
Make Waves in Learning! 25% off
for World Oceans Day
Use code OCEAN25


Share this article

Table of Contents
Latest updates.

CBSE Syllabus for Class 8 Maths 2024: Download PDF

NCERT Solutions for Visualizing Solid Shapes Exercise 10.3 Class 8 Maths

NCERT Solutions for Factorisation Exercise 14.1 Class 8 Maths

NCERT Books for Class 8 2024: Download PDF

CBSE Syllabus for Class 8 2025 – Download PDFs

NCERT Solutions for Comparing Quantities Exercise 8.1 Class 8 Maths

NCERT Solutions for Square and Square Roots Exercise 6.4 Class 8 Maths

NCERT Solutions for Direct and Inverse Proportions Exercise 13.1 Class 8 Maths

NCERT Solutions for Square and Square Roots Exercise 6.3 Class 8 Maths

NCERT Books for Class 8 English 2023
Tag cloud :.
- entrance exams
- engineering
- ssc cgl 2024
- Written By Anjali Choudhury
- Last Modified 27-07-2022
Linear Equation Word Problem: Check Important Questions
Linear equations in one variable in Class 8 Math teach us that a mathematical equation can take many distinct forms with various variables, degrees, coefficients, and other factors. However, a mathematical expression with a polynomial whose highest power is 1 and which only has one variable is known as a linear equation in one variable.
The topics explained in this chapter strongly emphasise what a linear equation in one variable means and how to use it to solve certain problems. There are many different kinds of linear equations, as previously discussed, and each one can be solved differently. This chapter details how to convert a word problem into a linear mathematical equation and what methods to use to solve it. Continue reading this article to learn more about the linear equation word problem.
Introduction to Linear Equations
A linear equation has terms that are either constants or the result of a constant and a variable. This variable only takes the form of a single power, ax + b = 0, where a and b are constants and a ≠ 0. It is a simple example of a linear equation with only one variable, x. An equivalence containing variables is referred to as an algebraic equation. The expression is referred to as LHS (Left Hand Side) on the left and RHS (Right Hand Side) on the right.
To find a linear equation’s solution is to solve a linear equation. The three basic forms of linear equations—those with one variable, those with two variables, and those with three variables—and their respective methods to find a solution are mentioned below:
- Graphical Method
- Elimination Method
- Substitution Method
- Cross Multiplication Method
- Matrix Method
- Determinants Method
Word Problems on Linear Equation
Some of the important word problems in Linear Equation Class 8 are mentioned below to help students with their exam preparation. Students must go through these questions and try to solve them using their problem-solving skills:
Q.1. The breadth of a rectangular garden is 2/3 of its length. If its perimeter is 40 m, find its dimensions.
Q.2. The difference between two positive numbers is 40, and the ratio of these integers is 1 : 3. Find the integers.
Q.3. The sum of a two-digit number and the number obtained by reversing its digits is 121. Find the number if its unit place digit is 5.
Q.4. If the length of the rectangle is increased by 40% and its breadth is decreased by 40%, what will be the percentage change in its perimeter?
Q.5. A fruit seller buys some oranges at the rate of ₹ 5 per orange. He also buys an equal number of bananas at the rate of ₹ 2 per banana. He makes a profit of 20% on oranges and a profit of 15% on bananas. In the end, he sold all the fruits. If he earned a profit of ₹ 390, find the number of oranges.
Q.6. A steamer goes downstream from one point to another in 7 hours. It covers the same distance upstream in 8 hours. If the speed of the stream is 2 km/h, find the speed of the steamer in still water and the distance between the ports.
Q.7. There is a narrow rectangular plot. The length and breadth of the plot are in the ratio of 11:4. At the rate of Rs. 100 per meter will cost the village panchayat Rs.75000 to fence the plot. What are the dimensions of the plot?
Q.8. Jane is 6 years older than her younger sister. After 10 years, the sum of their ages will be 50 years. Find their present ages.
Q.9. Ramesh is a cashier in a Canara bank. he has notes of denominations of Rs. 100, 50 and 10 respectively. The ratio of the number of these notes is 2:3:5, respectively. The total cash with Ramesh is 4,00,000. How many notes of each denomination does he have?
Q.10. Amina thinks of a number and subtracts 5/2 from it. She multiplies the result by 8. The final result is 3 times her original number. Find the number.
Q.11. A 300 m long wire is used for fencing a rectangular plot whose length is twice its width. Find the length and breadth of the plot.
Q.12. In a class of 42 students, the number of boys is 2/5 of the number of girls. Find the number of boys and girls in the class.
Q.13. My mother is 12 years more than twice my age. After 8 years, my mother’s age will be 20 years, less than three times my age. Find my age and my mother’s age.
Q.14. Adman’s father is 49 years old. He is 5 years older than four times Adman’s age. What is Adman’s age?
Q.15. The denominator of a fraction is greater than the numerator by 8. If the numerator is increased by 17 and the denominator is decreased by 1, the number obtained is 3/2. Find the fraction.
About Linear Equations in Class 8
When there are two or more numbers and one of them is unknown, the value of this integer can be determined using linear equations in one variable. Using the expression in equation form, it is simple to determine the value of an unknown integer. We advise students to get the most out of this chapter so they can easily solve linear equation problems in exams.
Linear equations in one variable is a critical topic in Mathematics studied in Class 8. There are five main topics in the chapter on linear equations in one variable. To ensure that you fully understand the concepts of linear equations in one variable, we advise you to go over each topic mentioned below carefully:
- Introduction
- Solving Equations Where Linear Expressions are On One Side and Numbers are On Other Side of Equation
- Applications of Linear Equations in One Variable
- Solving Equations with Variables on Both the Sides
- Reducing the Given Equations to Simpler Form
We hope this article on Linear Equation Word Problem has been helpful to you. Stay tuned to Embibe for such informative articles. We wish you the best. Happy learning!
Related Articles
CBSE Syllabus for Class 8 Maths 2023-24: Students in CBSE Class 8 need to be thorough with their syllabus so that they can prepare for the...
Class 8 Maths Chapter 10 Exercise 10.3: Chapter 10 of Class 8 Maths covers the concept of visualizing solid shapes. Detailed step-by-step solutions for all...
NCERT Exercise 14.1 Class 8 Maths Solutions: NCERT solutions for Class 8 Maths chapter 14 exercise 14.1 - Factorisation provides answers to all of the chapter's...
NCERT Books for Class 8 2023-24: The NCERT books are prescribed by the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE). CBSE and many state boards also...
CBSE Syllabus for Class 8 2025: The Syllabus is one of the important resources for CBSE Class 8 exam preparation. Students must thoroughly review the...
NCERT Solutions for Comparing Quantities Exercise 8.1 Class 8 Maths: The chapter lays primary focus on basic mathematical concepts for calculating and determining the value...
NCERT Solutions for Exercise 6.4 Class 8 Maths: Class 8 students should solve NCERT Exercise questions in order to achieve high grades. They should refer...
Exercise 13.1 Class 8 Maths NCERT Solutions: In this article we have provided the NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 13 exercise 13.1. The...
NCERT Solutions for Square and Square Roots Exercise 6.3 Class 8 Maths: A square is the value derived by multiplying a natural number with itself....
NCERT Books for Class 8 English: The Central Board of Secondary Education recommends (CBSE) books for Class 8 English. The books not only improve students' English...
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 16: Light – Download PDF
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 16: Chapter 16 in Class 8 Science discusses about Light, laws of reflection, uses of light, and several...
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths 2024 – Download PDF
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths: The NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths cover all of the questions from the textbooks prescribed by the CBSE...
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 History 2024: Chapter 6
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 History Chapter 6 2023-24: In the CBSE Class 8 History Chapter 6, students will learn about weavers, iron smelters, and...
NCERT Solutions for Direct and Inverse Proportions Exercise 13.2 Class 8 Maths
NCERT Solutions for Direct and Inverse Proportions Exercise 13.2 Class 8 Maths: The solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 13 Exercise 13.2 comprises a total...
NCERT Books for Class 8 Maths 2024: Download PDF
NCERT Books for Class 8 Maths 2023-24: NCERT books are used by the Central Board of Secondary Education(CBSE) for all classes. They are great resources...
NCERT Solutions for Factorisation Exercise 14.3 Class 8 Maths
NCERT Solutions for Factorisation Exercise 14.3 Class 8 Maths: Factorisation of a number means breaking a number into factors whose product leads to that number....
NCERT Books for Class 8 Science 2024
NCERT Books for Class 8 Science: Science is one of the most important subjects for CBSE Class 8 students, and a clear understanding of the...
NCERT Books For Class 8 Social Science 2024: Download PDF
NCERT Books for Class 8 Social Science 2024: The NCERT Books for Class 8 Social Science books are prepared by highly skilled subject matter experts...
NCERT Solutions for Understanding Quadrilaterals Exercise 3.4 Class 8 Maths
Chapter 3 Exercise 3.4 Class 8 Maths NCERT Solutions: The NCERT Solutions for Understanding Quadrilaterals Exercise 3.4 Class 8 Maths are provided on this page. These...
RBSE Board Class 8 Syllabus 2024 (Latest) – Check Chapter & Topics
RBSE Board Class 8 Syllabus 2024: The class 8 curriculum is created for the Rajasthan Board by the Rajasthan Board of Secondary Education (RBSE). The...
Gujarat Board Class 8 Books 2024
Have you ever wondered why you remember movie dialogues or songs even after seeing them once, but you mostly can’t remember a Maths formula or...
8th ICSE Chapter
Do you ever wonder why all the famous novels are being made into movies these days? This is because most people prefer to watch movies...
8th ICSE Preparation Tips
8th ICSE Preparation Tips: The Council for the Indian School Certificate Examinations conducts the ICSE Class 8 examination. Students who are in Class 8 must...
Nagaland Board Class 8 Books 2023
Did you know books are the best and most valuable resources that help you easily understand the most difficult concepts? Are you preparing for the...
Nagaland Board Class 8 Study Material 2022
How much time does it take to prepare for the Nagaland Board Class 8 exams? This is a question that is answered differently by different...
Mizoram Board Class 8 Study Material 2023
Are digital textbooks better than our old textbooks? In some ways, yes. Digital textbooks come with several additional benefits. The content is easier to access...
Mizoram Board Class 8 Books: Get Best Preparation Books
As the phrase goes, "There is only one thing that could replace a book: Next Book". What if I told you there is a far...

39 Insightful Publications

Embibe Is A Global Innovator

Innovator Of The Year Education Forever

Interpretable And Explainable AI

Revolutionizing Education Forever

Best AI Platform For Education

Enabling Teachers Everywhere

Decoding Performance

Leading AI Powered Learning Solution Provider

Auto Generation Of Tests

Disrupting Education In India

Problem Sequencing Using DKT

Help Students Ace India's Toughest Exams

Best Education AI Platform

Unlocking AI Through Saas

Fixing Student’s Behaviour With Data Analytics

Leveraging Intelligence To Deliver Results

Brave New World Of Applied AI

You Can Score Higher

Harnessing AI In Education

Personalized Ed-tech With AI

Exciting AI Platform, Personalizing Education

Disruptor Award For Maximum Business Impact

Top 20 AI Influencers In India

Proud Owner Of 9 Patents

Innovation in AR/VR/MR

Best Animated Frames Award 2024
Trending Searches
Previous year question papers, sample papers.
Achieve Your Best With 3D Learning, Book Practice, Tests & Doubt Resolutions at Embibe

Get free access to 3D videos, questions mock tests and more !
Enter mobile number.
By signing up, you agree to our Privacy Policy and Terms & Conditions
- RD Sharma Solutions
- Chapter 9 Linear Equation In One Variable
RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 9 Linear Equation in One Variable
Mathematics is one of the scoring subjects where students secure maximum marks in the exam. When it comes to preparing for the annual exam, it is the toughest time when most students struggle to solve problems. So, here at BYJU’S, our expert faculty have formulated RD Sharma Class 8 Maths Solutions , which help students prepare for their exams effortlessly. All the solutions are well designed, keeping in mind the latest CBSE syllabus and exam pattern. Also, students can learn easy tricks and shortcut methods by practising these solutions on a regular basis. The PDFs of this chapter are available here, and students can download them for free from the links provided below.
Chapter 9 – Linear Equation in One Variable contains four exercises, and the RD Sharma Solutions available on this page provide solutions to the questions present in each exercise. Now, let us have a look at the concepts covered in this chapter.
- Linear equation and its definitions.
- A solution of a linear equation.
- Solving equations having variable terms on one side and number(s) on the other side.
- Transposition method for solving linear equations in one variable.
- Cross-multiplication method for solving equations.
- Applications of linear equations to practical problems.
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 1 Rational Numbers
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Powers
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 3 Squares and Square Roots
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 4 Cubes and Cube Roots
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 5 Playing with Numbers
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 6 Algebraic Expressions and Identities
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 7 Factorization
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 8 Division of Algebraic Expressions
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 9 Linear Equations in One Variable
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 10 Direct and Inverse Variations
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 11 Time and Work
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 12 Percentage
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 13 Profit, Loss, Discount and Value Added Tax (VAT)
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 14 Compound Interest
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 15 Understanding Shapes – I (Polygons)
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 16 Understanding Shapes – II (Quadrilaterals)
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 17 Understanding Shapes – II (Special Types of Quadrilaterals)
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 18 Practical Geometry (Constructions)
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 19 Visualising Shapes
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 20 Mensuration – I (Area of a Trapezium and a Polygon)
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 21 Mensuration – II (Volumes and Surface Areas of a Cuboid and a Cube)
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 22 Mensuration – III (Surface Area and Volume of a Right Circular Cylinder)
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 23 Data Handling – I (Classification and Tabulation of Data)
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 24 Data Handling – II (Graphical Representation of Data as Histograms)
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 25 Data Handling – III (Pictorial Representation of Data as Pie Charts)
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 26 Data Handling – IV (Probability)
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 27 Introduction to Graphs
- Exercise 9.1 Chapter 9 Linear Equations in One Variable
- Exercise 9.2 Chapter 9 Linear Equations in One Variable
- Exercise 9.3 Chapter 9 Linear Equations in One Variable
- Exercise 9.4 Chapter 9 Linear Equations in One Variable
carouselExampleControls111

