey responses are used to measure a candidate’s key personality traits and compare these with how they are currently behaving in the workplace.
The results from the survey indicate whether a candidate is behaving naturally in their current role, or whether they are making changes to their behaviour.
This article will help you pass the McQuaig Word Survey assessment test by giving you all the tools and practice questions you will need.

The Caliper test is an assessment used by employers to gain a better understanding of a candidate’s personality traits, cognitive abilities and motivations.
The Caliper test is used to help employers predict a candidate's suitability for a role.
In this article, we'll take a detailed look at what the Caliper test is and how it is scored.
We’ll also share some tips on how you can perform at your best when taking your Caliper assessment test.

More and more employers are choosing to use psychometric testing as a part of their recruitment processes as it helps to highlight those candidates who are most likely to be suited to the roles they are looking to fill.
Employers will often use this form of testing when recruiting for mid-to-high level managerial roles or positions that require a specific set of skills.
Using the results of assessments, recruiters and employers are able to see the strengths and skills of individuals as well as being able to predict future performance.
One of the most popular options for psychometric testing is the Criteria Cognitive Aptitude test – more commonly known as the CCAT.

The Bennett Mechanical Comprehension Test (BMCT) , also referred to as the Bennett Mechanical Aptitude Test, is considered the most popular mechanical aptitude test.
However, it is also believed to be the hardest one to pass.
The BMCT requires you to have a knowledge and understanding of physical principles and answer 55 questions about the application of these concepts within 25 minutes.
You typically need to score in the top 20% of candidates to progress to the next stage of recruitment.

If you have applied for a job, apprenticeship or college course in the UK or Australia, you may have been asked to complete a Basic and Key Skills Builder or BKSB assessment) .
The initial BKSB assessment determines suitable applicants for an apprenticeship or places a student in the correct class level on a college course. The assessment tests you on your maths and English skills to identify areas that need improvement.
This guide will explain the BKSB assessment in detail, provide example questions, and answer your queries about the test content and format.

There are a variety of tests and assessments that can be used by companies for candidates applying for jobs.
One of those is the Thomas GIA Test .
This article will define what the Thomas GIA Test is and who it is for, in addition to looking at what the test involves, how it is scored and tips for the next chance to pass the test.
You will also find Thomas GIA test examples and explanations for each answer.

The IE Global Admissions Test (ieGAT) is an entrance exam for the IE University (IEU) in Spain.
It covers numerical , logical and verbal reasoning .
Not every IE program requires an ieGAT score. However, as the programs that do are highly competitive, those who take the ieGAT Test must prepare themselves to achieve the best score possible.
This article will help you understand:
- What the ieGAT is
- The structure
- ieGAT scoring
- How to register for the ieGAT
- The best ways to prepare

More and more companies are introducing psychometric testing as a part of their recruitment processes.
This means that, if you are considering changing careers or applying for a new role within your existing industry, you may need to take an assessment.
One of the most popular tests for corporate employers is the test by Sova Assessment .

The United States Postal Service (USPS) provides extensive career opportunities and seemingly endless possibilities for professional development.
However, anyone looking to work at the USPS must pass a Virtual Entry Assessment designed to find suitable applicants for the role they are trying to fill.
This article covers the Postal Exam 474 , including its main parts, how to pass it and how to prepare for the Virtual Entry Assessment.
Let's start by looking at what exactly the 474 Virtual Entry Assessment is.

Developed by Drs Joyce and Robert Hogan in the 1980s, the Hogan assessment is a collection of tests designed to assess personality traits, leadership skills and cognitive abilities.
The Hogan assessment is generally used as a pre-employment test for management roles.
This article will guide you through the online Hogan tests , provide a range of sample questions, discuss how the Hogan Assessment results are calculated and recommend ways that you can prepare to take the Hogan assessment yourself.
If you’ve recently applied for a managerial or executive role, you may have been asked to take a Saville Analysis Aptitude Test , also known as the Swift Aptitude test.
The Swift Analysis Aptitude Test was created by Saville Assessment, which is a huge name in the test publishing market.

The CAT4 cognitive ability test is an examination designed to measure a student’s academic progress.
When the CAT4 test is scored, teachers and parents will be given a summary of the academic potential of the student.
Any student taking the test will be asked questions that will measure their non-verbal reasoning abilities, verbal reasoning skills, quantitative reasoning abilities and spatial awareness .
In this article, you’ll learn more about what types of questions are asked to examine these skills.

The Korn Ferry Leadership Potential Assessment (KFALP) is used to test candidates to see if they have the potential to become leaders and managers.
It uses seven different categories, known as Seven Signposts, to assess potential leaders:
- Learning Agility
- Leadership Traits
- Derailment Risks
This article will examine the theory behind the assessment, the different topics that are tested and how the assessment is scored.
There will also be example questions so that you know what to expect when you take the KFALP and some tips to help you score as highly as possible when you take the test.

Pymetrics tests identify specific behavioral characteristics and traits.
This article examines why pymetrics tests are used and what to expect in your assessment.
Tips are included to help you get the best results.

The McQuaig Mental Agility Test (MMAT) is a 15-minute timed test that is designed to assess your ability to think quickly.
In this short test, you will face questions that will allow you to demonstrate your speed of thought and general mental agility, which are useful aptitudes when it comes to many jobs in different industries.
In this article, find out more about the structure of the test, the different types of McQuaig Mental Agility test questions and what to expect on the day. You’ll also get some mental agility practice test questions and top tips to help you be successful in the MMAT.

The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) is responsible for the enforcement of federal law and the protection of national security in the US.
Working for the FBI can be highly stressful. As a special agent for the FBI, the working week is likely to be 50 hours or more.
Special agents must be willing to be based anywhere in the world. They are expected to carry a firearm and work in potentially dangerous situations.
With this in mind, the FBI has a rigorous application and selection process for potential new recruits. It can take more than 20 months to complete the entire process and commence employment with the FBI.

This guide to the USPS postal exam 955 will take you through the different sections of the test, including example questions, provide tips on how you can prepare for the exam and answer several frequently asked questions.
The USPS postal exam 955 is used to screen applicants for mechanic and technician positions , such as electronic technicians or motor vehicle mechanics. It also sometimes referred to as the postal maintenance 955 exam, USPS maintenance mechanic 955 test or the 955 maintenance exam.
It tests applicants’ suitability by assessing personal characteristics, work experience, and electronic and technical knowledge and skills.
The USPS postal exam 955 replaced the previous 931, 932 and 933 exams .
The USPS postal exam 955 is free of charge , but you will need access to the internet and an email address.

If you are looking to work in the United States Postal Service, you will need to pass the USPS Postal Exam 476.
The USPS Postal Exam 476 is an online test that screens for the best candidates. The exam is used to find suitable candidates for a range of positions, including mail processing clerk, data conversion operator and clerk-related positions.
This article will outline what the USPS Postal Exam 476 includes, with particular attention to the separate sections of the examination.
In addition to this, how the exam is scored and how you can best prepare for it will be covered. There will also be a list of frequently asked questions for you to refer to if you have any doubts.

A List of Amazon Assessment Tests Available for Practice in 2024
- Amazon Work Simulation Assessment
- Amazon Maintenance Technician Test
- Amazon Coding Assessment
- Amazon Workstyle Assessment
- Amazon Area Manager Assessment
- Amazon Operations Manager Assessment
- Amazon Online MBA Assessment
- Amazon RME Apprenticeship Skills Battery Test
- Amazon Financial Analyst Assessment
- Amazon ATA Technical Assessment
- Amazon Control Systems Technician Test
- Amazon Warehouse Assessment Test
The Amazon assessment test is an essential way for the corporation to find the best-suited employees.
It is a series of challenges used to evaluate all its candidates during the recruitment process.
Amazon online assessments typically include both numerical and verbal reasoning tests.
These types of tests examine a potential candidate’s logical skills.
Candidates will also have to sit work-style assessments that simulate the working environment at Amazon.
Other Amazon exams include:
- The Amazon coding assessment (also known as the Amazon SDE online assessment)
- The work sample simulation
- An Amazon versant test
These last two, amongst others, will be discussed later in this article.
This Amazon reviewer job article will also discuss how to pass the Amazon assessment tests, some Amazon assessment answers you should know and what you need to do to best prepare yourself.
There is also a comprehensive list of frequently asked questions from those who are interested in taking these Amazon job tests to find employment with the company.

What Is the SHL Verbal Reasoning Test?
The SHL Verbal Reasoning Test is a graduate-level and above pre-employment aptitude test that is used in graduate and management recruitment for many roles across different industries.
The test is usually taken online, and it is designed to evaluate candidates on their ability to understand written information and make informed, reasoned and logical decisions based on that information.
SHL is a well-established test publisher, providing tests for more than 10,000 companies around the world. It offers a range of tests, including psychometric, behavioural and personality assessments that are based in occupational psychology and aptitude science.
The tests have specific aims – and recruitment teams use SHL tests like the Verbal Reasoning Test to filter through similarly qualified candidates to find the applicants who have what it takes to be successful in a graduate or management level role.
When taking a verbal reasoing test, bear in mind that you might also be asked to take numerical reasoning tests, logical reasoning tests or personality tests along side.

IQ stands for intelligence quotient and is usually thought to represent the reasoning skills of individuals.
The idea of intelligence relates to how quickly people can solve problems or puzzles, use logic to answer questions, or quickly recall information and facts they’ve heard.
The first type of IQ test was created by a French psychologist named Alfred Binet.
The assessment that he made is still used and is known as the Stanford-Binet intelligence test.

Considering cheating on your GMAT (Graduate Management Admission Test) Exam?
Want to know how to do it, if you should do it and what the consequences will be?
Well you came to the right place!
Read on to find out more about cheating on the GMAT exam, but be warned...
... it's certainly not something I advise!

Do you have an upcoming online aptitude test ?
Are you looking for the best aptitude test prep material to give you the very best chance of getting the highest possible grade?
If so, this article will help you.
Aptitude tests are a crucial part of your job search, and you usually only have one chance to showcase your skills.
Psychometric aptitude tests can measure many different aptitudes and skill sets, in many different formats:
- Numerical reasoning
- Verbal reasoning
- Diagrammatic or inductive reasoning
- Mechanical reasoning
- Personality types
- Situational judgement and work environment tests
- Work style tests
Aptitude tests can be challenging and it is important to be fully prepared before you attend your job interview or assessment centre.
Several free and paid aptitude test preparation websites offer preparation packs to help you score the best you can.

Those dreaming of working for the TSA will most likely need to take a challenging exam called the TSA CBT Test during the hiring process. Here we’ll look at exactly what it involves and how you can make sure you pass it. Read on to find out more.
If you plan to work as an inspector, manager, marshal or security officer in any agency governed by the Transportation Security Administration, you must pass the TSA CBT test as part of your application process.
Read on to learn more about this assessment, including its purpose, what types of questions it has, how challenging it is and how to prepare for it.
You'll also be provided with a few example questions to help you get an idea of what this test looks like.
Let’s get started.

Aptitude tests are administered to understand your inherent abilities to reason and respond to specific tasks.
They are widely used in various forms to screen candidates or evaluate existing employees for a future job role.
The most generic and widely used aptitude tests are curated to measure different facets of your abilities, mainly on the following areas:
- Abstract Reasoning
- Numerical Reasoning
- Logical Reasoning
- Verbal Reasoning
- Attention to Detail
Apart from these base types, there are various other specialized aptitude tests which you may face in specific industries or based on your role in different career stages.
We have discussed each of the most common job related aptitude tests in detail.
Illustrative examples and helpful hints are provided throughout to aid your preparation.
Read on to find out more.

The Cognify test is a game-based cognitive assessment designed to measure an individual's cognitive aptitude to measure key job performance linked abilities and skills in a prospective candidate.
The Cognify test was once a product of Revelian, an Australian assessment company, but was later acquired by CriteriaCorp.
Moving away completely from the question-answer based template of traditional tests, Cognify uses an innovative approach where candidates don't face a series of questions on a screen.
Instead, the Cognify Assessment comprises 6-7 timed game-based mini-tests categorized into three cognitive abilities categories:
- Problem-Solving
- Verbal Knowledge
Well, before you start raising your eyebrows at the mention of ‘game-based’ and dismiss it as just another fad, pay attention!
Cognify assessment is credited as having brought a paradigm shift in the field of psychometric testing.
Many Tier-I graduate recruiters globally have started using this assessment in their candidate selection process.

The train driver test is used to establish whether a candidate is suitable for work as a train driver. This unique suite of tests includes psychometric assessment tools such as:
- The Group Bourdon Test (GBT)
- Test of Everyday Attention (TEA-OCC)
- Adaptive Tachistoscopic Traffic Perception Test (ATAVT)
- Situational judgement tests
- Vigilance tests
- Written communication tests
What Is the Train Driver Test?
In most countries, you will need to sit the train driver online test if you want to work as a train driver. If you have been asked to sit the assessments, there is no train driver psychometric test cost associated with the train driver exam.
Working as a train driver is a challenging and demanding role. As a train driver, you must be able to ensure the safety of passengers at all times.
The UK’s train driving tests are some of the most challenging. As well as testing aptitude for the job role, they are used to assess whether candidates have the mental abilities to cope with the stress and demands of the job role.
The train driver test is used to establish whether a candidate is suitable for work as a train driver. The train driver test is a unique group of psychometric tests for train drivers designed to assess the psychomotor and cognitive skills needed to work safely as a train driver.
![problem solving cognitive test Predictive Index Tests Fully Explained [With Example Questions + Answers]](https://www.datocms-assets.com/7756/1671731172-predictive-index-tests-none-x2.png?auto=%20compress%2C%20enhance%2Cformat&crop=focalpoint&fit=crop&fp-x=0.5&fp-y=0.5&h=300&w=300)
The Predictive Index (PI) test is a popular type of pre-employment testing used to accurately measure an individual’s cognitive ability and behavioral profile during the hiring process in a wide range of industries and organizations. They are most commonly used during the early stages of the recruitment process.
The PI cognitive test assesses verbal, numerical and analytical reasoning ability.
The PI behavioral test creates a behavioral persona that describes character traits and tendencies.

A mechanical aptitude reasoning test is an important way to assess your knowledge on mechanical topics for potential roles in the army, emergency services and many other professions. Here, you will get all the information you need on what a mechanical comprehension test is and how to pass it.
Those applying for jobs related to the army, the emergency services engineering service, and similar occupations that require mechanical aptitude, are likely to be asked to take a mechanical reasoning test as part of the recruitment process.
Mechanical aptitude tests assess knowledge in electricity, optics, pressure and other fields of mechanics related to a specific industry.
From this article, you'll learn what mechanical reasoning tests look like, when to take them, what to expect from these assessment types, and how to practise and prepare for them.
Let’s get started!