Previous Next
Access Answers to Maths RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Chapter 9 Linear Equation in One Variable
Exercise 9.1 page no: 9.5.
Solve each of the following equations and also verify your solution:
1. 9 ¼ = y – 1 1/3
9 ¼ = y – 1 1/3
37/4 = y – 4/3
Upon solving, we get,
y = 37/4 + 4/3
By taking LCM for 4 and 3, we get 12
y = (37×3)/12 + (4×4)/12
= 111/12 + 16/12
= (111 + 16)/12
∴ y = 127/12
Verification
RHS = y – 1 1/3
= 127/12 – 4/3
= (127 – 16)/12
= 9 ¼
2. 5x/3 + 2/5 = 1
5x/3 + 2/5 = 1
5x/3 = 1 – 2/5 (by taking LCM)
By using cross-multiplication, we get,
5x = (3×3)/5
x = 9/(5×5)
∴ x = 9/25
LHS = 5x/3 + 2/5
= 5/3 × 9/25 + 2/5
= 3/5 + 2/5
= (3 + 2)/5
3. x/2 + x/3 + x/4 = 13
x/2 + x/3 + x/4 = 13
let us take LCM for 2, 3 and 4, which is 12
(x×6)/12 + (x×4)/12 + (x×3)/12 = 13
6x/12 + 4x/12 + 3x/12 = 13
(6x+4x+3x)/12 = 13
13x/12 = 13
13x = 12×13
∴ x = 12
LHS = x/2 + x/3 + x/4
= 12/2 + 12/3 + 12/4
= 6 + 4 + 3
4. x/2 + x/8 = 1/8
x/2 + x/8 = 1/8
let us take LCM for 2 and 8, which is 8
(x×4)/8 + (x×1)/8 = 1/8
4x/8 + x/8 = 1/8
∴ x = 1/5
LHS = x/2 + x/8
= (1/5)/2 + (1/5)/8
= 1/10 + 1/40
= (4 + 1)/40
5. 2x/3 – 3x/8 = 7/12
2x/3 – 3x/8 = 7/12
By taking LCM for 3 and 8, we get 24
(2x×8)/24 – (3x×3)/24 = 7/12
16x/24 – 9x/24 = 7/12
(16x-9x)/24 = 7/12
7x/24 = 7/12
7x×12 = 7×24
x = (7×24)/(7×12)
∴ x = 2
LHS = 2x/3 – 3x/8
= 2(2)/3 – 3(2)/8
= 4/3 – 6/8
= 4/3 – 3/4
= (16 – 9)/ 12
6. (x + 2) (x + 3) + (x – 3) (x – 2) – 2x(x + 1) = 0
(x + 2) (x + 3) + (x – 3) (x – 2) – 2x(x + 1) = 0
Upon expansion, we get,
x 2 + 5x + 6 + x 2 – 5x +6 – 2x 2 – 2x =0
-2x + 12 = 0
By dividing the equation using -2, we get,
x – 6 = 0
∴ x = 6
LHS = (x + 2) (x + 3) + (x – 3) (x – 2) – 2x(x + 1)
= (6 + 2) (6 + 3) + (6 – 3) (6 – 2) – 2(6) (6 + 1)
= (8) (9) + (3) (4) – 12(7)
= 72 + 12 – 84
= 84 – 84
7. x/2 – 4/5 + x/5 + 3x/10 = 1/5
x/2 – 4/5 + x/5 + 3x/10 = 1/5
x/2 + x/5 + 3x/10 = 1/5 + 4/5
by taking LCM for 2, 5 and 10, which is 10
(x×5)/10 + (x×2)/10 + (3x×1)/10 = 5/5
5x/10 + 2x/10 + 3x/10 = 1
(5x+2x+3x)/10 = 1
∴ x = 1
LHS = x/2 – 4/5 + x/5 + 3x/10
= ½ – 4/5 + 1/5 + 3(1)/10
= (5 – 8 + 2 + 3)/10
= (10 – 8)/10
8. 7/x + 35 = 1/10
7/x + 35 = 1/10
7/x = 1/10 – 35
= ((1×1) – (35×10))/10
= (1 – 350)/10
7/x = -349/10
x = -70/349
∴ x = -70/349
LHS = 7/x + 35
= 7/(-70/349) + 35
= (-7 × 349)/70 + 35
= -349/10 + 35
= (-349 + 350)/ 10
9. (2x-1)/3 – (6x-2)/5 = 1/3
(2x-1)/3 – (6x-2)/5 = 1/3
By taking LCM for 3 and 5, which is 15
((2x-1)×5)/15 – ((6x-2)×3)/15 = 1/3
(10x – 5)/15 – (18x – 6)/15 = 1/3
(10x – 5 – 18x + 6)/15 = 1/3
(-8x + 1)/15 = 1/3
(-8x + 1)3 = 15
-24x + 3 = 15
-24x = 15 – 3
∴ x = -1/2
LHS = (2x – 1)/3 – (6x – 2)/5
= [2(-1/2) – 1]/3 – [6(-1/2) – 2]/5
= (- 1 – 1)/3 – (-3 – 2)/5
= – 2/3 – (-5/5)
= (-2 + 3)/3
10. 13(y – 4) – 3(y – 9) – 5(y + 4) = 0
13(y – 4) – 3(y – 9) – 5(y + 4) = 0
13y – 52 – 3y + 27 – 5y – 20 = 0
13y – 3y – 5y = 52 – 27 + 20
∴ y = 9
LHS = 13(y – 4) – 3 (y – 9) – 5 (y + 4)
= 13 (9 – 4) – 3 (9 – 9) – 5 (9 + 4)
= 13 (5) – 3 (0) – 5 (13)
= 65 – 0 – 65
11. 2/3(x – 5) – 1/4(x – 2) = 9/2
2/3(x – 5) – 1/4(x – 2) = 9/2
2x/3 – 10/3 – x/4 + 2/4 = 9/2
2x/3 – 10/3 – x/4 + 1/2 = 9/2
2x/3 – x/4 = 9/2 + 10/3 – 1/2
By taking LCM for (3 and 4 is 12) (2 and 3 is 6)
(2x×4)/12 – (x×3)/12 = (9×3)/6 + (10×2)/6 – (1×3)/6
8x/12 – 3x/12 = 27/6 + 20/6 – 3/6
(8x-3x)/12 = (27+20-3)6
5x/12 = 44/6
5x×6 = 44×12
LHS = 2/3 (x – 5) – ¼ (x – 2)
= 2/3 [(88/5) – 5] – ¼ [(88/5) – 2]
= 2/3 [(88 – 25)/5] – ¼ [(88 – 10)/5]
= 2/3 × 63/5 – ¼ × 78/5
= 42/5 – 39/10
= (84 – 39)/10
EXERCISE 9.2 PAGE NO: 9.11
Solve each of the following equations and also check your results in each case:
1. (2x+5)/3 = 3x – 10
(2x+5)/3 = 3x – 10
Let us simplify,
(2x+5)/3 – 3x = – 10
By taking LCM
(2x + 5 – 9x)/3 = -10
(-7x + 5)/3 = -10
-7x + 5 = -30
-7x = -30 – 5
Let us verify the given equation now,
By substituting the value of ‘x’, we get,
(2×5 + 5)/3 = 3(5) – 10
(10+5)/3 = 15-10
Hence, the given equation is verified
2. (a-8)/3 = (a-3)/2
(a-8)/3 = (a-3)/2
(a-8)2 = (a-3)3
2a – 16 = 3a – 9
2a – 3a = -9 + 16
By substituting the value of ‘a’ we get,
(-7 – 8)/3 = (-7 – 3)/2
-15/3 = -10/2
3. (7y + 2)/5 = (6y – 5)/11
(7y + 2)/5 = (6y – 5)/11
(7y + 2)11 = (6y – 5)5
77y + 22 = 30y – 25
77y – 30y = -25 – 22
By substituting the value of ‘y’, we get,
(7(-1) + 2)/5 = (6(-1) – 5)/11
(-7 + 2)/5 = (-6 – 5)/11
-5/5 = -11/11
4. x – 2x + 2 – 16/3x + 5 = 3 – 7/2x
x – 2x + 2 – 16/3x + 5 = 3 – 7/2x
Let us rearrange the equation
x – 2x – 16x/3 + 7x/2 = 3 – 2 – 5
By taking LCM for 2 and 3, which is 6
(6x – 12x – 32x + 21x)/6 = -4
-17x/6 = -4
By cross-multiplying
-17x = -4×6
x = -24/-17
24/17 – 2(24/17) + 2 – (16/3)(24/17) + 5 = 3 – (7/2)(24/17)
24/17 – 48/17 + 2 – 384/51 + 5 = 3 – 168/34
By taking 51 and 17 as the LCM we get,
(72 – 144 + 102 – 384 + 255)/51 = (102 – 168)/34
-99/51 = -66/34
-33/17 = -33/17
5. 1/2x + 7x – 6 = 7x + 1/4
1/2x + 7x – 6 = 7x + 1/4
1/2x + 7x – 7x = 1/4 + 6 (by taking LCM)
1/2x = (1+ 24)/4
1/2x = 25/4
4x = 25 × 2
(1/2) (25/2) + 7(25/2) – 6 = 7(25/2) + 1/4
25/4 + 175/2 – 6 = 175/2 + 1/4
By taking LCM for 4 and 2 is 4
(25 + 350 – 24)/4 = (350+1)/4
351/4 = 351/4
6. 3/4x + 4x = 7/8 + 6x – 6
3/4x + 4x = 7/8 + 6x – 6
3/4x + 4x – 6x = 7/8 – 6
By taking 4 and 8 as LCM
(3x + 16x – 24x)/4 = (7 – 48)/8
-5x/4 = -41/8
-5x(8) = -41(4)
-40x = -164
x = -164/-40
(3/4)(41/10) + 4(41/10) = 7/8 + 6(41/10) – 6
123/40 + 164/10 = 7/8 + 246/10 – 6
(123 + 656)/40 = (70 + 1968 – 480)/80
779/40 = 1558/80
779/40 = 779/40
7. 7x/2 – 5x/2 = 20x/3 + 10
7x/2 – 5x/2 = 20x/3 + 10
7x/2 – 5x/2 – 20x/3 = 10
By taking LCM for 2 and 3 is 6
(21x – 15x – 40x)/6 = 10
-34x/6 = 10
(7-/2)(-30/17) – (5/2)(-30/17) = (20/3)(-30/17) + 10
-210/34 +150/34 = -600/51 + 10
-30/17 = (-600+510)/51
-30/17 = -30/17
8. (6x+1)/2 + 1 = (7x-3)/3
(6x+1)/2 + 1 = (7x-3)/3
(6x + 1 + 2)/2 = (7x – 3)/3
(6x + 3)3 = (7x – 3)2
18x + 9 = 14x – 6
18x – 14x = -6 – 9
(6(-15/4) + 1)/2 + 1 = (7(-15/4) – 3)/3
(3(-15/2) + 1)/2 + 1 = (-105/4 -3)/3
(-45/2 + 1)/2 + 1 = (-117/4)/3
(-43/4) + 1 = -117/12
(-43+4)/4 = -39/4
-39/4 = -39/4
9. (3a-2)/3 + (2a+3)/2 = a + 7/6
(3a-2)/3 + (2a+3)/2 = a + 7/6
(3a-2)/3 + (2a+3)/2 – a = 7/6
((3a-2)2 + (2a+3)3 – 6a)/6 = 7/6
(6a – 4 + 6a + 9 – 6a)/6 = 7/6
(6a + 5)/6 = 7/6
By substituting the value of ‘a’, we get,
(3(1/3)-2)/3 + (2(1/3) + 3)/2 = 1/3 + 7/6
(1-2)/3 + (2/3 + 3)/2 = (2+7)/6
-1/3 + (11/3)/2 = 9/6
-1/3 + 11/6 = 3/2
(-2+11)/6 = 3/2
10. x – (x-1)/2 = 1 – (x-2)/3
x – (x-1)/2 = 1 – (x-2)/3
x – (x-1)/2 + (x-2)/3 = 1
(6x – (x-1)3 + (x-2)2)/6 = 1
(6x – 3x + 3 + 2x – 4)/6 = 1
(5x – 1)/6 = 1
5x – 1 = 6
7/5 – (7/5 – 1)/2 = 1 – (7/5 – 2)/3
7/5 – (2/5)/2 = 1 – (-3/5)/3
7/5 – 2/10 = 1 + 3/15
(14 – 2)/10 = (15+3)/15
12/10 = 18/15
11. 3x/4 – (x-1)/2 = (x-2)/3
3x/4 – (x-1)/2 = (x-2)/3
3x/4 – (x-1)/2 – (x-2)/3 = 0
By taking LCM for 4, 2 and 3, which is 12
(9x – (x-1)6 – (x-2)4)/12 = 0
(9x – 6x + 6 – 4x + 8)/12 = 0
(-x + 14)/12 = 0
-x + 14 = 0
3(14)/4 – (14-1)/2 = (14-2)/3
42/4 – 13/2 = 12/3
(42 – 26)/4 = 4
12. 5x/3 – (x-1)/4 = (x-3)/5
5x/3 – (x-1)/4 = (x-3)/5
5x/3 – (x-1)/4 – (x-3)/5 = 0
By taking LCM for 3, 4 and 5, which is 60
((5x×20) – (x-1)15 – (x-3)12)/60 = 0
(100x – 15x + 15 -12x + 36)/60 = 0
(73x + 51)/60 = 0
73x + 51 = 0
(20x – (x-1)3)/12 = (-51/73 – 3)/5
(20x – 3x + 3)/12 = (-270/73)/5
(17x + 3)/12 = -270/365
(17(-51/73) + 3)/12 = -54/73
(-867/73 + 3)/12 = -54/73
((-867 + 219)/73)/12 = -54/73
(-648)/876 = -54/73
-54/73 = -54/73
13. (3x+1)/16 + (2x-3)/7 = (x+3)/8 + (3x-1)/14
(3x+1)/16 + (2x-3)/7 = (x+3)/8 + (3x-1)/14
(3x+1)/16 + (2x-3)/7 – (x+3)/8 – (3x-1)/14 = 0
By taking LCM for 16, 7, 8 and 14, which is 112
((3x+1)7 + (2x-3)16 – (x+3)14 – (3x-1)8)/112 = 0
(21x + 7 + 32x – 48 – 14x – 42 – 24x + 8)/112 = 0
(21x + 32x – 14x – 24x + 7 – 48 – 42 + 8)/112 = 0
(15x – 75)/112 = 0
15x – 75 = 0
(3(5)+1)/16 + (2(5)-3)/7 = (5+3)/8 + (3(5)-1)/14
(15+1)/16 + (10-3)/7 = 8/8 + (15-1)/14
16/16 + 7/7 = 8/8 + 14/14
1 + 1 = 1 + 1
14. (1-2x)/7 – (2-3x)/8 = 3/2 + x/4
(1-2x)/7 – (2-3x)/8 = 3/2 + x/4
(1-2x)/7 – (2-3x)/8 – x/4 = 3/2
By taking LCM for 7, 8 and 4, which is 56
((1-2x)8 – (2-3x)7 – 14x)/56 = 3/2
(8 – 16x – 14 + 21x – 14x)/56 = 3/2
(-9x – 6)/56 = 3/2
2(-9x-6) = 3(56)
-18x – 12 = 168
-18x = 168+12
x = 180/-18
(1-2(-10))/7 – (2-3(-10))/8 = 3/2 + (-10)/4
(1+20)/7 – (2+30)/8 = 3/2 – 5/2
21/7 – 32/8 = 3/2 – 5/2
3 – 4 = -2/2
15. (9x+7)/2 – (x – (x-2)/7) = 36
(9x+7)/2 – (x – (x-2)/7) = 36
Let us simplify the given equation into a simple form
(9x+7)/2 – (7x-x+2)/7 = 36
(9x+7)/2 – (6x+2)/7 = 36
By taking LCM for 2 and 7 is 14
(7(9x+7) – 2(6x+2))/14 = 36
(63x+49 – 12x – 4)/14 = 36
(51x + 45)/14 = 36
51x + 45 = 36(14)
51x + 45 = 504
51x = 504-45
(9(9)+7)/2 – (6(9)+2)/7 = 36
(81+7)/2 – (54+2)/7 = 36
88/2 – 56/7 = 36
44 – 8 = 36
16. 0.18(5x – 4) = 0.5x + 0.8
0.18(5x – 4) = 0.5x + 0.8
0.18(5x – 4) – 0.5x = 0.8
0.90x – 0.72 – 0.5x = 0.8
0.90x – 0.5x = 0.8 + 0.72
0.40x = 1.52
x = 1.52/0.40
0.18(5(3.8)-4) = 0.5(3.8) + 0.8
0.18(19-4) = 1.9 + 0.8
17. 2/3x – 3/2x = 1/12
2/3x – 3/2x = 1/12
By taking LCM for 3x and 2x, which is 6x
((2×2) – (3×3))/6x = 1/12
(4-9)/6x = 1/12
-5/6x = 1/12
2/3(-10) – 3/2(-10) = 1/12
-2/30 + 3/20 = 1/12
((-2×2) + (3×3))/60 = 1/12
(-4+9)/60 = 1/12
5/60 = 1/12
1/12 = 1/12
18. 4x/9 + 1/3 + 13x/108 = (8x+19)/18
4x/9 + 1/3 + 13x/108 = (8x+19)/18
4x/9 + 13x/108 – (8x+19)/18 = -1/3
By taking LCM for 9, 108 and 18, which is 108
((4x×12) + 13x×1 – (8x+19)6)/108 = -1/3
(48x + 13x – 48x – 114)/108 = -1/3
(13x – 114)/108 = -1/3
(13x – 114)3 = -108
39x – 342 = -108
39x = -108 + 342
4(6)/9 + 1/3 + 13(6)/108 = (8(6)+19)/18
24/9 + 1/3 + 78/108 = 67/18
8/3 + 1/3 + 13/18 = 67/18
((8×6) + (1×6) + (13×1))/18 = 67/18
(48 + 6 + 13)/18 = 67/18
67/18 = 67/18
19. (45-2x)/15 – (4x+10)/5 = (15-14x)/9
(45-2x)/15 – (4x+10)/5 = (15-14x)/9
By rearranging
(45-2x)/15 – (4x+10)/5 – (15-14x)/9 = 0
By taking LCM for 15, 5 and 9, which is 45
((45-2x)3 – (4x+10)9 – (15-14x)5)/45 = 0
(135 – 6x – 36x – 90 – 75 + 70x)/45 = 0
(28x – 30)/45 = 0
28x – 30 = 0
(45-2(15/14))/15 – (4(15/14) + 10)/5 = (15 – 14(15/14))/9
(45- 15/7)/15 – (30/7 + 10)/5 = (15-15)/9
300/105 – 100/35 = 0
(300-300)/105 = 0
20. 5(7x+5)/3 – 23/3 = 13 – (4x-2)/3
5(7x+5)/3 – 23/3 = 13 – (4x-2)/3
(35x + 25)/3 + (4x – 2)/3 = 13 + 23/3
(35x + 25 + 4x – 2)/3 = (39+23)/3
(39x + 23)/3 = 62/3
(39x + 23)3 = 62(3)
39x + 23 = 62
39x = 62 – 23
(35x + 25)/3 – 23/3 = 13 – (4x-2)/3
(35+25)/3 – 23/3 = 13 – (4-2)/3
60/3 – 23/3 = 13 – 2/3
(60-23)/3 = (39-2)/3
37/3 = 37/3
21. (7x-1)/4 – 1/3(2x – (1-x)/2) = 10/3
(7x-1)/4 – 1/3(2x – (1-x)/2) = 10/3
Upon expansion
(7x-1)/4 – (4x-1+x)/6 = 10/3
(7x-1)/4 – (5x-1)/6 = 10/3
By taking LCM for 4 and 6, we get 24
((7x-1)6 – (5x-1)4)/24 = 10/3
(42x – 6 – 20x + 4)/24 = 10/3
(22x – 2)/24 = 10/3
22x – 2 = 10(8)
22x – 2 = 80
(7(41/11)-1)/4 – (5(41/11)-1)/6 = 10/3
(287/11 – 1)/4 – (205/11 – 1)/6 = 10/3
(287-11)/44 – (205-11)/66 = 10/3
276/44 – 194/66 = 10/3
69/11 – 97/33 = 10/3
((69×3) – (97×1))/33 = 10/3
(207 – 97)/33 = 10/3
110/33 = 10/3
10/3 = 10/3
22. 0.5(x-0.4)/0.35 – 0.6(x-2.71)/0.42 = x + 6.1
0.5(x-0.4)/0.35 – 0.6(x-2.71)/0.42 = x + 6.1
Let us simplify
(0.5/0.35)(x – 0.4) – (0.6/0.42)(x – 2.71) = x + 6.1
(x – 0.4)/0.7 – (x – 2.71)/0.7 = x + 6.1
(x – 0.4 – x + 2.71)/0.7 = x + 6.1
-0.4 + 2.71 = 0.7(x + 6.1)
0.7x = 2.71 – 0.4 – 4.27
x = -1.96/0.7
0.5(-2.8 – 0.4)/0.35 – 0.6(-2.8 – 2.71)/0.42 = -2.8 + 6.1
-1.6/0.35 + 3.306/0.42 = 3.3
-4.571 + 7.871 = 3.3
23. 6.5x + (19.5x – 32.5)/2 = 6.5x + 13 + (13x – 26)/2
6.5x + (19.5x – 32.5)/2 = 6.5x + 13 + (13x – 26)/2
6.5x + (19.5x – 32.5)/2 – 6.5x – (13x – 26)/2 = 13
(19.5x – 32.5)/2 – (13x – 26)/2 = 13
(19.5x – 32.5 – 13x + 26)/2 = 13
(6.5x – 6.5)/2 = 13
6.5x – 6.5 = 13×2
6.5x – 6.5 = 26
6.5x = 26+6.5
6.5x = 32.5
x = 32.5/6.5
6.5(5) + (19.5(5) – 32.5)/2 = 6.5(5) + 13 + (13(5) – 26)/2
32.5 + (97.5 – 32.5)/2 = 32.5 + 13 + (65 – 26)/2
32.5 + 65/2 = 45.5 + 39/2
(65 + 65)/2 = (91+39)/2
130/2 = 130/2
24. (3x – 8) (3x + 2) – (4x – 11) (2x + 1) = (x – 3) (x + 7)
(3x – 8) (3x + 2) – (4x – 11) (2x + 1) = (x – 3) (x + 7)
9x 2 + 6x – 24x – 16 – 8x 2 – 4x + 22x + 11 = x 2 + 7x – 3x – 21
9x 2 + 6x – 24x – 16 – 8x 2 – 4x + 22x + 11 – x 2 – 7x + 3x + 21 = 0
9x 2 – 8x 2 – x 2 + 6x – 24x – 4x + 22x – 7x + 3x – 16 + 21 + 11 = 0
-4x + 16 = 0
(3(4) – 8) (3(4) + 2) – (4(4) – 11) (2(4) + 1) = (4 – 3) (4 + 7)
(12-8) (12+2) – (16-11) (8+1) = 1(11)
4 (14) – 5(9) = 11
56 – 45 = 11
25. [(2x+3) + (x+5)] 2 + [(2x+3) – (x+5)] 2 = 10x 2 + 92
Let us simplify the given equation
By using the formula (a+b) 2
9x 2 + 48x + 64 + x 2 – 4x + 4 = 10x 2 + 92
9x 2 – 10x 2 + x 2 + 48x – 4x = 92 – 64 – 4
(106/11) 2 + (-16/11) 2 = (360 + 11132)/121
11236/121 + 256/121 = 11492/121
11492/121 = 11492/121
EXERCISE 9.3 PAGE NO: 9.17
Solve the following equations and verify your answer:
1. (2x-3) / (3x+2) = -2/3
(2x-3) / (3x+2) = -2/3
Let us perform cross-multiplication we get,
3(2x – 3) = -2(3x + 2)
6x – 9 = -6x – 4
When rearranged,
6x + 6x = 9 – 4
Now let us verify the given equation,
(2(5/12) – 3) / (3(5/12) + 2) = -2/3
((5/6)-3) / ((5/4) + 2) = -2/3
((5-18)/6) / ((5+8)/4) = -2/3
(-13/6) / (13/4) = -2/3
(-13/6) × (4/13) = -2/3
-4/6 = -2/3
-2/3 = -2/3
2. (2-y) / (y+7) = 3/5
(2-y) / (y+7) = 3/5
Let us perform cross-multiplication, we get,
5(2-y) = 3(y+7)
10 – 5y = 3y + 21
10 – 21 = 3y + 5y
8y = – 11
(2 – (-11/8)) / ((-11/8) + 7) = 3/5
((16+11)/8) / ((-11+56)/8) = 3/5
(27/8) / (45/8) = 3/5
(27/8) × (8/45) = 3/5
27/45 = 3/5
3. (5x – 7) / (3x) = 2
(5x – 7) / (3x) = 2
5x – 7 = 2(3x)
5x – 7 = 6x
5x – 6x = 7
(5(-7) – 7) / (3(-7)) = 2
(-35 – 7) / -21 = 2
-42/-21 = 2
4. (3x+5) / (2x + 7) = 4
(3x+5) / (2x + 7) = 4
3x + 5 = 4(2x+7)
3x + 5 = 8x + 28
3x – 8x = 28 – 5
(3(-23/5) + 5) / (2(-23/5) + 7) = 4
(-69/5 + 5) / (-46/5 + 7) = 4
(-69+25)/5 / (-46+35)/5 = 4
-44/5 / -11/5 = 4
-44/5 × 5/-11 = 4
5. (2y + 5) / (y + 4) = 1
(2y + 5) / (y + 4) = 1
2y + 5 = y + 4
2y – y = 4 – 5
(2(-1) + 5) / (-1 + 4) = 1
(-2+5) / 3 = 1
6. (2x + 1) / (3x – 2) = 5/9
(2x + 1) / (3x – 2) = 5/9
9(2x + 1) = 5(3x – 2)
18x + 9 = 15x – 10
18x – 15x = -10 – 9
(2(-19/3) + 1) / (3(-19/3) – 2) = 5/9
(-38/3 + 1) / (-57/3 – 2) = 5/9
(-38 + 3)/3 / (-57 – 6)/3 = 5/9
-35/3 / -63/3 = 5/9
-35/3 × 3/-63 = 5/9
-35/-63 = 5/9
7. (1 – 9y) / (19 – 3y) = 5/8
(1 – 9y) / (19 – 3y) = 5/8
8(1- 9y) = 5(19-3y)
8 – 72y = 95 – 15y
8 – 95 = 72y – 15y
(1 – 9(-29/19)) / (19 – 3(-29/19)) = 5/8
(19+261)/19 / (361+87)/19 = 5/8
280/19 × 19/448 = 5/8
280/ 448 = 5/8
8. 2x / (3x + 1) = 1
2x / (3x + 1) = 1
2x = 1(3x + 1)
2x = 3x + 1
2x – 3x = 1
2(-1) / (3(-1) + 1) = 1
-2 /(-3+1) = 1
9. y – (7 – 8y)/9y – (3 + 4y) = 2/3
y – (7 – 8y)/9y – (3 + 4y) = 2/3
(y – 7 + 8y) / (9y – 3 – 4y) = 2/3
(-7 + 9y) / (5y – 3) = 2/3
3(-7 + 9y) = 2(5y – 3)
-21 + 27y = 10y – 6
27y – 10y = 21 – 6
15/17 – (7-8(15/17))/ 9(15/17) – (3 + 4(15/17)) = 2/3
15/17 – (7 – 120/17) / 135/17 – (3 + 60/17) = 2/3
15/17 – ((119-120)/17) / 135/17 – ((51+60)/17) = 2/3
15/17 – (-1/17) / 135/17 – (111/17) = 2/23
((15 + 1)/17) / ((135-111)/17) = 2/3
16/17 / 24/17 = 2/3
16/24 = 2/3
10. 6/ 2x – (3 – 4x) = 2/3
6/ 2x – (3 – 4x) = 2/3
6/(2x – 3 + 4x) = 2/3
6/(6x – 3) = 2/3
3(6) = 2(6x – 3)
18 = 12x – 6
12x = 18 + 6
6/ (6(2) – 3) = 2/3
6/(12-3) = 2/3
11. 2/3x – 3/2x = 1/12
4-9/6x = 1/12
By cross-multiplying, we get,
12(-5) = 1 (6x)
2/-30 – 3/-20 = 1/12
-4+6/60 = 1/12
12. (3x + 5)/ (4x + 2) = (3x + 4)/(4x + 7)
(3x + 5)/ (4x + 2) = (3x + 4)/(4x + 7)
(3x + 5)/ (4x + 2) – (3x + 4)/(4x + 7) = 0
By taking LCM as (4x + 2) (4x + 7)
((3x + 5) (4x + 7) – (3x + 4) (4x + 2)) / (4x + 2) (4x + 7) = 0
(3x + 5) (4x + 7) – (3x + 4) (4x + 2) = 0
12x 2 + 21x + 20x + 35 – 12x 2 – 6x – 16x – 8 = 0
19x + 35 – 8 = 0
(3(-27/19) +5) / (4(-27/19) + 2) = (3(-27/19) + 4) / (4(-27/19) + 7)
(-81/19 + 5) / (-108/19 + 2) = (-81/19 + 4) / (-108/19 + 7)
((-81+95)/19) / ((-108+38)/19) = ((-81+76)/19) / ((-108+133)/19)
14/19 / -70/19 = -5/19 / 25/19
-14/70 = -5/25
-1/5 = -1/5
13. (7x – 2) / (5x – 1) = (7x +3)/(5x + 4)
(7x – 2) / (5x – 1) = (7x +3)/(5x + 4)
(7x – 2) / (5x – 1) – (7x +3)/(5x + 4) = 0
By taking LCM as (5x – 1) (5x + 4)
((7x-2) (5x+4) – (7x+3)(5x-1)) / (5x – 1) (5x + 4) = 0
(7x-2) (5x+4) – (7x+3)(5x-1) = 0
Upon simplification,
35x 2 + 28x – 10x – 8 – 35x 2 + 7x – 15x + 3 = 0
10x – 5 = 0
(7(1/2) – 2) / (5(1/2) – 1) = (7(1/2) + 3) /(5(1/2) + 4)
(7/2 – 2) / (5/2 – 1) = (7/2 + 3) / (5/2 + 4)
((7-4)/2) / ((5-2)/2) = ((7+6)/2) / ((5+8)/2)
(3/2) / (3/2) = (13/2) / (13/2)
14. ((x+1)/(x+2)) 2 = (x+2) / (x + 4)
((x+1)/(x+2)) 2 = (x+2) / (x + 4)
(x+1) 2 / (x+2) 2 – (x+2) / (x + 4) = 0
By taking LCM as (x+2) 2 (x+4)
((x+1) 2 (x+4) – (x+2) (x+2) 2 ) / (x+2) 2 (x+4) = 0
(x+1) 2 (x+4) – (x+2) (x+2) 2 = 0
Let us expand the equation
(x 2 + 2x + 1) (x + 4) – (x + 2) (x 2 + 4x + 4) = 0
x 3 + 2x 2 + x + 4x 2 + 8x + 4 – (x 3 + 4x 2 + 4x + 2x 2 + 8x + 8) = 0
x 3 + 2x 2 + x + 4x 2 + 8x + 4 – x 3 – 4x 2 – 4x – 2x 2 – 8x – 8 = 0
-3x – 4 = 0
(x+1) 2 / (x+2) 2 = (x+2) / (x + 4)
(-4/3 + 1) 2 / (-4/3 + 2) 2 = (-4/3 + 2) / (-4/3 + 4)
((-4+3)/3) 2 / ((-4+6)/3) 2 = ((-4+6)/3) / ((-4+12)/3)
(-1/3) 2 / (2/3) 2 = (2/3) / (8/3)
1/9 / 4/9 = 2/3 / 8/3
15. ((x+1)/(x-4)) 2 = (x+8)/(x-2)
((x+1)/(x-4)) 2 = (x+8)/(x-2)
(x+1) 2 / (x-4) 2 – (x+8) / (x-2) = 0
By taking LCM as (x-4) 2 (x-2)
((x+1) 2 (x-2) – (x+8) (x-4) 2 ) / (x-4) 2 (x-2) = 0
(x+1) 2 (x-2) – (x+8) (x-4) 2 = 0
(x 2 + 2x + 1) (x-2) – ((x+8) (x 2 – 8x + 16)) = 0
x 3 + 2x 2 + x – 2x 2 – 4x – 2 – (x 3 – 8x 2 + 16x + 8x 2 – 64x + 128) = 0
x 3 + 2x 2 + x – 2x 2 – 4x – 2 – x 3 + 8x 2 – 16x – 8x 2 + 64x – 128 = 0
45x – 130 = 0
(x+1) 2 / (x-4) 2 = (x+8) / (x-2)
(26/9 + 1) 2 / (26/9 – 4) 2 = (26/9 + 8) / (26/9 – 2)
((26+9)/9) 2 / ((26-36)/9) 2 = ((26+72)/9) / ((26-18)/9)
(35/9) 2 / (-10/9) 2 = (98/9) / (8/9)
(35/-10) 2 = (98/8)
(7/2) 2 = 49/4
49/4 = 49/4
16. (9x-7)/(3x+5) = (3x-4)/(x+6)
(9x-7)/(3x+5) = (3x-4)/(x+6)
(9x-7)/(3x+5) – (3x-4)/(x+6) = 0
By taking LCM as (3x+5) (x+6)
((9x-7) (x+6) – (3x-4) (3x+5)) / (3x+5) (x+6) = 0
(9x-7) (x+6) – (3x-4) (3x+5) = 0
9x 2 + 54x – 7x – 42 – (9x 2 + 15x – 12x – 20) = 0
44x – 22 = 0
(9(1/2) – 7) / (3(1/2) + 5) = (3(1/2) – 4) / ((1/2) + 6)
(9/2 – 7) / (3/2 + 5) = (3/2 – 4) / (1/2 + 6)
((9-14)/2) / ((3+10)/2) = ((3-8)/2) / ((1+12)/2)
-5/2 / 13/2 = -5/2 / 13/2
-5/13 = -5/13
17. (x+2)/(x+5) = x/(x+6)
(x+2)/(x+5) = x/(x+6)
(x+2)/(x+5) – x/(x+6) = 0
By taking LCM as (x+5) (x+6)
((x+2) (x+6) – x(x+5)) / (x+5) (x+6) = 0
(x+2) (x+6) – x(x+5) = 0
Upon expansion,
x 2 + 8x + 12 – x 2 – 5x = 0
3x + 12 = 0
(-4 + 2) / (-4 + 5) = -4 / (-4 + 6)
-2/1 = -4 / (2)
18. 2x – (7-5x) / 9x – (3+4x) = 7/6
2x – (7-5x) / 9x – (3+4x) = 7/6
(2x – 7 + 5x) / (9x – 3 – 4x) = 7/6
(7x – 7) / (5x – 3) = 7/6
6(7x – 7) = 7(5x – 3)
42x – 42 = 35x – 21
42x – 35x = -21 + 42
(7(3) -7) / (5(3) – 3) = 7/6
(21-7) / (15-3) = 7/6
14/12 = 7/6
19. (15(2-x) – 5(x+6)) / (1-3x) = 10
15(2-x) – 5(x+6) / (1-3x) = 10
(30-15x) – (5x + 30) / (1-3x) = 10
(30-15x) – (5x + 30) = 10(1- 3x)
30- 15x – 5x – 30 = 10 – 30x
30- 15x – 5x – 30 + 30x = 10
(15(2-x) – 5(x+6)) / (1-3x) = 10
(15(2-1) – 5(1+6)) / (1- 3) = 10
(15 – 5(7))/-2 = 10
(15-35)/-2 = 10
-20/-2 = 10
20. (x+3)/(x-3) + (x+2)/(x-2) = 2
(x+3)/(x-3) + (x+2)/(x-2) = 2
By taking LCM as (x-3) (x-2)
((x+3)(x-2) + (x+2) (x-3)) / (x-3) (x-2) = 2
(x+3)(x-2) + (x+2) (x-3) = 2 ((x-3) (x-2))
x 2 + 3x – 2x – 6 + x 2 – 3x + 2x – 6 = 2(x 2 – 3x – 2x + 6)
2x 2 – 12 = 2x 2 – 10x + 12
2x 2 – 2x 2 + 10x = 12 + 12
(12/5 + 3)/(12/5 – 3) + (12/5 + 2)/(12/5 – 2) = 2
((12+15)/5)/((12-15)/5) + ((12+10)/5)/((12-10)/5) = 2
(27/5)/(-3/5) + (22/5)/(2/5) = 2
-27/3 + 22/2 = 2
((-27×2) + (22×3))/6 = 2
(-54 + 66)/6 = 2
21. ((x+2) (2x-3) – 2x 2 + 6)/(x-5) = 2
((x+2) (2x-3) – 2x 2 + 6)/(x-5) = 2
(x+2) (2x-3) – 2x 2 + 6) = 2(x-5)
2x 2 – 3x + 4x – 6 – 2x 2 + 6 = 2x – 10
x = 2x – 10
x – 2x = -10
((10+2) (2(10) – 3) – 2(10) 2 + 6)/ (10-5) = 2
(12(17) – 200 + 6)/5 = 2
(204 – 194)/5 = 2
22. (x 2 – (x+1) (x+2))/(5x+1) = 6
(x 2 – (x+1) (x+2))/(5x+1) = 6
(x 2 – (x+1) (x+2)) = 6(5x+1)
x 2 – x 2 – 2x – x – 2 = 30x + 6
-3x – 2 = 30x + 6
30x + 3x = -2 – 6
((-8/33) 2 – ((-8/33)+1) (-8/33 + 2))/(5(-8/33)+1) = 6
(64/1089 – ((-8+33)/33) ((-8+66)/33)) / (-40+33)/33) = 6
(64/1089 – (25/33) (58/33)) / (-7/33) = 6
(64/1089 – 1450/1089) / (-7/33) = 6
((64-1450)/1089 / (-7/33)) = 6
-1386/1089 × 33/-7 = 6
1386 × 33 / 1089 × -7 = 6
23. ((2x+3) – (5x-7))/(6x+11) = -8/3
((2x+3) – (5x-7))/(6x+11) = -8/3
3((2x+3) – (5x-7)) = -8(6x+11)
3(2x + 3 – 5x + 7) = -48x – 88
3(-3x + 10) = -48x – 88
-9x + 30 = -48x – 88
-9x + 48x = -88 – 30
x = -118/39
((2(-118/39) + 3) – (5(-118/39) – 7)) / (6(-118/39) + 11) = -8/3
((-336/39 + 3) – (-590/39 – 7)) / (-708/39 + 11) = -8/3
(((-336+117)/39) – ((-590-273)/39)) / ((-708+429)/39) = -8/3
(-219+863)/39 / (-279)/39 = -8/3
644/-279 = -8/3
-8/3 = -8/3
24. Find the positive value of x for which the given equation is satisfied:
(i) (x 2 – 9)/(5+x 2 ) = -5/9
(x 2 – 9)/(5+x 2 ) = -5/9
9(x 2 – 9) = -5(5+x 2 )
9x 2 – 81 = -25 – 5x 2
9x 2 + 5x 2 = -25 + 81
x 2 = 56/14
x = √4
(ii) (y 2 + 4)/(3y 2 + 7) = 1/2
(y 2 + 4)/(3y 2 + 7) = 1/2
2(y 2 + 4) = 1(3y 2 + 7)
2y 2 + 8 = 3y 2 + 7
3y 2 – 2y 2 = 7 – 8
y = √-1
EXERCISE 9.4 PAGE NO: 9.29
1. Four-fifth of a number is more than three-fourths of the number by 4. Find the number.
Let us consider the number as ‘x’
So, Three-fourth of the number is 3x/4
Fourth-fifth of the number is 4x/5
4x/5 – 3x/4 = 4
By taking LCM of 5 and 4, we get 20
(16x – 15x)/20 = 4
16x – 15x = 4(20)
∴ The number is 80.
2. The difference between the squares of two consecutive numbers is 31. Find the numbers.
Let the two consecutive numbers be x and (x – 1)
x 2 – (x-1) 2 = 31
By using the formula (a-b) 2 = a 2 + b 2 – 2ab
x 2 – (x 2 – 2x + 1) = 31
x 2 – x 2 + 2x – 1 = 31
2x – 1 = 31
Two consecutive numbers are, x and (x-1) : 16 and (16-1) =15
∴ The two consecutive numbers are 16 and 15.
3. Find a number whose double is 45 greater than its half.
2x – x/2 = 45
(4x-x)/2 = 45
∴ The number is 30.
4. Find a number such that when 5 is subtracted from 5 times that number, the result is 4, more than twice the number.
Then, five times the number will be 5x
And, two times, the number will be 2x
5x – 5 = 2x + 4
5x – 2x = 5 + 4
∴ The number is 3.
5. A number whose fifth part increased by 5 is equal to its fourth part diminished by 5. Find the number.
x/5 + 5 = x/4 – 5
x/5 – x/4 = -5 – 5
By taking LCM for 5 and 4, which is 20
(4x-5x)/20 = -10
4x – 5x = -10(20)
∴ The number is 200.
6. A number consists of two digits whose sum is 9. If 27 is subtracted from the number the digits are reversed. Find the number.
We know that one of the digits be ‘x’
The other digit is 9-x
So, the two digit number is 10(9-x) + x
The number obtained after interchanging the digits is 10x + (9-x)
10(9-x) + x – 27 = 10x + (9-x)
90 – 10x + x – 27 = 10x + 9 – x
-10x + x – 10x + x = 9 – 90 + 27
The two-digit number is 10(9-x) + x
Substituting the value of x, we get,
10(9-x) + x
10(9 – 3) + 3
∴ The number is 63.
7. Divide 184 into two parts such that one-third of one part may exceed one-seventh of another part by 8.
Let one of the numbers be ‘x’
The other number is 184 – x
So, One-third of one part may exceed one-seventh of another part by 8.
x/3 – (184-x)/7 = 8
LCM for 3 and 7 is 21
(7x – 552 + 3x)/21 = 8
(7x – 552 + 3x) = 8(21)
10x – 552 = 168
10x = 168 + 552
∴ One of the numbers is 72, and the other number is 184 – x => 184 – 72 = 112.
8. The numerator of a fraction is 6 less than the denominator. If 3 is added to the numerator, the fraction is equal to 2/3. What is the original fraction equal to?
Let us consider the denominator as x and numerator as (x-6)
By using the formula,
Fraction = numerator/denominator = (x-6)/x
(x – 6 + 3)/x = 2/3
(x – 3)/x = 2/3
3(x-3) = 2x
3x – 9 = 2x
3x – 2x = 9
∴ The denominator is x = 9, numerator is (x-6) = (9-6) = 3
And the fraction = numerator/denominator = (x-6)/x = 3/9 = 1/3
9. A sum of Rs 800 is in the form of denominations of Rs 10 and Rs 20. If the total number of notes be 50. Find the number of notes of each type.
Let the number of 10Rs notes be x
Number of 20Rs notes be 50 – x
Amount due to 10Rs notes = 10 × x = 10x
Amount due to 20Rs notes = 20 × (50 – x) = 1000 – 20x
So the total amount is Rs 800
10x + 1000 – 20x = 800
-10x = 800 – 1000
-10x = -200
x = -200/-10
∴ The number of 10Rs notes is 20
Number of 20Rs notes are 50 – 20 = 30
10. Seeta Devi has Rs 9 in fifty-paise and twenty five-paise coins. She has twice as many twenty- five paise coins as she has fifty-paise coins. How many coins of each kind does she have?
Let the number of fifty paise coins be x
The number of twenty-five paise coins be 2x
Amount due to fifty paise coins = (50×x)/100 = 0.50x
Amount due to twenty five paise coins = (25×2x)/100 = 0.50x
So the total amount is Rs 9
0.50x + 0.50x = 9
∴ The number of fifty paise coins is x = 9
Number of twenty-five paise coins, 2x = 2×9 = 18
11. Sunita is twice as old as Ashima. If six years is subtracted from Ashima’s age and four years added to Sunita’s age, then Sunita will be four times Ashima’s age. How old were they two years ago?
Let the present age of Ashima be ‘x’ years
The present age of Sunita is 2x years
Ashima’s new age = (x – 6) years
Sunita’s new age = (2x + 4) years
So, (2x + 4) = 4 (x – 6)
2x + 4 = 4x – 24
2x – 4x = -24 – 4
∴ The age of Ashima is x years = 14 years
Age of Sunita is 2x years = 2(14) = 28 years