If you would like to take a free practice Cognitive Ability Test before reading this article, click here .
If you would like to purchase an online Cognitive Ability Test prep pack, visit our partner website JobTestPrep .
The following tests are common cognitive ability tests:
- Spatial Reasoning
- Mechanical Reasoning
- Logical Ability Tests
- Space Visualization
- Information Processing
- Visual Pursuit
- Manual Speed and Accuracy

Spacial Reasoning Definition
A spatial awareness test is a type of assessment that tests your ability to think in three dimensions and use your imagination to see movement through space.
Someone with good spatial awareness will be able to see in their mind how different shapes interact and be able to manipulate them to make a reasoned and logical decision.
The test is based on pictures, diagrams and shapes. You will need to mentally manipulate the presented image by disassembling or reassembling, rotating, seeing it in a mirror image or from different angles, or otherwise visualizing it differently to find the right answer to the question from the multiple-choice options provided.
Spatial awareness is something that we use to a greater or lesser degree every day, from understanding our position relative to other things around us to imagining the route we will take to get from one place to another.
Spatial reasoning tests are distinct from other similar assessments such as diagrammatic reasoning tests and abstract reasoning tests. It is important to understand how they differ as they are often included in aptitude tests and cognitive assessments alongside spatial reasoning tests.

Psychometric tests are often used by organizations as part of the recruitment process. Different types of psychometric tests are designed to measure various aspects of cognitive ability, reasoning capabilities and personality traits. Potential employers use the results to assess a candidate’s suitability for a role. A psychometric test is generally administered online; this helps hiring managers filter applicants quickly and easily.

Are you considering cheating on your upcoming SHL tests ?
In this full disclosure article, I’ll tell you why people cheat on tests, how people cheat, and whether or not it’s worth doing..
Don't cheat!
Practice... it's the only legitimate way to improve your scores, you'll sleep better at night and probably get better results in your tests too.
Still want to read about how to cheat on a test?

Numerical Reasoning Tests can be very tricky.
And when it comes to results, preparation and practice are key.
But that's easier said than done.
If you're researching this type of aptitude test for the first time or if you want to improve your numerical ability , perform better on tests and get more job offers this article will provide some practical strategies that you can use immediately .
For the best chance of success, read the article below slowly, work through the example questions , follow our tips and actionable advice and then start taking practice tests .
Ready to get started?
Let's go!...
Want to try a practice test before reading this article?
You can take our free numerical test right here:

The in tray exercise (also called an e-tray exercise ) is a popular assessment activity which employers use to evaluate the skills of applicants in a workplace situation.
If you have an In Tray exercise coming up as part of your interview process, this article will help you prepare.
Within these exercises, candidates will be presented with a given scenario, along with a set of tasks to complete which may include things like responding to email messages, reports or briefing documents.

What Is a Situational Judgment Test?
A situational judgement test (SJT) is a psychometric test that is often used as part of the recruitment process for graduate and managerial positions as well as roles that are customer-facing in a wide range of industries.
The SJT is designed to assess how a candidate deals with work-related problems and situations, focusing on essential aptitudes , competencies and soft skills that are not always easy to evaluate in other ways.
Although SJTs are usually bespoke to the company (or in some cases, the specific role), they tend to follow the same basic structure.
Each question is formed by presenting a fictional yet realistic work-based scenario. This might be text-based, it may include some illustrations or it could be animated or acted out in a video.
Following the scenario, there will be several options that you can choose from, each giving a possible course of action to follow to solve the issue that is presented in the situation given.
The answer that you choose will be compared to the benchmark answers that the recruitment team is using – these represent the core competencies for the role, as well as alignment with company values.

SHL assessment tests are important steps in many job interviews and career advancement opportunities. Therefore, it is essential to have a comprehensive understanding of how the different types of SHL tests work and how you can prepare for them in order to get top scores.
In this article, we will provide an overview of how SHL assessments work, sample SHL test questions, tips on improving your test performance, and strategies for prepping and succeeding with any SHL test.
What Is an SHL Assessment Test?
SHL is a global assessment company that is well known and recognised as a leader in pre-employment psychometric tests; the tests that SHL publishes are used by 75% of the FTSE 100 and they are available in more than 40 languages.
So if you are applying for a new role (especially for a graduate position), you are likely to come across them in the recruitment process.
In addition, the company offers consultancy and management services via its TalentCentral platform.
The SHL assessment are a series of tests that can be delivered individually or in a battery, and some of them are bespoke to the company that is using them, making them an excellent way for the recruitment team to ensure that the applicants for a role have the basic competencies, personality traits, work behaviours and cognitive abilities to be successful.

Sind Sie auf der Suche nach kostenlosen psychometrischen Tests zur Übung?
Dann ist diese Seite genau das Richtige für Sie.
Was ist ein psychometrischer Test?
Psychometrische Tests (auch Eignungstests genannt) sind fester Bestandteil von Jobinterviews vieler Unternehmen auf der ganzen Welt.
Diese Tests bestehen normalerweise aus einer Reihe von zeitlich erfassten Fragen , die meist numerischen (mathematischen Fragen), verbalen (Fragen zum Leseverständnis) oder logischen (diagrammatischen Fragen) Ursprungs sind.

Testes psicométricos (também conhecidos como testes de aptidão) são uma parte comum do processo de entrevistas de emprego em muitas companhias no mundo todo.
Geralmente, esses testes consistem de uma série de questões com um certo tempo de resposta.
As questões costumam ser numéricas (questões matemáticas), verbais (compreensão textual) ou lógicas (questões de diagrama).

Testes SHL . Se você está lendo isso, há uma boa chance de você ter acabado de descobrir que fará um desses testes difíceis como parte de um processo de recrutamento em andamento.
Se você chegou tão longe e agora está se sentindo tenso para se sentar na frente de um ‘abstract quiz’, não se preocupe...
Nós cuidaremos de você.

El Razonamiento Inductivo está basado en patrones y es otra variante de las muchas pruebas psicométricas utilizadas por los empleadores como una forma de determinar la idoneidad de un candidato para sus roles.
En un nivel similar al del razonamiento esquemático , el razonamiento inductivo probará tu habilidad para aplicar la lógica y la razón para la resolución de problemas.
Cómo funcionan las pruebas inductivas
Dentro de la prueba se te presentará una serie de diagramas los cuales se vincularán mediante una regla subyacente.
Esta regla afectará el diseño del diagrama y tu tarea será identificar el patrón.
Bonificación: puedes obtener acceso ilimitado y gratuito a la práctica de prueba (durante 30 minutos) en nuestro sitio web asociado JobTestPrep: Clic aquí .
Por lo general, se espera que los candidatos seleccionen entre 4 y 6 posibles respuestas completas bajo condiciones de tiempo.
Las pruebas de razonamiento inductivo a menudo complementan otras pruebas como las de razonamiento verbal o numérico.
A veces las empresas requieren que complete una prueba de juicio situacional o un cuestionario de personalidad junto con la evaluación de razonamiento inductivo.
Los resultados de cada prueba se revisarán individualmente y luego colectivamente para determinar si tú serías una buena opción para la empresa.
¿Por qué los empleadores utilizan estas pruebas?
Algunas veces se las denomina prueba de razonamiento abstracto, las evaluaciones de razonamiento inductivo están diseñadas para evaluar tus habilidades en la resolución de problemas y el razonamiento lógico.
Cuando completes la prueba, los reclutadores buscarán tu capacidad para trabajar de manera efectiva con información desconocida para alcanzar una solución viable.
Las pruebas se utilizan a menudo para evaluar tu capacidad de pensar creativamente, aplicar habilidades analíticas y diseñar soluciones innovadoras, mientras que a menudo son un indicador de tu nivel general de inteligencia.
Como tal, es esencial que realices el trabajo preparatorio necesario antes de la prueba real para asegurarte de poder completarla exitosamente y crear una buena impresión.
La prueba de razonamiento inductivo es frecuentemente usada por empleadores corporativos; es común esperar que se complete al menos una prueba psicométrica como parte del proceso de reclutamiento.
Los empleadores utilizarán estas pruebas para ver la eficacia con la que trabajas bajo presión y tu enfoque de la evaluación.
Las pruebas de razonamiento inductivo son usadas predominantemente en los roles técnicos o aquellos que requieren una resolución frecuente de problemas y los empleadores las utilizan para evaluar cómo identificas patrones, con qué eficacia puedes identificar reglas y consistencias de datos y si puedes predecir la secuencia de objetos a medida que evolucionan.
En términos de evaluación psicométrica, el razonamiento inductivo, el razonamiento abstracto y el razonamiento esquemático son tres pruebas que a menudo se superponen con la evaluación. Los proveedores utilizan nombres diferentes para cada uno, lo que hace que las cosas sean un poco más confusas.
Estas pruebas ciertamente varían entre los empleadores y la etapa en el proceso de reclutamiento también será diferente.
Algunas empresas los utilizan como un ejercicio de selección previa a la entrevista para limitar un conjunto de candidatos, mientras que otras organizaciones pueden usarlos hacia el final del proceso de reclutamiento o como parte de los días de evaluación.
Contenido de la prueba de Razonamiento Inductivo
La mayoría de las pruebas de razonamiento inductivo presentan una serie de secuencia de palabras, ilustraciones o formas y te piden que decidas cuál es la siguiente.
Esto requiere prestar atención a los detalles, a la resolución de problemas y perseverancia para alcanzar la respuesta requerida, todo lo cual se evalúa en condiciones de tiempo, lo que agrega aún más presión.
La prueba en sí misma requerirá que compares varios elementos incluyendo colores y formas, o que los clasifiques basándote en cantidad o tamaño.
Como un ejemplo, se te proporcionará un juego de seis cuadros conteniendo una cantidad de formas y luego se te pedirá que elabores una secuencia lógica para cada cuadro.
Para obtener la respuesta correcta, deberías identificar un patrón tal como similitudes, diferencias o una combinación de ambos.
Estas tareas pueden parecer extremadamente complejas, por ello es importante realizar tantas prácticas de pruebas similares como sea posible antes de la prueba real y también tanta práctica como puedas antes de la entrevista o del día de evaluación.
Asegúrate de llegar a tiempo y haber dormido bien la noche anterior, de lo contrario, es posible que te falte la concentración y que parezca que no entiendes lo que te piden que hagas.
Una aproximación a las Pruebas de Razonamiento Inductivo
Cuando comienzas la prueba, lee la pregunta detenidamente y trata de observar solamente a un elemento de la forma a la vez.
Es muy fácil sentirse abrumado por el contenido de una evaluación de razonamiento inductivo, por lo que la mejor manera de abordarla es intentar y decidir el patrón, considerando específicamente el tamaño, la orientación y la ubicación de la forma interior.
Los patrones están diseñados para ser complicados en tomarte el tiempo y utilizar tu lógica para resolver el problema.
Si estás teniendo una particular dificultad en identificar un patrón, trata de observarlo desde el final en lugar del principio.
Esto puede resaltar de manera efectiva algo que quizás hayas omitido usando el método tradicional de revisar las formas.
Toma conciencia de la hora pero no mires el reloj, y no te asustes en la medida de lo posible; esto sólo hará las cosas más difíciles.
Las pruebas de razonamiento inductivo son creadas para ser completadas bajo presión, por lo que la práctica de completar las pruebas en condiciones de tiempo puede ayudar de manera significativa.
Practicar es una de las mejores maneras de prepararte mentalmente para cualquier prueba psicométrica y el razonamiento inductivo no es diferente a ello.
Nada te preparará mejor para la evaluación que realizar una cantidad de exámenes de práctica, muchos de las cuales puedes encontrar en línea gratuitamente.
Cuando te familiarizas con el formato de la prueba y te acostumbras a responder preguntas rápidamente y trabajar bajo presión, es mucho más probable que tengas éxito que si no realizas ningún trabajo de preparación o práctica anteriormente.

¿Qué son las pruebas psicométricas?
Las pruebas psicométricas (también conocidas como Pruebas de Aptitud ) son ahora una parte común de los procesos de selección y evanotluación, por lo tanto un requisito necesario para solicitar trabajo.
Si tú aún no has completado una, es muy probable que lo necesites en algún momento en el futuro. Con esto en mente, hemos preparado para ti la Guía actual para las pruebas psicométricas para explicar qué son, cómo se utilizan y cómo completarlas con éxito.
Antes de comenzar con el artículo a continuación, ten en cuenta que tenemos tres pruebas psicométricas de práctica disponibles para que las pruebes.

Las pruebas de razonamiento verbal están diseñadas para examinar tu nivel de comprensión del pasaje de un texto.
Estas pruebas son un ejemplo de una prueba de habilidad (a veces conocida como pruebas de aptitud) y son utilizadas por los empleadores en combinación con pruebas de razonamiento numérico y pruebas de razonamiento lógico .
Las pruebas de razonamiento verbal tienen como objetivo identificar tu capacidad máxima de comprensión, o en otras palabras, el párrafo de un texto más desafiante que tú podrás entender.

Numerische Tests können knifflig sein. Übung und die richtige Vorbereitung sind der Schlüssel zum Erfolg.
Aber das ist leichter gesagt als getan…
Wenn Du zum ersten Mal über diese Tests nachliest oder wenn Du nach Wegen suchst um deine Fähigkeiten zu verbessern, besser abzuschneiden und mehr Interviews und Jobangebote zu bekommen, ist dieser Artikel ideal für Dich.
Hier erfährst Du von Strategien die Du sofort praktisch einsetzen kannst.
Falls du einen Übungstest machen möchtest kannst du hier jederzeit einen der kostenlosen numerischen Tests ausprobieren. Dieser Test beinhaltet zehn Fragen (mit Antworten und ausführlichen Erklärungen).
Wie kann man sein Ergebnis so schnell und effektiv wie möglich verbessern , selbst bis in der 99% Bereich ?
Lies den Artikel am besten langsam durch, folge unseren Tipps und unseren Empfehlungen – so hast du die größten Erfolgschancen. Wenn du damit fertig bist kannst du einen unserer Übungstests kostenlos ausprobieren.
Bonus: Kostenloser uneingeschränkter Zugang zum Eignungs-Übungstest (für 30 Minuten) auf unserer Partner-Webseite JobTestPrep.

Microsoft is one of the world's most commonly used computer software.
If you're working in an office, you are almost certain to use applications such as Microsoft Word, Excel, Outlook or PowerPoint.
Therefore, it makes perfect sense that employers want to know that you are proficient in these applications as part of their hiring process.
If your job requires data analysis or compiling data streams, you will likely need to be adept at using Microsoft Excel.
In these circumstances, you may be asked to participate in an Excel assessment test so a hiring manager can confirm that you know how to make the most out of the program.
With this in mind, we will look at what you could expect from a Microsoft Excel test.
Then, we'll take you through a series of Microsoft Excel practice test questions, and we'll give you everything you need to know so you can prepare for the Excel assessment.