Two years ago, age of Ashima is 14 – 2 = 12 years, age of Sunita = 28 – 2 = 26 years
12. The ages of Sonu and Monu are in the ratio 7:5 ten years hence, the ratio of their ages will be 9:7. Find their present ages.
Let the present age of Sonu be 7x years
The present age of Monu is 5x years
Sonu’s age after 10 years = (7x + 10) years
Monu’s age after 10 years = (5x + 10) years
(7x + 10) / (5x + 10) = 9/7
by using cross-multiplication, we get,
7(7x + 10) = 9(5x + 10)
49x + 70 = 45x + 90
49x – 45x = 90 – 70
∴ Present age of Sonu is 7x = 7(5) = 35years
Present age of Monu is 5x = 5(5) = 25years
13. Five years ago, a man was seven times as old as his son. Five years hence, the father will be three times as old as his son. Find their present ages.
Let the age of the son five years ago be x years
The age of man five years ago be 7x years
After five years, the son’s age is x + 5 years
After five years father’s age is 7x + 5 years
So, since five years, the relation in their ages are
7x + 5 + 5 = 3(x + 5 + 5)
7x + 10 = 3x + 15 + 15
7x + 10 = 3x + 30
7x – 3x = 30 – 10
∴ Present father’s age is 7x + 5 = 7(5) + 5 = 35 + 5 = 40years
Present son’s age is x + 5 = 5 + 5 = 10years
14. I am currently 5 times as old as my son. In 6 years time, I will be three times as old as he will be then. What are our ages now?
Let the present son’s age be x years
Present father’s age be 5x years
Son’s age after 6 years = (x + 6) years
Fathers’ age after 6 years = (5x + 6) years
5x + 6 = 3(x + 6)
5x + 6 = 3x + 18
5x – 3x = 18 – 6
∴ present son’s age is x = 6years
Present father’s age is 5x = 5(6) = 30years
15. I have Rs 1000 in ten and five rupee notes. If the number of ten rupee notes that I have is ten more than the number of five rupee notes, how many notes do I have in each denomination?
Let the number of five rupee notes be x
The number of ten rupee notes be (x + 10)
Amount due to five rupee notes = 5 × x = 5x
Amount due to ten rupee notes = 10 (x + 10) = 10x + 100
The total amount = Rs 1000
5x + 10x +100 = 1000
∴ the number of five rupee notes is x = 60
The number of ten rupee notes is x + 10 = 60+10 = 70
16. At a party, colas, squash and fruit juice were offered to guests. A fourth of the guests drank colas, a third drank squash, two-fifths drank fruit juice, and just three did not drink anything. How many guests were in all?
Let the number of guests be x
The given details are the number of guests who drank colas are x/4
The number of guests who drank squash is x/3
The number of guests who drank fruit juice is 2x/5
The number of guests who did not drink anything was 3
x/4 + x/3 + 2x/5 + 3 = x
By taking LCM for 4, 3 and 5, we get 60
(15x+20x+24x-60x)/60 = -3
(15x+20x+24x-60x) = -3(60)
∴ The total number of guests in all was 180
17. There are 180 multiple choice questions in a test. If a candidate gets 4 marks for every correct answer and for every unattempted or wrongly answered question, one mark is deducted from the total score of correct answers. If a candidate scored 450 marks in the test, how many questions did he answer correctly?
Let the number of correct answers be x
The number of questions answered wrong is (180 – x)
Total score when answered right = 4x
Marks deducted when answered wrong = 1(180 – x) = 180 – x
4x – (180 – x) = 450
4x – 180 + x = 450
5x = 450 + 180
∴ 126 questions he answered correctly.
18. A labourer is engaged for 20 days on the condition that he will receive Rs 60 for each day he works, and he will be fined Rs 5 for each day he is absent. If he receives Rs 745 in all, how many days he remained absent?
Let us consider the number of absent days as x
So, the number of present days is (20 – x)
The wage for one day of work = Rs 60
Fine for absent day = Rs 5
60(20 – x) – 5x = 745
1200 – 60x – 5x = 744
-65x = 744-1200
-65x = -456
x = -456/-65
∴ For 7 days, the labourer was absent.
19. Ravish has three boxes whose total weight is 60 ½ Kg. Box B weighs 3 ½ kg more than box A, and box C weighs 5 1/3 kg more than box B. Find the weight of box A.
The given details are the total weight of three boxes is 60 ½ kg = 121/2 kg
Let the weight of box A be x kg
Weight of box B be x + 7/2 kg
Weight of box C be x + 7/2 + 16/3 kg
x + x + 7/2 + x + 7/2 + 16/3 = 121/2
3x = 121/2 – 7/2 – 7/2 – 16/3
3x = (363 – 21 – 21 – 32)/6
∴ The weight of box A is 289/18 kg
20. The numerator of a rational number is 3 less than the denominator. If the denominator is increased by 5 and the numerator by 2, we get the rational number 1/2. Find the rational number.
Le the denominator be x and the numerator be (x – 3)
By using the formula
Fraction = numerator/denominator
= (x – 3)/x
So, when the numerator is increased by 2 and Denominator is increased by 5, then the fraction is ½
(x – 3 + 2)/(x + 5) = 1/2
(x – 1)/(x + 5) = 1/2
By using cross-multiplication, we get
2(x – 1) = x + 5
2x – 2 = x + 5
2x – x = 2 + 5
∴ Denominator is x = 7, numerator is (x – 3) = 7 – 3 = 4
And the fraction = numerator/denominator = 4/7
21. In a rational number, twice the numerator is 2 more than the denominator, if 3 is added to each, the numerator and the denominator. The new fraction is 2/3. Find the original number.
Le the numerator be x and the denominator be (2x – 2)
= x / (2x – 2)
So, the numerator and denominator are increased by 3, then the fraction is 2/3
(x + 3)/(2x – 2 + 3) = 2/3
(x + 3)/(2x + 1) = 2/3
3(x + 3) = 2(2x + 1)
3x + 9 = 4x + 2
3x – 4x = 2 – 9
∴ The numerator is x = 7, denominator is (2x – 2) = (2(7) – 2) = 14-2 = 12
And the fraction is numerator/denominator = 7/12
22. The distance between two stations is 340 km. Two trains start simultaneously from these stations on parallel tracks to cross each other. The speed of one of them is greater than that of the other by 5 km/hr. If the distance between the two trains after 2 hours of their start is 30 km, find the speed of each train.
Let the speed of one train be x km/hr.
The speed of the other train be (x + 5) km/hr.
The total distance between the two stations = 340 km
Distance = speed × time
So, the distance covered by one train in 2 hrs. Will be x×2 = 2x km
Distance covered by the other train in 2 hrs. Will be 2(x + 5) = (2x + 10) km
The distance between the trains is 30 km
2x + 2x + 10 + 30 = 340
4x + 40 = 340
4x = 340 – 40
∴ The speed of one train is x = 75 km/hr.
Speed of other train is (x + 5) = 75 + 5 = 80 km/hr.
23. A steamer goes downstream from one point to another in 9 hours. It covers the same distance upstream in 10 hours. If the speed of the stream is 1 km/hr., find the speed of the steamer in still water and the distance between the ports.
Let the speed of the steamer be x km/hr.
Speed of stream = 1 km/hr.
Downstream speed = (x + 1) km/hr.
Upstream speed = (x – 1) km/hr.
= (x + 1) × 9 and
= (x – 1) × 10
9x + 9 = 10x – 10
9x – 10x = -10 -9
x = 19 km/hr.
∴ The speed of the steamer in still water is 19 km/hr.
Distance between the ports is 9(x + 1) = 9(19+1) = 9(20) = 180 km.
24. Bhagwanti inherited Rs 12000.00. She invested part of it at 10% and the rest at 12%. Her annual income from these investments is Rs 1280.00 How much did she invest at each rate?
At a rate of 10%, let the investment be Rs x
At the rate of 12%, the investment will be Rs (12000 – x)
At 10% of rate the annual income will be x × (10/100) = 10x/100
At 12% of rate, the annual income will be (12000 – x) × 12/100 = (144000 – 12x)/100
Total investment = 1280
So, 10x/100 + (144000 – 12x)/100 = 1280
(10x + 144000 – 12x)/100 = 1280
(144000 – 2x)/100 = 1280
144000 – 2x = 1280(100)
-2x = 128000 – 144000
-2x = -16000
x = -16000/-2
∴ At 10% of rate, she invested Rs 8000, and at 12% of the rate she invested Rs (12000 – x) = Rs (12000 – 8000) = Rs 4000
25. The length of a rectangle exceeds its breadth by 9 cm. If length and breadth are each increased by 3 cm, the area of the new rectangle will be 84 cm 2 more than that of the given rectangle. Find the length and breadth of the given rectangle.
Let the breadth of the rectangle be x meter
Length of the rectangle be (x + 9) meter
Area of the rectangle length×breadth = x(x +9) m 2
When length and breadth increased by 3cm, then,
New length = x + 9 + 3 = x + 12
New breadth = x + 3
So, the area is
(x + 12) (x + 3) = x (x + 9) + 84
x 2 + 15x + 36 = x 2 + 9x + 84
15x – 9x = 84 – 36
∴ The length of the rectangle (x + 9) = (8 + 9) = 17cm, and the breadth of the rectangle is 8cm.
26. The sum of the ages of Anup and his father is 100. When Anup is as old as his father now, he will be five times as old as his son Anuj is now. Anuj will be eight years older than Anup is now, when Anup is as old as his father. What are their ages now?
Let the age of Anup be x years
So the age of Anup’s father will be (100 – x) years
The age of Anuj is (100-x)/5 years
So, When Anup is as old as his father after (100 – 2x) years,
Then Anuj’s age = present age of his father (Anup) + 8
Present age of Anuj + 100 – 2x = Present age of Anup + 8
(100 – x)/5 + (100 – 2x) = x + 8
(100-x)/5 – 3x = 8 – 100
(100 – x – 15x)/5 = -92
100 – 16x = -460
-16x = -460 – 100
-16x = -560
x = -560/-16
∴ The present age of Anup is 35 years then, the age of Anup’s father will be (100-x) = 100-35 = 65 years
The age of Anuj is (100-x)/5 = (100 – 35)/5 = 65/5 = 13 years
27. A lady went shopping and spent half of what she had on buying hankies and gave a rupee to a beggar waiting outside the shop. She spent half of what was left on lunch and followed that up with a two rupee tip. She spent half of the remaining amount on a book and three rupees on bus fare. When she reached home, she found that she had exactly one rupee left. How much money did she start with?
Let the amount lady had be Rs x
Amount spent for hankies and given to beggar is x/2 + 1
Remaining amount is x – (x/2 + 1) = x/2 – 1 = (x-2)/2
Amount spent for lunch (x-2)/2×1/2 = (x-2)/4
The amount given as a tip is Rs 2
Remaining amount after lunch = (x-2)/2 – (x-2)/4 – 2 = (2x – 4 – x + 2 – 8)/4 = (x – 10)/4
Amounts spent for books =1/2 × (x-10)/4 = (x-10)/8
The bus fare is Rs 3
Amount left = (x-10)/4 – (x-10)/8 – 3 = (2x – 20 – x + 10 – 24)/8 = (x-34)/8
So from the question, we know that the amount left = Rs 1
(x-34)/8 = 1
x – 34 = 8
∴ the lady started with Rs. 42
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Grade 8 Algebra Word Problems
These lessons cover some examples and solutions for algebra word problems that you will commonly encounter in grade 8.
Related Pages More Math Word Problems Algebra Word Problems
How to write algebra word problems into systems of linear equations and solve systems of linear equations using elimination and substitution methods?
Grade 8 Algebra Word Problems How to solve algebra word problems using systems of linear equations?
Example: Devon is going to make 3 shelves for her father. He has a piece of lumber 12 feet long. She wants the top shelf to be half a foot shorter than the middle shelf, and the bottom shelf to be half a foot shorter than twice the length of the top shelf. How long will each shelf be if she uses the entire 12 feet of wood?
Grade 8 Algebra Word Problems - Line Segments
Example: If JK = 7x + 9, JL = 114 and KL = 9x + 9. Find KL.
Grade 8 number word problems - common core How to write word problems into systems of linear equations and solve systems of linear equations using elimination and substitution methods?
Example 1: The sum of two numbers is 361 and the difference between the two numbers is 173. What are the two numbers?
Example 2: There are 356 Grade 8 students at Euclid’s Middle School. Thirty-four more than four times the number of girls is equal to half the number of boys. How many boys are in Grade 8 at Euclid’s Middle School? How many girls?
Example 3: A family member has some five-dollar bills and one-dollar bills in their wallet. Altogether she has 18 bills and a total of $62. How many of each bill does she have?
Example 1: A friend bought 2 boxes of pencils and 8 notebooks for school and it cost him $11. He went back to the store the same day to buy school supplies for his younger brother. He spent $11.25 on 3 boxes of pencils and 5 notebooks. How much would notebooks cost?
- A farm raises cows and chickens. The farmer has a total of 42 animals. One day he counts the legs of all of his animals and realizes he has a total of 114. How many cows does the farmer have? How many chickens?
- The length of a rectangle is 4 times the width. The perimeter of the rectangle is 45 inches. What is the area of the rectangle?
- The sum of the measures of angles x and y is 127". If the measure of angle x is 34° more than half the measure of angle y, what is the measure of each angle?