What Is a Cubiks Test?
The Cubiks tests were developed by the Cubiks assessment consultancy, which was founded in 2000.
In 2019, Cubiks was acquired by PSI Talent Management UK, an award-winning provider of psychometric assessments.
In 2022, PSI Services became Talogy.
Cubiks tests are available in more than 50 countries around the world. Many highly-regarded employers in the UK use Cubiks tests, including:
- The UK Civil Service
- National Audit Office
- National Health Service
Cubiks tests are designed to help employers and organisations with recruitment, employee development and talent management. They are well known for their intuitive interface and easy-to-interpret structure.
When applying for job roles, you may be asked to complete one or more types of Cubiks test as part of the screening and selection process.
If you are already working, your employer might ask you to sit a Cubiks test assessment as part of the career development programme or talent management process.
This article offers an overview of what to expect from the Cubiks test. It also includes some Cubiks online test example questions and tips on how to succeed when taking the Cubiks test.

The Korn Ferry assessment is a tool used in the recruiting process for leadership positions.
The tests assess candidates across a range of skills, including:
- Logic reasoning ability
- Numerical reasoning ability
- Verbal reasoning ability
- Personality traits
As a result, the Korn Ferry assessment allows businesses to secure the best talent and identify individuals to be promoted to management positions.
The Korn Ferry assessment is an evaluation tool used by companies across the globe to ensure they employ the best talent.
The assessment comprises a series of smaller tests focusing on:
- Reading comprehension
- Personality
- Leadership assessments
As well as a tool utilized during the interview process, the Korn Ferry assessments are often used when looking to promote team members into management positions.
This article will discuss the Korn Ferry assessment, explaining exactly what it involves and giving tips to enable the best chance of success.
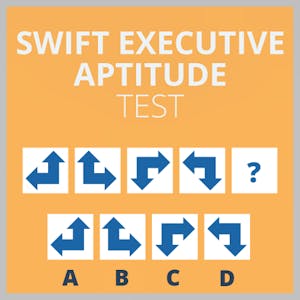
If you are applying for an executive-level or management role, you might be expected to take an aptitude test as part of the recruitment process.
The Swift Executive Aptitude Test is a short assessment designed to measure specific aptitudes that are necessary for success in a leadership position.
In this article, you will discover more about the test, the structure of the assessment, and example questions.
You will also learn what you will need to bear in mind to be successful in the test, including tips about preparation and a breakdown of what to expect from the scoring.
This numerical reasoning practice test has 10 questions.
The test has a mixture of numerical questions that vary in difficulty.
Answers and full explanations are provided after you have completed a question. You should aim to complete the test within 10 minutes.
Make sure you read and fully understand each question before answering. Work quickly, but don't rush. You cannot afford to make mistakes on a real test.

What is a Verbal Reasoning Test?
A Verbal Reasoning Test is a type of cognitive assessment designed to evaluate an individual's ability to comprehend and analyze written information, make logical deductions and draw conclusions based on the presented text.
These tests are often used in various educational and employment settings to assess a person's verbal reasoning skills, which are essential for tasks that involve understanding and interpreting written or spoken language.

This inductive reasoning practice test has nine questions (and includes answers and full explanations).
This abstract reasoning practice test has 10 questions (and answers with full explanations).
For each question, choose which of the figures in the bottom line – A, B, C, D or E – completes the series in the top line.
The level of difficulty varies significantly, from easy to extremely hard. Items having the solution based on one rule are easy, while those with the solution based on four rules are extremely hard; the others are in between - medium and hard, respectively.
Your goal is to understand the logic of each question (the rules behind it). Do not despair if you can’t find the solution immediately, especially for the very hard questions!

What is a Cognitive Test?
A cognitive test is an assessment tool designed to measure an individual's cognitive abilities, which are the mental processes involved in acquiring, processing, storing and using information.
Cognitive assessments are used to evaluate various aspects of cognitive functioning, including memory, attention, problem-solving, reasoning, language comprehension, and more.
Cognitive function tests are commonly employed in several contexts, including education, clinical psychology, neuropsychology and employment assessment.
This cognitive ability practice test has been designed to help you prepare for the real thing.

What Is a Deductive Reasoning Test?
A deductive reasoning test is a type of cognitive assessment that measures a person's ability to draw logical conclusions based on given information or premises.
Deductive reasoning is a form of logical thinking that involves moving from general statements or principles to specific conclusions. In other words, it is the process of applying a general rule or premise to a specific situation to determine a particular outcome.
In a deductive reasoning test, you are typically presented with a set of premises or statements that establish certain conditions or facts. You are then asked to use these premises to determine a valid conclusion.
The conclusions you reach must follow logically from the given premises, and the test assesses your ability to make accurate deductions based on the provided information.
Deductive reasoning tests are often used in educational settings, as part of standardized testing, and in various employment assessments.
They are designed to evaluate an individual's problem-solving skills, critical thinking ability, and their capacity to analyze information and reach logical conclusions.
These tests can take various formats, including multiple-choice questions, true or false questions or scenario-based questions where you need to determine the correct outcome based on the information provided.
Success in deductive reasoning tests often requires a strong understanding of logical principles and the ability to apply them effectively to specific situations.

What is Logical Reasoning?
Logical reasoning, often referred to as logical thinking or critical thinking, is a cognitive process that involves the ability to analyze information, identify patterns, make sound judgments and draw valid conclusions.
It is a fundamental skill that plays a crucial role in problem-solving, decision-making and rational thinking.
Logical reasoning involves breaking down complex information or situations into smaller, more manageable parts. It requires examining details and understanding the relationships between various elements.
What are the Types of Logical Reasoning Tests?
Logical reasoning tests come in various forms and are used by employers, educational institutions, and standardized testing organizations to assess an individual's ability to think critically and solve problems.
Here are some common types of logical reasoning tests:
- Verbal Reasoning Tests
Reading Comprehension: These tests assess your ability to understand and analyze written information, make inferences, and draw conclusions from passages of text.
Critical Thinking Tests: These tests evaluate your ability to analyze and evaluate arguments, identify assumptions, and assess the validity of statements or claims.
Analogical Reasoning Tests: Analogical reasoning involves recognizing relationships between words or concepts and applying these relationships to solve problems. For example, you might be asked to complete an analogy like "A is to B as C is to what?"
- Numerical Reasoning Tests
Numerical Computation: These tests assess your basic arithmetic skills, including addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
Numerical Sequences: These tests require you to identify patterns and relationships within number sequences and use them to predict the next number.
Data Interpretation: In these tests, you are presented with data in the form of tables, graphs, or charts, and you must interpret the information to answer questions.
- Abstract Reasoning Tests
Non-Verbal Reasoning: Abstract reasoning tests evaluate your ability to recognize patterns, shapes, and relationships among visual elements. They often involve series of diagrams or figures, and you must identify the logical rules governing them.
Inductive Reasoning: Inductive reasoning tests present you with a series of visual or abstract patterns and require you to identify the underlying rules and predict the next pattern in the sequence.
- Spatial Reasoning Tests
Spatial Awareness: These tests measure your ability to visualize and manipulate objects in three-dimensional space. You may be asked to complete puzzles, identify rotated or mirrored images, or solve spatial problems. Diagrammatic Reasoning Tests:
Diagram Interpretation: Diagrammatic reasoning tests use diagrams or symbols to present problems. You must analyze the diagrams to draw conclusions or identify patterns.
Syllogism and Logic Tests
Syllogisms: Syllogism tests present logical statements and ask you to determine whether a conclusion is valid based on the given premises.
Symbolic Logic: These tests involve working with formal logic symbols to evaluate logical arguments.
Inference and Deduction Tests
Inference Tests: Inference tests assess your ability to make logical deductions and draw conclusions based on a set of statements or information.
Deductive Reasoning: Deductive reasoning tests require you to apply deductive logic principles to solve problems and make decisions.
- Mechanical Reasoning Tests
Mechanical Understanding: These tests evaluate your knowledge of mechanical and physical concepts, such as gears, pulleys, levers, and basic physics principles.
- Cognitive Ability Tests
Cognitive Ability Tests: These assessments often include a combination of various reasoning types and are designed to measure overall cognitive abilities.
What are the Common Logic Tests Employers Use?
Employers often use a variety of logic tests to assess the cognitive abilities and problem-solving skills of job applicants. The specific logic tests used can vary depending on the nature of the job and the industry.
Here are some common logic tests that employers may use during the hiring process:
- Logical Deduction and Syllogism Tests
- Data Interpretation Tests
- Diagrammatic Reasoning Tests
This is a 10 question practice logical reasoning test .
After you have given an answer to a question, the correct answer (and a full explanation of that answer) will be given.
What are the Topics Covered by a Logical Reasoning Test?
Syllogism, statements and assumptions, logical deduction, cause and effect, statements and conclusions, logical problems.

Set of 10 questions, along with correct answers and explanations for each.
Topics Covered:
General concepts, levers, springs, pulleys, area and volume, gears, inclined plane, basic electrical circuitry.
Difficulty Level:
Take a free practice mechanical reasoning test.

Situational awareness, evaluation of alternatives.
Take a Free Practice Situational Judgement Test

Block counting, 3D rotation, 2D rotation, reflection, broken shapes, transforming 2D to 3D, isometric view, difference in 2D versus 3D viewing.

What Is the Watson Glaser Critical Thinking Test?
The Watson-Glaser Critical Thinking Test, often referred to as the Watson-Glaser test, is a widely used assessment tool designed to evaluate an individual's critical thinking skills.
It is commonly administered as part of the hiring process for various professional and managerial positions, particularly in fields where critical thinking and problem-solving abilities are highly valued, such as law, finance and management.
This is a nine question diagrammatic reasoning practice test.
We recommend a time limit of nine minutes for this test.
After you have given your answer to a question, you will be shown the correct answer and given a full explanation.

What is the Critical Thinking Test?
The Critical Thinking Test is a comprehensive evaluation designed to assess individuals' cognitive capacities and analytical prowess.
This formal examination, often referred to as the critical thinking assessment, is a benchmark for those aiming to demonstrate their proficiency in discernment and problem-solving.
In addition, this evaluative tool meticulously gauges a range of skills, including logical reasoning, analytical thinking, and the ability to evaluate and synthesize information.
This article will embark on an exploration of the Critical Thinking Test, elucidating its intricacies and elucidating its paramount importance. We will dissect the essential skills it measures and clarify its significance in gauging one's intellectual aptitude.
We will examine examples of critical thinking questions, illuminating the challenging scenarios that candidates encounter prompting them to navigate the complexities of thought with finesse.
Critical Thinking Practice Test
Before going ahead to take the critical thinking test, let's delve into the realm of preparation. This segment serves as a crucible for honing the skills assessed in the actual examination, offering candidates a chance to refine their analytical blades before facing the real challenge. Here are some skills that will help you with the critical thinking assessment: Logical Reasoning: The practice test meticulously evaluates your ability to deduce conclusions from given information, assess the validity of arguments, and recognize patterns in logic. Analytical Thinking: Prepare to dissect complex scenarios, identify key components, and synthesize information to draw insightful conclusions—a fundamental aspect of the critical thinking assessment. Problem-Solving Proficiency: Navigate through intricate problems that mirror real-world challenges, honing your capacity to approach issues systematically and derive effective solutions. What to Expect: The Critical Thinking Practice Test is crafted to mirror the format and complexity of the actual examination. Expect a series of scenarios, each accompanied by a set of questions that demand thoughtful analysis and logical deduction. These scenarios span diverse fields, from business and science to everyday scenarios, ensuring a comprehensive evaluation of your critical thinking skills. Examples of Critical Thinking Questions Scenario: In a business context, analyze the potential impacts of a proposed strategy on both short-term profitability and long-term sustainability. Question: What factors would you consider in determining the viability of the proposed strategy, and how might it affect the company's overall success? Scenario: Evaluate conflicting scientific studies on a pressing environmental issue.
Question: Identify the key methodologies and data points in each study. How would you reconcile the disparities to form an informed, unbiased conclusion?
Why Practice Matters
Engaging in the Critical Thinking Practice Test familiarizes you with the test format and cultivates a mindset geared towards agile and astute reasoning. This preparatory phase allows you to refine your cognitive toolkit, ensuring you approach the assessment with confidence and finesse.
We'll navigate through specific examples as we proceed, offering insights into effective strategies for tackling critical thinking questions. Prepare to embark on a journey of intellectual sharpening, where each practice question refines your analytical prowess for the challenges ahead.

This is a three question practice in-tray exercise.
If you get a question wrong, make sure you find out why and learn how to answer this type of question in the future.
Take a Free Practice In-Tray Exercise

Talent Q is a popular psychometric test provider used by employers worldwide to identify and develop top talent.
There are several test types published under the Talent Q name including numerical, verbal and logical reasoning, error checking, situational judgement tests and personality questionnaires.
Talent Q tests can be blended into custom assessments to suit a wide range of roles at varying levels of employment.
What Is the Talent Q Test?
The Talent Q test , or Talent Q assessment, is a term that refers to a collection of aptitude, performance and personality tests administered by the global consulting group, Korn Ferry.
Talent Q tests span five areas of assessment:
- Cognitive ability
- Competencies
- Situational judgement
- Motivations
They are commonly used to evaluate a candidate’s skills and job readiness in the early stages of recruitment.
Employers may also use a Talent Q psychometric test when looking to promote internally or to inform employee development.
Talent Q tests are increasingly popular with a range of employers because of the way they are designed, offering test flexibility and a reliable indicator of an applicant’s full potential.
Which Companies Use the Talent Q Test?
Talent Q tests are used by an increasing number of organizations due to their accuracy, versatility and reliability. Some of the major global employers known to make use of the Talent Q test library include:
- Virgin Atlantic
- Royal Mail Group
- Lloyds Banking Group
- AstraZeneca

What Is the PwC Assessment Test?
When you apply for a coveted role at PwC, you will be asked to undertake a PwC assessment test as part of the recruitment process.
The PwC test are used to evaluate candidates on measurable skills, abilities, aptitudes and personality traits that are needed for success in the type (and level) of the role that you have applied for.
PwC is one of the Big Four accounting firms globally, and from their headquarters in London, England, they have offices in 157 countries, a presence in 742 locations, and they currently employ nearly 300,000 staff.
With roles available in various departments, from consulting to legal, operations to audit, and tax to technology, competition for advertised jobs is fierce, and the PwC assessments are recognised as being particularly challenging to help narrow down the candidate pool to those applicants who really have what it takes to be successful.
In fact, less than 50% of candidates will advance past the screening tests as the benchmark for a passing mark is very high.

'AON assessments' are the new name for the cut-e tests, and they are often used as pre-employment evaluations for different skills, aptitudes, competencies and personality traits for various roles across different industries.
The AON assessments are characterized by being very short online assessment tests, and in many cases, candidates will be required to take more than one as part of a recruitment process.
With so much content to cover in all the different types of tests, it can be difficult to know what to expect from the AON assessments, which is where this guide will help.
Below you will learn more about why AON assessments are used and which companies use them as part of their hiring process.
We will discuss some of the features that the assessments have in common, as well as the most popular tests that are used by recruiters.
There will be some example questions with answers to get you familiar with the type of content you will be facing in certain tests and some helpful information regarding the way the AON assessments are scored and how you can give yourself the best chance to demonstrate that you have what it takes to be successful.
What Is the AON Assessment Test?
AON is well-known as a global financial services firm, and they acquired the cut-e testing battery so that they can provide top-of-the-range candidate evaluation and personnel development tools based on a scientific framework and testing methodology.

The CogAT Grade 4 test is used to understand a student’s thinking and reasoning abilities. It is not a test of learned knowledge; rather, it is a diagnosis of how they learn.
The 4th Grade CogAT test measures reasoning ability in three key areas: verbal, non-verbal and quantitative.
The assessment is often used to identify students for gifted and talented education programs.
If your child has been selected to sit the CogAT test in 4th grade, it can be confusing to know what to do to help.
This article will help you to answer these questions:
- What is the CogAT test ?
- What skills is the test assessing?
- What is the format of the test?
- How can I help my child prepare?
- What skills can we practice?
- What is the scoring system?

When applying for a job application, you may find that, along with providing your CV and attending an interview, you will be required to complete an IKM assessment .
This assessment will serve as a supplement to your overall application. So, you must understand what it entails and how it contributes to your application.
This article will explain the specifics of the IKM assessment, why it is important and how you can prepare for it.
What Is IKM?
The International Knowledge Measurement Service (IKM) offers organizations various assessments for employees and candidates among various career disciplines.
Among other things, this assessment ensures that employees hold the necessary requirements to go through the organization’s recruitment process.
Employee candidates will take the IKM assessment online remotely (self-supervised) or with client-side supervision from the organization.
The IKM assessment uses adaptive testing, meaning the difficulty of questions is dynamically selected based on the employee candidate’s previous answers .
This ensures that the assessment questions are neither too difficult nor too easy, greatly reducing the testing time.

The CAT4 Level D is a cognitive ability test used by a number of UK secondary schools. Typically taken by pupils in Year 7, the CAT4 Level D tests a child’s verbal, non-verbal, quantitative and spatial reasoning skills to give an accurate picture of their learning potential.

The Delta Assessment Test is a group of online tests that forms part of the Delta Airlines hiring process.
If you are applying for job roles with Delta, you may be asked to complete one or more of the Delta Assessment Tests.
Your test results will help the hiring manager to decide whether you are suitable for the job role you have applied for.
The tests you are asked to take will vary according to the job role.

The Deloitte immersive online assessment is a psychometric aptitude-style test. It is used to identify a candidate’s strengths and weaknesses.
Questions vary but are likely to include situational judgment style questions that link to the roles at Deloitte.
Candidates are also tested on their numerical reasoning and presented with personality questions.

Competition is tough for jobs on the Crossover recruitment platform.
There are thousands of applicants for each role, and only the top 1% are offered a contract .
After a successful initial application, the first step is taking the Crossover Cognitive Aptitude Test (CCAT).
To help you prepare, this article covers the following:
- How Crossover works
- The recruitment process
- What to expect in the CCAT
- The scoring system
- Tips to help you prepare

The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) is the domestic intelligence and security service of the USA.
The agency investigates serious offenses such as terrorism, public corruption, cyber-attacks, and violent and organized crime.
The FBI's mission is to protect the American people and uphold the American Constitution.
The FBI has over 37,000 employees across hundreds of locations in the US.
To work for the FBI, you must fulfill specific criteria which include:
- Be a US citizen
- Be able to obtain an FBI Top Secret clearance
- Pass the FBI polygraph examination
- Pass the FBI Phase 1 test
- Adhere to the FBI drug policy
Roles available at the FBI include computer scientists, nurses, engineers, technicians, contract specialists, and of course, police officers.
It is important to note that the recruitment process can take over one year, so you must be willing to wait several months for the chance of your dream role.
In this FBI Phase 1 test prep guide, we will delve into the role of FBI special agents – upholders of the law that seek out cybercrime and infiltrate organized attacks such as terrorism.
When applying to be a special agent, you are required to take the FBI Phase 1 test .
What Is the FBI Phase 1 Test?
The FBI Phase 1 test is an assessment that evaluates your personality and suitability for a role as a Special Agent at the FBI.
The test is conducted online and is split into five parts.
As the second stage of the process, the FBI Phase 1 test is done after the successful completion of a written application.
The test is designed to assess several skills and qualities that are required for a role as an FBI special agent.
These include critical thinking, logical reasoning and personality. The test will also assess your background experiences.
Your answers are then compared to the benchmark of what is suitable for an FBI agent.
The five sections of the FBI Phase 1 test are:
- Logical reasoning
- Figural reasoning
- Personality Test
- Preferences and interests
- Situational responses
The assessment takes three hours to complete.
When applying for roles at the FBI, long waiting times are typical. The full special agent recruitment process can take over 20 months to complete.
If this is your dream job, it is certainly worth the wait as it is one of the most attractive career paths within any government agency.
To reflect this, the recruitment process is challenging and designed to reduce the number of candidates who could move on to the next stage.
This ensures that only the very best move through the application phases. In fact, only 30% of candidates can pass the FBI Phase 1 test.
You may have taken a personality test before, but the FBI Phase 1 test questions are framed and marked in a different way to other assessments.
Therefore, you should ensure you use FBI Phase 1 test practice questions and prepare in advance of the test.
It can be hard to plan for, but this is essential to get into the top 30% of successful candidates.
If you pass the FBI Phase 1 test, you will undergo background checks and receive an invitation to a regional meet-and-greet interview.

The main purpose of the CogAT Test grade 3 is to find out if a third grader is showing signs of being very smart.
Most of the questions on the test are about verbal, numerical and non-verbal reasoning. It's meant to show how a child might compare to other kids his or her own age. The CogAT grade 3 test can also be used to make individualized learning plans for kids.
The CogAT (Cognitive Abilities Test) is a standardized test used to measure children's cognitive abilities in the 3rd grade – age 9.
This test assesses a range of cognitive abilities, including verbal, quantitative and nonverbal reasoning. The CogAT is often used to identify gifted children and help educators develop appropriate educational plans.
This article will give insights and tips into how your child could pass the CogAT Test for 3rd grade students.

The MAP Test 2nd grade is a computerized test taken by children in the 2nd grade. It is designed to evaluate what the children already know and what they are ready to learn.
The test includes three sections:
Schools may not administer all three sections and may instead focus on one or two sections to measure pupils’ progress in those subjects.

The NEO Personality Inventory is a psychometric tool used to evaluate personality traits.
It is acknowledged globally and is used by recruiters and employers before hiring and, more broadly, to evaluate career potential.
The NEO Personality Inventory test is heavily associated with the 'Five-Factor Model' (which you may also know as the 'Big Five Personality Test') to identify personality traits.
It is widely believed that each person's personality can be broken down into five main categories. The NEO PI personality test looks at each of these five categories separately to create an understanding of who you are.
In this article, we'll look at the NEO PI test, why employers use it, and what you could expect if invited to participate in a NEO Personality Inventory test.

The Air Traffic Controller (ATC) Test, also known as the Air Traffic Skills Assessment (ATSA) is an exam used as part of the air traffic controller hiring process. It is a challenging assessment consisting of seven subtests designed to evaluate an applicant's aptitude for the role.
Becoming an air traffic controller is a challenging and rewarding career that requires extensive training. The Air Traffic Controller Test (previously known as the Air Traffic Selection and Training (AT-SAT) exam) is an important part of the selection process.
The Air Traffic Skills Assessment (ATSA) measures a candidate's ability to handle the demands of the job.
In this article, you’ll find example questions, a guide and tips for preparing for the ATSA exam.
This article relates specifically to the ATC test used in the US. Candidates in other countries may be expected to take a different version of the test.

What is the CliftonStrengths test? This online assessment analyzes your personality and strengths for personal and professional development. You can purchase the basic test from Gallup for $19.99 and get a basic understanding of your top five personality themes. Or take the comprehensive version for $59.99 and receive a report that ranks all 34 themes and highlights your areas of excellence as well as your blind spots.
When applying for a job, you may find that the recruitment process consists of many different steps. There is the initial application form to start and usually an interview to finish. In the middle, there may be an assessment – an aptitude, intelligence or personality test.
The CliftonStrengths test is one assessment used by employers during the onboarding process. It was previously known as the CliftonStrengthsFinder.
In this guide, you will learn about the CliftonStrengths personality test and how it is used in recruitment.

The police psychological exam is a crucial part of the hiring process for law enforcement agencies. It is a personality test that confirms how suitable an applicant is for working in the police. The police psych test is used by most law enforcement agencies across the United States, although key details may differ from state to state.
What Is the Police Psychological Exam?
The police psychological exam is a series of tests and assessments administered to individuals who are seeking to become police officers.
The purpose of the exam is to evaluate a candidate's psychological fitness for the job and identify any potential psychological issues that may interfere with the candidate's ability to perform police work.

In this comprehensive guide , you’ll discover everything you need to know about the Capital One assessment and interview process.
These are designed to help the company select the best candidates for its team. To increase your chance of getting hired, it's important to be prepared.
Find out what to expect, how to prepare and the skills and qualities Capital One hiring managers are looking for in a candidate.
What Is the Capital One Assessment Test?
Capital One is an established financial services company with a focus on technology and innovation.
To become an employee, or ‘associate’, at Capital One you'll need to pass a series of online assessments and interviews .
The Capital One hiring process is as follows:

CogAT stands for Cognitive Abilities Test. These tests are normally administered by a classroom teacher or instructor, although some schools employ a specialist or test proctor to administer the test.
Many parents are interested in learning more about helping their children to succeed academically.
Achieving a high CogAT score could mean your child is eligible to join gifted or talented programs designed to enhance their development and learning.
In other schools, it is used as a tool to identify a pupil’s individual strengths or predict their future academic performance.
The CogAT test for 2nd grade is a cognitive ability test aimed at children around the age of eight years old.
It is often used as a pre-admission exam by gifted and talented schools and programs. It is designed to evaluate pupils’ cognitive abilities, including basic linguistic and math skills.
The test is made up of three sections or batteries:
- Non-verbal battery
- Verbal battery
- Quantitative battery
On the CogAT test 2nd grade, candidates are required to read the test questions instead of listening to the questions being read by the test proctor.
If you are looking for ideas on how to prepare your child for the CogAT test 2nd grade, read on to learn more.
What Is CogAT Test 2nd Grade?
The CogAT (Cognitive Abilities Test) was developed by Riverside Publishing, which is part of Houghton Mifflin Harcourt.
It is designed to assess problem-solving and reasoning skills in the following areas:
- Quantitative
Research has shown that high levels of ability in these three areas is linked to academic success.
If your child is considered potentially talented or gifted, they may be asked to sit a CogAT as part of the program entrance process.
Different CogAT tests are available for different age groups, from Kindergarten (K) up to grade 12.
In this article, you can find more information on the CogAT test 2nd grade. The CogAT test is used by schools across the US to help them identify exceptionally gifted pupils.
Each of the test levels corresponds to the age of the pupil sitting the test. For example, if your child is in grade 6 (aged 12), they will be sitting the Level 12 version of the test. Occasionally, schools may choose to administer a higher level CogAT to talented or gifted pupils; however, this is unusual.
Second grade pupils being considered for gifted programs will usually sit the CogAT Level 8 test. This test is made up of 154 questions and takes 122 minutes to complete.

Many schools use the CogAT Test 6th Grade to assess the non-verbal, verbal and quantitative abilities of sixth-grade students.
The Level 12 CogAT test is a useful tool for checking a student’s individual academic strengths and weaknesses. It can also be used as a screening assessment for entry into the gifted and talented program.
What Is the CogAT Test 6th Grade?
'CogAT' is an acronym for Cognitive Aptitude Test .
CogAT tests are usually administered at school by a teacher or instructor, although some schools employ test proctors and specialists to administer the tests.
This guide is designed to support you and your child through the CogAT Test 6th Grade. You can use it to find out what to expect from the test and tips on how to prepare for it.
We have also included information on the purpose of the test and how to interpret your child’s results.

The Procter and Gamble Assessment Test describes a series of pre-employment screening tests used by Procter and Gamble (P&G).
If you have applied for a job at P&G, you will be expected to sit these tests as part of the hiring process.
Each of the different tests is designed to assess a specific aptitude that is required for a job role at P&G.
In this article, you can learn more about the different tests used by Procter and Gamble. We have also provided tips on how to prepare for the assessments.

This guide includes useful tips and Renaissance Star testing sample questions to help students prepare for the test and feel confident on test day.
You can find detailed information on interpreting and understanding your Renaissance Star Test scores in our dedicated article .

What Is the 6th Grade MAP Test?
The MAP Growth test system was created by educators from Oregon and Washington who established the Northwest Evaluation Association (NWEA) back in 1973.
Their goal was to create an assessment that could accurately measure and track academic progress in children to ensure they graduated high school with all the essential skills and knowledge they required.
In 2000, the first MAP Growth Test was published.
The test is administered in all grades and is based on a set of learning principles known as the Common Core Principles .

The CCAT test grade 3 is a standardized assessment administered to grade 3 students in Canada.
It measures verbal, quantitative and non-verbal reasoning skills and is used to identify a student's learning potential, typically for admission to gifted educational programs.
The CCAT test grade 3 is an assessment commonly used by schools in Canada.
If you’re the parent or guardian of a child preparing for the test, this CCAT grade 3 guide will tell you everything you need to know.
What Is the CCAT Test Grade 3?
The CCAT test (Canadian Cognitive Abilities Test) is a standardized assessment administered to students in grade levels K-12 in the Canadian educational system.
Rather than a measure of academic achievement, the test assesses a child's ability to learn, reason, and problem-solve.
The Independent School Entrance Examination (ISEE) test is used by many independent and magnet schools in the US and overseas as an admission test for children across the entire school age range, but more commonly from year five upwards.
It assesses a child’s academic levels of reasoning across math and literacy in comparison to children of the same age, the norm for that school grade and other applicants to the school.
Created and administered by the Educational Records Bureau (ERB), the ISEE test is available to be taken online or in a pen and paper format.
What Are the ISEE Levels?
There are four levels of the ISEE test.
- ISEE primary for entry into years two to four
- ISEE lower level for entry into years five to six
- ISEE middle level for entry into years seven to eight
- ISEE upper level for entry into years nine to 12
Each level of the ISEE test is created to be relevant to a specific school age group, increasing in complexity with each year and level.

An employer’s recruitment process can include a wide range of assessments and interviews for the candidate to take that indicate to the employer how an individual might fare in the job.
One common way to measure job performance though is by getting candidates to take the PI Cognitive Assessment, which measures mental ability and critical thinking skills.
This article will look in detail at the assessment, its format, who uses it, example questions and PI Cognitive Assessment tips on how to be successful when taking it.