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Linear Equations in One Variable
- NCERT Solutions
- Chapter 2 Linear Equations In One Variable

NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Chapter 2 Maths Linear Equations in One Variable - FREE PDF Download
In Class 8 Maths NCERT Solutions for Chapter 2, students will learn about Linear Equations in One Variable. The NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 PDF file, which is available for free, can help students score good marks. Students can download this PDF file by visiting Vedantu. Linear Equations in One Variable Class 8 chapter is crucial as it lays the groundwork for more advanced algebraic concepts that students will encounter in higher classes. The Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Solutions is created according to the latest CBSE Class 8 Maths Syllabus and is structured to gradually build students' understanding and problem-solving skills through a variety of examples and exercises.

Glance on Maths Chapter 2 Class 8 - Linear Equations in One Variable | Vedantu
In maths class 8 chapter 2 we understand what an equation is and how to recognize a linear equation with one variable (ax + b = 0, where a and b are constants, and x is the variable).
Solving linear equations: Different methods for solving equations, including:
Adding or subtracting constants from both sides.
Multiplying or dividing both sides by the same non-zero number.
This article contains chapter notes, formulas, exercise links and important questions for chapter 2 - Linear Equations in One Variable.
There are two exercises (20 fully solved questions) in Class 8th Maths Chapter 2 Linear Equations in One Variable.
Access Exercise-wise NCERT Solutions for Chapter 2 Maths Class 8
Current Syllabus Exercises of Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 |
|
|
Exercises Under NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Linear Equations in One Variable
Exercise 2.1: This exercise contains 10 questions. This exercise covers how to solve equations with variables on both sides.
Exercise 2.2: This exercise contains 10 questions. This exercise deals with how to reduce equations into simpler form.
Access NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 – Linear Equations in One Variable
Exercise 2.1.
1. Solve and check result: $3x=2x+18$
\[3x=2x+18\]
On Transposing \[2x\] to L.H.S, we obtain
\[3x-2x=18\]
L.H.S \[=3x=3\times 18=54\]
R.H.S \[=2x+18=2\times 18+18=36+18=54\]
L.H.S. = R.H.S.
Hence, the result obtained above is correct.
2. Solve and check result: $5t-3=3t-5$
Ans:
\[5t-3=3t-5\]
On Transposing \[3t\] to L.H.S and \[-3\] to R.H.S, we obtain
\[5t-3=-5-\left( -3 \right)\]
On dividing both sides by\[2\], we obtain
L.H.S \[=5t-3=5\times \left( -1 \right)-3=-8\]
R.H.S \[=3t-5=3\times \left( -1 \right)-5=-3-5=-8\]
Hence, the result obtained above is correct.
3. Solve and check result: $5x+9-5+3x$
\[5x+9=5+3x\]
On Transposing \[3x\] to L.H.S and \[9\] to R.H.S, we obtain
\[5x-3x=5-9\]
L.H.S \[=5x+9=5\times \left( -2 \right)+9=-10+9=-1\]
R.H.S \[=5+3x=5+3\times \left( -2 \right)=5-6=-1\]
4. Solve and check result: $4z+3=6+2z$
\[4z+3=6+2z\]
On Transposing \[2z\] to L.H.S and \[3\] to R.H.S, we obtain
\[4z-2z=6-3\]
Dividing both sides by\[2\] , we obtain
L.H.S \[=4z+3=4\times \left( \frac{3}{2} \right)+3=6+3=9\]
R.H.S \[=6+2z=6+2\times \left( \frac{3}{2} \right)=6+3=9\]
5. Solve and check result: $2x-1=14-x$
\[2x-1=14-x\]
Transposing x to L.H.S and $1$ to R.H.S, we obtain
\[2x+x=14+1\]
Dividing both sides by \[3\], we obtain
L.H.S \[=2x-1=2\times \left( 5 \right)-1=10-1=9\]
R.H.S \[=14-x=14-5=9\]
6. Solve and check result: $8x+4=3\left( x-1 \right)+7$
\[8x+4=3\left( x-1 \right)+7\]
\[8x+4=3x-3+7\]
Transposing \[3x\] to L.H.S and $4$ to R.H.S, we obtain
\[8x-3x=-3+7-4\]
\[5x=-7+7\]
L.H.S \[=8x+4=8\times \left( 0 \right)+4=4\]
R.H.S \[=3\left( x-1 \right)+7=3\left( 0-1 \right)+7=-3+7=4\]
7. Solve and check result: $x=\frac{4}{5}\left( x+10 \right)$
\[x=\frac{4}{5}\left( x+10 \right)\]
Multiplying both sides by\[5\], we obtain
\[5x=4\left( x+10 \right)\]
\[5x=4x+40\]
Transposing \[4x\] to L.H.S, we obtain
L.H.S \[=x=40\]
R.H.S \[=\frac{4}{5}\left( x+10 \right)=\frac{4}{5}\left( 40+10 \right)=\frac{4}{5}\times 50=40\]
8. Solve and check result: $\frac{2x}{3}+1=\frac{7x}{15}+3$
\[\frac{2x}{3}+1=\frac{7x}{15}+3\]
Transposing \[\frac{7x}{15}\] to L.H.S and $1$ to R.H.S, we obtain
\[\frac{2x}{3}-\frac{7x}{15}=3-1\]
\[\frac{5\times 2x-7x}{15}=2\]
\[\frac{3x}{15}=2\]
\[\frac{x}{5}=2\]
Multiplying both sides by\[5\] , we obtain
L.H.S \[=\frac{2x}{3}+1=\frac{2\times 10}{3}+1=\frac{2\times 10+1\times 3}{3}=\frac{23}{3}\]
R.H.S\[=\frac{7x}{15}+3=\frac{7\times 10}{15}+3=\frac{7\times 2}{3}+3=\frac{14}{3}+3=\frac{14+3\times 3}{3}=\frac{23}{3}\]
9. Solve and check result: $2y+\frac{5}{3}=\frac{26}{3}-y$
\[2y+\frac{5}{3}=\frac{26}{3}-y\]
Transposing y to L.H.S and \[\frac{5}{3}\] to R.H.S, we obtain
\[2y+y=\frac{26}{3}-\frac{5}{3}\]
\[3y=\frac{21}{3}=7\]
Dividing both sides by$3$, we obtain
\[y=\frac{7}{3}\]
L.H.S \[=2y+\frac{5}{3}=2\times \frac{7}{3}+\frac{5}{3}=\frac{14}{3}+\frac{5}{3}=\frac{19}{3}\]
R.H.S = \[\frac{26}{3}-y=\frac{26}{3}-\frac{7}{3}=\frac{19}{3}\]
L.H.S. = R.H.S. Hence, the result obtained above is correct.
10. Solve and check result: $3m=5m-\frac{8}{5}$
\[3m=5m-\frac{8}{5}\]
Transposing \[5m\] to L.H.S, we obtain
\[3m-5m=-\frac{8}{5}\]
\[-2m=-\frac{8}{5}\]
Dividing both sides by\[-2\] , we obtain
\[m=\frac{4}{5}\]
L.H.S \[=3m=3\times \frac{4}{5}=\frac{12}{5}\]
R.H.S \[5m-\frac{8}{5}=5\times \frac{4}{5}-\frac{8}{5}=\frac{12}{5}\]
Exercise 2.2
1. Solve the linear equation $\frac{x}{2}-\frac{1}{5}=\frac{x}{3}+\frac{1}{4}$
\[\frac{x}{2}-\frac{1}{5}=\frac{x}{3}+\frac{1}{4}\]
L.C.M. of the denominators, \[2,3,4,\text{and 5,}\]is 60
Multiplying both sides by 60 , we obtain
\[60\left( \frac{x}{2}-\frac{1}{5} \right)=60\left( \frac{x}{3}+\frac{1}{4} \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow 30x-12=20x+15\] (Opening the brackets)
\[\Rightarrow 30x-20x=15+12\]
\[\Rightarrow 10x=27\]
\[\Rightarrow x=\frac{27}{10}\]
2. Solve the linear equation$\frac{n}{2}-\frac{3n}{4}+\frac{5n}{6}=21$
\[\frac{n}{2}-\frac{3n}{4}+\frac{5n}{6}=21\]
L.C.M. of the denominators, \[2,4,\text{ and }6\text{ is }12\].
Multiplying both sides by\[12\], we obtain
\[6n-9n+10n=252\]
\[\Rightarrow 7n=252\]
\[\Rightarrow n=\frac{252}{7}\]
\[\Rightarrow n=36\]
3. Solve the linear equation $x+7-\frac{8x}{3}=\frac{17}{6}-\frac{5x}{2}$
\[x+7-\frac{8x}{3}=\frac{17}{6}-\frac{5x}{2}\]
L.C.M. of the denominators, \[2,3,\text{ and }6,\text{is }6\].
Multiplying both sides by \[6\], we obtain
\[6x+42-16x=17-15x\]
\[\Rightarrow 6x-16x+15x=17-42\]
\[\Rightarrow 5x=-25\]
\[\Rightarrow x=\frac{-25}{5}\]
\[\Rightarrow x=-5\]
4. Solve the linear equation $\frac{x-5}{3}=\frac{x-3}{5}$
\[\frac{x-5}{3}=\frac{x-3}{5}\]
L.C.M. of the denominators, \[3\text{ and }5,\text{ is }15\].
Multiplying both sides by\[15\], we obtain
\[5\left( x-5 \right)=3\left( x-3 \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow 5x-25=3x-9\] (Opening the brackets)
\[\Rightarrow 5x-3x=25-9\]
\[\Rightarrow 2x=16\]
\[\Rightarrow x=\frac{16}{2}\]
\[\Rightarrow x=8\]
5. Solve the linear equation $\frac{3t-2}{4}-\frac{2t+3}{3}=\frac{2}{3}-t$
\[\frac{3t-2}{4}-\frac{2t+3}{3}=\frac{2}{3}-t\]
L.C.M. of the denominators, \[3\text{ and }4,\text{is}\,12\].
Multiplying both sides by \[12\], we obtain
\[3\left( 3t-2 \right)-4\left( 2t+3 \right)=8-12t\]
\[\Rightarrow 9t-6-8t-12=8-12t\] (Opening the brackets)
\[\Rightarrow 9t-8t+12t=8+6+12\]
\[\Rightarrow 13t=26\]
\[\Rightarrow t=\frac{26}{13}\]
\[\Rightarrow t=2\]
6. Solve the linear equation$m-\frac{m-1}{2}=1-\frac{m-2}{3}$
\[m-\frac{m-1}{2}=1-\frac{m-2}{3}\]
L.C.M. of the denominators, \[2\text{ and }3,\text{ is}\,\text{ }6\].
\[6m-3\left( m-1 \right)=6-2\left( m-2 \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow 6m-3m+3=6-2m+4\] (Opening the brackets)
\[\Rightarrow 6m-3m+2m=6+4-3\]
\[\Rightarrow 5m=7\]
\[\Rightarrow m=\frac{7}{5}\]
7. Simplify and solve the linear equation $3\left( t-3 \right)=5\left( 2t+1 \right)$
\[3\left( t-3 \right)=5\left( 2t+1 \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow 3t-9=10t+5\] (Opening the brackets)
\[\Rightarrow -9-5=10t-3t\]
\[\Rightarrow -14=7t\]
\[\Rightarrow t=\frac{-14}{7}\]
\[\Rightarrow t=-2\]
8. Simplify and solve the linear equation$15\left( y-4 \right)-2\left( y-9 \right)+5\left( y+6 \right)=0$
\[15\left( y-4 \right)-2\left( y-9 \right)+5\left( y+6 \right)=0\]
\[\Rightarrow 15y-60-2y+18+5y+30=0\] (Opening the brackets)
\[\Rightarrow 18y-12=0\]
\[\Rightarrow 18y=12\]
\[\Rightarrow y=\frac{12}{8}=\frac{2}{3}\]
9.Simplify and solve the linear equation $3\left( 5z-7 \right)-2\left( 9z-11 \right)=4\left( 8z-13 \right)-17$
\[3\left( 5z-7 \right)-2\left( 9z-11 \right)=4\left( 8z-13 \right)-17\]
\[\Rightarrow 15z-21-18z+22=32z-52-17\] (Opening the brackets)
\[\Rightarrow -3z+1=32z-69\]
\[\Rightarrow -3z-32z=-69-1\]
\[\Rightarrow -35z=-70\]
\[\Rightarrow z=\frac{70}{~35}=2\]
10. Simplify and solve the linear equation $0.25\left( 4f-3 \right)=0.05\left( 10f-9 \right)$
\[0.25\left( 4f-3 \right)=0.05\left( 10f-9 \right)\]
$\frac{1}{4}\left( 4f-3 \right)=\frac{1}{20}\left( 10f-9 \right)$
Multiplying both sides by\[20\], we obtain
\[5\left( 4f-3 \right)=10f-9\]
\[\Rightarrow 20f-15=10f-9\] (Opening the brackets)
\[\Rightarrow 20f-10f=-9+15\]
\[\Rightarrow 10f=6\]
\[\Rightarrow f=\frac{3}{5}=0.6\]
Overview of Deleted Syllabus for CBSE Class 8 Maths Linear Equations In One Variable
Chapter | Dropped Topics |
Linear Equations in One Variable | 2.2 - Solving Equations which have linear expressions on one side and numbers on the other side |
2.3 - Some Applications | |
2.5 - Some more applications | |
2.7 - Equations Reducible to the linear forms. |
Class 8 Maths Chapter 2: Exercises Breakdown
Exercises | Number of Questions |
Exercise 2.1 | 10 Questions with Solutions |
Exercise 2.2 | 10 Questions with Solutions |
Conclusion
NCERT Maths Class 8 Solutions Vedantu's Linear Equations in One Variable provide a thorough understanding of this significant subject. Students can build a solid foundation in Linear Equations by concentrating on important ideas such as reducing equations into simpler forms, solving equations with variables on both sides. It's important to pay attention to the step-by-step solutions provided in the NCERT Solutions, as they help clarify concepts and reinforce problem-solving techniques. In previous years' exams, typically 2 to 3 questions have been asked from Ch 2 Maths Class 8. These questions often cover a variety of problem types, including basic equation solving, application-based word problems, and questions involving equations with variables on both sides. This pattern has been consistent across multiple exam papers and sources.
Other Study Material for CBSE Class 8 Maths Chapter 2
S. No | Important links for Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Linear Equations in One Variable |
1. |
|
2. |
|
3. |
|
4. |
|
5. |
|
6. |
|
Chapter-Specific NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths
Given below are the chapter-wise NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths . Go through these chapter-wise solutions to be thoroughly familiar with the concepts.
NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter-wise List |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

FAQs on NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Linear Equations in One Variable
1. Give an example of an equation that is not linear but can be reduced to a linear form.
Sometimes we come across equations that are not linear as per the definition of linear equations but can be reduced to a linear form and then the method of solving linear equations can be applied to them to solve them. The example below illustrates one such equation and how to solve it:
(X + 1)/(2x + 6) = 3/8
To reduce this nonlinear equation into a linear equation we multiply both sides by the denominator of LHS which is 2x + 6.
(X + 1)/(2x + 6) * (2x + 6) = 3/8 * (2x + 6)
X + 1 = 6x + 18/8 - This is a linear equation now. We can solve it by multiplying both sides with LCM of denominators which is 8
8 * (x + 1) = 8 * (6x + 18/8)
8x + 8 = 6x + 18
Now moving all variable to LHS and all constant to RHS we get:
8x - 6x = 18 - 8
2. Mention some of the important features of a linear equation.
A linear equation is characterized by the following key properties:
The highest power of the variable involved in a linear equation is 1.
The linear equation can have one or two variables in it.
A linear equation has an equality sign. The expression on the left side of the equality is called LHS (left-hand side), and the expression on the right side of the equality sign is termed as RHS (right-hand side).
The two expressions, LHS and RHS, are equal for only certain values of the variables. These values of the variables are the solutions of the linear equation.
The points of a linear equation with just one variable can be marked on the number line.
3. What are the sub-topics covered in Chapter 2 of Class 8 Maths?
The concepts covered in Chapter 2 of Class 8 Maths are :
2.1 Introduction
2.2 Solving equations which have a Linear expression on one side and numbers on the other side
2.3 Some applications
2.4 Solving equations having the variables on both sides
2.5 Some more applications
2.6 Reducing equations to a simpler form
2.7 Equations reducible to linear form.
4. How many exercises are there in Chapter 2 of Class 8 Maths?
Chapter 2, “Linear Equations In One Variable”, consists of 2 exercises -
Exercise 2.1 contains 12 questions.
Exercise 2.2 contains 16 questions.
Students can practise all the questions in the NCERT solutions designed by the experts at Vedantu to get well versed in this chapter. Download these solutions on the Vedantu website or the app for free of cost to prepare for the exams. These questions will help the students to secure a perfect score in the exams.
5. Do I need to practice all the questions given in NCERT Solutions?
Yes, you need to practice all the questions given in the NCERT Solutions. NCERT Solutions prepared by the experts at Vedantu will help the students clear all their doubts in the chapter and practice more to get a perfect score in the exam. You can download the solutions of this chapter by clicking on NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 to ace your exams. These solutions are available on Vedantu (vedantu.com) free of cost. You can download it through the Vedantu app as well.
6. Are NCERT Solutions Chapter 2 Class 8 Maths important for your exams?
Undoubtedly, NCERT Answers Chapter 2 Class 8 Mathematics are significant for your examinations because they include the majority of the problems. Vedantu's NCERT Answers Chapter 2 Class 8 Mathematics assist students in gaining a thorough understanding of all subjects. These solutions assist students in revising and practising all of the issues handled by professionals before to tests.
7. Where to download NCERT Solutions for Chapter 2 Class 8 Maths?
Students of Class 8 can download the NCERT Solutions for Chapter 2 using the link NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 from Vedantu’s app or website (vedantu.com). Since the solutions are based on the CBSE syllabus, students will be able to practice all the problems. The experts at Vedantu prepare these solutions, keeping in mind the students so that they can excel in their exams.
8. How can you tell if an equation is NOT linear in one variable?
The equation has multiple variables (e.g., 2x + y = 5).
The variable has an exponent higher than 1 (e.g., x^2 + 3x = 4).
It's a constant expression with no variable (e.g., 5 + 7 = 12).
9. What are the steps that are involved in solving a Ch 2 Maths Class 8 linear equation?
Step 1: Identify like terms
Combine terms on one side of the equation that have the same variable
For example 3x + 5x becomes 8x.
Step 2: Isolate the variable
Using addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division (on both sides equally!), get the variable by itself on one side of the equation.
Step 3: Simplify
If there's a coefficient multiplying the variable, simplify by dividing both sides by that number.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths
Ncert solutions for class 8.
- Class 6 Maths
- Class 6 Science
- Class 6 Social Science
- Class 6 English
- Class 7 Maths
- Class 7 Science
- Class 7 Social Science
- Class 7 English
- Class 8 Maths
- Class 8 Science
- Class 8 Social Science
- Class 8 English
- Class 9 Maths
- Class 9 Science
- Class 9 Social Science
- Class 9 English
- Class 10 Maths
- Class 10 Science
- Class 10 Social Science
- Class 10 English
- Class 11 Maths
- Class 11 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 11 English
- Class 12 Maths
- Class 12 English
- Class 12 Economics
- Class 12 Accountancy
- Class 12 Physics
- Class 12 Chemistry
- Class 12 Biology
- Class 12 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 12 Physical Education
- GST and Accounting Course
- Excel Course
- Tally Course
- Finance and CMA Data Course
- Payroll Course
Interesting
- Learn English
- Learn Excel
- Learn Tally
- Learn GST (Goods and Services Tax)
- Learn Accounting and Finance
- GST Tax Invoice Format
- Accounts Tax Practical
- Tally Ledger List
- GSTR 2A - JSON to Excel
Are you in school ? Do you love Teachoo?
We would love to talk to you! Please fill this form so that we can contact you
You are learning...
Chapter 2 Class 8 Linear Equations in One Variable
Click on any of the links below to start learning from Teachoo ...
Updated for new NCERT - 2023-24 Book.
Get NCERT Solutions of all Exercise Questions and Examples of Chapter 2 Class 8 Linear Equations in One Variable free at Teachoo. Answers to each and every question with detailed explanation for your understanding. Best answers guaranteed!
We studied Equations and Expressions in Algebra ( Chapter 9 Class 8 ). Equation has an = sign, expression does not have it
In this chapter, we will learn
- What is an Equation
- What is a Linear Equation
- What is a Linear Equation in one variable
- Solving Linear Equations - by taking variables on one side, numbers on the side
- Making Equations from Statements , and then Solving.
- Perimeter and Area Questions
- Fraction questions - where we need to find Numerator or Denominator
- Cost, Sale, Profit Questions
- Questions where we have Consecutive Numbers
- Questions involving Consecutive Multiples
- Coins and Currency Notes Questions
- Questions where numbers are added or subtracted
- Questions where a Two Digit number is given, and we reverse its digits
- Questions involving Age
Click on an exercise or topic link below to start doing the chapter.
Note: Important Questions of this chapter have been marked. When you click on a link, at the bottom of the page there is a list with arrows. In that list, you can find all the questions of that exercise and find Important Questions marked as blue.
Serial order wise
Concept wise.
What's in it?

Hi, it looks like you're using AdBlock :(
Please login to view more pages. it's free :), solve all your doubts with teachoo black.
NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Linear Equations in One Variable
NCERT solutions for class 8 maths chapter 2 linear equations in one variable tell us that a Mathematical equation can come in many different forms with several variables, differing degrees, number of coefficients , etc. However, a linear equation in one variable is defined as a mathematical expression in which the highest power of the polynomial is 1 and it consists of a single variable. These solutions greatly emphasize on the meaning of a linear equation in one variable and how to effectively solve problems based on the same. As mentioned before there can be many types of linear equations and each has its own method of solving. Thus, students need to go through the NCERT solutions class 8 maths chapter 2 in order to get a good understanding of the procedures. This is a very important chapter because as kids proceed to higher grades they will have to build on the concepts taught in this lesson to solve problems on sister chapters such as linear equations in two variables .
Class 8 maths NCERT solutions chapter 2 comprises a well-structured and detailed explanation of all the NCERT textbook questions. They have been presented using vernacular language so that these solutions can be comprehended by kids of all intelligence levels. NCERT solutions Chapter 2 linear equations in one variable also give real-life applications of the topic helping students to get a holistic view of it. In this article, we will take a deeper look into the subtopics associated with this lesson and also you can find some of these in the exercises given below.
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Ex 2.1
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Ex 2.2
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Ex 2.3
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Ex 2.4
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Ex 2.5
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Ex 2.6
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 PDF
An important topic covered in this chapter is how to interpret a word problem into a linear mathematical equation and what techniques have to be applied in order to solve them. The NCERT solutions class 8 maths chapter 2 acts as a guide for kids when they solve NCERT problems. As these are well-crafted solutions students can refer to them for clarity of concepts. Given below are the exercise-wise links to all the NCERT solutions .
☛ Download Class 8 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 2
NCERT Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Download PDF

NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 2
As this chapter is long and has various methods and formulas required to solve a linear equation students need to regularly visit the above links and practice the solutions. This will help them gain confidence thus, helping kids to get the best possible score in an examination. A detailed breakdown of all the components in the NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 linear equations in one variable is given below.
- Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Ex 2.1 - 12 Questions
- Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Ex 2.2 - 16 Questions
- Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Ex 2.3 - 10 Questions
- Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Ex 2.4 - 10 Questions
- Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Ex 2.5 - 10 Questions
- Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Ex 2.6 - 7 Questions
☛ Download Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 NCERT Book
Topics Covered: The important topics covered under class 8 maths NCERT solutions chapter 2 are solving equations with only numbers on one side, applications of linear equations, determining the value of an equation with variables on both sides, and simplifying linear equations .
Total Questions: Class 8 maths chapter 2 Linear Equations in One Variable has a total of 65 well-researched questions out of which 20 are straightforward, 38 are of a medium level, and 7 complex problems.
List of Formulas in NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 2
NCERT solutions class 8 maths chapter 2 does not have formulas that need to be memorized as kids have to rely on their calculation and analytical skills in order to solve the problem sums. However, there are some pointers and steps that need to be kept in mind while attempting any question in this particular lesson. Given below are the necessary steps that kids need to follow for going through the NCERT solutions for class 8 maths chapter 2.
- In case of a problem sum read the question with care so as to translate it into the correct mathematical linear equation.
- In an equation take all the terms with variables on one side and the constant on the other side of the equal sign to solve it.
- Always simplify an equation into the standard form of a linear equation, i.e., ax + b = 0 before solving it.
Important Questions for Class 8 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 2
| CBSE Important Questions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Exercise 2.1 |
|---|
| CBSE Important Questions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Exercise 2.2 |
|---|
| CBSE Important Questions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Exercise 2.3 |
|---|
| CBSE Important Questions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Exercise 2.4 |
|---|
| CBSE Important Questions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Exercise 2.5 |
|---|
| CBSE Important Questions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Exercise 2.6 |
|---|
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Video Chapter 2
| NCERT Class 8 Maths Videos for Chapter 2 | |
|---|---|
| Video Solutions for Class 8 Maths Exercise 2.1 | |
| Video Solutions for Class 8 Maths Exercise 2.2 | |
| Video Solutions for Class 8 Maths Exercise 2.3 | |
| Video Solutions for Class 8 Maths Exercise 2.4 | |
| Video Solutions for Class 8 Maths Exercise 2.5 | |
| Video Solutions for Class 8 Maths Exercise 2.6 | |
FAQs on NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 2
Why are ncert solutions class 8 maths chapter 2 important.
While solving sums kids are bound to hit some form of a roadblock due to doubt or an incorrect result. In order to combat this confusion, the NCERT solutions class 8 maths chapter 2 is important. They give a step-by-step solution to all NCERT textbook questions helping kids to identify and work on their pain points.
Do I Need to Practice all Questions Provided in NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Linear Equations in One Variable?
The questions in the NCERT coursebook are handpicked by experts. They cover a wide variety of topics to give students an all-around experience. Thus, it is imperative to practice all problems in the NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Linear Equations in One Variable to build a robust mathematical foundation for this lesson.
What are the Important Topics Covered in NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 2?
All topics in the NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 are essential as they cover different aspects of linear equations. However, kids need to reserve an ample amount of time to practice converting a word problem to a linear equation and the methods that can be used to solve the same.
How Many Questions are there in NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Linear Equations in One Variable?
There are a total of 65 sums in the NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Linear Equations in One Variable that have been split into 6 exercises. Each exercise covers a different topic. The questions are a mix of easy and difficult to give children the opportunity of exploring the different ways in which a problem can be framed.
How CBSE Students can utilize NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 effectively?
To effectively utilize the NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 kids must go through the solved examples, highlights, and theory that the exercises are based on. Once they get an understanding of the underlying concepts students can proceed to practicing the NCERT questions and using the solutions as a reference.
Why Should I Practice NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Linear Equations in One Variable Chapter 2?
Practice is the road to perfection. Students must revise the NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Linear Equations in One Variable Chapter 2 so that they can clear their concepts and solve problems with ease. If kids practice these solutions with dexterity and sincerity they are sure to ace any exam be it home or competitive.
Word Problems on Linear Equations
Worked-out word problems on linear equations with solutions explained step-by-step in different types of examples.
There are several problems which involve relations among known and unknown numbers and can be put in the form of equations. The equations are generally stated in words and it is for this reason we refer to these problems as word problems. With the help of equations in one variable, we have already practiced equations to solve some real life problems.
Steps involved in solving a linear equation word problem: ● Read the problem carefully and note what is given and what is required and what is given. ● Denote the unknown by the variables as x, y, ……. ● Translate the problem to the language of mathematics or mathematical statements. ● Form the linear equation in one variable using the conditions given in the problems. ● Solve the equation for the unknown. ● Verify to be sure whether the answer satisfies the conditions of the problem.
Step-by-step application of linear equations to solve practical word problems:
1. The sum of two numbers is 25. One of the numbers exceeds the other by 9. Find the numbers.
Solution: Then the other number = x + 9 Let the number be x. Sum of two numbers = 25 According to question, x + x + 9 = 25 ⇒ 2x + 9 = 25 ⇒ 2x = 25 - 9 (transposing 9 to the R.H.S changes to -9) ⇒ 2x = 16 ⇒ 2x/2 = 16/2 (divide by 2 on both the sides) ⇒ x = 8 Therefore, x + 9 = 8 + 9 = 17 Therefore, the two numbers are 8 and 17.
2.The difference between the two numbers is 48. The ratio of the two numbers is 7:3. What are the two numbers? Solution: Let the common ratio be x. Let the common ratio be x. Their difference = 48 According to the question, 7x - 3x = 48 ⇒ 4x = 48 ⇒ x = 48/4 ⇒ x = 12 Therefore, 7x = 7 × 12 = 84 3x = 3 × 12 = 36 Therefore, the two numbers are 84 and 36.
3. The length of a rectangle is twice its breadth. If the perimeter is 72 metre, find the length and breadth of the rectangle. Solution: Let the breadth of the rectangle be x, Then the length of the rectangle = 2x Perimeter of the rectangle = 72 Therefore, according to the question 2(x + 2x) = 72 ⇒ 2 × 3x = 72 ⇒ 6x = 72 ⇒ x = 72/6 ⇒ x = 12 We know, length of the rectangle = 2x = 2 × 12 = 24 Therefore, length of the rectangle is 24 m and breadth of the rectangle is 12 m.
4. Aaron is 5 years younger than Ron. Four years later, Ron will be twice as old as Aaron. Find their present ages.
Solution: Let Ron’s present age be x. Then Aaron’s present age = x - 5 After 4 years Ron’s age = x + 4, Aaron’s age x - 5 + 4. According to the question; Ron will be twice as old as Aaron. Therefore, x + 4 = 2(x - 5 + 4) ⇒ x + 4 = 2(x - 1) ⇒ x + 4 = 2x - 2 ⇒ x + 4 = 2x - 2 ⇒ x - 2x = -2 - 4 ⇒ -x = -6 ⇒ x = 6 Therefore, Aaron’s present age = x - 5 = 6 - 5 = 1 Therefore, present age of Ron = 6 years and present age of Aaron = 1 year.
5. A number is divided into two parts, such that one part is 10 more than the other. If the two parts are in the ratio 5 : 3, find the number and the two parts. Solution: Let one part of the number be x Then the other part of the number = x + 10 The ratio of the two numbers is 5 : 3 Therefore, (x + 10)/x = 5/3 ⇒ 3(x + 10) = 5x ⇒ 3x + 30 = 5x ⇒ 30 = 5x - 3x ⇒ 30 = 2x ⇒ x = 30/2 ⇒ x = 15 Therefore, x + 10 = 15 + 10 = 25 Therefore, the number = 25 + 15 = 40 The two parts are 15 and 25.
More solved examples with detailed explanation on the word problems on linear equations.
6. Robert’s father is 4 times as old as Robert. After 5 years, father will be three times as old as Robert. Find their present ages. Solution: Let Robert’s age be x years. Then Robert’s father’s age = 4x After 5 years, Robert’s age = x + 5 Father’s age = 4x + 5 According to the question, 4x + 5 = 3(x + 5) ⇒ 4x + 5 = 3x + 15 ⇒ 4x - 3x = 15 - 5 ⇒ x = 10 ⇒ 4x = 4 × 10 = 40 Robert’s present age is 10 years and that of his father’s age = 40 years.
7. The sum of two consecutive multiples of 5 is 55. Find these multiples. Solution: Let the first multiple of 5 be x. Then the other multiple of 5 will be x + 5 and their sum = 55 Therefore, x + x + 5 = 55 ⇒ 2x + 5 = 55 ⇒ 2x = 55 - 5 ⇒ 2x = 50 ⇒ x = 50/2 ⇒ x = 25 Therefore, the multiples of 5, i.e., x + 5 = 25 + 5 = 30 Therefore, the two consecutive multiples of 5 whose sum is 55 are 25 and 30.
8. The difference in the measures of two complementary angles is 12°. Find the measure of the angles. Solution: Let the angle be x. Complement of x = 90 - x Given their difference = 12° Therefore, (90 - x) - x = 12° ⇒ 90 - 2x = 12 ⇒ -2x = 12 - 90 ⇒ -2x = -78 ⇒ 2x/2 = 78/2 ⇒ x = 39 Therefore, 90 - x = 90 - 39 = 51 Therefore, the two complementary angles are 39° and 51°
9. The cost of two tables and three chairs is $705. If the table costs $40 more than the chair, find the cost of the table and the chair. Solution: The table cost $ 40 more than the chair. Let us assume the cost of the chair to be x. Then the cost of the table = $ 40 + x The cost of 3 chairs = 3 × x = 3x and the cost of 2 tables 2(40 + x) Total cost of 2 tables and 3 chairs = $705 Therefore, 2(40 + x) + 3x = 705 80 + 2x + 3x = 705 80 + 5x = 705 5x = 705 - 80 5x = 625/5 x = 125 and 40 + x = 40 + 125 = 165 Therefore, the cost of each chair is $125 and that of each table is $165.
10. If 3/5 ᵗʰ of a number is 4 more than 1/2 the number, then what is the number? Solution: Let the number be x, then 3/5 ᵗʰ of the number = 3x/5 Also, 1/2 of the number = x/2 According to the question, 3/5 ᵗʰ of the number is 4 more than 1/2 of the number. ⇒ 3x/5 - x/2 = 4 ⇒ (6x - 5x)/10 = 4 ⇒ x/10 = 4 ⇒ x = 40 The required number is 40.
Try to follow the methods of solving word problems on linear equations and then observe the detailed instruction on the application of equations to solve the problems.
● Equations
What is an Equation?
What is a Linear Equation?
How to Solve Linear Equations?
Solving Linear Equations
Problems on Linear Equations in One Variable
Word Problems on Linear Equations in One Variable
Practice Test on Linear Equations
Practice Test on Word Problems on Linear Equations
● Equations - Worksheets
Worksheet on Linear Equations
Worksheet on Word Problems on Linear Equation
7th Grade Math Problems 8th Grade Math Practice From Word Problems on Linear Equations to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math . Use this Google Search to find what you need.
New! Comments
|
What’s this? | Facebook X Pinterest WhatsApp Messenger |
- Preschool Activities
- Kindergarten Math
- 1st Grade Math
- 2nd Grade Math
- 3rd Grade Math
- 4th Grade Math
- 5th Grade Math
- 6th Grade Math
- 7th Grade Math
- 8th Grade Math
- 9th Grade Math
- 10th Grade Math
- 11 & 12 Grade Math
- Concepts of Sets
- Probability
- Boolean Algebra
- Math Coloring Pages
- Multiplication Table
- Cool Maths Games
- Math Flash Cards
- Online Math Quiz
- Math Puzzles
- Binary System
- Math Dictionary
- Conversion Chart
- Homework Sheets
- Math Problem Ans
- Free Math Answers
- Printable Math Sheet
- Funny Math Answers
- Employment Test
- Math Patterns
- Link Partners
- Privacy Policy
| E-mail Address | |
| First Name | |
| to send you Math Only Math. |
Recent Articles
Comparing unlike fractions | unlike fractions | equivalent fraction.
Jul 14, 24 02:54 PM

Worksheet on Comparison of Like Fractions | Greater & Smaller Fraction
Jul 14, 24 02:09 PM
Worksheet on Reducing Fraction | Simplifying Fractions | Lowest Form
Jul 14, 24 12:14 PM

Fraction in Lowest Terms |Reducing Fractions|Fraction in Simplest Form
Jul 13, 24 04:22 PM

Conversion of Improper Fractions into Mixed Fractions |Solved Examples
Jul 13, 24 03:17 PM
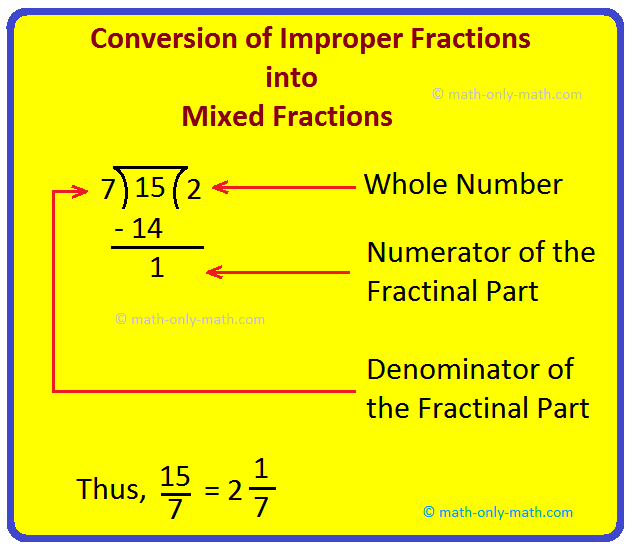
© and ™ math-only-math.com. All Rights Reserved. 2010 - 2024.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12
NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Maths Chapter 4 Linear Equations in One Variable
June 21, 2022 by Sastry CBSE
NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Maths Chapter 4 Linear Equations in One Variable are part of NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Maths . Here we have given NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Maths Chapter 4 Linear Equations in One Variable.
NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Maths Chapter 4 Linear Equations in One Variable

Question. 4 The shifting of a number from one side of an equation to other is called (a) transposition (b) distributivity (c) commutativity (d) associativity . Solution. (a) The shifting of a number from one side of an equation to other side is called transposition. e.g. x +a = 0is the equation, x = -a Here, number ‘a’ shifts from left hand side to right hand side.
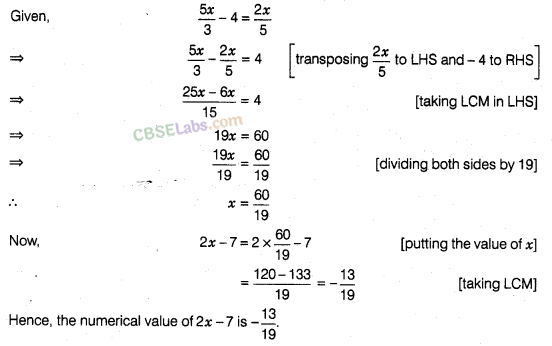
Question. 6 The value of x, for which the expressions 3x – 4 and 2x + 1 become equal, is (a) -3 (b) 0 (c) 5 x (d) 1 Solution. (c) Given expressions 3x – 4 and 2x + 1 are equal. Then, 3x-4 = 2x + 1 3x- 2x = 1 + 4 [transposing 2x to LHS and -4 to RHS] x = 5 Hence, the value of x is 5.
Question. 7 If a and b are positive integers, then the solution of the equation ax = b has to be always (a) positive (b) negative (c) one (d) zero Solution. (a) If ax = b, then x = \(\frac { b }{ a }\) Since, a and b are positive integers. So,\(\frac { b }{ a }\) is also positive integer, Hence, the solution of the given equation has to be always positive.
Question. 8 Linear equation in one variable has (a) only one variable with any power (b) only one term with a variable (c) only one variable with power 1 (d) only constant term Solution. (c) Linear equation in one variable has only one variable with power 1. e.g. 3x + 1 = 0,2y – 3 = 7 and z + 9 = – 2 are the linear equations in one variable.
Question. 9 Which of the following is a linear expression? (a) \({ x }^{ 2 }\) +1 (b) y + \({ y }^{ 2 }\) (c) 4 (d) 1 + z Solution. (d) We know that, the algebraic expression in one variable having the highest power of the variable as 1, is known as the linear expression. Here, 1 + z is the only linear expression, as the power of the variable z is 1.
Question.10 A linear equation in one variable has (a) only one solution (b) two solutions (c) more than two solutions (d) no solution Solution. (a) A linear equation in one variable has only one solution. e.g. Solution of the linear equation ax + b = 0 is unique, i.e. x = \(\frac { -b }{ a }\)

Question. 13 The digit in the ten’s place of a two-digit number is 3 more than the digit in the unit’s place. Let the digit at unit’s place be b. Then, the number is (a) 11b+30 (b) 10b+ 30 (c) 11 b + 3 (d) 10b + 3 Solution. (a) Let digit at unit’s place be b. Then, digit at ten’s place = (3 + b) Number = 10 (3 + b) + b – 30 + 10b + b = 11b + 30
Question. 14 Arpita’s present age is thrice of Shilpa. If Shilpa’s age three years ago was x, then Arpita’s present age is (a) 3 (x – 3) (b)3x + 3 (c) 3x – 9 (d) 3(x + 3) Solution. (d) Given, Shilpa’s age three years ago = x Then, Shilpa’s present age = (x + 3) Arpita’s present age = 3 x Shilpa’s present age = 3 (x + 3)

Fill in the Blanks In questions 16 to 32, fill in the blanks to make each statement true. Question. 16 In a linear equation, the——— power of the variable appearing in the equation is one. Solution. highest e.g. x + 3 = O and x + 2 = 4 are the linear equations.
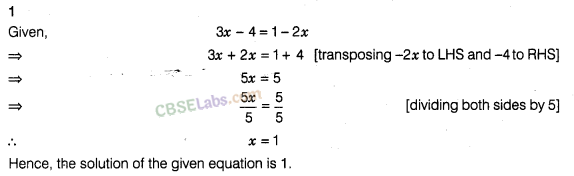
Question. 19 Any value of the variable, which makes both sides of an equation equal, is known as a———–of the equation. Solution. e.g. x + 2 = 3 => x = 3-2 = 1 [transposing 2 to RHS] Hence, x = 1 satisfies the equation and it is a solution of the equation.

Question. 23 A term of an equation can be transposed to the other side by changing its—-. Solution. sign e.g. x + a = 0 is a linear equation. . => x = -a Hence, the term of an equation can be transposed to the other side by changing its sign.
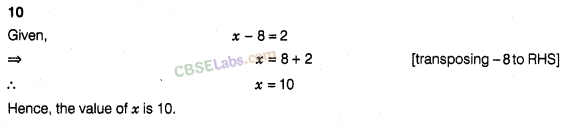
Question. 30 Convert the statement ‘adding 15 to 4 times x is 39’ into an equation. Solution. 4x+ 15=39 To convert the given statement into an equation, first x is multiplied by 4 and then 15 is added to get the result 39. i.e. 4x + 15=39
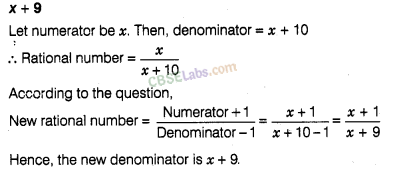
True/False In questions 33 to 48, state whether the statements are True or False. Question. 33 3 years ago, the age of boy was y years. His age 2 years ago was (y — 2) years. Solution. False Given, 3 yr ago, age of boy = y yr Then, present age of boy = (y + 3)yr 2 yr ago, age of boy = y + 3-2 = (y + 1)yr
Question. 34 Shikha’s present age is p years. Reemu’s present age is 4 times the present age of Shikha. After 5 years, Reemu’s age will be 15p years. Solution. False Given, Shikha’s present age = pyr Then, Reemu’s present age = 4 x (Shikha’s present age) = 4pyr After 5 yr, Reemu’s age = (4p+5)yr
Question. 35 In a 2-digit number, the unit’s place digit is x. If the sum of digits be 9, then the number is (10x – 9). Solution. False Given, unit’s digit = x and sum of digits = 9 Ten’s digit = 9 – x Hence, the number = 10 (9 -x)+x = 90 -10x + x = 90 – 9x
Question. 36 Sum of the ages of Anju and her mother is 65 years. If Anju’s present age is y years, then her mother’s age before 5 years is (60 – y) years. Solution. True Given, Anju’s present age = y yr Then, Anju’s mother age = (65 – y)yr Before 5 yr, Anju’s mother age = 65 – y – 5 = (60 – y)yr
Question. 37 The number of boys and girls in a class are in the ratio 5 : 4. If the number of boys is 9 more than the number of girls, then number of boys is 9. Solution. False Let the number of boys be 5x and the number of girls be 4x. According to the question, – 5x – 4x = 9 => x = 9 Hence, number of boys = 5 x 9 = 45
Question. 38 A and B are together 90 years old. Five years ago, A was thrice as old as B was. Hence, the ages of A and B five years back would be (x – 5) years and (85 – x) years, respectively. Solution. True Let the age of A be x yr. Then, age of S = (90 – x) yr Five years ago, the age of A = (x- 5) yr The age of B= 90-x-5 = (85-x)yr Hence, the ages of A and 8 five years back would be (x – 5) yr and (85 – x) yr, respectively.
Question. 39 Two different equations can never have the same answer. Solution. False Two different equations may have the same answer. e.g.2x + 1 = 2 and 2x – 5 = – 4 are the two linear equations whose solution is \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
Question. 40 In the equation 3x – 3 = 9, transposing – 3 to RHS, we get 3x = 9. Solution. False Given, 3x – 3 = 9 => 3x = 9 + 3 [transposing -3 to RHS] => 3x = 12
Question. 41 In the equation 2x = 4 – x, transposing – x to LHS, we get x = 4. Solution. False Given, 2x = 4-x => 2x + x = 4 [transposing -x to LHS] => 3x = 4
Question. 46 If x is an even number, then the next even number is 2(x +1). Solution. False Given, x is an even number. Then, the next even number is (x + 2).
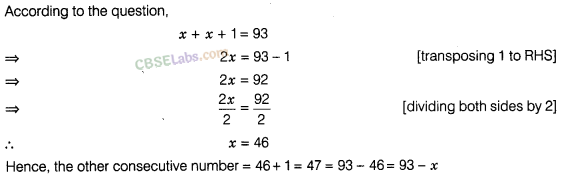
NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Maths Solutions
- Chapter 1 Rational Numbers
- Chapter 2 Data Handling
- Chapter 3 Square-Square Root and Cube-Cube Root
- Chapter 4 Linear Equations in One Variable
- Chapter 5 Understanding Quadrilaterals and Practical Geometry
- Chapter 6 Visualising Solid Shapes
- Chapter 7 Algebraic Expressions, Identities and Factorisation
- Chapter 8 Exponents and Powers
- Chapter 9 Comparing Quantities
- Chapter 10 Direct and Inverse Proportion
- Chapter 11 Mensuration
- Chapter 12 Introduction to Graphs
- Chapter 13 Playing with Numbers
NCERT Exemplar Solutions
We hope the NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Maths Chapter 4 Linear Equations in One Variable help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Maths Chapter 4 Linear Equations in One Variable, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
Free Resources
NCERT Solutions
Quick Resources
WorkSheets Buddy
Download Math, Science, English and Many More WorkSheets