The Raven’s Progressive Matrices is a test that is often used as part of the recruitment process for high-level management and analytical roles.
In this article, you will learn more about the test, its history and background, as well as the different types of tests that are available and what you can expect if you are going to be taking the test.
You will also find some example questions that you can expect to see in each type of test and get helpful pointers that you can use to prepare and do well in the assessment.

If you are applying for a role with the United States Postal Service (USPS) , you will usually be asked to complete at least one of four 477 Virtual Entry Assessments as part of the recruitment process.
These exams are used to evaluate various skills, aptitudes, personality traits and work preferences, which can show whether you have what it takes to be successful in the role in the future.
The USPS 477 Exam is sometimes referred to as the CS VEA, which relates to customer service.

An iReady level score of 3.00 or over means the student is working at or above the level required to meet the standard for their grade.
The level score is calculated in line with expectations when the test was administered, not in comparison to the expected score by the end of the school year.
What Are the iReady Diagnostic Scores?
The iReady diagnostic test is administered to US school children in grades K to eight.
The purpose of this school assessment test is to help parents and teachers check a student’s academic process at the beginning, middle and end of each school year.
It is a computer-adaptive test, which means the questions are adjusted to become more difficult if a series of correct answers is given.
As a result, the test is designed to challenge the skill level of the student sitting the test, as well as assess their strengths and opportunities for growth.
If a student answers a few questions in a row incorrectly, the questions that follow will be easier.
Many people find i-Ready Diagnostic scores difficult to interpret.
As a child progresses through each academic year and moves up the year groups, their expected score will change.
The average score increases year on year, too.
In this article, you can learn more about the different types of iReady diagnostic scores, how these scores are displayed, and how to interpret them to better understand a student’s iReady test performance.

There are two types of HESI Exam:
- The Admissions (A2) test
- The Exit exam
The minimum passing score for the Admissions test is usually between 75 and 80 for each section, although this varies between schools.
The composite score range for the Admissions (A2) test is 750 to 900, with 900 being the maximum possible score.
The HESI Exit Exam score ranges between 0 to 1,500. 850 is considered to be an acceptable score, although HESI recommends a minimum score of 900.
If you want to sit your NCLEX licensing exam, you will need to achieve a score of at least 850 on the HESI Exit Exam.
HESI is an acronym for Health Education Systems Incorporated .
As a company, HESI administers exams and provides study material to help prepare students for the NCLEX professional licensure exam.
If you want to work as a nurse in the US, many nursing and healthcare programs use HESI tests to screen prospective students and determine suitability and readiness for specific study routes.
In this article, you can learn more about the HESI score ranges and passing scores required for each of these tests and what impact your HESI results may have on acceptance into your preferred nursing program.
The Mettl tests are developed by the world's largest assessment provider, Mercer Mettl.
The tests have been designed to analyze various competencies, including verbal, logical and numerical reasoning.
Alongside, the Mettl assessments evaluate candidates' personalities and working styles, establishing whether they are an accurate fit for the role and the broader company.
The Mettl tests are a comprehensive recruitment tool provided by Mercer Mettl – the world's largest assessment provider.
Moreover, the Mettl tests are designed to assess various skills, including numerical , verbal and abstract reasoning.
The assessments are also constructed to understand candidates' behaviors and personality types.
This guide explains everything you need to know about the Mettl test, including tips on how to pass the test in 2024.
What Is the Mettl Test?
As mentioned, the Mettl test is a comprehensive recruitment tool designed to test a range of skills.
It allows employers to ensure they recruit the most suitable candidates for the role.

The MAP Test Grade 7 tests students’ proficiency in mathematics, reading and language usage.
Developed by the Northwest Evaluation Association (NWEA), it measures individual growth over time, adapting question difficulty based on responses.
This online test lasts around two to three hours, and the results are used to inform teaching or gauge students' ability levels.
Scoring is based on the RIT (Rasch Unit) scale, indicating a student's instructional level and growth potential in each subject area.
MAP Grade 7 Sample Question

The CogAT Kindergarten Test is an assessment designed to measure a child's abilities in various cognitive areas.
It plays a critical role in identifying a child's strengths and weaknesses and determining their readiness for advanced academic programs.
In this comprehensive study guide for 2024, you will explore the purpose, format, and structure of the CogAT Kindergarten Test.
Additionally, you will get valuable insights on how to prepare your child for the test, sample questions to familiarize yourself with the test content, strategies for success and answers to frequently asked questions.
Understanding the CogAT Kindergarten Test: Purpose, Format, and Structure
The purpose of the CogAT Kindergarten Test is to assess a child's cognitive abilities in areas such as verbal, quantitative, and nonverbal reasoning.
By evaluating these different components, the test provides educators and parents with valuable information about a child's potential and can help guide educational decisions.

Administered at college and university level, the Accuplacer test is used by some educational institutions to determine how prepared a student is for the next steps in their academic career.
This guide looks specifically at Accuplacer test scores – how they are awarded and what they mean – so you can better understand how your Accuplacer score might impact your learning experience.
Accuplacer test scores are a set of metrics that evaluate a student's knowledge and skills in specific subject areas including reading, writing and math.

The i-Ready Diagnostic Test is an internet-based adaptive diagnostic test linked to the i-Ready educational learning program.
Students from kindergarten to grade 12 take the test three times each year. The test is divided into two subtests:
i-Ready test results are used to help teaching staff create a personalized learning plan according to a student’s strengths and weaknesses.
What Is the i-Ready Diagnostic Test?
The i-Ready Diagnostic Test is a computer-adaptive, untimed assessment for students between grades K and 12.
Administered by Curriculum Associates , teachers can use it to monitor a student’s ability and progress throughout the school year.
In most cases, the i-Ready Diagnostic Test is administered three times each year. It is split into two subtests: math and reading.

The Cognitive Abilities Test (CogAT) 5th Grade Level is a crucial assessment tool for students between 10 and 11 years old.
Designed to measure verbal, nonverbal, and quantitative abilities, this standardized test plays a pivotal role in identifying students for gifted programs.
In this article, you’ll learn what the CogAT 5th grade test is, which subjects are tested, along with example questions and how best to prepare.

What Is the CogAT 5 Grade Test?
The Cognitive Abilities Test (CogAT) is a widely used standardized test designed to assess your child’s cognitive abilities in various areas.
The CogAT 5th Grade Level is specifically tailored for students in the 5th grade and measures their abilities in three main cognitive areas:
- Quantitative Reasoning
- Non-Verbal Reasoning

The State of Texas Assessments of Academic Readiness (STAAR) test is a standardized assessment issued to public school students in Texas in grades 3 to 12.
Below you’ll find a range of STAAR test practice questions to help you prepare – whether you’re a parent coaching a child through their exam prep or a high school student revising for a test of your own.
For more info on the STAAR Test, read our dedicated article.

The 7 best rated resume writing services:
- TopResume – Best for personalized expertise
- TopStack Resume – Best for navigating careers
- ResumeCompanion – Best for affordable excellence
- Resumeble – Best for ATS-optimized resumes
- ResumeSpice – Best for executive service
- Craft Resumes – Best for a quick turnaround
- Resume.com – Best for those on a budget

The Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children (WISC-V) is a commonly used assessment for judging a child's intelligence. More than that, it can help to understand their reasoning and thinking abilities to support their development.
Here’s everything you need to know about this test.
The Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children - Fifth Edition (WISC-V) is an individually administered and extensive evaluation tool used to assess children's reasoning and general thinking abilities.
It's typically given to children between ages 6 and 16.
After completing a test, children are awarded a Full-Scale Intelligence Quotient (IQ) score, along with age-based scores and rankings in several cognitive function fields.
Here we’ll provide an all-around study guide for parents whose children are required or scheduled to take the WISC-V test.
We’ll also include a comprehensive explanation of how it is constructed, its key features, tips for preparing, and a few example questions.
Let’s take a look!

The STAR assessments utilize a scoring system comprising scaled scores ranging from 0 to 1,400.
These scores reflect a student's proficiency level in subjects such as reading and math.
Benchmark categories provide descriptive labels for performance levels, while percentile rank compares a student's performance to a national reference group.
Additionally, grade equivalent scores and domain scores offer insights into grade-level equivalence and specific skill areas.
The STAR Assessment can play a crucial role in evaluating your child’s academic ability and guiding educational strategies.
Understanding its scoring system, test format and significance is important for parents and educators alike.
This article aims to provide comprehensive insights into the STAR Assessment, including its purpose, score interpretation and effective strategies to help children excel in these standardized tests.

The CogAT raw score represents how many questions were answered correctly on the CogAT test. This information is used to create the Universal Scale Score (between 100 and 150), which you will see on your child’s CogAT score report.
Here is an image of a typical score report:

With the MAP Growth Test used in many schools across the United States, MAP (Measures of Academic Progress) scores are an important part of your child’s life.
The MAP testing scores chart a student’s academic growth in a way that highlights areas of excellence and improvement.
It is essential that you understand how NWEA MAP scores are calculated so you can best support your child throughout their learning journey.
This guide will explain how to find and improve your child’s NWEA Map Scores.
The main three sections for the Upper and Middle level tests have a maximum score of 800. They have a total scaled score that ranges between 1,500 to 2,400.
Navigating the SSAT involves understanding its scoring system.
In this guide, you can explore the SSAT Score Chart and understand score ranges and percentile ranking and how they matter in private school admissions.
It's a comprehensive resource for decoding SSAT scores and making informed decisions about your child’s education.
What Is the SSAT Test?
The SSAT stands for the Secondary School Admission Test. The SSAT was first administered in 1957.
It is a standardized test designed for students seeking admission to private middle and high schools.
The primary purpose of the SSAT is to assess the skills and knowledge of students applying to independent or private schools.
It aims to provide an accurate measure of a student's academic abilities and readiness for a challenging curriculum.

The Microsoft Codility Test evaluates coding skills and algorithmic thinking.
Designed to streamline Microsoft’s recruitment process, the Microsoft Codility Test assesses candidates' ability to solve real-world problems efficiently.
Candidates can prepare using coding practice platforms and mastering programming languages. It's an integral tool in selecting skilled software engineers for Microsoft's diverse roles.

The Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium Test, known as the SBAC test, is a standardized assessment of English and math used by schools in participating states.
Administered to students in grades K to 12, it measures grade level proficiency and academic progress through computer-adaptive testing and performance tasks.
The Smarter Balanced Test is an educational tool developed and administered by the Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium (SBAC), hence the abbreviation SBAC test.
In this article we explore what the test involves, what the results mean and how to help a student prepare for their SBAC assessment.
What Is the SBAC Test?
The SBAC assessment is a set of standardized tests that evaluate how well students are performing in the subjects of English Language Arts (ELA) and mathematics.
These assessments are taken by students ranging from elementary school to high school in multiple states across the US.
The tests are developed and managed by the Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium (SBAC), a collaborative group of states working together.

FireTEAM Test Prep: Top Tips:
- Master time management
- Brush up on basic concepts
- Diversify your reading
- Play observational and memory games
- Assess your communication style
- Prioritize rest and sleep
If you're considering a career in firefighting, taking the FireTEAM test is a pivotal step that can open doors to various fire departments across the US.
This article covers everything you need to know to put in a strong performance, including an overview of its format, practice questions and FireTEAM test tips to help you create an effective study plan.
A career in the fire service is a challenging – but extremely rewarding – journey. Such an important, high-pressure job requires a high level of physical, mental and emotional skills.
As well as the necessary personality traits, you generally need a high school diploma or GED. If you have a college degree, you have a better chance of securing a role in the fire service.
You will also be required to take a series of assessments that evaluate your physical and mental strength. One of the assessments used by Californian fire departments is the FCTC Written Test. To become a firefighter in California, you must pass this entry-level test.
In this guide, we will explore what the FCTC Written Test includes and how you can prepare for success.

To successfully enlist in the US Marine Corps, certain standards must be met. Marines require both physical and mental strength as well as discipline, determination and the ability to overcome obstacles. This is sometimes referred to as the ‘Marine Mindset’.
One of the ways candidates who wish to enlist will be assessed is by taking a test known as the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB).
A good score on the test suggests that a candidate possesses the mental skillset to be successful in the military.
Marines need to be able to make quick, accurate decisions and adapt to and overcome threats and obstacles on the battlefield.

The PiCAT test is a commonly used assessment tool for those applying to military positions, such as those in the US Navy or the US Army.
This article explores the PiCAT test in more detail. We look at the test format to familiarize individuals with what the Navy PiCAT and Army PiCAT test covers.
Preparation is vital to performing to the best of your ability in the PiCAT test.
The article includes PiCAT practice test questions, answers to help you prepare, and tips to give you the best opportunity to approach the test positively.

The SHL Deductive Reasoning Test is an assessment employers use to evaluate candidates' logical thinking skills.
It presents logical arguments and requires candidates to determine if conclusions follow from given premises.
Candidates can prepare by practicing tests, honing logical reasoning skills, and familiarizing themselves with formal logic rules to excel in this assessment.
What Is the SHL Deductive Reasoning Test?
The SHL Deductive Reasoning Test is a cognitive assessment tool used in the recruitment and selection processes for many roles in several industries.
SHL (Saville and Holdsworth Ltd.) is a well-known company specializing in psychometric assessments and organizational talent measurement solutions.
SHL assessment tools are used in the early stages of the recruitment process, enabling recruiters to identify candidates with the specific aptitudes needed for success in a role in an organization.
Mastering the Pipefitter Test is crucial for those entering the field.
This guide provides valuable insights, a pipefitter sample test and strategies to conquer the examination.
Discover expert tips to excel in your pipefitting career by navigating the challenges of this important assessment.
What Is the Pipefitter Assessment Test?
The Pipefitter test is an important evaluation tool for individuals aspiring to secure roles as pipefitters in the construction and industrial sectors.
Qualifications and certifications necessary for such positions can vary by state. This makes the pipefitter assessment test a valuable method of demonstrating skills and knowledge.
The National Center for Construction Education and Research (NCCER) administers the most popular pipefitter assessment test, designed to assess the potential skills of candidates.
It covers the principles related to the installation and maintenance of both high and low-pressure pipe systems.
In addition, it focuses on how these are used across various sectors, including manufacturing, electricity generation and climate control systems in buildings.

The HSBC Online Immersive Assessment contains 38 questions over five subtests. The test includes a combination of behavioural questions and cognitive ability exercises.
It is an untimed assessment, but most candidates can answer all test questions within 50 minutes.
Some people find the test difficult, but adequate preparation will stand you in good stead to pass the assessment.
What Is the HSBC Hiring Process Like?
HSBC is a major global bank and financial institution. It offers services via three global businesses and serves millions of customers daily.
The hiring process at HSBC comprises four key stages:
- Initial Screening and Application
- HSBC Online Immersive Assessment
- Online Job Simulation Assessment
What Is the Electronic Data Processing Test?
The Electronic Data Processing Test (EDPT) is a pre-employment test taken by military candidates who want to transfer to IT or computer programming roles within the Marine Corps or Air Force.
The EDPT test is one of the most challenging pre-employment tests currently on the market with a pass rate of around 10%.
It is 90 minutes long and has 120 multiple-choice questions. This means you have around 45 seconds to answer each question.