Grade 8 Linear Equations in One Variable Worksheets
Grade 8 maths linear equation in one variable multiple choice questions (mcqs).
1. The solution of 2x – 3 = 7 is: (a) 2 (b) -2 (c) 5 (d) -5
2. Which of the following is not a linear equation. (a) 2x + 5 = 1 (b) x – 1 = 0 (c) y + 1 = 0 (d) 5x + 3
3. The present age of Sahil’s mother is three times the present age of Sahil. After 5 years their ages will add to 66 years. Find the present age of Sahil. (a) 12 (b) 14 (c) 16 (d) 20
4. Find the solution of 2x + 3 = 7 (a) 2 (b) -2 (c) 3 (d) None of these
5. Solve: 8x = 20 + 3x (a) 4 (b) -4 (c) 2 (d) None of these
10. Solve: 8x + 3 = 27 (a) 3 (b) -3 (c) 2 (d) None of these
11. Solve : 5x – 7 = 2x + 8 (a) 5 (b) -9 (c) 5 (d) 9
13. Two numbers are in the ratio 5 : 3. If they differ by 18, what are the numbers? (a) 45, 27 (b) 50, 32 (c) 40, 22 (d) None of these
14. Solve: 2x -3 = x + 2 (a) 5 (b) -9 (c) 5 (d) 9
15. Solve: 3x = 2x + 18 (a) 18 (b) -18 (c) 14 (d) None of these
16. Solve: 5t – 3 = 3t – 5 (a) 1 (b) -1 (c) 2 (d) None of these
17. Solve: 5x + 9 = 5 + 3x (a) 2 (b) -2 (c) 3 (d) None of these
19. Solve: 2x – 1 = 14 – x (a) 5 (b) -9 (c) 5 (d) 9
20. Solve: 8x + 4 = 3(x – 1) + 7 (a) 1 (b) -1 (c) 0 (d) None of these
Class 8 Maths Linear Equation in One Variable Solve
Class 8 Maths Linear Equation in One Variable Short Answer Type Questions
1. Interior angles of a triangle are in the ratio 2 : 3 : 4. Find the angles of the triangle. 2. If father is twice as old as his son and also 32 years older than his son. What is the age of father? Solve for: 8x + 25 = 4x +105 4. Sides of rectangle are is the ratio 15 : 4. If the perimeter of the rectangle is 38 cms then find the sides of rectangle. 5. Form an equation of “7 added to thrice a number is 118” and also find the number. 6. If sum of two numbers is 29 and one of them is 18. Form the equation for finding the another number.
Class 8 Maths Linear Equation in One Variable Long Answer Type Questions
Worksheets for Class 8 Maths
Share this:.
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
WORD PROBLEMS ON LINEAR EQUATIONS IN ONE VARIABLE
Problem 1 :
A class of 45 students is divided into two groups. If one group has 9 students less than the other, how many stidents are in the smaller group?
Let x be the number of students in one of the two groups.
Number of students in the other group is (x - 9).
Given : Total number of students in the class is 45.
x + (x - 9) = 45
x + x - 9 = 45
2x - 9 = 45
Add 9 to both sides.
Divide both sides by 2.
x - 9 = 27 - 9 = 18
There are 18 students in the smaller group.
Problem 2 :
Subtracting 17 from four times of a number results 35. Find the number.
Let x be the number.
Given : When 17 is subtracted 17 from four times of the number is equal to 35.
Then, we have
4x - 17 = 35
Add 17 to both sides.
Divide both sides by 4.
The number is 13.
Problem 3 :
9 less than five times of a number is equal 3 more than two times of the same number. Find the number.
Five times of the number = 5x
9 less than five times of the number = 5x - 9 ----(1)
Two times of the number = 2x
3 more than two times of the number = 2x + 3 ----(2)
From the given information,
5x - 9 = 2x + 3
The number is 4.
Problem 4 :
The length of one of the sides of a triangle is 7 cm and the lengths of the remaining two sides differ by 4 cm. If the perimeter of the triangle is 33 cm, find the lengths of the missing sides of the triangle.
Since the lengths of the two sides of the triangle differ by 4 cm, the lengths can be assumed as x and (x + 4).
The sides of the triangle are
7 cm, x cm, (x + 4) cm
Perimeter of the triangle = 33 cm
7 + x + (x + 4) = 33
7 + x + x + 4 = 33
2x + 11 = 33
Subtract 11 from both sides.
x + 4 = 11 + 4 = 15
The missing sides of the triangle are 11 cm and 15 cm.
Problem 5 :
One-sixth of a number is greater than one-seventh of the same number by 1. Find the number.
One-sixth of the number =( ⅙ )x = ˣ⁄₆
One-seventh of the number = ( ⅐ )x = ˣ⁄₇
ˣ⁄₆ = ˣ⁄₇ + 1
Least common multiple of the denominators (6, 7) is 42.
Multiply both sides of the equation by 42 to get rid of the denominators 6 and 7.
42( ˣ⁄₆ ) = 42( ˣ⁄₇ + 1 )
7x = 42( ˣ⁄₇ ) + 42
7x = 6x + 42
The number is 42.
Problem 6 :
Three times of my age 5 years ago is equal to 5 less than two times of my age 5 years hence. How old am i now?
Let x be the your present age.
Your age 5 years ago = x - 5
Three times of your age 5 years ago :
= 3x - 15----(1)
Your age 5 years hence = x + 5
Two times of my age 5 years hence = 2(x + 5)
5 less than two times of my age 5 years hence :
= 2x + 10 - 5
= 2x + 5 ----(2)
3x - 15 = 2x + 5
You are 20 years old now.
Problem 7 :
One number is 4 times the another number, and they sum to -20. What is the greater of the two numbers?
Let x be one of the numbers.
Then the other number is 4x.
Given : Sum of the two numbers is -20.
x + 4x = -20
Divide both sides by 5.
4x = 4(-4) = -16
The two numbers are -4 and -16.
The greater one is -4.
Problem 8 :
Paulina owns a certain number of dishes. 24 added to 3 times the number of dishes is equal to 9 times the number of dishes. How many dishes does Palina own?
Let x be the numbers of dishes Paulina owns.
Given : 24 added to 3 times the number of dishes is equal to 9 times the number of dishes.
3x + 24 = 9x
Subtract 3x from both sides.
Divide both sides by 6.
Paulina owns 4 dishes.
Problem 9 :
There is a monthly subscription fee of $15 for a movie rental sevice and $3 for each movie rented. Last month, Adam paid $33 for the movie rental sevice. How many movies did Adam rent last month.
Let x be the numbers of movies Adam rented last month.
Amount paid by Adam last month = 3x + 15
It is given that Adam paid $33 for the movie rental sevice.
3x + 15 = 33
Subtract 15 from both sides.
Divide both sides by 3.
Adam rented 6 movies last month.
Problem 10 :
In a fraction, the numerator is less than the denominator by 7. If 4 is added to the numerator and the denominator 2 is added to the denominator, the fraction becomes ¾ . Find the fraction.
Let x be the denominator.
Given : The numerator is less than the denominator by 7.
From the above information,
fraction = ⁽ˣ ⁻ ⁷⁾⁄ₓ ----(1)
Given : If 4 is added to the numerator and the denominator 2 is added to the denominator, the fraction becomes ¾ .
From the above information, we have
⁽ˣ ⁻ ⁷ ⁺ ⁴⁾⁄₍ₓ ₊ ₂₎ = ¾
⁽ˣ ⁻ ³⁾⁄₍ₓ ₊ ₂₎ = 3/4
4(x - 3) = 3(x + 2)
4x - 12 = 3x + 6
Substitute x =18 in (1).
fraction = ⁽¹⁸ ⁻ ⁷⁾⁄₁₈
= ¹¹⁄₁₈
Kindly mail your feedback to [email protected]
We always appreciate your feedback.
© All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com
- Sat Math Practice
- SAT Math Worksheets
- PEMDAS Rule
- BODMAS rule
- GEMDAS Order of Operations
- Math Calculators
- Transformations of Functions
- Order of rotational symmetry
- Lines of symmetry
- Compound Angles
- Quantitative Aptitude Tricks
- Trigonometric ratio table
- Word Problems
- Times Table Shortcuts
- 10th CBSE solution
- PSAT Math Preparation
- Privacy Policy
- Laws of Exponents
Recent Articles
Bodmas rule worksheet.
Jul 13, 24 09:37 PM
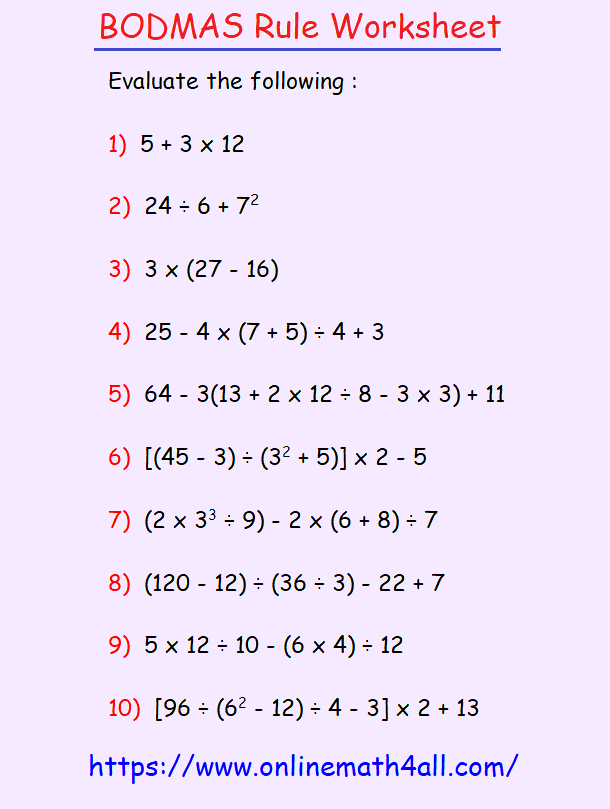
BODMAS Rule
Jul 13, 24 09:36 PM
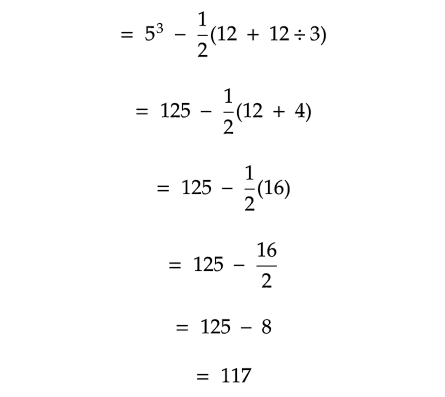
Pre Calculus Problems and Solutions (Part - 5)
Jul 13, 24 10:31 AM
Class 8 Maths MCQ – Linear Equations in One Variable
This set of Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Multiple Choice Questions & Answers (MCQs) focuses on “Linear Equations in One Variable”. These MCQs are created based on the latest CBSE syllabus and the NCERT curriculum, offering valuable assistance for exam preparation.
More MCQs on Class 8 Maths Chapter 2:
- Chapter 2 – Linear Equations in One Variable MCQ (Set 2)
- Chapter 2 – Linear Equations in One Variable MCQ (Set 3)
- Chapter 2 – Linear Equations in One Variable MCQ (Set 4)
- Chapter 2 – Linear Equations in One Variable MCQ (Set 5)
- Chapter 2 – Linear Equations in One Variable MCQ (Set 6)
- Chapter 2 – Linear Equations in One Variable MCQ (Set 7)
To practice all chapters and topics of class 8 Mathematics, here is complete set of 1000+ Multiple Choice Questions and Answers .
- Practice Class 9 Mathematics MCQs
- Check Class 8 - Mathematics Books
- Practice Class 10 Mathematics MCQs
Recommended Articles:
- Class 8 Maths MCQ – Reduce the Linear Equation and Find the Value of the Variable
- Class 8 Maths MCQ – Applications of Linear Equation (Just Solving the Equations)
- Class 8 Maths MCQ – Reduce the Given Linear Equations to a Simpler Form
- Class 12 Maths MCQ – Methods of Solving First Order & First Degree Differential Equations
- Solving Linear Equations in One Variable Using C
- Fourier Analysis Questions and Answers – Linear Difference Equations and Z – Transforms
- Class 11 Maths MCQ – Graphical Solution of Linear Variable in Two Variables
- Class 10 Maths MCQ – Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
- Class 12 Maths MCQ – Linear First Order Differential Equations – 1
- Class 9 Maths MCQ – Linear Equations in Two Variables
- Linear Integrated Circuits MCQ Questions
- C++ Algorithm Library
- Probability MCQ Questions
- Visual Basic MCQ Questions
- Numerical Methods MCQ Questions
- JavaScript MCQ Questions
- Automata Theory MCQ Questions
- Engineering Mathematics MCQ Questions
- Event Handling in Java with Examples
- Computational Fluid Dynamics MCQ Questions

Register here
In case you want to be notified about school in your locality then please register here.
- Are you a Parent or Student?
- Are you a Teacher?
- Are you a School Supplier?

- Our other Domains Olympiad Preparation Math Square Science Square English Square Cyber Square School Square Scholar Square Global Olympiads NCERT Solutions CBSE Sample Papers
- Join WhatsApp Channel
- Apply for CREST Olympiads

Linear Equations

- An equation which has only one variable is called Linear Equation
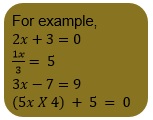
Solving equations which have linear equations on one side and numbers on the other side
EXAMPLE 1: Solve 3x + 15 = 1
- We need to keep the variable on the left side and numerical terms on the right side. Because of this, we have to transport 15 to the right side by changing its sign i.e., -15. => 3x + 15 = 1 => 3x = 1-15
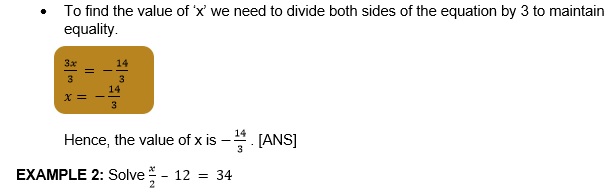
- We need to keep the variable on the left side and numerical terms on the right side. Because of this, we have to transport -12 to the other side by changing its sign i.e., +12.

Solving equations having variables having the variable on both sides
EXAMPLE 1: Solve .
- Simplify the given equation. => =>
- Bring the variable terms on the left side of the equation and the other numerical terms on the right side of the equation. => =>
- Now, to find the value of ‘x’ we need to divide both sides of the equation by 6 to maintain equality.

Application of Linear Equations
Linear equations are used to find the value of an unknown quantity. Have a look at the following examples:
EXAMPLE 1: The sum of the digits of a 2 digit number 13. The numbers obtained by interchanging the digits is 14 more than the given number. Find the number.
SOLUTION: Let the digit at units place be x and the number at tens place be y.
=> y + x = 13 [sum is 13 given] => y = 13 – x [Transposing x to the other side by changing its sign] Thus, the formed number is= [Since x is at ones place and y=13-x is at tens place] After interchanging the digits, the number is= [Now x is at tens place & y=13-x is at one's place] The interchanged number is greater than the original number by 14. [Given]
New number Old number Difference
- Simplify => => => =>
- Transpose the variable term ‘x’ on the left side of the equation and other numerical terms on the right side of the equation by changing their sign. => 18x – 117 = 14 => 18x = 131
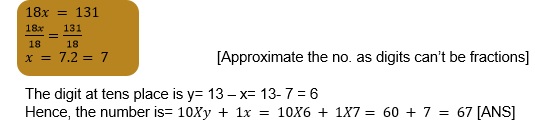
EXAMPLE 2: The distance between town A and town B is 123 km. Two buses begin their journey from these towns and move directly toward each other. From town A, the bus is moving at a speed of 45 km per hour and from town B, the bus is moving at 67 km per hour. Assuming the buses start at the same time, find how far is their meeting point from town A. SOLUTION: Let the buses meet after t hours.
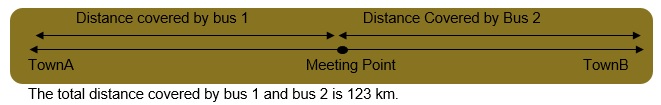
We know that distance= speed X time Distance covered by bus 1 = 45 X t Distance covered by bus 2 = 67 X t Therefore, 45t + 67t = 123
The distance travelled by bus 1 from city A to the meeting point= speed of bus 1 X time taken by it to reach the meeting point. =45 X 1.098= 49.41 km Thus, the distance of reaching point from town A is 49.41km. [ANS]
Reducing Equation to Simpler Form

Equations reducible to linear form

- Now, simplify => 6x + 12 + 12x + 15 = 14x + 16 => 18x + 27 = 14x +16
- Transpose the variable term ‘x’ to the left side and the numerical terms on the right side of the equation by changing their sign. => 18x – 14x = 16 – 27 => 4x = 11
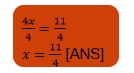
Practice these questions
Q3) Three numbers are in the ratio 1:2:3. If the sum of the largest and the smallest equals the second and 45. Find the numbers.
Q4) Find the number whose 1/6 th part decreased 7 equals its 8/9 th part diminished by 1.
Q5) The difference between two numbers is 23. And the quotient obtained by dividing the larger number by the smaller one is 4. Find the numbers.
Q6) A man cycles to the office from his house at a speed of 5km per hour and reaches 6 minutes late. If he cycles at a speed of 7km/hr, he reaches 8 minutes early. What is the distance between the office and his house? Q7) Suraj is now half as old as his father. 20 years ago, Suraj’s father was six times Suraj’s age. What are their ages now? Q8) The perimeter of an isosceles triangle is 91cm. If the length of each equal side is 2cm more than the length of its base. Find the lengths of the sides of the triangle. Q9) The age of a boy in months is equal to the age of his grandfather in years. If the difference between their ages is 66 years, find their ages.
- The basic principle used in solving any linear equation is that any operation performed on one side of the equation must also be performed on the other side of the equation.
- Any term in an equation can be transposed from one side to other side by changing its sign.
- In cross multiplication, we multiply the numerator of LHS by the denominator of RHS and the denominator of LHS by the numerator of RHS and the resultant expression are equal to each other.
- Practical problems are based on the relations between some known and unknown quantities. We convert such problems into equations and then solve them.
Quiz for Linear Equations
Q.1 |
Solve : y+9=15 |
| a) | 4 |
| b) | 6 |
| c) | 5 |
| d) | 2 |
Q.2 |
Solve: (8x-3)/3x =2 |
| a) | 3/2 |
| b) | 2 |
| c) | 1/2 |
| d) | 1 |
Q.3 |
The sum of two numbers is 20. If one of them is 11, the other is? |
| a) | 12 |
| b) | 10 |
| c) | 9 |
| d) | 15 |
Q.4 |
The value of x satisfying the equation : 2(x+3)-3x+5 = 12 |
| a) | 1 |
| b) | -1 |
| c) | 2 |
| d) | -2 |
Q.5 |
The length of a rectangle is 4 cm more than its width. If its perimeter is 200 cm, then the width is? |
| a) | 48 |
| b) | 50 |
| c) | 52 |
| d) | 44 |
Q.6 |
The solution of ax+b=0 is |
| a) | x = a/b |
| b) | x = -a/b |
| c) | x=b/a |
| d) | x=-b/a |
Q.7 |
If 8x-2 = 25+17x , then x is |
| a) | integer |
| b) | fraction |
| c) | irrational number |
| d) | cannot be solved |
Q.8 |
The share of A, when Rs. 30 is divided between A and B and A gets Rs.12 more than B. |
| a) | 22 |
| b) | 9 |
| c) | 10 |
| d) | 21 |
Q.9 |
When a number is divided by 9, the answer is -4. What is the number? |
| a) | 36 |
| b) | -36 |
| c) | -24 |
| d) | 24 |
Q.10 |
Solve: 4z + 3 = 6 + 2z |
| a) | z=2 |
| b) | z=2.5 |
| c) | z=1 |
| d) | z=1.5 |
Your Score: 0 /10
Other Chapters of Class 8
Quick Links

SchoolPlus Program
Yearlong program for Olympiads preparation & to build necessary skills for future.