While the minimum ASVAB score varies between military branches, the minimum acceptable score is 31.
However, as the majority of candidates score between 30 and 70, you want to aim for a percentile rank of at least 60.
The ASVAB Test Score Report is a valuable document that provides detailed information about your aptitudes, skills, and qualifications for military service.
It includes Career Exploration Scores to guide career choices, individual scores on ASVAB subtests to assess specific abilities and the critical AFQT score that determines your eligibility for enlistment.
Understanding the information presented in this report is essential for making informed decisions about your military career options.
What Is in the ASVAB Test Score Report?
The ASVAB (Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery) Test Score Report provides a comprehensive overview of your performance on the ASVAB test, which is a critical step in the military enlistment process.
The report helps you and military recruiters assess your aptitudes, skills, and potential for various military occupations.
What Is the ACCUPLACER Reading Comprehension Test?
The Accuplacer Reading Comprehension test is part of a suite of assessments that are used to evaluate students prior to entry at college.
While the Accuplacer test battery is not used to determine whether a student will achieve a placement at college, the results are used to ensure that the student is studying at an appropriate level and is ready for education at this level.
Created by the College Board, which is a not-for-profit organization that is also responsible for creating assessments like the SATs, the Accuplacer tests are designed to offer better opportunities to students and make entry to top colleges accessible to all.

- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Photography
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- Auto Racing
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
What cognitive tests can show — and what they can’t
FILE - President Joe Biden, speaks during a presidential debate hosted by CNN with Republican presidential candidate former President Donald Trump, June 27, 2024, in Atlanta. Political opponents, armchair pundits and even nervous supporters are demanding that President Joe Biden undergo cognitive testing after his dismal debate performance – even though his physician says he gets, and passes, an annual neurologic exam. (AP Photo/Gerald Herbert, File)
The memorandum released by the White House from President Joe Biden’s physician Kevin C. O’Connor to White House press secretary Karine Jean-Pierre is photographed Monday, July 8, 2024, in Washington. Political opponents, armchair pundits and even nervous supporters are demanding that President Joe Biden undergo cognitive testing after his dismal debate performance – even though his physician says he gets, and passes, an annual neurologic exam. (AP Photo/Jon Elswick)
- Copy Link copied
WASHINGTON (AP) — It’s the new chant in Washington politics: “Get a cognitive test!”
Political opponents, armchair pundits and even nervous supporters are demanding that President Joe Biden undergo such testing after his dismal debate performance – even though his physician says he gets, and passes, an annual neurologic exam.
Former President Donald Trump, who’s only a few years younger, makes his own gaffes . He recently bragged about passing a 2018 cognitive test – while calling the doctor who administered it by the wrong name .
With all the concern, what can cognitive testing actually tell about a person’s brain health – and what can’t they answer? And presidents aside, does the average older adult need one?
What are cognitive tests?
They’re brief screening tools, a 10-minute series of questions to assess different brain functions. Two of the most common are called the MMSE, Mini-Mental State Exam, and the MoCA, Montreal Cognitive Assessment.
Recalling a list of five unrelated nouns or seeing how many words beginning with F you can say in a minute can assess short-term memory and language. Counting backward by 7s tests attention and concentration. Drawing a clock with the correct time is a clue to spatial awareness.
How reliable are cognitive screenings?
They don’t diagnose health problems. A bad score is just a red flag that indicates a need for further testing to see if there is a health problem and uncover what kind, said Dr. James Galvin, a neurologist at the University of Miami.
This article is part of AP’s Be Well coverage, focusing on wellness, fitness, diet and mental health. Read more Be Well.
A good score usually is good news. But the highly educated especially tend to be good test-takers even if cognitive trouble is starting to brew. So if someone scores OK yet they, a family member or the doctor sees some day-to-day concern, more testing still could be warranted.
“We simply use it as a benchmark to determine our suspicion level,” Galvin said.
When and how often should cognitive screenings be done?
“A screening test is exactly a snapshot in time. So it tells you in that moment how someone does on that test,” Galvin stressed. “It doesn’t tell you how a person is functioning in their everyday life.”
Simply reporting a concern is reason enough for a primary care doctor to perform one. But it’s also supposed to be part of the annual Medicare wellness visit for those 65 and older.
Galvin wouldn’t discuss Biden or Trump because he hasn’t examined them — but said that generally it’s a good idea for seniors to get checked yearly to spot changes. It’s much like how doctors don’t assume your blood pressure’s still fine, they measure it.
How is a cognitive test different from a neurologic exam?
Cognitive screenings are “pencil and paper tests” usually handled by primary care doctors, while neurologic exams generally are performed by a specialist, Galvin said.
It’s a very detailed physical exam. Doctors watch the patient’s speech patterns and behavior, test how key nerves are functioning, check reflexes that can signal brain diseases and assess muscle tone and function.
If either kind of test signals real cognitive concerns, the next step may be more intensive neuropsychological testing — an exam that often lasts up to three hours.
After an exhaustive interview of the patient and any accompanying family members, the neuropsychologist goes through tests and tasks designed to check specific brain functions – intelligence, memory, verbal ability, problem-solving and reasoning skills, visual and auditory responses, emotion and mood. They may use puzzles, objects to rearrange, or drawing and writing tests.
Blood tests and brain scans also may be ordered. Special types of PET scans can detect Alzheimer’s hallmark amyloid plaques and tau tangles in the brain. An MRI can detect past strokes, helpful in diagnosing vascular dementia.
How can you tell if cognitive concerns are a disease or just getting older?
“Age makes us do things a lot slower,” Galvin said. “We move slower. We think slower. But we’re still moving correctly and we’re still thinking correctly – it just takes us longer.”
Examples of slower cognitive “processing” might be difficulty remembering a name, numbers or specific details under pressure – but they come back to you later.
Galvin noted that sometimes, reversible health problems mimic cognitive trouble. For example, urinary tract infections are notorious for causing sudden confusion in older people. Certain medications affect memory, as can thyroid problems, depression, even poorly controlled diabetes.
Anyone who’s worried about their memory should talk to their doctor, or seek a specialist, “who can reassure you that everything’s OK or develop a treatment plan that’s specific for you,” he said.
The Associated Press Health and Science Department receives support from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute’s Science and Educational Media Group. The AP is solely responsible for all content.
What cognitive tests can show -- and what they can't
Washington politics is drawing attention to cognitive testing, a 10-minute series of questions to assess different brain function
WASHINGTON -- It’s the new chant in Washington politics: “Get a cognitive test!”
Political opponents, armchair pundits and even nervous supporters are demanding that President Joe Biden undergo such testing after his dismal debate performance – even though his physician says he gets, and passes, an annual neurologic exam.
Former President Donald Trump, who’s only a few years younger, makes his own gaffes . He recently bragged about passing a 2018 cognitive test – while calling the doctor who administered it by the wrong name .
With all the concern, what can cognitive testing actually tell about a person’s brain health – and what can’t they answer? And presidents aside, does the average older adult need one?
They’re brief screening tools, a 10-minute series of questions to assess different brain functions. Two of the most common are called the MMSE, Mini-Mental State Exam, and the MoCA, Montreal Cognitive Assessment.
Recalling a list of five unrelated nouns or seeing how many words beginning with F you can say in a minute can assess short-term memory and language. Counting backward by 7s tests attention and concentration. Drawing a clock with the correct time is a clue to spatial awareness.
They don’t diagnose health problems. A bad score is just a red flag that indicates a need for further testing to see if there is a health problem and uncover what kind, said Dr. James Galvin, a neurologist at the University of Miami.
A good score usually is good news. But the highly educated especially tend to be good test-takers even if cognitive trouble is starting to brew. So if someone scores OK yet they, a family member or the doctor sees some day-to-day concern, more testing still could be warranted.
“We simply use it as a benchmark to determine our suspicion level,” Galvin said.
“A screening test is exactly a snapshot in time. So it tells you in that moment how someone does on that test,” Galvin stressed. “It doesn’t tell you how a person is functioning in their everyday life.”
Simply reporting a concern is reason enough for a primary care doctor to perform one. But it’s also supposed to be part of the annual Medicare wellness visit for those 65 and older.
Galvin wouldn't discuss Biden or Trump because he hasn't examined them — but said that generally it's a good idea for seniors to get checked yearly to spot changes. It's much like how doctors don’t assume your blood pressure’s still fine, they measure it.
Cognitive screenings are “pencil and paper tests” usually handled by primary care doctors, while neurologic exams generally are performed by a specialist, Galvin said.
It’s a very detailed physical exam. Doctors watch the patient’s speech patterns and behavior, test how key nerves are functioning, check reflexes that can signal brain diseases and assess muscle tone and function.
If either kind of test signals real cognitive concerns, the next step may be more intensive neuropsychological testing — an exam that often lasts up to three hours.
After an exhaustive interview of the patient and any accompanying family members, the neuropsychologist goes through tests and tasks designed to check specific brain functions – intelligence, memory, verbal ability, problem-solving and reasoning skills, visual and auditory responses, emotion and mood. They may use puzzles, objects to rearrange, or drawing and writing tests.
Blood tests and brain scans also may be ordered. Special types of PET scans can detect Alzheimer’s hallmark amyloid plaques and tau tangles in the brain. An MRI can detect past strokes, helpful in diagnosing vascular dementia.
“Age makes us do things a lot slower,” Galvin said. “We move slower. We think slower. But we’re still moving correctly and we’re still thinking correctly – it just takes us longer.”
Examples of slower cognitive “processing” might be difficulty remembering a name, numbers or specific details under pressure – but they come back to you later.
Galvin noted that sometimes, reversible health problems mimic cognitive trouble. For example, urinary tract infections are notorious for causing sudden confusion in older people. Certain medications affect memory, as can thyroid problems, depression, even poorly controlled diabetes.
Anyone who's worried about their memory should talk to their doctor, or seek a specialist, “who can reassure you that everything's OK or develop a treatment plan that's specific for you,” he said.
The Associated Press Health and Science Department receives support from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute’s Science and Educational Media Group. The AP is solely responsible for all content.
Trending Reader Picks

New report critical of UK trans care study
- Jul 9, 4:47 PM

Voice box transplant helped a cancer patient speak
- Jul 9, 7:00 AM

Finnish lawmakers approve controversial law to turn away migrants at border with Russia
- Jul 12, 8:23 AM

Pro-Trump group seeks removal from Project 2025
- Jul 12, 5:50 PM

Holocaust orphan meets family after DNA tests
- Jul 11, 12:46 PM
ABC News Live
24/7 coverage of breaking news and live events

- support@iqtests.com
- 866-483-2010
What Does An IQ Of 125 Mean

A 125 IQ score is above average. But what does it mean for you? This article explains the significance of a 125 IQ score, how it compares to other scores, and the intellectual abilities it reflects.
Key Takeaways
- An IQ score of 125 is categorized as ‘above average’ or ‘bright’, placing individuals well above the average population and indicating superior problem-solving, learning, and reasoning abilities.
- While an IQ of 125 suggests strong cognitive abilities such as advanced analytical skills, rapid comprehension, robust memory, and creativity, it does not encompass all aspects of intelligence such as emotional intelligence, creativity, or practical skills.
- IQ tests, including the Wechsler Intelligence Scales and Stanford-Binet Intelligence Scale, measure specific cognitive abilities and offer a standardized approach, but they have limitations and may not fully capture an individual’s overall intelligence or potential for success.
What Does a 125 IQ Score Mean for Your Intelligence?
An IQ score of 125 is a significant indicator of above-average intellectual abilities and potential. Grasping the meaning of an IQ score of 125 requires an understanding of what IQ represents and how it is measured. IQ, or Intelligence Quotient, is a numerical representation of a person’s cognitive abilities and potential. It’s designed to provide an estimate of an individual’s intellectual capabilities compared to the general population.
The average IQ score typically falls within the range of 85 to 115. This range encompasses about 68% of the population, representing what is considered “average” intelligence. When we look at an IQ score of 125, we’re venturing into territory that surpasses this average range, indicating enhanced cognitive abilities.
IQ scores are always interpreted relative to the average performance of the population, taking into account the iq range. This comparative approach allows us to understand where an individual stands in terms of their cognitive abilities relative to others. An IQ of 125 places a person well above the average, suggesting superior problem-solving skills, faster learning capabilities, and potentially more advanced reasoning abilities. By using IQ measures, we can better assess these cognitive abilities.
On the IQ scale, a score between 115 and 129 is categorized as “above average” or “bright”. This classification indicates that individuals with an IQ of 125 possess intellectual capabilities that exceed those of the majority of the population. They often demonstrate a quicker grasp of complex concepts, show enhanced analytical skills, and may excel in academic or professional settings that require high cognitive function. However, recall that IQ merely represents one facet of a person’s overall intelligence and doesn’t include other important factors like emotional intelligence, creativity, or practical skills.
Understanding an IQ of 125
A deeper exploration into the concept of IQ and its measurement is required to truly comprehend the significance of an IQ of 125. As we’ve established, IQ stands for Intelligence Quotient and is a measure of a person’s intellectual abilities and potential. It’s important to note that IQ scores are not just arbitrary numbers; they are carefully calculated and interpreted relative to the average performance of the population, providing an estimate of cognitive abilities.
An IQ score of 125 lies within the “above average” or “bright” range of 115 to 129 on the IQ scale. This classification suggests that individuals with this score possess cognitive abilities that surpass those of the average person. To put it into perspective, a score of 116 or more is considered above average, with scores of 130 or higher signaling a high IQ. Therefore, an IQ of 125 sits comfortably in the upper echelons of cognitive ability, just shy of what would be classified as “highly gifted.”
What does this mean in practical terms? An IQ of 125 suggests:
- Above-average reasoning and problem-solving skills
- High intellectual potential
- Remarkable capacity to adapt to new situations and tackle new challenges
- Excelling in academic settings and grasping complex concepts with relative ease
- Aptitude in fields that require analytical thinking and creative problem-solving
- Individuals with an IQ of 125 may demonstrate these qualities.
Understanding that an IQ score represents a person’s performance compared to others of the same age is vital. This age-relative scoring ensures that the measure remains relevant across different stages of life. However, it’s equally important to remember that IQ tests are designed to measure specific aspects of intelligence, primarily focusing on problem-solving and reasoning abilities. While a score of 125 certainly indicates above-average cognitive skills, it doesn’t encompass all aspects of intelligence or predict success in every area of life.
Cognitive Abilities at an IQ Level of 125
Individuals with an IQ of 125 typically exhibit a range of enhanced cognitive abilities that set them apart from the average population. One of the most notable characteristics is their advanced analytical capabilities. These individuals often excel at processing complex ideas and drawing connections between seemingly unrelated data points. This skill can be particularly valuable in fields that require deep analysis and strategic thinking, such as scientific research, data analysis, or strategic planning in business.
Another significant cognitive trait associated with an IQ of 125 is the ability to quickly grasp and understand complex concepts. This rapid comprehension can be a significant advantage in academic and research-based professions, where the ability to assimilate new information quickly and effectively is crucial. It allows these individuals to stay ahead of the curve in fast-paced, knowledge-intensive environments.
Memory function is another area where those with an IQ of 125 often excel. They typically demonstrate robust memory capabilities, with a particular strength in associative memory. This means they’re adept at connecting new information to prior knowledge, creating a web of understanding that enhances both retention and recall. This ability can be particularly beneficial in fields that require the integration of diverse information, such as medicine, law, or interdisciplinary research.
Creativity and divergent thinking are often pronounced in individuals with an IQ of 125. This manifests as an ability to envision multiple solutions to a problem or generate novel ideas. Such cognitive flexibility can be invaluable in fields that prize innovation, such as entrepreneurship, product design, or creative arts. It also contributes to their problem-solving prowess, allowing them to approach challenges from various angles and find efficient solutions in both personal and professional settings.
Lastly, individuals with this IQ level often demonstrate an impressive ability to handle multitasking and work efficiently under pressure. This skill is particularly valuable in dynamic environments such as finance, project management, or emergency services, where the ability to juggle multiple tasks and make quick, accurate decisions is crucial. It’s worth noting that while these cognitive abilities are often associated with an IQ of 125, intelligence is multifaceted.
A study found at least three factors crucial to predicting intelligence: short-term memory, reasoning, and a verbal component. This underscores the complexity of intelligence and the importance of considering multiple cognitive aspects beyond just IQ scores.
Real World Scenarios for a 125 IQ Score
In real-world scenarios, individuals with an IQ of 125 often find themselves excelling in roles that demand critical thinking and creative problem-solving. These cognitive strengths make them well-suited for fields such as engineering, where complex problems need innovative solutions, or strategic planning, where the ability to analyze multiple variables and predict outcomes is crucial. For instance, a software engineer with this IQ level might excel at developing efficient algorithms or designing robust system architectures, leveraging their ability to process complex information and envision multiple solutions.
Leadership roles often come naturally to those with an IQ of 125, as they frequently exhibit strong leadership qualities. Their ability to quickly grasp complex concepts, combined with their problem-solving skills, allows them to make informed decisions and guide teams effectively. In a corporate setting, for example, a manager with this IQ level might excel at developing comprehensive business strategies, identifying market trends, and leading their team through challenging projects.
The technology sector is another area where individuals with a 125 IQ often thrive. Their logical reasoning skills and technical aptitude make them well-suited for roles in software development, data science, or cybersecurity. A data scientist with this IQ level, for instance, might excel at developing sophisticated machine learning models, interpreting complex datasets, and deriving actionable insights that drive business decisions.
One of the key strengths of individuals with an IQ of 125 is their ability to demonstrate practical problem-solving skills in real-world scenarios. They often use heuristics - mental shortcuts or rules of thumb - to quickly evaluate situations and take action. This skill is particularly valuable in fast-paced environments where decisions need to be made swiftly and accurately.
For example, a person with an IQ of 125 might excel at:
- Quickly assessing market trends and making investment recommendations as a financial analyst
- Efficiently processing vast amounts of information to make informed decisions
- Adapting to new situations and finding creative solutions
- Analyzing complex problems and breaking them down into manageable parts
- Identifying patterns and trends in data
These practical problem-solving skills can be a valuable asset in a variety of fields and industries.
Moreover, their heightened adaptability, often attributed to enhanced neuroplasticity, allows them to swiftly adjust to new situations or concepts. This adaptability can be a significant asset in today’s rapidly changing work environments, where the ability to learn new skills and adapt to new technologies is increasingly valuable.
The Bell Curve and IQ Distribution
Understanding the distribution of IQ scores across the population is key to fully appreciating the significance of a 125 IQ score. This distribution follows what’s known as a bell curve, with the majority of scores clustering around the average and fewer scores at the extremes. This statistical model provides a visual representation of how cognitive abilities are spread throughout the population and helps us contextualize individual scores.
At the center of this bell curve is the average IQ score, which falls between 85 and 115. This range represents approximately 68% of the population, encompassing what we consider “average” intelligence. As we move away from this central range, the number of individuals decreases, representing those with below-average and above-average IQ scores. When we consider an IQ score of 125, we’re looking at a point on the curve that’s significantly above this average range.
An IQ of 125 places an individual in the 95th percentile of the population. This means that a person with this score has a higher IQ than 95% of the population - a truly remarkable achievement. To put it another way, only about 1 in 20 people will have an IQ score equal to or higher than 125. This statistic underscores just how exceptional this level of cognitive ability is.
It’s worth noting that the range between 115 and 130, which includes our focus score of 125, represents about 13.6% of the population. This group, often referred to as “bright” or “above average,” forms a significant subset of high-performing individuals who often excel in academic and professional settings that require advanced cognitive abilities. In this context, the average score serves as a benchmark to identify these individuals.
Measuring IQ: Tests and Methods
Intelligence tests, also known as IQ tests, are standardized assessments focusing mainly on problem-solving and logical reasoning skills, designed to measure cognitive abilities. These tests have been developed and refined over decades to provide a reliable measure of intellectual potential. While there are numerous IQ tests available, some have gained prominence due to their comprehensive nature and widespread use.
One of the most widely used IQ tests globally is the Wechsler Intelligence Scales. This test reports a deviation IQ where the mean test score is set at 100, allowing for easy comparison of test scores across different age groups. Another prominent test is the Stanford-Binet Intelligence Scale, which also employs deviation scoring. Both these tests assess various aspects of intelligence, including verbal comprehension, perceptual reasoning, working memory, and processing speed.
For those seeking a test that’s less dependent on language or cultural background, Raven’s Progressive Matrices offer a non-verbal alternative. This test focuses on abstract reasoning and problem-solving abilities, making it particularly useful in cross-cultural studies or for individuals with language barriers. Additionally, the Kaufman Adolescent and Adult Intelligence Test provides a unique approach by classifying scores in a symmetrical, non-evaluative fashion, avoiding medical diagnostic implications.
Regardless of the specific test used, most IQ assessments aim to measure both fluid and crystallized intelligence. Fluid intelligence refers to the ability to solve new problems and adapt to novel situations, while crystallized intelligence involves using learned knowledge and experiences. Assessments typically cover key areas such as:
- Verbal reasoning
- Spatial awareness
- Visual abilities
These tests help gauge various cognitive skills and abilities. It’s important to note that while IQ tests have applications in education, psychological research, and sometimes in employment recruitment, they provide just one perspective on a person’s overall cognitive abilities and potential for success.
Standard Deviation and IQ Scores
Comprehending the concept of standard deviation is vital for interpreting IQ scores. The IQ distribution follows a bell curve with an average (mean) score of 100 and a standard deviation of 15 points. This standardized approach allows for consistent comparisons across different tests and populations. The standard deviation serves as a measure of variability, indicating how scores are spread out from the average.
In the context of IQ scores:
- One standard deviation corresponds to 15 IQ points.
- Approximately 68% of the population falls within one standard deviation of the mean, scoring between 85 and 115.
- Scores between 115 and 130 (including our focus score of 125) fall within the second standard deviation above the mean, representing approximately 13.6% of the population.
This standardized scoring system allows for meaningful comparisons and interpretations of cognitive abilities across different individuals and groups, using the same test.
High IQ Societies and Membership
Several exclusive societies offer membership based on cognitive abilities for individuals with exceptionally high IQ scores. These organizations provide a platform for intellectual exchange, social interaction, and sometimes, collaborative research among high-IQ individuals. Some of the most well-known high-IQ societies include:
- Mensa International
- The Triple Nine Society
- The Prometheus Society
- The Mega Society
Mensa International, perhaps the most famous of these societies, requires an IQ score in the top 2 percent of the population, which translates to approximately 130 or higher. Intertel sets a slightly higher bar, requiring an IQ in the top 1 percent, or about 135. For those with even higher scores, the Triple Nine Society admits individuals with IQs in the top 0.1 percent, which corresponds to a score of around 146.
At the extreme end of the spectrum are societies like the Prometheus Society and the Mega Society. The Prometheus Society has a threshold at the 99.997th percentile, requiring an IQ of about 160. The Mega Society, considered one of the most exclusive high IQ societies in the world, admits only those with IQs in the top 0.0001 percent, equivalent to an IQ score of around 171.3. While an IQ of 125 is certainly above average, it falls short of the requirements for these elite societies, highlighting the exceptional nature of the cognitive abilities required for membership.
Famous People with Similar IQ Scores
When discussing IQ scores, it’s often intriguing to consider notable individuals who have achieved similar results. One fascinating example is Richard Feynman, a renowned physicist known for his groundbreaking work in quantum mechanics and particle physics. Despite his significant contributions to science, including the development of the Feynman diagram, Feynman reportedly had an IQ score in the 120s. This case illustrates that an IQ in this range can be associated with extraordinary scientific achievements and innovative thinking.
On a starkly different note, Ted Bundy, one of the most notorious serial killers in American history, was reported to have an IQ of 124. This unsettling example serves as a potent reminder that while a high IQ may correlate with certain cognitive capabilities, it doesn’t necessarily equate to positive or ethical achievements. Intelligence, as measured by IQ tests, is just one aspect of a person’s overall character and potential.
These examples, along with several other notable individuals reported to have IQ scores around 125, demonstrate that a high IQ score can be associated with significant achievements and diverse contributions across various fields. However, they also underscore the complexity of human intelligence and potential. While an IQ of 125 certainly indicates above-average cognitive abilities, it’s clear that factors such as:
- Perseverance
- Opportunity
- Ethical considerations
play crucial roles in determining an individual’s ultimate impact and success in life.
Emotional Intelligence and Other Factors
Although IQ is a significant measure of cognitive ability, other factors contributing to overall intelligence and success should also be considered. One such factor that has gained significant attention in recent years is Emotional Intelligence (EQ). Research has shown that emotional intelligence can be even more important than IQ in predicting success and effectiveness, particularly in leadership roles.
Emotional intelligence encompasses a range of skills that are vital for personal and professional success. These include:
- Self-awareness
- Self-regulation
- Social skills
People with higher emotional intelligence tend to perform better in both personal and professional domains. They are often more adept at managing stress, communicating effectively, resolving conflicts, and navigating complex social situations.
One key aspect of emotional intelligence is self-regulation, which involves managing negative emotions and adapting to changes. This skill is particularly valuable in professional contexts, where the ability to maintain composure under pressure and adapt to evolving circumstances is often crucial. Moreover, resilience, another component of emotional intelligence, helps individuals cope with stress and avoid burnout.
In the workplace, emotional intelligence plays a significant role in job performance and the ability to handle workplace stress. Individuals with higher EQ are often better equipped to manage their emotions, work effectively in teams, and lead others. They tend to excel in roles that require strong interpersonal skills, such as management, sales, or customer service.
Perhaps one of the most encouraging aspects of emotional intelligence is that, unlike IQ, it can be learned and improved upon. This means that individuals can actively work on enhancing their emotional intelligence throughout their lives, potentially leading to improved personal relationships, better job performance, and greater overall life satisfaction.
While an IQ of 125 certainly provides a strong cognitive foundation, combining this with a high EQ can lead to even greater success and fulfillment in both personal and professional spheres.
Limitations of IQ Testing
Despite IQ tests providing valuable insights into certain cognitive abilities, recognizing their limitations is important. One of the primary criticisms of IQ tests is that they measure only specific aspects of intelligence, such as reasoning and critical thinking. This narrow focus means that other crucial forms of intelligence, like emotional and social intelligence, are not captured by traditional IQ tests.
Moreover, it’s crucial to understand that IQ tests primarily measure how well an individual performs on the test itself and little more. This means that the results may not always accurately reflect a person’s real-world problem-solving abilities or their potential for success in various life domains. It’s also worth noting that there is no single, comprehensive ‘IQ test’ that can measure all aspects of intelligence. Different tests may focus on different cognitive skills, leading to variations in results.