Olympiad Exam Dates
Time to mark your calendar with the upcoming Olympiads exam schedule.

LIVE Classes for Olympiads
Take your Olympiad preparation to next-level by taking LIVE Classes.

Olympiad Test Series
Assess your performance by taking topic-wise and full length mock tests.

India’s First Summer Olympiads
Know your true potential by participating in Unicus Olympiads for classes 1-11.
Asia’s Biggest Winter Olympiads
Give wings to your innovation by appearing in CREST Olympiads for Prep/KG to classes 1-10.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Class 8 Math (India) - Hindi
Course: class 8 math (india) - hindi > unit 2.
- Two-step equation word problem: garden (Hindi)
Word problems linear equations (basic)
- Sums of consecutive integers (Hindi)
- Sums of consecutive integers
- Two-step equation word problem: oranges (Hindi)
- Linear equations word problems (advanced)
- Your answer should be
- an integer, like 6
- a simplified proper fraction, like 3 / 5
- a simplified improper fraction, like 7 / 4
- a mixed number, like 1 3 / 4
- an exact decimal, like 0.75
- a multiple of pi, like 12 pi or 2 / 3 pi
Word Problems Linear Equations
Andymath.com features free videos, notes, and practice problems with answers! Printable pages make math easy. Are you ready to be a mathmagician?
\(\textbf{1)}\) Joe and Steve are saving money. Joe starts with $105 and saves $5 per week. Steve starts with $5 and saves $15 per week. After how many weeks do they have the same amount of money? Show Equations \(y= 5x+105,\,\,\,y=15x+5\) Show Answer 10 weeks ($155)
\(\textbf{2)}\) mike and sarah collect rocks. together they collected 50 rocks. mike collected 10 more rocks than sarah. how many rocks did each of them collect show equations \(m+s=50,\,\,\,m=s+10\) show answer mike collected 30 rocks, sarah collected 20 rocks., \(\textbf{3)}\) in a classroom the ratio of boys to girls is 2:3. there are 25 students in the class. how many are girls show equations \(b+g=50,\,\,\,3b=2g\) show answer 15 girls (10 boys), \(\textbf{4)}\) kyle makes sandals at home. the sandal making tools cost $100 and he spends $10 on materials for each sandal. he sells each sandal for $30. how many sandals does he have to sell to break even show equations \(c=10x+100,\,\,\,r=30x\) show answer 5 sandals ($150), \(\textbf{5)}\) molly is throwing a beach party. she still needs to buy beach towels and beach balls. towels are $3 each and beachballs are $4 each. she bought 10 items in total and it cost $34. how many beach balls did she get show equations show answer 4 beachballs (6 towels), \(\textbf{6)}\) anna volunteers at a pet shelter. they have cats and dogs. there are 36 pets in total at the shelter, and the ratio of dogs to cats is 4:5. how many cats are at the shelter show equations \(c+d=40,\,\,\,5d=4c\) show answer 20 cats (16 dogs), \(\textbf{7)}\) a store sells oranges and apples. oranges cost $1.00 each and apples cost $2.00 each. in the first sale of the day, 15 fruits were sold in total, and the price was $25. how many of each type of frust was sold show equations \(o+a=15,\,\,\,1o+2a=25\) show answer 10 apples and 5 oranges, \(\textbf{8)}\) the ratio of red marbles to green marbles is 2:7. there are 36 marbles in total. how many are red show equations \(r+g=36,\,\,\,7r=2g\) show answer 8 red marbles (28 green marbles), \(\textbf{9)}\) a tennis club charges $100 to join the club and $10 for every hour using the courts. write an equation to express the cost \(c\) in terms of \(h\) hours playing tennis. show equation the equation is \(c=10h+100\), \(\textbf{10)}\) emma and liam are saving money. emma starts with $80 and saves $10 per week. liam starts with $120 and saves $6 per week. after how many weeks will they have the same amount of money show equations \(e = 10x + 80,\,\,\,l = 6x + 120\) show answer 10 weeks ($180 each), \(\textbf{11)}\) mark and lisa collect stamps. together they collected 200 stamps. mark collected 40 more stamps than lisa. how many stamps did each of them collect show equations \(m + l = 200,\,\,\,m = l + 40\) show answer mark collected 120 stamps, lisa collected 80 stamps., \(\textbf{12)}\) in a classroom, the ratio of boys to girls is 3:5. there are 40 students in the class. how many are boys show equations \(b + g = 40,\,\,\,5b = 3g\) show answer 15 boys (25 girls), \(\textbf{13)}\) lisa is selling handmade jewelry. the materials cost $60, and she sells each piece for $20. how many pieces does she have to sell to break even show equations \(c=60,\,\,\,r=20x\) show answer 3 pieces, \(\textbf{14)}\) tom is buying books and notebooks for school. books cost $15 each, and notebooks cost $3 each. he bought 12 items in total, and it cost $120. how many notebooks did he buy show equations \(b + n = 12,\,\,\,15b+3n=120\) show answer 5 notebooks (7 books), \(\textbf{15)}\) emily volunteers at an animal shelter. they have rabbits and guinea pigs. there are 36 animals in total at the shelter, and the ratio of guinea pigs to rabbits is 4:5. how many guinea pigs are at the shelter show equations \(r + g = 36,\,\,\,5g=4r\) show answer 16 guinea pigs (20 rabbits), \(\textbf{16)}\) mike and sarah are going to a theme park. mike’s ticket costs $40, and sarah’s ticket costs $30. they also bought $20 worth of food. how much did they spend in total show equations \(m + s + f = t,\,\,\,m=40,\,\,\,s=30,\,\,\,f=20\) show answer they spent $90 in total., \(\textbf{17)}\) the ratio of red marbles to blue marbles is 2:3. there are 50 marbles in total. how many are blue show equations \(r + b = 50,\,\,\,3r=2b\) show answer 30 blue marbles (20 red marbles), \(\textbf{18)}\) a pizza restaurant charges $12 for a large pizza and $8 for a small pizza. if a customer buys 5 pizzas in total, and it costs $52, how many large pizzas did they buy show equations \(l + s = 5,\,\,\,12l+8s=52\) show answer they bought 3 large pizzas (2 small pizzas)., \(\textbf{19)}\) the area of a rectangle is 48 square meters. if the length is 8 meters, what is the width of the rectangle show equations \(a=l\times w,\,\,\,l=8,\,\,\,a=48\) show answer the width is 6 meters., \(\textbf{20)}\) two numbers have a sum of 50. one number is 10 more than the other. what are the two numbers show equations \(x+y=50,\,\,\,x=y+10\) show answer the numbers are 30 and 20., \(\textbf{21)}\) a store sells jeans for $40 each and t-shirts for $20 each. in the first sale of the day, they sold 8 items in total, and the price was $260. how many of each type of item was sold show equations \(j+t=8,\,\,\,40j+20t=260\) show answer 5 jeans and 3 t-shirts were sold., \(\textbf{22)}\) the ratio of apples to carrots is 3:4. there are 28 fruits in total. how many are apples show equations \(\)a+c=28,\,\,\,4a=3c show answer there are 12 apples and 16 carrots., \(\textbf{23)}\) a phone plan costs $30 per month, and there is an additional charge of $0.10 per minute for calls. write an equation to express the cost \(c\) in terms of \(m\) minutes. show equation the equation is \(\)c=30+0.10m, \(\textbf{24)}\) a triangle has a base of 8 inches and a height of 6 inches. calculate its area. show equations \(a=0.5\times b\times h,\,\,\,b=8,\,\,\,h=6\) show answer the area is 24 square inches., \(\textbf{25)}\) a store sells shirts for $25 each and pants for $45 each. in the first sale of the day, 4 items were sold, and the price was $180. how many of each type of item was sold show equations \(t+p=4,\,\,\,25t+45p=180\) show answer 0 shirts and 4 pants were sold., \(\textbf{26)}\) a garden has a length of 12 feet and a width of 10 feet. calculate its area. show equations \(a=l\times w,\,\,\,l=12,\,\,\,w=10\) show answer the area is 120 square feet., \(\textbf{27)}\) the sum of two consecutive odd numbers is 56. what are the two numbers show equations \(x+y=56,\,\,\,x=y+2\) show answer the numbers are 27 and 29., \(\textbf{28)}\) a toy store sells action figures for $15 each and toy cars for $5 each. in the first sale of the day, 10 items were sold, and the price was $110. how many of each type of item was sold show equations \(a+c=10,\,\,\,15a+5c=110\) show answer 6 action figures and 4 toy cars were sold., \(\textbf{29)}\) a bakery sells pie for $2 each and cookies for $1 each. in the first sale of the day, 14 items were sold, and the price was $25. how many of each type of item was sold show equations \(p+c=14,\,\,\,2p+c=25\) show answer 11 pies and 3 cookies were sold., \(\textbf{for 30-33}\) two car rental companies charge the following values for x miles. car rental a: \(y=3x+150 \,\,\) car rental b: \(y=4x+100\), \(\textbf{30)}\) which rental company has a higher initial fee show answer company a has a higher initial fee, \(\textbf{31)}\) which rental company has a higher mileage fee show answer company b has a higher mileage fee, \(\textbf{32)}\) for how many driven miles is the cost of the two companies the same show answer the companies cost the same if you drive 50 miles., \(\textbf{33)}\) what does the \(3\) mean in the equation for company a show answer for company a, the cost increases by $3 per mile driven., \(\textbf{34)}\) what does the \(100\) mean in the equation for company b show answer for company b, the initial cost (0 miles driven) is $100., \(\textbf{for 35-39}\) andy is going to go for a drive. the formula below tells how many gallons of gas he has in his car after m miles. \(g=12-\frac{m}{18}\), \(\textbf{35)}\) what does the \(12\) in the equation represent show answer andy has \(12\) gallons in his car when he starts his drive., \(\textbf{36)}\) what does the \(18\) in the equation represent show answer it takes \(18\) miles to use up \(1\) gallon of gas., \(\textbf{37)}\) how many miles until he runs out of gas show answer the answer is \(216\) miles, \(\textbf{38)}\) how many gallons of gas does he have after 90 miles show answer the answer is \(7\) gallons, \(\textbf{39)}\) when he has \(3\) gallons remaining, how far has he driven show answer the answer is \(162\) miles, \(\textbf{for 40-42}\) joe sells paintings. each month he makes no commission on the first $5,000 he sells but then makes a 10% commission on the rest., \(\textbf{40)}\) find the equation of how much money x joe needs to sell to earn y dollars per month. show answer the answer is \(y=.1(x-5,000)\), \(\textbf{41)}\) how much does joe need to sell to earn $10,000 in a month. show answer the answer is \($105,000\), \(\textbf{42)}\) how much does joe earn if he sells $45,000 in a month show answer the answer is \($4,000\), see related pages\(\), \(\bullet\text{ word problems- linear equations}\) \(\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\), \(\bullet\text{ word problems- averages}\) \(\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\), \(\bullet\text{ word problems- consecutive integers}\) \(\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\), \(\bullet\text{ word problems- distance, rate and time}\) \(\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\), \(\bullet\text{ word problems- break even}\) \(\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\), \(\bullet\text{ word problems- ratios}\) \(\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\), \(\bullet\text{ word problems- age}\) \(\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\), \(\bullet\text{ word problems- mixtures and concentration}\) \(\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\), linear equations are a type of equation that has a linear relationship between two variables, and they can often be used to solve word problems. in order to solve a word problem involving a linear equation, you will need to identify the variables in the problem and determine the relationship between them. this usually involves setting up an equation (or equations) using the given information and then solving for the unknown variables . linear equations are commonly used in real-life situations to model and analyze relationships between different quantities. for example, you might use a linear equation to model the relationship between the cost of a product and the number of units sold, or the relationship between the distance traveled and the time it takes to travel that distance. linear equations are typically covered in a high school algebra class. these types of problems can be challenging for students who are new to algebra, but they are an important foundation for more advanced math concepts. one common mistake that students make when solving word problems involving linear equations is failing to set up the problem correctly. it’s important to carefully read the problem and identify all of the relevant information, as well as any given equations or formulas that you might need to use. other related topics involving linear equations include graphing and solving systems. understanding linear equations is also useful for applications in fields such as economics, engineering, and physics., about andymath.com, andymath.com is a free math website with the mission of helping students, teachers and tutors find helpful notes, useful sample problems with answers including step by step solutions, and other related materials to supplement classroom learning. if you have any requests for additional content, please contact andy at [email protected] . he will promptly add the content. topics cover elementary math , middle school , algebra , geometry , algebra 2/pre-calculus/trig , calculus and probability/statistics . in the future, i hope to add physics and linear algebra content. visit me on youtube , tiktok , instagram and facebook . andymath content has a unique approach to presenting mathematics. the clear explanations, strong visuals mixed with dry humor regularly get millions of views. we are open to collaborations of all types, please contact andy at [email protected] for all enquiries. to offer financial support, visit my patreon page. let’s help students understand the math way of thinking thank you for visiting. how exciting.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Word Problems. Question.13: A positive number is 5 time another number. If 21 is added to both the numbers, then one of the new numbers become twice of other new numbers. ... Extra Practice Questions For Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Linear Equations in One Variable. 1. The tens and unit digits of a number are the same. By adding the number to its ...
Linear Equations in One Variable Class 8 Extra Questions Very Short Answer Type. Question 1. Identify the algebraic linear equations from the given expressions. (a) x 2 + x = 2 is not a linear equation. (b) 3x + 5 = 11 is a linear equation. (c) 5 + 7 = 12 is not a linear equation as it does not contain variable.
a) A term may be transposed from one side of the equation to the other side but its sign will not change. b) We cannot subtract the same number from both sides of an equation. c) =1 is the solution of equation 4( +5)=24 SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS Q.7 Solve the following equations and check the solutions:
Some of the important word problems in Linear Equation Class 8 are mentioned below to help students with their exam preparation. Students must go through these questions and try to solve them using their problem-solving skills: Q.1. The breadth of a rectangular garden is 2/3 of its length. If its perimeter is 40 m, find its dimensions. Q.2.
The method of solving linear equations in one variable in contextual problems involving multiplication and division (word problems) (avoid complex coefficients in the equations). Disclaimer: Dropped Topics - 2.2 Solving Equations Which Have Linear Expressions on One Side and Numbers on the Other Side, 2.3 Some Applications, 2.5 Some More ...
Chapter 9 - Linear Equation in One Variable contains four exercises, and the RD Sharma Solutions available on this page provide solutions to the questions present in each exercise. Now, let us have a look at the concepts covered in this chapter. Linear equation and its definitions. A solution of a linear equation.
Find KL. Show Video Lesson. Grade 8 number word problems - common core. How to write word problems into systems of linear equations and solve systems of linear equations using elimination and substitution methods? Example 1: The sum of two numbers is 361 and the difference between the two numbers is 173.
There are 6 problems in Chapter 2 of the NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths that deal with linear equations in one variable. The key ideas presented in this chapter are: 2.1 The Start 2.2 Solving Equations with Numbers and Linear Expressions on One Side 2.3 Some Applications Solving Equations with a Variable on Both Sides, Section 2.4 2.5 A Few Additional Uses 2.6 Simplification Equations ...
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Linear Equations In One Variable includes the definition and standard form of a Linear Equation. ... These questions often cover a variety of problem types, including basic equation solving, application-based word problems, and questions involving equations with variables on both sides. ...
Get NCERT Solutions of all Exercise Questions and Examples of Chapter 2 Class 8 Linear Equations in One Variable free at Teachoo. Answers to each and every question with detailed explanation for your understanding. Best answers guaranteed! We studied Equations and Expressions in Algebra ( Chapter 9 Class 8 ). Equation has an = sign, expression ...
Thus, it is imperative to practice all problems in the NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Linear Equations in One Variable to build a robust mathematical foundation for this lesson. ... However, kids need to reserve an ample amount of time to practice converting a word problem to a linear equation and the methods that can be used to solve the same.
️📚👉 Watch Full Free Course Videos: https://www.magnetbrains.com ️📚👉 Grab Notes by Expert Teachers Here: https://www.pabbly.com/out/magnet-brains ️ ...
Linear equations word problems. Google Classroom. Microsoft Teams. Andrei wants to fill a glass tank with spherical marbles and then fill the remaining space with water. The variable w models the amount of water (in liters) Andrei uses if he uses n marbles. w = 32 − 0.05 n. What is the volume of each marble?
Step-by-step application of linear equations to solve practical word problems: 1. The sum of two numbers is 25. One of the numbers exceeds the other by 9. Find the numbers. Let the number be x. Therefore, the two numbers are 8 and 17. 2.The difference between the two numbers is 48. The ratio of the two numbers is 7:3.
Solution. (a) If ax = b, then x = b a. Since, a and b are positive integers. So, b a is also positive integer, Hence, the solution of the given equation has to be always positive. Question. 8 Linear equation in one variable has. (a) only one variable with any power. (b) only one term with a variable.
Unit test. Level up on all the skills in this unit and collect up to 800 Mastery points! Learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, finance, history, and more. Khan Academy is a nonprofit with the mission of providing a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere.
Download free printable worksheets for Class 8 Linear Equations with important questions, solutions and test papers. These worksheets cover all topics and chapters as per the latest CBSE NCERT syllabus and books.
5. Form an equation of "7 added to thrice a number is 118" and also find the number. 6. If sum of two numbers is 29 and one of them is 18. Form the equation for finding the another number. Class 8 Maths Linear Equation in One Variable Long Answer Type Questions. 1. A number consists of two digits whose sum is 9.
Solution : Let x be the number. One-sixth of the number = (⅙)x =ˣ⁄₆. One-seventh of the number = (⅐)x=ˣ⁄₇. From the given information, ˣ⁄₆= ˣ⁄₇+ 1. Least common multiple of the denominators (6, 7) is 42. Multiply both sides of the equation by 42 to get rid of the denominators 6 and 7.
This set of Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Multiple Choice Questions & Answers (MCQs) focuses on "Linear Equations in One Variable". These MCQs are created based on the latest CBSE syllabus and the NCERT curriculum, offering valuable assistance for exam preparation. 1. Find the solution for the equation 3x + 3 = 4. a) 3. b) 1 3.
To eliminate the denominator terms, multiply both sides of the equation by the LCM of 6 and 8. Application of Linear Equations. Linear equations are used to find the value of an unknown quantity. Have a look at the following examples: EXAMPLE 1: The sum of the digits of a 2 digit number 13. The numbers obtained by interchanging the digits is 14 ...
Word problems linear equations (basic) A positive number is 5 times another number. If we add 2 to both the numbers, then one of them becomes 4 times the other. Find the smaller number. Learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, finance, history, and more. Khan Academy is a nonprofit ...
In Summary. Linear equations are a type of equation that has a linear relationship between two variables, and they can often be used to solve word problems. In order to solve a word problem involving a linear equation, you will need to identify the variables in the problem and determine the relationship between them.