Another limitation of IQ testing is the influence of external factors on test performance. While IQ is generally considered relatively stable, factors such as education and environment can influence scores over time. This means that an individual’s IQ score may not be a fixed, immutable number, but rather a snapshot of their cognitive abilities at a particular point in time, influenced by their experiences and opportunities. Some of the external factors that can influence IQ scores include:
- Quality of education
- Socioeconomic status
- Cultural background
- Access to resources and opportunities
It is important to consider these factors when interpreting IQ scores and to recognize that they may not provide a complete picture of an individual’s intelligence or potential.
Perhaps most importantly, inaccurate measurements or overemphasis on IQ scores can lead to significant issues. An IQ test that inaccurately measures an individual’s intelligence could potentially lead to problems such as low confidence or unrealistic expectations. This underscores the importance of viewing IQ scores as just one piece of a much larger puzzle when it comes to understanding an individual’s overall intelligence and potential for success.
In conclusion, an IQ score of 125 represents a level of cognitive ability that is significantly above average, placing an individual in the 95th percentile of the population. This score is associated with enhanced analytical abilities, quick comprehension of complex concepts, strong memory function, and creative problem-solving skills. However, it’s crucial to remember that IQ is just one aspect of intelligence. Factors such as emotional intelligence, creativity, perseverance, and practical skills all play vital roles in determining an individual’s overall capabilities and potential for success.
While IQ tests provide valuable insights into certain cognitive abilities, they have limitations and should not be viewed as a comprehensive measure of a person’s worth or potential. As we continue to explore and understand the multifaceted nature of human intelligence, it’s clear that nurturing a wide range of skills and intelligence is key to personal growth and success in our complex, ever-changing world.
- What Does An IQ Of 121 Mean
- What Does An IQ Of 122 Mean
- What Does An IQ Of 123 Mean
- What Does An IQ Of 124 Mean
- What Does An IQ Of 126 Mean
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Heart Disease
- Digestive Health
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Diet & Nutrition
- Supplements
- Health Insurance
- Public Health
- Patient Rights
- Caregivers & Loved Ones
- End of Life Concerns
- Health News
- Thyroid Test Analyzer
- Doctor Discussion Guides
- Hemoglobin A1c Test Analyzer
- Lipid Test Analyzer
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) Analyzer
- What to Buy
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Medical Expert Board
Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) Test for Dementia
- Goals of Testing
- How It Works
MoCA vs. MMSE
- Interpretation
- Pros and Cons
The Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) is a test used to detect mild cognitive decline and early signs of dementia . It can help identify people at risk of Alzheimer's disease and screen for conditions like Parkinson's disease , brain tumors , substance abuse, and head trauma.
Introduced in 2005, the MoCA test is an update from the older Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) introduced in 1975. It contains 30 questions and takes 10 minutes to complete. While the MOCA test is useful in detecting dementia, it cannot differentiate between the different dementia types .
This article looks at what is involved in a MoCA test, including how it is scored and how the scores are interpreted. It also explains the different conditions the MOCA test can be applied to as well as the advantages and disadvantages of this important screening tool.
Purpose of the MoCA Test
The MoCA test is a simple, in-office tool that can quickly determine if there is any impairment in a person's cognitive function , including their ability to understand, reason, and remember.
The test is used for adults 55 to 85 with early signs of dementia (the progressive loss of intellectual functioning, especially memory and abstract thinking),
If the test indicates that a person has mild cognitive impairment (MCI) , additional evaluations may be done to check for suspected causes, like:
- Alzheimer's disease
- Parkinson's disease
- Vascular dementia
- Lewy body dementia
- Frontotemporal lobe dementia
- Huntington's disease
- Brain tumors (both benign and cancerous)
- Brain metastases (the spread of cancer to the brain)
The MoCA test can also check for MCI in people with known conditions such as:
- Traumatic brain injury
- Multiple sclerosis
- Schizophrenia
How Common Is Dementia?
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), around 5.8 million people in the United States have Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias. Over 95% of those affected are 65 or older. By 2060, the number of Alzheimer’s cases is predicted to rise to 14 million.
How the MoCA Works
The MoCA test is based on scores with a maximum score of 30. It takes 10 to 12 minutes to complete.
The MoCA test examines seven domains (aspects) of cognitive function with a total of 11 different exercises and tasks:
- Executive and visuospatial function : You will first be given a picture with numbered dots (1, 2, 3, 4, 5) and lettered dots (A, B, C, D, E) and asked to connect them sequentially, alternating numbers and letters. Next, you will be given a drawing of a three-dimensional cube and asked to make a copy. Finally, you will be asked to draw a dial clock that reads 10 minutes past 11:00.
- Naming : You will be shown pictures of three animals and asked what type of animal they are.
- Attention: You will first be given a series of numbers and asked to repeat them forward or backward. You will then be given a series of letters and asked to pick out the letter "A." Finally, you will be given several numbers and asked to subtract them from 100.
- Language : You will first be asked to repeat back two different sentences verbatim. You will then be shown a series of capital letters and asked to pick out all of the "As."
- Abstraction : You will be asked what is in common between two different things (such as an apple and an orange, or a car and an airplane),
- Delayed recall : You will be given five words and asked to repeat them back after five minutes.
- Orientation : You will be asked about the date, month, year, day, city, and place you are in.
The MoCA is similar to an older test called the Mini-Mental State Exam (MMSE). Both tests use a 30-point scale and take only a few minutes to complete.
Both the MoCA and MMSE have their benefits, limitations, and uses:
- MOCA: This test is better at distinguishing between normal cognition and MCI. The test is harder than the MMSE and less informative in people with moderate to severe dementia as their ability to complete the task rapidly falls away. The MoCA is used primarily for the early detection of dementia.
- MMSE: This test is better for people with known dementia. Because it is less difficult, it can detect subtle changes in cognition even if certain domains are unaffected. (For instance, a highly educated person might still have high executive function but be unable to recall the names of their grandkids.) Because of this, the MMSE is better suited to monitor the decline in cognition.
On their own, neither test can diagnose the cause of cognitive impairment or dementia.
30 questions with a maximum score of 30
Evaluates 7 domains of cognition
(executive/visuospatial function, naming, attention, language, abstraction, recall, and orientation)
A score of less than 26 indicates mild cognitive impairment
Take around 10 to 12 minutes to complete
Questions are more difficult
Has a higher sensitivity for mild cognitive impairment but less value for people with moderate to severe dementia
Better at detecting early dementia
11 questions with a maximum score of 30
Evaluate 5 domains of cognition (orientation, registration, attention/calculation, recall, and language)
A score of less than 25 indicates mild cognitive impairment
Takes around 7 to 8 minutes to complete
Questions are less difficult
Has a lower sensitivity for mild cognitive impairment but is able to monitor for subtle changes in people with moderate to severe dementia
Better at monitoring people with known dementia
Scoring the MoCA Test
The total score on the MoCA test ranges from 0 to 30. The scoring per domain is broken downs as follows:
| Domain | Maximum Score |
|---|---|
| Executive/visuospatial function | 5 points |
| Naming | 3 points |
| Attention | 6 points |
| Language | 3 points |
| Abstraction | 2 points |
| Recall | 5 points |
| Orientation | 6 points |
Because a person's education can limit their comprehension of certain tasks, 1 point is added to the total score if a person has 12 years or less of formal education.
Interpreting the Results
After tallying the MoCA scores, the results can be interpreted as follows:
| Interpretation | Score range |
|---|---|
| Normal cognition | 26-30 points |
| Mild cognitive impairment | 18-25 points |
| Moderate cognitive impairment | 10-17 points |
| Severe cognitive impairment | Under 10 points |
Advantages vs. Disadvantages
Among the advantages of the MoCA test:
- It is simple and brief.
- It has a high sensitivity for mild cognitive impairment.
- It is an objective test that is less vulnerable to subjective interpretation.
- It is available in more than 35 languages as well as versions for people with blindness or hearing impairment.
- Unlike the MMSE, it is not copyrighted and therefore free for non-profit use.
Among the disadvantages of the MoCA test:
- Training is needed for the test to be administered and scored correctly.
- A person’s education level can influence the results. ( Poverty can also influence the results as it is linked to lower educational status.)
- Certain mental health problems can skew the results and lead to incorrect findings. People with depression, for example, often score lower without having actual cognitive impairment.
- The test cannot determine which type of dementia is involved.
How Accurate is the MoCA Test?
The MoCA test is generally better at detecting MCI and early dementia than the MMSE test. This is based on comparisons of the sensitivity (the ability to correctly identify people with a disease) and specificity (the ability to correctly identify people without a disease) of both tests.
A 2015 study published in BMC Geriatrics reported that the MoCA has a sensitivity and specificity of 90% and 87%, respectively, in detecting MCI. By contrast, the MMSE has a sensitivity and specificity of 18% and 100%.
MMSE was only better at detecting when someone doesn't have MCI.
The MoCA test is a simple, in-office test that can detect mild cognitive impairment and the early onset of dementia. It does so based on 11 questions that evaluate seven domains of cognitive function. The MoCA has a maximum score of 30, and anything below 26 is a sign of cognitive impairment.
Gluhm A, Goldstein J, Loc K, Colt A, Van Liew C, Corey-Bloom M. Cognitive performance on the Mini-Mental State Examination and the Montreal Cognitive Assessment across the healthy adult lifespan. Cogn Behav Neurol. 2013 Mar;26(1):1–5. doi:10.1097/WNN.0b013e31828b7d26
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Minorities and women are at greater risk for Alzheimer's disease .
Kim H, Yu KH, Lee BC, Kim BC, Kang Y. Validity of the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) index scores: a comparison with the cognitive domain scores of the Seoul Neuropsychological Screening Battery (SNSB). Dement Neurocogn Disord . 2021;20(3):28-37. doi:10.12779/dnd.2021.20.3.28
Dautzenberg G, Lijmer J, Beekman A. Diagnostic accuracy of the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) for cognitive screening in old age psychiatry: determining cutoff scores in clinical practice. Avoiding spectrum bias caused by healthy controls. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry . 2020;35(3):261-269. doi:10.1002/gps.5227
Trzepacz PT, Hochstelter H, Wang S, Walker B, Saykin AJ. Relationship between the Montreal Cognitive Assessment and Mini-mental State Examination for assessment of mild cognitive impairment in older adults . BMC Geriatr. 2015;15:107. doi:10.1186/s12877-015-0103-3
By Andrew Rosenzweig, MD Andrew Rosenzweig, MD, MPH, is an Alzheimer's disease expert and the chief clinical officer for MedOptions.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A cognitive test is an assessment tool designed to measure an individual's cognitive abilities, which are the mental processes involved in acquiring, processing, storing and using information. Cognitive assessments are used to evaluate various aspects of cognitive functioning, including memory, attention, problem-solving, reasoning, language ...
The Universal Cognitive Aptitude Test (UCAT) is a job application assessment that measures your critical thinking, problem-solving, analytical, and mathematical abilities. It consists of 40 questions, and you are given 20 minutes to complete it.
Cognitive ability test. Article author: Dr. Edwin van Thiel, updated July 6, 2022 What is a cognitive ability test? A cognitive ability test, or a cognitive test in general, is simply put a measurement of a mental performance.This can be a very specific one, such as solving a mathematical sum, or a very broad measurement such as determining someone's general intelligence.
Cognitive tests measure a candidate's thinking abilities, including, reasoning, perception, memory, problem-solving skills, and verbal reasoning. They are usually used by potential employers to assess an applicant's thinking abilities. The questions featured in these tests tend to include verbal analogies, arithmetic calculations, spatial ...
Our cognitive ability tests focus on precise evaluation of your analytical skills, adaptability, and problem-solving prowess. Utilizing state-of-the-art adaptive technology, our test questions constantly evolve to maintain up-to-date with industry trends and standards, offering a true measure of your cognitive strengths.
The Critical Thinking Test is a comprehensive evaluation designed to assess individuals' cognitive capacities and analytical prowess. This formal examination, often referred to as the critical thinking assessment, is a benchmark for those aiming to demonstrate their proficiency in discernment and problem-solving.
This problem resolution test presents candidates with typical problem-solving scenarios like 1) scheduling based on a diverse set of conditions, 2) identifying the right sequence of actions based on several business rules, and 3) drawing conclusions based on textual and numerical information. Check out our practice preview questions to see the ...
Most cognitive ability tests for employee selection require you to use more general skill sets, such as problem-solving, decision-making and time management, rather than specific knowledge.. You are presented with a task or information, and you need to use the resources in front of you to answer the questions. The exception here is mechanical reasoning, which does measure industry-specific ...
A cognitive ability test is a pre-employment test used to measure a candidate's cognitive skills and mental abilities, such as problem solving, spatial reasoning, and numerical reasoning. They are designed to evaluate a candidate's mental abilities and aptitudes to predict their performance in various tasks or roles.
The questions in a cognitive ability test, therefore, are not hard. It is the pressure from the timing and the unfamiliar circumstances that make them difficult. This is why practice is so important. History of Cognitive Ability Tests. Cognitive ability, or general intelligence, was first tested for in the early 19th century.
SHL's cognitive assessments are automated, remotely proctored, and ask fewer questions thanks to our unique partial-scoring methodology. Assess high candidate volumes faster and more reliably, so your teams can make confident, efficient hiring decisions. Provide all candidates with truly engaging experiences.
The Reasoning Cognitive Assessment (CAB-RS) provides you with a precise assessment of relevant cognitive skills, such as your working memory, your processing speed, updating and planning. ... is a digitized replica of the task of the same name (Hinz, 1989). This task seeks to measure high-order cognitive problem solving and learning of complex ...
Test Your Problem-Solving Skills. Personalize Your Emails Personalize your monthly updates from BrainFacts.org by choosing the topics that you care about most! Sign Up Find a Neuroscientist Engage local scientists to educate your community about the brain. ...
Cognify is an immersive, game-based assessment of cognitive aptitude that measures a candidate's problem solving skills, critical thinking, and verbal knowledge. Main Navigation. Products. Assess. Cognitive Aptitude ... An overall percentile is provided, along with percentiles for the three categories of problem solving, numerical reasoning ...
Psychometric properties of the Problem Solving test. The metrics reported below are based on a sample size (N) of at least 1,000 candidates unless indicated otherwise. Reliability: Cronbach's alpha coefficient = .72. Face validity: Candidates rated this test as accurately measuring their skills (average score of 3.88 out of 5.00).
Cognitive Ability Tests. Cognitive ability tests assess abilities involved in thinking (e.g., reasoning, perception, memory, verbal and mathematical ability, and problem solving). Such tests pose questions designed to estimate applicants' potential to use mental processes to solve work-related problems or to acquire new job knowledge.
A cognitive ability test is an assessment that measures an individual's mental capabilities and potential. These tests evaluate a person's intelligence, problem-solving skills, and decision-making abilities. They provide insights into how individuals process and use information, make decisions, and solve problems.
Cognitive and neuropsychological tests measure memory, language skills, math skills, visual and spatial skills, and other abilities related to mental functioning to help them diagnose a patient's condition accurately. For example, people with Alzheimer's disease often show changes in so-called executive functions (such as problem-solving ...
The cognitive assessment is useful to test for cognitive impairment—a deficiency in knowledge, thought process, or judgment. Psychiatrists often perform cognitive testing during the Mental Status Exam. ... Abstract reasoning refers to analyzing information, detecting patterns and relationships, or solving problems on an intangible ...
What is cognitive ability? Cognitive ability (also known as cognitive function or capacity) is the human ability to learn, solve problems, perform tasks, and acquire and use new information.Cognitive ability encompasses many mental skills, such as learning, thinking, concentration, memory, perception, problem-solving, language processing, decision-making, executive function, and others.
After an exhaustive interview of the patient and any accompanying family members, the neuropsychologist goes through tests and tasks designed to check specific brain functions - intelligence, memory, verbal ability, problem-solving and reasoning skills, visual and auditory responses, emotion and mood.
How is a cognitive test different from a neurologic exam? ... memory, verbal ability, problem-solving and reasoning skills, visual and auditory responses, emotion and mood. They may use puzzles ...
What cognitive tests can show — and what they can't ... problem-solving and reasoning skills, visual and auditory responses, emotion and mood. They may use puzzles, objects to rearrange, or ...
Generally, cognitive tests measure a range of mental abilities such as: awareness of people, time, and place (orientation) short- and long-term memory; language and communication skills; problem ...
A cognitive test is an assessment tool designed to measure an individual's cognitive abilities, which are the mental processes involved in acquiring, processing, storing and using information. Cognitive assessments are used to evaluate various aspects of cognitive functioning, including memory, attention, problem-solving, reasoning, language ...
Typically, a cognitive screening could be warranted if a person is having problems with memory, personality changes, or balance, or if they are repeating themself, forgetting parts of their past ...
After an exhaustive interview of the patient and any accompanying family members, the neuropsychologist goes through tests and tasks designed to check specific brain functions - intelligence, memory, verbal ability, problem-solving and reasoning skills, visual and auditory responses, emotion and mood.
He recently bragged about passing a 2018 cognitive test ... problem-solving and reasoning skills, visual and auditory responses, emotion and mood. They may use puzzles, objects to rearrange, or ...
Intelligence tests, also known as IQ tests, are standardized assessments focusing mainly on problem-solving and logical reasoning skills, designed to measure cognitive abilities. These tests have been developed and refined over decades to provide a reliable measure of intellectual potential.
The Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) is a test used to detect mild cognitive decline and early signs of dementia. It can help identify people at risk of Alzheimer's disease and screen for conditions like Parkinson's disease, brain tumors, substance abuse, and head trauma. Introduced in 2005, the ...